Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Animal Cell Parts and Functions: Organelle Summary of Function
Uploaded by
Dorothy Mayo Mejes0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pagesOriginal Title
Plant parts
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pagesAnimal Cell Parts and Functions: Organelle Summary of Function
Uploaded by
Dorothy Mayo MejesCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
GENERAL METHODS OF TEACHING The discovery learning method is a
constructivist theory, meaning it
INDUCTIVE METHOD is based on the idea that students
Inductive is a way to describe something construct their own understanding and
that leads to something else, so when knowledge of the world through
applied to reasoning it just means you experiencing things and reflecting on
collect information and draw conclusions those experiences. ... Teachers will give
from what you observe. Logical types may students a problem and some resources to
already be familiar with the word inductive solve it
as it relates to reasoning.
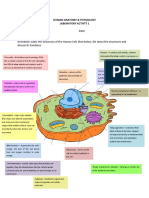
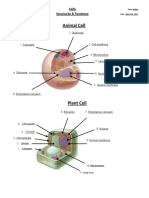
ANIMAL CELL PARTS AND
DEDUCTIVE FUNCTIONS
Deductive reasoning is a logical process in
which a conclusion is based on the
concordance of multiple premises that are Organelle Summary of function
generally assumed to be true. Deductive Cell Protects the cell
reasoning is sometimes referred to as top- membrane Controls the entry
down logic. Its counterpart, inductive and exit of
reasoning, is sometimes referred to as molecules
bottom-up logic. Gives the cell a
shape
TIME TESTED INSTRUCTIONAL PROCEDURE
Adheres to
Mastery learning is a set of group- neighboring cells
based, individualized, teaching and to form tissue
learning strategies based on the premise Helps the cell to
that students will achieve a high level of communicate with
understanding in a given domain if they the exterior
are given enough time
cytoplasm
Integration method of teaching “an &
integrated approach allows learners to Cytoskeleto
explore, gather, process, refine and The cytoplasm
n holds water and
present information about topics they
want to investigate without the constraints nutrients
imposed by traditional subject barriers” The cytoskeleton
(pigdon and woolley, 1992). An integrated gives structural
approach allows students to engage in rigidity to cell
purposeful, relevant learning. The cytoskeleton
helps movement of
Discussion method definition discussion organelles and
method of teaching is a group activity chromosomes
involving the teacher and the student to
define the problem and seek its solution. Nucleus Command center
Discussion method is also described as a of the cell
constructive process involving listening
Duplicate and
,thinking ,as well as the speaking ability of
store genetic
the student
information
Inquiry-based learning is an approach Makes ribosomes
to learning that emphasizes the student's Sends commands
role in the learning process. Rather than to ribosomes for
the teacher telling students what they protein synthesis
need to know, students are encouraged to
explore the material, ask questions, and
share ideas.
Ribosomes Protein synthesis reproductive tract
Endoplasmi Summary of the function
c of the smooth er:
Reticulum
PLANT CELL PARTS AND
(er) FUNCTIONS
Lipid synthesis
Detoxification of
alcohol and drugs
Summary of the function
of the rough er: cell wall surrounds the plant
cell - gives it shape
Protein synthesis and protection
cell a protective outer
Golgi Processes and membrane covering - regulates
apparatus packages proteins interaction between
and transports the cell and its
them to other environment
parts of the cell or
outside the cell. cytoplasm a gel-like material
inside the cell where
most of the cell's life
Mitochondri Converts food we
processes take place
a eat into energy we
use nuclear allows certain
Assist in cell membrane substances to pass
growth, cell cycle between the nucleus
and cellular death and the rest of the cell
Lysosomes nucleus the control center of
Break down
& peroxiso the cell
cellular waste into
mes building blocks chromosom contains the code that
Destroy foreign es controls the cell -
invaders transmits hereditary
Peroxisomes break characteristics
down hydrogen
peroxide – harmful nucleolus the area of the
compound nucleus where
Peroxisomes are ribosomes are made
involved in the
mitochondri releases energy from
synthesis of lipids
a digested foods
and bile acids
chloroplasts manufactures food in
Vacuoles Store food, water the plant cell through
and waste photosynthesis
Golgi bodies packages and
Cilia Lung cells use cilia transmits cellular
&flagellum to move mucus out material throughout
of the lungs the cell
A sperm cell uses
its flagellum to vacuole storage space for
swim through the water, wastes, & other
female
cellular material environment determine how an organism
will develop and function.
endoplasmic place where materials
reticulum are processed and INHERITED CAUSES OF VARIATION
moved around inside
the cell Variation in a characteristic that is a result
of genetic information from the parents is
ribosomes produces proteins called inherited variation . Children usually
within the cell look a little like their father, and a little
like their mother, but they will not be
lysosomes contains digestive
chemicals that help identical to either of their parents.
break down food
molecules
cytoskeleto helps the animal cell
n maintain its shape and
move
Heredity explains why offspring resemble,
but are not identical to, their parents and
is a unifying biological principle. Heredity
refers to specific mechanisms by which
characteristics or traits are passed from
one generation to the next via genes.
Genes encode the information for making
specific proteins, which are responsible for
the specific traits of an individual. Each
gene can have several variants, called
alleles, which code for different variants of
the trait in question. Genes reside in a
cell’s chromosomes, each of which
contains many genes. Every cell of any
individual organism contains the identical
set of chromosomes. When organisms
reproduce, genetic information is
transferred to their offspring. In species
that reproduce sexually, each cell contains
two variants of each chromosome, one
inherited from each parent. Thus sexual
reproduction gives rise to a new
combination of chromosome pairs with
variations between parent and offspring.
Very rarely, mutations also cause
variations, which may be harmful, neutral,
or occasionally advantageous for an
individual. Environmental as well as
genetic variation and the relative
dominance of each of the genes in a pair
play an important role in how traits
develop within an individual. Complex
relationships between genes and
interactions of genes with the
You might also like
- Organelles in Eukaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesOrganelles in Eukaryotic CellsKking Chung100% (3)
- Gen Bio Module 3Document7 pagesGen Bio Module 3Jann Ranniel PanlilioNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure 2Document5 pagesCell Structure 2slombez 150% (1)
- Ivy Jean MartinezDocument11 pagesIvy Jean MartinezmarjmarjNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Parts of Cell and Function Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellsDocument2 pagesActivity 1 Parts of Cell and Function Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellsRIVERA, BRENNAN L.No ratings yet
- Activity 1 Gen Bio 1Document3 pagesActivity 1 Gen Bio 1Villanueva, Liv Harlet A.No ratings yet
- Structures of A Cell: Instruction GuideDocument9 pagesStructures of A Cell: Instruction GuideGissele AbolucionNo ratings yet
- Central Mindanao University Department of Biology: "The CellDocument6 pagesCentral Mindanao University Department of Biology: "The CellNEIL MARTINEZNo ratings yet
- Cell Bio Quiz 1Document3 pagesCell Bio Quiz 1raphaelNo ratings yet
- The Human CellDocument1 pageThe Human CellAira Viloria Orbillo100% (1)
- Acfrogahwtgjhymcdbhqd9juy0ihb5dgzqyobwgygm44pyrxkeh Dixuo Odyslryl Jpqgjhd4udt63zm6ot2mgudp GWKKKDFLLJD 4nxfp5i Pvcee 9pyuxltmliuwhn9qmanxfhy82jt1l4Document8 pagesAcfrogahwtgjhymcdbhqd9juy0ihb5dgzqyobwgygm44pyrxkeh Dixuo Odyslryl Jpqgjhd4udt63zm6ot2mgudp GWKKKDFLLJD 4nxfp5i Pvcee 9pyuxltmliuwhn9qmanxfhy82jt1l4s20003No ratings yet
- What Is A Cell - Learn Science at ScitableDocument5 pagesWhat Is A Cell - Learn Science at ScitableChristopher BrownNo ratings yet
- CLIL Lesson Plan TemplatekkDocument10 pagesCLIL Lesson Plan Templatekkmgg9st6k5jNo ratings yet
- The Human CellDocument3 pagesThe Human CellA HNo ratings yet
- 2f7a3f9c-cb36-469b-96f4-72c9e24a82c0Document12 pages2f7a3f9c-cb36-469b-96f4-72c9e24a82c0Kalina KichukovaNo ratings yet
- Learning Packet in Level 1-Anatomy and Physiology: College of Nursing School Year 2021-2022Document18 pagesLearning Packet in Level 1-Anatomy and Physiology: College of Nursing School Year 2021-2022Zyke NovenoNo ratings yet
- Premidterms NotesDocument4 pagesPremidterms NotesRenee Andrei Concepcion MozarNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesAnimal Cell Lesson PlanGilda Genive AriolaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Reviewer 2Document3 pagesAnaphy Reviewer 2Christopher Valle ArgelNo ratings yet
- Assignment in General Biology 1Document3 pagesAssignment in General Biology 1neil aldwin garciaNo ratings yet
- LAS 4 - Plant and Animal CellsDocument7 pagesLAS 4 - Plant and Animal CellsJeanne RanielleNo ratings yet
- Organelle Present/Absent Description FunctionDocument5 pagesOrganelle Present/Absent Description FunctionTania BacsinNo ratings yet
- Cell Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesCell Lesson PlanRONALD ARTILLERONo ratings yet
- Answer Sheet in General Biology Week 2 ACTIVITY 1: Prokaryotic Cell vs. Eukaryotic CellDocument6 pagesAnswer Sheet in General Biology Week 2 ACTIVITY 1: Prokaryotic Cell vs. Eukaryotic CellMark Joedel MendezNo ratings yet
- Cell Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesCell Lesson PlanRONALD ARTILLERONo ratings yet
- Salud - Lab Activity 3 - The Cell - Biochem - BSN 1-Coc A. PDFDocument5 pagesSalud - Lab Activity 3 - The Cell - Biochem - BSN 1-Coc A. PDFFaye SaludNo ratings yet
- 1.3.1 - Differences Between Eukaryotes and ProkaryotesDocument4 pages1.3.1 - Differences Between Eukaryotes and ProkaryotescarlNo ratings yet
- Material For Genbio Week 1Document6 pagesMaterial For Genbio Week 1John Ferri PatunganNo ratings yet
- PortfolioDocument27 pagesPortfolioNathalieNo ratings yet
- Cell, Basic Structure of All Living Creatures: Life Science, Human BiologyDocument11 pagesCell, Basic Structure of All Living Creatures: Life Science, Human BiologyAshleigh Jenson WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- Term 1 - Grade 8 Science CH 7 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument3 pagesTerm 1 - Grade 8 Science CH 7 Cell Structure and Functionprakashjoshi23aprilNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell WorksheetDocument3 pagesPlant Cell WorksheetPaola RiveraNo ratings yet
- BEST - BCL - 1 - 2 - Response - What Do They Have in CommonDocument6 pagesBEST - BCL - 1 - 2 - Response - What Do They Have in CommonmtauhidNo ratings yet
- Group 3Document2 pagesGroup 3Rane MandapatNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document4 pagesActivity 1sharksiedNo ratings yet
- MYP Unit Planner: Stage 1: Integrate Significant Concept, Area of Interaction and Unit QuestionDocument6 pagesMYP Unit Planner: Stage 1: Integrate Significant Concept, Area of Interaction and Unit QuestionAlib BudiyantoNo ratings yet
- Plant CellDocument4 pagesPlant CellMaria Fe IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lecture: Bachelor of Science in Medical Laboratory ScienceDocument10 pagesBiochemistry Lecture: Bachelor of Science in Medical Laboratory ScienceDCRUZNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & FunctionDocument76 pagesCell Structure & FunctionMilka RahmanNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document4 pagesActivity 1sharksiedNo ratings yet
- Based On Annex 2B.6 To Deped Order No. 42, S. 2016 Daily Lesson Plan Senior High School Balanacan National High School Melody A. Magahis-MendozaDocument3 pagesBased On Annex 2B.6 To Deped Order No. 42, S. 2016 Daily Lesson Plan Senior High School Balanacan National High School Melody A. Magahis-MendozaMelodyNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Cell Structure Practice (1) - 3Document3 pagesKami Export - Cell Structure Practice (1) - 3Achionta NandyNo ratings yet
- M3 - Exercise 4. Plant and Animal CellDocument10 pagesM3 - Exercise 4. Plant and Animal CellVanessa RafaelNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Teacher: Reda QuidetDocument25 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Teacher: Reda QuidetJuanito MerciNo ratings yet
- Cell ReviewerDocument7 pagesCell ReviewerMar LagmayNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology and Diagnostic Intro To CytogeneticsDocument6 pagesMolecular Biology and Diagnostic Intro To Cytogeneticselijah montefalcoNo ratings yet
- Basic Building Blocks of Life Smallest Living Unit of An OrganismDocument2 pagesBasic Building Blocks of Life Smallest Living Unit of An OrganismkikomagsaysayNo ratings yet
- NUDES Lab Activity 2Document5 pagesNUDES Lab Activity 2Ella RetizaNo ratings yet
- Week 2: September 20-25: MC 2: BiochemistryDocument6 pagesWeek 2: September 20-25: MC 2: BiochemistryMary Rose CuentasNo ratings yet
- Review Workshop 5THDocument5 pagesReview Workshop 5THjairo gomezNo ratings yet
- Andrea Redinger Biology Unit 5 - Cells: Stage 1 Desired ResultsDocument8 pagesAndrea Redinger Biology Unit 5 - Cells: Stage 1 Desired ResultsMegan FarrenNo ratings yet
- Bio Project PendingDocument11 pagesBio Project PendingShashank vermaNo ratings yet
- O Level - CellsDocument12 pagesO Level - CellsArif UllahNo ratings yet
- Demonstration Lesson Plan in Animal and Plant CellsDocument5 pagesDemonstration Lesson Plan in Animal and Plant CellsCristina AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 1 NotesDocument6 pagesBiology Chapter 1 Notesmohan.shenoy52No ratings yet
- Biyani's Think Tank: Cell Biology & GeneticsDocument81 pagesBiyani's Think Tank: Cell Biology & GeneticsAkshay chandrakarNo ratings yet
- 2 - Cell+WSDocument3 pages2 - Cell+WSRohan SoniNo ratings yet
- Module 1-2Document21 pagesModule 1-2Edel Ruth Pal-Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2Document4 pagesGen Bio 2Melrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- Sperm Morphology - 2019 FinalDocument44 pagesSperm Morphology - 2019 FinalDr Jitu moni DasNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Unit-I MCQSDocument3 pagesCell Biology Unit-I MCQSsankar100% (1)
- Zoo Lab ActivityDocument1 pageZoo Lab ActivityHarold DavidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Cell Division MYM (Answer)Document7 pagesChapter 3 Cell Division MYM (Answer)AISHAH NAZIRAH100% (1)
- Characteristics of Prokaryotic CellsDocument2 pagesCharacteristics of Prokaryotic CellsOrange HopeNo ratings yet
- The Ribosomes and The ER: The Cytoplasm: The Factory FloorDocument7 pagesThe Ribosomes and The ER: The Cytoplasm: The Factory FloorMarco Fidel Naranjo GómezNo ratings yet
- Class 9th Cell - The Unit of LifeDocument40 pagesClass 9th Cell - The Unit of LifeKabir RaiNo ratings yet
- Integrated Principles of ZoologyDocument41 pagesIntegrated Principles of ZoologyEstherNo ratings yet
- NameDocument6 pagesNameromeyer81No ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Structure PDFDocument2 pagesEukaryotic Cell Structure PDFAaronNo ratings yet
- The Cell Nattapat2021Document119 pagesThe Cell Nattapat2021Poochita SongsriNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis ExamDocument13 pagesMitosis and Meiosis ExamCearra Mae EbronaNo ratings yet
- Magic School Bus EssayDocument3 pagesMagic School Bus Essayapi-311220565No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document96 pagesChapter 3Sinclyr Valenciano100% (2)
- Lesson 2 - Prokaryotic CellsDocument2 pagesLesson 2 - Prokaryotic CellsKerberos DelabosNo ratings yet
- Las Science 7 Melc 4 q2 Week4Document8 pagesLas Science 7 Melc 4 q2 Week4Heena Grace Presidente100% (1)
- Protein SortingDocument13 pagesProtein Sortingdkshukla79100% (4)
- Cell Division Assignment#2 .123Document3 pagesCell Division Assignment#2 .123jaeminsoftboiNo ratings yet
- M-Caps-01: Botany: NEET - XI StudyingDocument3 pagesM-Caps-01: Botany: NEET - XI StudyingAlokSinghNo ratings yet
- Gnbio1 Module 2Document35 pagesGnbio1 Module 2Ggggnek OhculNo ratings yet
- CellDocument44 pagesCellIngridNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument19 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of Lifethinkiit100% (1)
- CellDocument4 pagesCellPrincess MillanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 The Cell CycleDocument8 pagesChapter 12 The Cell CycleMicky Bandera100% (2)
- Grade 8 Osmeña Q4 - Week 2Document48 pagesGrade 8 Osmeña Q4 - Week 2SHAIRA LYN CUMILANGNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cell BiologyDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Cell BiologyMustafa Khandgawi100% (3)
- Cells: A. Ultrastructure & Function of The CellDocument9 pagesCells: A. Ultrastructure & Function of The CellRhea Lyn LamosteNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesLesson PlanFritzel NavarroNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1Document35 pagesExercise 1Van Labasano67% (3)