Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ST ND RD TH ST TH ST TH
Uploaded by
Christian ManiponOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ST ND RD TH ST TH ST TH
Uploaded by
Christian ManiponCopyright:
Available Formats
Rosas, Roland Ace S.
BEEd-3A
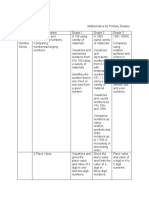
CONTENT GRADE 1 GRADE 2 GRADE 3
NUMBER 1. VISUALIZING *Visualizes and*Visualizes and *Visualizes numbers up
AND AND represents numbers represents numbers to 10,000 with
NUMBER REPRESENTING from 0-100 usingfrom 0-1000 with emphasis numbers
SENSE NUMBERS, variety of materials emphasis numbers 1001-10000
COMPARING 101-1000 using variety
NUMBERS/ARR *Counts the number of of materials
ANGING objects in a given set *Compares numbers up
NUMBERS by ones and tens to 10,000 using relation
*Group objects in ones, symbols
*Identifies the number tens, and hundreds
that is one more or one
less from a given *Orders 4- to 5-digit
number *Visualizes and counts numbers in increasing
numbers by 10s, 50s, or decreasing order
*Compares two sets and 100s
using the expressions
“less than” “more than”
and “as many as” and *Compares numbers
orders sets from least up to 1000 using
to greatest and vice relation symbols and
versa orders numbers up to
1000 in increasing or
*Visualizes and counts decreasing order
by 2s, 5s, and 10s
through 100.
*Compares numbers
up to 100 using relation
symbol and orders
them in increasing or
decreasing order
2. PLACE Value of a digit in one- Value of a digit in Value of a digit in 4- to
VALUE and two-digit numbers three-digit numbers 5-digit numbers.
3. READING *Reads and writes *Reads and writes Reads and writes
AND WRITING numbers up to 100 in numbers up to 1000 in numbers up to 10,000
NUMBERS IN symbols and in words symbol and in words in symbols and in
WORDS words
*Renames numbers *Write three-digit
into tens and ones numbers in expanded
form
4. ROUNDING Rounds numbers to the
OF NUMBERS nearest ten, hundred
and thousand
5. ORDINAL 1st, 2nd, 3rd, up to 10th 1st through the 20th 21st to 100th object
NUMBERS object object
6. BILLS AND Up to PhP100 and their Through PhP100 Through PhP1000
COINS notation (pesos-coins only; using relations
centavo-coins peso-
bills only and combined
peso-coins and peso-
bills)
7. ADDING *Illustrates addition as *Illustrates the *Adds 3- to 4-digit
NUMBERS “putting together or properties of addition numbers up to three
combining or joining (commutative, addends with sums up
sets” associative, identity) to 10,000 without and
and applies each in with regrouping
*Visualizes and adds appropriate and
the ff. numbers using relevant situations *Estimates the sum of
appropriate techniques: 3- to 4-digit addends
a. two one-digit *Visualizes, represents, with reasonable results
numbers with sums up and adds the following
to 18 numbers with the sums *Adds mentally the
b. three one-digit to 1000 without and following numbers
numbers with regrouping: using appropriate
c. numbers with sums a. 2-digit by 3-digit strategies:
through 99 without and numbers a. 2-digit and 1-digit
with regrouping b. 3-digits by 3-digit numbers without or with
numbers regrouping
*Visualizes and solves b. 2- to 3- digit numbers
one-step routine and *Adds mentally the with multiples of
non-step routine following numbers hundreds
problems involving using appropriate
addition of whole strategies: *Solves routine and
numbers including a. 1- to 2-digit numbers non-routine problems
money with sums up to with sums to 50 involving addition of
99 using appropriate b. 3-digit numbers and whole numbers with
problem solving 1-digit numbers sums up to 10,000
strategies c. three-digit numbers including money using
and tens (multiple of 10 appropriate problem
up to 900) solving strategies and
tools.
*Solves routine and
non-routine problems
involving addition of
whole numbers
including money with
sums up to 1000 using
appropriate problem
solving strategies and
tools
8. *Illustrates subtraction Visualizes, represents, *Estimates the
SUBTRACTING as “taking away” or and subtracts 2- to 3- difference of two
NUMBERS “comparing” elements digit numbers with numbers with three to
of sets minutes up to 1000 four digits with
using appropriate reasonable results.
*Visualizes, represents, solving strategies and
and subtracts the tools *Subtracts mentally the
following numbers: following numbers
a. one-digit numbers using appropriate
with minuends through strategies:
18 (basic facts) a. 1- to 2-digit numbers
b. one- to two-digit without and with
numbers with regrouping
minuends up to 99 b. 2- to 3-digit numbers
without regrouping multiples of hundreds
c. one- to two- digit without and with
numbers with regrouping
minuends up to 99 with
regrouping *Solves routine and
non-routine problems
*Subtracts mentally involving subtraction
one-digit numbers from without or with addition
two-digit minuends of whole numbers
without regrouping including money using
using appropriate appropriate problem
strategies solving strategies and
tools
*Visualizes, represents,
and solves routine and
non-routine problems
involving subtraction of
whole numbers
including money with
minuends up to 99 with
and without regrouping
using appropriate
problem solving
strategies and tools
9. DIVISION *Visualizes and *Visualizes division of
represents division, numbers up to 100 by
and writes a related 6, 7, 8, and 9
equation for each type (multiplication table of
of situation: equal 6, 7, 8, and 9).
sharing, repeated
subtraction, equal *Visualizes and states
jumps on the number basic division facts of
line, and formation of numbers up to 10
equal groups of
objects. *Divides numbers
without or with
*Visualizes division of remainder:
numbers up to 100 by a. 2- to 3-digit numbers
2,3,4,5, and 10 by 1- to 2- digit
(multiplication table of numbers
2, 3, 4, 5 and 10) b. 2-3 digit numbers by
10 and 100
*Divides mentally
numbers by 2,3,4,5 *Estimates the quotient
and 10 using of 2- to 3- digit numbers
appropriate strategies by 1- to 2- digit
(multiplication table of numbers.
2, 3, 4, 5 and 10)
*Divides mentally 2-
*Solves routine and digit numbers by 1-digit
non-routine problems numbers without
involving division of remainder using
numbers by 2,3,4,5 appropriate strategies.
and 10 and with any of
the other operations of *Solves routine and
whole numbers non-routine problems
including money using involving division of 2-
appropriate problem to 4-digit numbers by 1-
solving strategies and to 2-digit numbers
tools. without or with any of
the other operations of
whole numbers
including money using
appropriate problem
solving strategies and
tools.
10. *Illustrates and writes a *Visualizes
MULTIPLICATIO related equation for multiplication of
N each type of numbers 1 to 10 by 6,
multiplication: repeated 7, 8 and 9
addition, array,
counting by multiples, *Visualizes and states
and equal jumps on the basic multiplication
number line. facts for numbers up to
10
*Illustrates the
following properties of *Illustrates the
multiplication and apply properties of
each in relevant multiplication in
situation: relevant situations
(a) identity, (commutative property,
(b) zero, and, distributive property o
(c) commutative. associative property.
*Visualizes *Multiplies numbers:
multiplication of a. 2- to 3-digit numbers
numbers 1 to 10 by by 1-digit numbers
2,3,4,5 and 10. without or with
regrouping
*Multiplies mentally b. 2-digit numbers by 2-
2,3,4,5 and 10 using digit numbers without
appropriate strategies regrouping
c. 2-digit numbers by 2-
*Solves routine and digit numbers with
non-routine problems regrouping
using appropriate d. 2- to 3-digit numbers
problem solving by multiples of 10 and
strategies and tools: 100
a. multiplication of e. 1- to 2-digit numbers
whole numbers by 1000
including money b.
multiplication and *Estimate the product
addition or subtraction of 2- to 3-digit numbers
of whole numbers and 1- to 2-digit
including money numbers with
reasonable results
*Multiplies mentally 2-
digit by 1-digit numbers
without regrouping with
products of up to 100
*Solves routine and
non-routine problems
involving multiplication
without or with addition
and subtraction of
whole numbers
including money using
appropriate problem
solving strategies and
tools.
*Visualizes and states
the multiples of 1- to 2-
digit numbers.
11. FRACTION *Visualizes, represents *Visualizes and
and identifies unit represents fractions
fractions with that are equal to one
denominators of 10 and greater than one
and below. using regions,, sets and
number line
*Reads and writes unit
fractions *Reads and writes
fractions that are equal
*Compares using to one and greater than
relation symbol and one in symbols and in
arranges in increasing words
or decreasing order the
unit fractions. *Represents, compares
and arranges dissimilar
*Identifies other fractions in increasing
fractions less than one or decreasing order.
with denominators 10
and below. *Visualizes and
generates equivalent
*Visualizes (using fractions.
group of objects and
number line), reads
and writes similar
fractions
*Compares similar
fractions using relation
symbols.
*Arranges similar
fractions in increasing
or decreasing order.
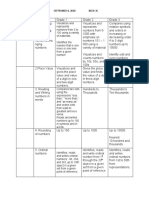
GEOMETR 1. BASIC *4 basic shapes Constructs squares, *Recognizes and draws
Y SHAPES rectangles, triangles, a point, line, line
Identifies, names, and circles, half-circles, and segment and ray.
describes the four quarter circles using
basic shapes (square, cut-outs and square *Recognizes and draws
rectangle, triangle and grids. parallel, intersecting
circle) in 2-dimensional and perpendicular
(flat/plane) and 3- lines.
dimensional (solid)
object. *Visualizes, identifies
and draws congruent
*Draws the basic line segments
shapes
*Identifies and
visualizes symmetry in
the environment and in
design.
*Identifies and draws
the line of symmetry in
a given symmetrical
figure.
*Completes a
symmetric figure with
respect to a given line
of symmetry.
2. CONSTRUCT Constructs three Identifies straight lines
DIMENSIONAL dimensional objects and curves, flat and
OBJECTS (solid) using curved surfaces in a 3-
USING manipulative materials dimensional object
MANIPULATIVE
MATERIALS
PATTERNS 1. CONTINUOUS *Determines the Determines the missing Determines the missing
AND PATTERNS missing term/s using term/s in a given term/s in a given
ALGEBRA (LETTERS/NUM one attribute in a given continuous pattern combination of
BERS/EVENTS continuous pattern using two attributes continuous and
IN A GIVEN (letters/ numbers/ (any two of the repeating pattern.
REPEATING events) and in a given following: figures,
PATTERNS repeating pattern numbers, colors, sizes,
(LETTER, (letters, numbers, and orientations, etc.)
NUMBER/COLO colors, figures, sizes, e.g. 1, A, 2,B,3,C,__,__
R/FIGURES/SIZE etc.)
S,ETC.)
*Constructs equivalent
number expression
using addition and
subtraction. e.g. 6 + 5
= 12 – 1
*Identifies and creates
patterns to compose
and decompose using
addition
e.g. 7= 0+7, 1+6, 2+5,
3+4, 4+3, 5+2, 6+1,
7+0
*Visualizes and finds
the missing number in
an addition or
subtraction sentence
using a variety of ways
e.g. n + 2 = 5
5–n=3
MEASUREMENTS *Tells the days in a *Tells and writes time *Visualizes, represents,
week; months in a year in minutes including and converts time
in right order a.m. and p.m. using measure:
analog and digital a. from seconds to
*Determines the day or clocks. minutes, minutes to
the month using the hours, and hours to a
calendar *Visualizes, represents, day and vice versa
and solves problems b. days to week, month
*Tells and writes time involving time (minutes and year and vice
by hour, half-hour and including a.m. and p.m. versa
quarter-hour using and elapsed time in c. weeks to months and
analog clock. days). year and vice versa
d. months to year and
*Solves problems *Compares the vice versa.
involving time (days in following unit of
a week, months in a measures: *Solves problems
year, hour, half-hour, a. length in meters or involving conversion of
and quarter-hour) centimeters time measure.
b. mass in grams or
*Compares objects kilograms *Visualizes, and
using comparative c. capacity in mL or L represents, and
words: short, shorter, converts common units
shortest; long, longer, *Measures objects of measure from larger
longest; heavy, using appropriate to smaller unit and vice
heavier, heaviest; light, measuring tools and versa: meter and
lighter, lightest unit of length in m or centimeter, kilogram
cm and gram, liter and
*Estimates and milliliter.
measures length, *Estimates and
mass, and capacity measures length using *Visualizes, and
using non-standard meter or centimeter. represents, and solves
units. routine and non-routine
*Solves routine and problems involving
non-routine problems conversions of common
involving length. units of measure.
*Measures objects *Solves routine and
using appropriate non-routine problems
measuring tools and involving capacity
measuring units in g or measure.
kg.
*Visualizes, and
*Estimates and represents, and
measures mass using measures area using
gram or kilogram. appropriate unit.
*Solves routine and
non-routine problems
involving mass.
*Measures objects
using appropriate
measuring tools in mL
or L.
*Finds the area of a
given figure using
square-tile units i.e.
number of square-tiles
needed.
*Estimates the area of
a given figure using
any shape.
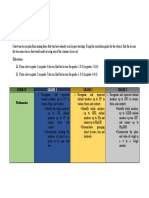
STATISTIC AND *Infers and interprets *Infers and interprets *Infers and interprets
PROBABILITY data presented in a data presented in a data presented in
pictograph without pictograph without and different kinds of bar
scales. with scales. graphs (vertical/
horizontal)
*Solves routine and *Solves routine and
non-routine problems non-routine problems *Solves routine and
using data presented in using data presented in non-routine problems
pictograph without a pictograph without using data presented in
scale and with scales. a single- bar graph
How were the lessons in number and number sense arranged?
The lessons in number and number sense arranged in manner that children could understand the
lesson easier. Where in the in grade 1 level it teaches the basic facts of number and number sense then as the
learning progresses when the learner know more about the basic fact. That is the time it introduce more detail
in the next grade level. For every grade level more and more details are introduce while at the same time they
are related to the basic.
How were the lessons in geometry arranged?
The lessons in geometry arranged into basic facts of geometry such shapes. Going to the different
details of shapes such as the line segments. For example in grade 1 level it teaches basic shape such as
square, triangle etc. Then in grade 3 level It teaches the details that formed this shape such as line segments.
So through the curriculum topic are presented repeated but other details are added and teaches with deeper
understanding.
How were the lessons in statistics and probability arranged?
The lessons in statistics and probability arranged in the manner that learners build upon previously
learned knowledge for example in grade 1 level student learn to interprets data presented in pictograph without
scale but grade 2 level the previous learned knowledge will be the basis of learning the topic in grade 2 level
which is to interprets data presented in pictograph with and without scale .
You might also like
- Healthy Chicken Pasta Recipes From EatingWell MagazineDocument10 pagesHealthy Chicken Pasta Recipes From EatingWell MagazineAlice GiffordNo ratings yet
- Trust Law: Common Law Property Settlor Trustees Beneficiary FiduciaryDocument8 pagesTrust Law: Common Law Property Settlor Trustees Beneficiary FiduciaryDekweriz100% (1)
- Cause and Effect Mini LessonDocument6 pagesCause and Effect Mini LessonIzzati Ariffin100% (1)
- Summary and analysis of O. Henry's "The Ransom of Red ChiefDocument1 pageSummary and analysis of O. Henry's "The Ransom of Red ChiefRohan Mehta100% (1)
- Grade 2. SSES Enhanced Mathematics Curriculum 1Document10 pagesGrade 2. SSES Enhanced Mathematics Curriculum 1Claudine C. Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Melc Math PDFDocument28 pagesMelc Math PDFAna Carla de CastroNo ratings yet
- Supercritical CO2 Extraction: A Clean Extraction MethodDocument6 pagesSupercritical CO2 Extraction: A Clean Extraction MethodPrincess Janine CatralNo ratings yet
- Enhanced SSES Mathematics Curriculum Grade 2Document10 pagesEnhanced SSES Mathematics Curriculum Grade 2nicole macabanteNo ratings yet
- Black Industries Lost Files - Terror in The DarknessDocument14 pagesBlack Industries Lost Files - Terror in The Darknessjadrax100% (8)
- HC - Come Home To Yourself PDFDocument133 pagesHC - Come Home To Yourself PDFOtilia100% (1)
- Gept reading試題Document13 pagesGept reading試題Bateman Patrick100% (1)
- Grade 1. SSES Enhanced Mathematics Curriculum 1Document7 pagesGrade 1. SSES Enhanced Mathematics Curriculum 1Jasmin Garcia100% (3)
- RPT Mathematics Year 2 (DLP) 2021 by Rozayus AcademyDocument16 pagesRPT Mathematics Year 2 (DLP) 2021 by Rozayus AcademyAzrin MohayaddinNo ratings yet
- Cagayan Electric vs. CIRDocument4 pagesCagayan Electric vs. CIRGladys BantilanNo ratings yet
- Curriculum EvaluationDocument7 pagesCurriculum EvaluationChristian Manipon86% (7)
- Unit Iii Phases and Process of Curriculum Development: C. ImplementationDocument38 pagesUnit Iii Phases and Process of Curriculum Development: C. ImplementationChristian Manipon100% (1)
- Unit Iii Phases and Process of Curriculum Development: C. ImplementationDocument38 pagesUnit Iii Phases and Process of Curriculum Development: C. ImplementationChristian Manipon100% (1)
- Scope & SequenceDocument12 pagesScope & SequenceQuinn HsimNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in The K-12 Basic Education Curriculum For The Primary EducationDocument15 pagesMathematics in The K-12 Basic Education Curriculum For The Primary EducationChristian ManiponNo ratings yet
- Bow Mathematics 3Document11 pagesBow Mathematics 3Richard MurilloNo ratings yet
- Math MappingDocument15 pagesMath MappingChristian ManiponNo ratings yet
- MATH (Mapping)Document7 pagesMATH (Mapping)Charol AoayNo ratings yet
- Unpacking The Melcs (Mathematics 2) Retained Learning Competencies Sample Learning Objectives First QuarterDocument2 pagesUnpacking The Melcs (Mathematics 2) Retained Learning Competencies Sample Learning Objectives First QuarterWinny Soquila FelipeNo ratings yet
- Carlos, Nimfa L. Beed-3ADocument13 pagesCarlos, Nimfa L. Beed-3AChristian ManiponNo ratings yet
- Math 3Document6 pagesMath 3Rovi ChellNo ratings yet
- MATHDocument3 pagesMATHShara Jane Sayco SamonteNo ratings yet
- Math 2Document8 pagesMath 2PRINCES SARAH REYES PERALTANo ratings yet
- Math 1 Course Outline SY 2019-2020Document4 pagesMath 1 Course Outline SY 2019-2020Camile GiloNo ratings yet
- Grade 1 Math MELC Quarterly BreakdownDocument67 pagesGrade 1 Math MELC Quarterly BreakdownMaricel ManlupigNo ratings yet
- DLL - Math 4Document8 pagesDLL - Math 4Vanessa Jane ObusaNo ratings yet
- Sukatan Pelajaran Matematik KBSRDocument13 pagesSukatan Pelajaran Matematik KBSRAhimin KerisimNo ratings yet
- Grade 1 Mathematics Standards and Learning OutcomesDocument132 pagesGrade 1 Mathematics Standards and Learning OutcomesGrade Five- Blessed Christine of the Holy CrossNo ratings yet
- RPT Maths Yr 4 2019Document20 pagesRPT Maths Yr 4 2019Khairul FizaNo ratings yet
- 2007 Mathematics Standards by ProgressionDocument27 pages2007 Mathematics Standards by ProgressionElaine EricksonNo ratings yet
- GRADE 1 MATHEMATICS MELC QUARTER 1 AND 2Document60 pagesGRADE 1 MATHEMATICS MELC QUARTER 1 AND 2Marichou GargarNo ratings yet
- Mapping of Melcs (Tos0key Stage 1Document9 pagesMapping of Melcs (Tos0key Stage 1mark san andresNo ratings yet
- Budget of Work in Mathematics 2 (K To 12) 1 TO4 QuarterDocument8 pagesBudget of Work in Mathematics 2 (K To 12) 1 TO4 QuarterEnteng ODNo ratings yet
- RPT Math DLP Year 2Document16 pagesRPT Math DLP Year 2Teck Bing LukNo ratings yet
- Budget of Work in Mathematics 2 (K To 12) 1 TO4 QuarterDocument8 pagesBudget of Work in Mathematics 2 (K To 12) 1 TO4 QuarterLea Garcia MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Numbers 0 To 10: Understand Addition As Combining Two Groups of ObjectsDocument12 pagesNumbers 0 To 10: Understand Addition As Combining Two Groups of ObjectsAnonymous r1vPtxUrNo ratings yet
- Peta Minda HSP Tahun 5 (Kump 3)Document12 pagesPeta Minda HSP Tahun 5 (Kump 3)Mariah Binti Mohd YassinNo ratings yet
- Power Competencies WorksheetDocument4 pagesPower Competencies WorksheetBeh BuriNo ratings yet
- Kryzel Lho B. España Bmsee-Iii Asynchronous Task For March 3, 2023Document1 pageKryzel Lho B. España Bmsee-Iii Asynchronous Task For March 3, 2023Kryzel Lho Baclaan EspañaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Structuring Competencies in A Definitive Budget of WorkDocument22 pagesMathematics Structuring Competencies in A Definitive Budget of WorkLily CallaNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Mathematics DLP Year 4 2020: Learning Area Content Standard Learning StandardDocument12 pagesYearly Plan Mathematics DLP Year 4 2020: Learning Area Content Standard Learning StandardSilvens Siga SilvesterNo ratings yet
- RPT Mathematics Year 3 (DLP)Document22 pagesRPT Mathematics Year 3 (DLP)NOOR FARISHA BINTI NASIR MoeNo ratings yet
- RPT Math DLP Year 2 2023-2024Document16 pagesRPT Math DLP Year 2 2023-2024MOHD ZULKIFLI BIN ZAKARIA KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- KSSR Mathematics Year 1 weekly lessonsDocument13 pagesKSSR Mathematics Year 1 weekly lessonsRacheleNo ratings yet
- Math Grade 3 Lesson GuideDocument5 pagesMath Grade 3 Lesson GuideDyames TVNo ratings yet
- MT DLP Y2-1Document16 pagesMT DLP Y2-1Nithia MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Primary Maths Calculation StrategyDocument129 pagesPrimary Maths Calculation StrategyOLIVEEN WILKS-SCOTTNo ratings yet
- Most Essential Learning Competencies Matrix: Grade 3 MathematicsDocument6 pagesMost Essential Learning Competencies Matrix: Grade 3 MathematicsAnna PatNo ratings yet
- RPT Math DLP Year 3 2023-2024Document21 pagesRPT Math DLP Year 3 2023-2024Khairul KrockNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Year 6: Pupils Will Be Taught To: Pupils Will BeabletoDocument11 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Year 6: Pupils Will Be Taught To: Pupils Will Beabletokunyit4No ratings yet
- Elementary Math CompetenciesDocument22 pagesElementary Math CompetenciesDianne Atting-DiazNo ratings yet
- Budget of Lessons Grade 1 - MathematicsDocument35 pagesBudget of Lessons Grade 1 - MathematicsDaffodilAbuke100% (1)
- RPT Math DLP Year 3 2022-2023Document22 pagesRPT Math DLP Year 3 2022-2023SIA HUAT CHUONG KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- 621f819b18d836148b7f91d0 - Maths ProgressionDocument8 pages621f819b18d836148b7f91d0 - Maths ProgressionFamily SivakumarNo ratings yet
- RPT Math DLP Year 3 2023-2024Document23 pagesRPT Math DLP Year 3 2023-2024Nurbaizura JuaNo ratings yet
- Malla Curricular de Matemática: Tercer Grado de PrimariaDocument4 pagesMalla Curricular de Matemática: Tercer Grado de PrimariaHeri ZoNo ratings yet
- 2023 ATP FP Mathematics Grade2 Term 1-4Document12 pages2023 ATP FP Mathematics Grade2 Term 1-4Grenadine ChiedzaNo ratings yet
- Math Tos ElementaryDocument82 pagesMath Tos ElementaryBenedicta UncianoNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Place Value Summative RubricDocument1 pageUnit 4 Place Value Summative Rubricapi-169564125No ratings yet
- Module 2 Unpacking CombiningDocument6 pagesModule 2 Unpacking Combiningcjade08No ratings yet
- ST ND RD TH ST TH ST THDocument9 pagesST ND RD TH ST TH ST THChristian ManiponNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Differences Between Primary and Intermediate AP CurriculumDocument3 pagesUnderstanding the Differences Between Primary and Intermediate AP CurriculumChristian ManiponNo ratings yet
- Carlos, Nimfa L. Beed-3ADocument13 pagesCarlos, Nimfa L. Beed-3AChristian ManiponNo ratings yet
- BEED 2A PORTFOLIO MATRIXDocument85 pagesBEED 2A PORTFOLIO MATRIXChristian ManiponNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Differences Between Primary and Intermediate AP CurriculumDocument3 pagesUnderstanding the Differences Between Primary and Intermediate AP CurriculumChristian ManiponNo ratings yet
- Reflection SummaryDocument1 pageReflection SummaryChristian ManiponNo ratings yet
- BEED 2A PORTFOLIO MATRIXDocument85 pagesBEED 2A PORTFOLIO MATRIXChristian ManiponNo ratings yet
- MTBMLE Chapter 1 Evaluation Activity SheetDocument3 pagesMTBMLE Chapter 1 Evaluation Activity SheetChristian ManiponNo ratings yet
- Reactionpaper 120516012113 Phpapp01Document4 pagesReactionpaper 120516012113 Phpapp01Christian ManiponNo ratings yet
- Carlos, Nimfa L. Beed-3ADocument13 pagesCarlos, Nimfa L. Beed-3AChristian ManiponNo ratings yet
- VutsDocument17 pagesVutsChristian ManiponNo ratings yet
- Agiagin ProposalDocument1 pageAgiagin ProposalChristian ManiponNo ratings yet
- 1 What Is The Title of The StoryDocument1 page1 What Is The Title of The StoryChristian ManiponNo ratings yet
- AbsDocument3 pagesAbsChristian ManiponNo ratings yet
- Instruction and NoteDocument1 pageInstruction and NoteChristian ManiponNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document21 pagesChapter 3Christian ManiponNo ratings yet
- V1 Budgetary RequirementDocument1 pageV1 Budgetary RequirementChristian ManiponNo ratings yet
- Agiagin ProposalDocument1 pageAgiagin ProposalChristian ManiponNo ratings yet
- Graphic Organizer for Roland Rosas' BEEd-1C ClassDocument2 pagesGraphic Organizer for Roland Rosas' BEEd-1C ClassChristian ManiponNo ratings yet
- Final RPDocument34 pagesFinal RPChristian ManiponNo ratings yet
- AbsDocument3 pagesAbsChristian ManiponNo ratings yet
- Playfair Cipher: Cipher Is A Manual Symmetric Encryption Technique and Was The First LiteralDocument9 pagesPlayfair Cipher: Cipher Is A Manual Symmetric Encryption Technique and Was The First LiteralJOHN CHARLASNo ratings yet
- 527880193-Interchange-2-Teacher-s-Book 2-331Document1 page527880193-Interchange-2-Teacher-s-Book 2-331Luis Fabián Vera NarváezNo ratings yet
- List of MBA Institutes in HyderabadDocument5 pagesList of MBA Institutes in Hyderabadebrandingindia1No ratings yet
- A Gringa in Oaxaca PDFDocument54 pagesA Gringa in Oaxaca PDFPeggy BryanNo ratings yet
- Statistical PhysicsDocument4 pagesStatistical PhysicsRenan ZortéaNo ratings yet
- Post Graduate Dip DermatologyDocument2 pagesPost Graduate Dip DermatologyNooh DinNo ratings yet
- The LOMA Weekly Herald Volume 1 Issue 6Document6 pagesThe LOMA Weekly Herald Volume 1 Issue 6LOMA MaksNo ratings yet
- MalayoDocument39 pagesMalayoRoxanne Datuin UsonNo ratings yet
- Speidel, M. O. (1981) - Stress Corrosion Cracking of Stainless Steels in NaCl Solutions.Document11 pagesSpeidel, M. O. (1981) - Stress Corrosion Cracking of Stainless Steels in NaCl Solutions.oozdemirNo ratings yet
- Atty. Monna Lissa C. Monje-Viray: Are Hereto Attached As Annex "A" and "A-1"Document6 pagesAtty. Monna Lissa C. Monje-Viray: Are Hereto Attached As Annex "A" and "A-1"MarianoFloresNo ratings yet
- Magh Bihu or Maghar DomahiDocument8 pagesMagh Bihu or Maghar Domahihackdarenot4No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - DynamicsDocument8 pagesChapter 2 - DynamicsTHIÊN LÊ TRẦN THUẬNNo ratings yet
- DSE2541 Data SheetDocument2 pagesDSE2541 Data SheetBERANGER DAVESNE DJOMALIA SIEWENo ratings yet
- AISD Fees Structure for 2023-24 Academic YearDocument2 pagesAISD Fees Structure for 2023-24 Academic YearKawsar AlamNo ratings yet
- SITXFSA001 - Assessment A - Short Answer - V2-1Document34 pagesSITXFSA001 - Assessment A - Short Answer - V2-1Namwetayeka Richald WanihaNo ratings yet
- Read Me 22222222222222Document2 pagesRead Me 22222222222222sancakemreNo ratings yet
- Hitachi - AssignmentDocument6 pagesHitachi - AssignmentPraveena IvanaNo ratings yet
- Document 3Document5 pagesDocument 3SOLOMON RIANNANo ratings yet
- Punctuation-Worksheet 18666Document2 pagesPunctuation-Worksheet 18666WAN AMIRA QARIRAH WAN MOHD ROSLANNo ratings yet
- Virtualization Types: OS, Hardware Emulation, and ParavirtualizationDocument7 pagesVirtualization Types: OS, Hardware Emulation, and ParavirtualizationvinoopnvNo ratings yet
- News TIA Portal V15 and V15 1 enDocument43 pagesNews TIA Portal V15 and V15 1 enjohanNo ratings yet
- Question 1 - Adjusting EntriesDocument10 pagesQuestion 1 - Adjusting EntriesVyish VyishuNo ratings yet