Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TMPG PPT Course Unit Assignment
Uploaded by
Justeen BalcortaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TMPG PPT Course Unit Assignment
Uploaded by
Justeen BalcortaCopyright:
Available Formats
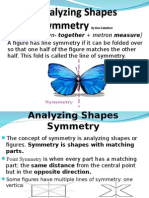
Geometry (Straight & Curved Lines) Line Symmetry
Definition of Terms Point Shape has line symmetry when one half of it is
the mirror image of the other half.
Has no dimension Symmetrical= Same on both sides
Usually represented by a small dot Symmetry: balanced proportions, or capable of
Indicates location division by a longitudinal plane into similar
halves.
A Symmetries preserve distances, angles, sizes,
and shapes.
Line
The Euclidean Plane
Extend in one dimension.
Represented with straight line with two arrow Types of symmetry that transform the plane, the
heads to indicate that the line extends without object is on four main types of Euclidean Planes
end in two directions.
A distance between 2 points. Translation
has no beginning or end Rotation
continues indefinitely in both directions Reflection
can be illustrated by drawing arrows at each end. Glide Reflection
-LINE SEGMENT- Translation
has a beginning point and an end point To translate an object means to move it without
line segment on a shape are called sides rotating or reflecting it. Every translation has a
can be found in many shapes direction and a distance.
A translation is a transformation that moves
Plane every point in a figure the same distance in the
same direction. For example, this transformation
Extend in two dimensions. moves the parallelogram to the right 5 units and
Represented by a slanted 4 sided figure, but you up 3 units. It is written (x,y)→(x+5,y+3).
must envision it extends without end, even
though there presentation has edges Rotation
Collinear Points To rotate an object means to turn it around.
Every rotation has a center and an angle.
Collinear points are points that lie on the same
Before Rotation After Rotation Center [Angle90
line.
]̊
Tessellation
Reflection
If many copies of a shape can be used to cover a
Symmetry is formed when any image is
surface, without leaving any gaps between them,
reflected or a mirror of itself one it her side of
then we say that the shape will tessellate.
the mirror line.
The pattern that is formed is called a tessellation.
A repeating pattern using regular polygons Glide Reflection
no gaps or overlaps
A glide reflection combines are flection with a
each vertex is the same
translation along the direction of the mirror line.
Glide reflections are the only type of symmetry
that involves more than one.
POWERPOINT PS.
What is Geometry
M.C Escher- Mauritis Cornelis Escher
The branch of mathematics that is concerned with
Kinds of Line
the properties and relationships of:
points, lines, angles, curves, surfaces, and solids.
The visual study of shapes, sizes, patterns, and Line
positions.
Line Segment
Ray
Line- We indicates a line with arrows at both ends to
show that the line continues forever in both directions.
Line Segment- A line segment is a part of a line with
end points at both ends.
Ray- A ray has an end point at one end and an arrow at
the other end to show that it starts from one point and
then goes on forever in one direction.
You might also like
- Analyzing Shapes Symmetry Gina Caballero - Math 111Document10 pagesAnalyzing Shapes Symmetry Gina Caballero - Math 111api-282159759No ratings yet
- Points, Lines, Angles, and Parallel LinesDocument14 pagesPoints, Lines, Angles, and Parallel LinesShafika Aida100% (2)
- Mathematics - Module 02 - NotesDocument10 pagesMathematics - Module 02 - NotesVinod RamdasNo ratings yet
- Plane and Solid Geometry Module Bsed Math1Document50 pagesPlane and Solid Geometry Module Bsed Math1Ces Sy100% (3)
- MATHEMATICSDocument10 pagesMATHEMATICSCzarina AntoninoNo ratings yet
- Mathemetical Concepts PDFDocument6 pagesMathemetical Concepts PDFRavindra DeyNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument43 pagesGeometryapi-349739676100% (1)
- Basic ConceptDocument40 pagesBasic ConceptRosemarie CortavistaNo ratings yet
- Plane and Solid Geometry - 1Document62 pagesPlane and Solid Geometry - 1Regielyn Pagad100% (2)
- Introduction To Solid MensurationDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Solid MensurationDanica AguilarNo ratings yet
- Solid Geometry: Clarita R. GuevaraDocument157 pagesSolid Geometry: Clarita R. GuevaraJoshua Saldaña100% (1)
- Isometric and Multi-View ProjectionsDocument17 pagesIsometric and Multi-View ProjectionsNwachukwu EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Solid Mensuration REVIEWERDocument5 pagesSolid Mensuration REVIEWER21-07543No ratings yet
- Math Reviewer Module1-2Document4 pagesMath Reviewer Module1-2Юрий ДесNo ratings yet
- 4 Types of Symmetry in The PlaneDocument5 pages4 Types of Symmetry in The PlaneRohit MaldeNo ratings yet
- Freize Patterns-WPS OfficeDocument12 pagesFreize Patterns-WPS OfficeMerylcyne Bangsao SimsimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 TransformationsDocument7 pagesChapter 5 Transformationsdenis kipkiruiNo ratings yet
- Summary About Plane Geometry: A Point Is An Exact Location. It Has No SizeDocument5 pagesSummary About Plane Geometry: A Point Is An Exact Location. It Has No SizeSherly Herawati Hestina PutriNo ratings yet
- 4 Types of Symmetry in The PlaneDocument5 pages4 Types of Symmetry in The PlaneDent KhairuddinNo ratings yet
- Day-4-UPCAMP-2018Document40 pagesDay-4-UPCAMP-2018afunabermudezNo ratings yet
- TransformationsDocument2 pagesTransformationsSolehah Abdul RahimNo ratings yet
- The Four Type of Symmetry in The PlaneDocument4 pagesThe Four Type of Symmetry in The PlaneHimansu MookherjeeNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing ReviewerDocument5 pagesEngineering Drawing ReviewerAngelo GranadaNo ratings yet
- Projective GeometryDocument61 pagesProjective GeometryAileen Grace Delima100% (4)
- Linear Equations: Open SentencesDocument57 pagesLinear Equations: Open SentencesEpoditmas SeyerNo ratings yet
- Basic Drafting ReviewerDocument5 pagesBasic Drafting ReviewerCristal Mea AndalesNo ratings yet
- Trigo and Plane Geo Supplementary Materials2Document5 pagesTrigo and Plane Geo Supplementary Materials2Ronieta VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Mathematics: Study Guide 4Document120 pagesFundamental Mathematics: Study Guide 4frans NgobeniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2: Crystal SymmetryDocument47 pagesLecture 2: Crystal SymmetryZul FadliNo ratings yet
- Solid MensurationDocument3 pagesSolid MensurationFranco Louis RomeroNo ratings yet
- Math PresentationDocument22 pagesMath PresentationMaame Somwaa Awua OkyereNo ratings yet
- Basic GeometryDocument24 pagesBasic GeometryEtha Cantik100% (1)
- Geometric Patterns NotesDocument2 pagesGeometric Patterns Notesgerzona73100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Essential of GeometryDocument14 pagesChapter 1 Essential of GeometryNina HNo ratings yet
- Final ModuleDocument5 pagesFinal ModuledatumanongnormalahNo ratings yet
- (Math) 062028Document19 pages(Math) 062028Eldrick CortezNo ratings yet
- Graphics, Visual&DesignDocument10 pagesGraphics, Visual&Designdarianne.pablo02No ratings yet
- A Geometry I and Trigonometry IDocument38 pagesA Geometry I and Trigonometry IA.BensonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document91 pagesLesson 1Anin Ziur100% (1)
- Geometry 1 - 1 Intro To Geometry HandoutDocument40 pagesGeometry 1 - 1 Intro To Geometry HandoutAlma ReynaldoNo ratings yet
- Mathematical SystemDocument4 pagesMathematical SystemIvory Vivien Yanna ForresterNo ratings yet
- Batangas State University: Geometry GeometryDocument2 pagesBatangas State University: Geometry GeometryRensieViqueFalculanNo ratings yet
- AF3Document2 pagesAF3hyacinth gulbenNo ratings yet
- Orthographic Projection: Review: Projections Orthographic ProjectionsDocument47 pagesOrthographic Projection: Review: Projections Orthographic ProjectionsLeo Dev WinsNo ratings yet
- Angles and Angle PropertiesDocument6 pagesAngles and Angle PropertiesDonna-Lisa YearwoodNo ratings yet
- Johnmarl 0.1Document3 pagesJohnmarl 0.1Shiela Mae CenenNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Term Picture/Symbol: Is A LocationDocument3 pagesVocabulary Term Picture/Symbol: Is A LocationdestinyNo ratings yet
- Reflection SymmetryDocument1 pageReflection SymmetryPearl Dianne VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Geometry AlchemistDocument104 pagesGeometry AlchemistpreetyNo ratings yet
- Solid Students Lecture1Document7 pagesSolid Students Lecture1Niño Bhoy FloresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-GeometryDocument12 pagesChapter 3-GeometryArianne Claire CelestialNo ratings yet
- Ch.21 - Navigational Mathematics PDFDocument12 pagesCh.21 - Navigational Mathematics PDFBechir SamyrNo ratings yet
- SymmetryDocument4 pagesSymmetryMidhun Bhuvanesh.B 7ANo ratings yet
- Plane Geometry-Group 6Document26 pagesPlane Geometry-Group 6oktavia anggiNo ratings yet
- What Is Mensuration? Basic Terms in Mensuration: Facts FactsDocument2 pagesWhat Is Mensuration? Basic Terms in Mensuration: Facts FactsRiz Ann PapaNo ratings yet
- Quillopas Julie Anne N BSN 1J MMW Act O1Document4 pagesQuillopas Julie Anne N BSN 1J MMW Act O1Tricia Fern MadayagNo ratings yet
- Lines & AnglesDocument15 pagesLines & AnglesSMK100% (1)
- Reflection in A LineDocument5 pagesReflection in A Lineapi-291428736No ratings yet
- Points Lines and PlanesDocument18 pagesPoints Lines and Planesfe nantezaNo ratings yet
- Exploring Information Quality in Accounting Information Systems AdoptionDocument12 pagesExploring Information Quality in Accounting Information Systems AdoptionJusteen BalcortaNo ratings yet
- FSCP Community PartnershipDocument17 pagesFSCP Community PartnershipJusteen BalcortaNo ratings yet
- TAEG (Reviewer)Document17 pagesTAEG (Reviewer)Justeen BalcortaNo ratings yet
- What Kinds of Merchandise, Products, and or Services Are Most Needed by The Communities Where The Students Live?Document2 pagesWhat Kinds of Merchandise, Products, and or Services Are Most Needed by The Communities Where The Students Live?Justeen BalcortaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Research (Midterm) Methods in Collecting DataDocument19 pagesReviewer in Research (Midterm) Methods in Collecting DataJusteen BalcortaNo ratings yet
- QUIZ 1: Interim Financial ReportingDocument13 pagesQUIZ 1: Interim Financial ReportingJusteen BalcortaNo ratings yet
- Our Lady of Fatima University: Dr. Ramonita SalazarDocument1 pageOur Lady of Fatima University: Dr. Ramonita SalazarJusteen Balcorta100% (1)
- TIKTOK (Ctriteria For Judging)Document1 pageTIKTOK (Ctriteria For Judging)Justeen BalcortaNo ratings yet
- Egg Shell MosaicDocument3 pagesEgg Shell MosaicJusteen BalcortaNo ratings yet
- Epap Reviewer (Prelim)Document9 pagesEpap Reviewer (Prelim)Justeen BalcortaNo ratings yet
- High Prices Most Unique ProductsDocument1 pageHigh Prices Most Unique ProductsJusteen BalcortaNo ratings yet
- EPAP 311: Assignmen T1Document9 pagesEPAP 311: Assignmen T1Justeen BalcortaNo ratings yet
- Heart Run, The KCB Lion's Den, Blaze by Safaricom and Equity's Wings To Fly Are But A Few Initiatives by Entrepreneurs That Are Contributing TowardsDocument1 pageHeart Run, The KCB Lion's Den, Blaze by Safaricom and Equity's Wings To Fly Are But A Few Initiatives by Entrepreneurs That Are Contributing TowardsJusteen BalcortaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Physical Education 2Document2 pagesLesson Plan in Physical Education 2Justeen BalcortaNo ratings yet
- Launching Adult ChildrenDocument3 pagesLaunching Adult ChildrenJusteen BalcortaNo ratings yet
- Measurement Week 10Document2 pagesMeasurement Week 10Justeen BalcortaNo ratings yet
- CPMT Act 1Document1 pageCPMT Act 1Justeen BalcortaNo ratings yet
- JEWELRYDocument2 pagesJEWELRYJusteen BalcortaNo ratings yet
- The Professional Attitude of Faculty Members2020Document60 pagesThe Professional Attitude of Faculty Members2020Justeen BalcortaNo ratings yet
- ThesisMath Chapter 1 5Document27 pagesThesisMath Chapter 1 5Justeen BalcortaNo ratings yet
- Epap ReviewerDocument9 pagesEpap ReviewerJusteen BalcortaNo ratings yet
- The Elements of Art: 3. FormDocument4 pagesThe Elements of Art: 3. FormJusteen BalcortaNo ratings yet
- Super Same: PDFDocument8 pagesSuper Same: PDFJusteen BalcortaNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy RevisedDocument10 pagesBloom's Taxonomy RevisedJusteen BalcortaNo ratings yet
- Linking Instructional Strategies To Learning Objectives: Verbal InformationDocument7 pagesLinking Instructional Strategies To Learning Objectives: Verbal InformationJusteen BalcortaNo ratings yet
- Visual SymbolsDocument15 pagesVisual SymbolsJusteen BalcortaNo ratings yet
- Group 1 ResearchDocument5 pagesGroup 1 ResearchJusteen BalcortaNo ratings yet
- Bosvark ZL08F Front-End Loader: Key FeaturesDocument2 pagesBosvark ZL08F Front-End Loader: Key FeaturesJaco Coetzer100% (1)
- Systemic Functional Grammar: A First Step Into The Theory:, IncludingDocument31 pagesSystemic Functional Grammar: A First Step Into The Theory:, Includingnona nonaNo ratings yet
- Dual Operational Amplifier: NJM4560D, NJM4560M, NJM4560E NJM4560LDocument4 pagesDual Operational Amplifier: NJM4560D, NJM4560M, NJM4560E NJM4560LPablo Diego Cecere CasadoNo ratings yet
- Non Destructive TestingDocument9 pagesNon Destructive TestingAhmed KhanNo ratings yet
- PWSMTS Full Test - 01 - Test PaperDocument9 pagesPWSMTS Full Test - 01 - Test PaperPranav kr. PrasadNo ratings yet
- EY Making India Brick by Brick PDFDocument96 pagesEY Making India Brick by Brick PDFRKVSK1No ratings yet
- Technical Information ASSET DOC LOC 17687504Document23 pagesTechnical Information ASSET DOC LOC 17687504SuparnoNo ratings yet
- ASC - General - Purpose - Capacitor For HallsensorDocument19 pagesASC - General - Purpose - Capacitor For HallsensorLusiNo ratings yet
- Mock 1 QP (PQ, Kine, Dyna)Document28 pagesMock 1 QP (PQ, Kine, Dyna)Tahmedul Hasan TanvirNo ratings yet
- IELTS Reading Skills & StrategiesDocument4 pagesIELTS Reading Skills & StrategiesThinn Thinn Oo100% (1)
- 2-Design of Slab Non-Traditional FORMWORK.Document55 pages2-Design of Slab Non-Traditional FORMWORK.Eslam SamirNo ratings yet
- Tut 1Document5 pagesTut 1foranangelqwertyNo ratings yet
- 09 Husserl - The Encyclopaedia Britannica Article - Draft EDocument19 pages09 Husserl - The Encyclopaedia Britannica Article - Draft EAleksandra VeljkovicNo ratings yet
- Owner'S Manual: Operation Maintenance Parts ListDocument130 pagesOwner'S Manual: Operation Maintenance Parts ListDmitryNo ratings yet
- Niir Modern Technology Petroleum Greases Lubricants Petro Chemicals 2nd Revised EditionDocument8 pagesNiir Modern Technology Petroleum Greases Lubricants Petro Chemicals 2nd Revised EditionM.ASNo ratings yet
- Bevel Gear Drive Screw Jack 6000Document5 pagesBevel Gear Drive Screw Jack 6000Elias YeshiwasNo ratings yet
- Product Service Manual and Parts List BM# 3266/005 (M8LKFX-912Y)Document30 pagesProduct Service Manual and Parts List BM# 3266/005 (M8LKFX-912Y)Castañeda JacvNo ratings yet
- Notes:-All Dimension Are in MM.: Investa Pumps Pvt. LTDDocument1 pageNotes:-All Dimension Are in MM.: Investa Pumps Pvt. LTDJairzhino EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Traffic Engineering Third Edition by Roess & Prasas 2004 PDFDocument802 pagesTraffic Engineering Third Edition by Roess & Prasas 2004 PDFdanielNo ratings yet
- Blue Green Illustrative Presentation Skills Infographic PosterDocument1 pageBlue Green Illustrative Presentation Skills Infographic Posterpriyaah23No ratings yet
- Activity 3 - MINITASK - CapacitorDocument13 pagesActivity 3 - MINITASK - CapacitorEssi Marie FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Recipe For BPP Ncii UaqteaDocument11 pagesRecipe For BPP Ncii UaqteaPJ ProcoratoNo ratings yet
- The Said and The UnsaidDocument19 pagesThe Said and The UnsaidOzana BudauNo ratings yet
- Ansi Ies RP-8-21Document547 pagesAnsi Ies RP-8-21cristianbaileyeNo ratings yet
- Sigur Ros Lyrics, Photos, Pictures, Paroles, Letras, Text For Every SongsDocument30 pagesSigur Ros Lyrics, Photos, Pictures, Paroles, Letras, Text For Every SongsDantés Viveros RNo ratings yet
- RCI Profile.Document10 pagesRCI Profile.quaiser_nikoNo ratings yet
- CHARLOTTEDocument18 pagesCHARLOTTEravenNo ratings yet
- Surge Impedance LoadingDocument2 pagesSurge Impedance LoadingAnbu AyyappanNo ratings yet
- Moc3052 PDFDocument9 pagesMoc3052 PDFHernan JavierNo ratings yet
- In-Depth: How Does A Child Get A Pectus Excavatum?Document12 pagesIn-Depth: How Does A Child Get A Pectus Excavatum?Gino VillanuevaNo ratings yet