Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Question Bundle - Multiple Topics 1
Uploaded by
Marinos EliadesOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Question Bundle - Multiple Topics 1
Uploaded by
Marinos EliadesCopyright:
Available Formats
Assessment 1.1.
1
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Units
Units and equations
1 Isaac Newton’s law of gravitation gives the magnitude of the attractive force F
between two point masses m1 and m2 a distance d apart:
Gm1m2
F
d2
Use this equation to determine the appropriate SI units for the universal
gravitational constant G.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 1 = 2 marks)
2 The drag force F acting on a small sphere of radius r moving at low velocity v
through a fluid is given by Stokes’ law:
F 6πηrv , where η is the viscosity of the fluid.
(a) Use this equation to determine the appropriate SI units for η.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(b) Show that your answer to (a) is equivalent to the Pa s.
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 2 = 3 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
1
Assessment 1.1.1
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Units
3 The time period T for the oscillations of a mass m suspended from a spring of
spring constant k depends only on m and k.
Use the fact that all equations in physics must balance in terms of units to
decide which one of the following equations could represent the time period.
Explain your answer.
m
A T 2π
k
m
B T 2π
k
k
C T 2π
m
k
D T 2π
m
(3)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 3 = 3 marks)
4 (a) Explain what is meant by a base unit.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(b) Explain what is meant by a derived unit.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
2
Assessment 1.1.1
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Units
F
(c) Pressure p is defined by the equation p , where F is the force acting
A
perpendicular to an area A. The pascal (Pa) is the derived unit for pressure.
Express this derived unit in the equivalent base units.
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 4 = 5 marks)
Electrical units
5 (a) Show that 1 Nm is equivalent to 1 VC.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(b) Express the ohm in SI base units.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 5 = 4 marks)
Standard form
6 (a) Calculate the electrical energy transferred by a 50 mW generator operating
for 50 ms. Express your answer in standard form.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
3
Assessment 1.1.1
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Units
(b) Calculate the cross-sectional area of a copper wire of diameter 250 μm.
Express your answer in standard form in m2.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 6 = 4 marks)
Interpreting graphs
7 (a) What is represented by the gradient of each of the graphs described below?
In each case, use a unit argument to justify your answer.
(i) Displacement against time for a rocket
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(ii) Velocity against time for a sprinter
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(iii) Energy transferred against time for an electric motor
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(iv) Force against extension for a spring obeying Hooke’s Law
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(v) Stress against strain for a metal wire obeying Hooke’s Law
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
4
Assessment 1.1.1
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Units
(b) What is represented by the area under each of the graphs described below?
In each case, use a unit argument to justify your answer.
(i) Velocity against time for a car
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(ii) Power against time for a generator
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(iii) Force against extension for a spring obeying Hooke’s Law
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(iv) Stress against strain for a metal wire obeying Hooke’s Law
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(v) Charge transferred against voltage for an electrical component
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 7 = 10 marks)
Order of magnitude
8 Give an order of magnitude estimate in SI units for each of the following
quantities.
(a) The time taken for light to reach the Earth from the Sun
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
5
Assessment 1.1.1
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Units
(b) The power output of a nuclear power station
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(c) The kinetic energy of a car travelling along a motorway
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(d) The momentum of a diving seagull
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(e) The number of blades of grass on a football pitch
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 8 = 10 marks)
TOTAL FOR ASSESSMENT = 41 MARKS
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
6
Assessment 1.1.2
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Estimation
There are no ‘right answers’ to these questions but there are certainly reasonable
and unreasonable answers! If you get stuck ask your teacher if you can have a hint
but don’t be tempted to do this until you have spent some time struggling with the
problem!
Estimation questions
1 Estimate the number of atoms in your body.
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
2 Estimate the number of atoms in a £1 coin.
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
3 Estimate the number of molecules in the Earth’s atmosphere.
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
4 Estimate the total electrical energy that can be delivered by an AA cell.
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
5 Estimate the pressure exerted on the ground when you stand on tiptoe.
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
1
Assessment 1.1.2
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Estimation
6 Estimate the drag on a car travelling at 30 ms−1 along a straight road.
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
7 Estimate the power output of a cyclist travelling at 15 ms−1.
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
8 Estimate the mass of air inside a cathedral.
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
9 Estimate the maximum electrical power output from a wind turbine with a radius
of 10 m.
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
10 Estimate the delay between seeing a batsman striking a cricket ball and hearing
the impact for a spectator in the crowd.
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
11 Estimate the breaking stress for a human hair.
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
2
Assessment 1.1.2
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Estimation
12 Estimate the mass of the Earth.
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
13 Estimate the time taken for light to cross the diameter of a hydrogen atom.
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
14 Estimate the volume of an elephant.
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
15 Estimate the terminal velocity of a tennis ball dropped from the top of a tall
building.
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
16 Estimate the Young modulus of rubber. Why is this not a fixed value?
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
17 Estimate the thickness of a sheet of printer paper.
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
3
Assessment 1.1.2
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Estimation
18 Estimate the spring constant for a car’s suspension.
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
19 Estimate the minimum wind speed that would blow a man over.
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
20 Estimate the drift velocity of electrons through the filament of a torch.
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
Fermi questions
1 How many golf balls fit in a suitcase?
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
2 Estimate the speed of a bee’s wingtip in flight.
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
3 How many garbage trucks would be needed to take away all of the rock in
Mount Everest?
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
4
Assessment 1.1.2
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Estimation
4 How many photons are emitted by a camera flashlight when it flashes once?
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
5 Estimate the power output of the Sun.
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
6 Estimate the number of dimples on a golf ball.
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
7 How long would it take a snail to complete a 100 m race?
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
8 If all the atoms in a human being were placed end to end how long would the
line be?
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
9 How far can a car go before it rubs off one layer of molecules from its tyres?
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
5
Assessment 1.1.2
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Estimation
10 What would be the world record for the high jump if the event was held on the
Moon?
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
11 What is the minimum diameter of parachute needed to allow a human to land
safely after jumping from an aircraft?
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
12 What is the ratio of energy stored in a car battery to energy stored in an AA cell?
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
13 How many words are there in an English version of the Bible?
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
14 How long would it take to fill a swimming pool from a kitchen tap?
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
15 How many petrol stations are there in the UK?
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
6
Assessment 1.1.2
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Estimation
16 How many ants live in an ant colony?
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
17 What is the speed of the Moon?
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
18 Would it be possible for an ant the size of an elephant to evolve on Earth?
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
19 How could you measure the mass of an astronaut inside an orbiting space
station?
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
20 How many car mechanics are there in Manchester?
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
7
Assessment 2.1
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Motion
1 Which of the following is a vector?
A kinetic energy
B momentum
C mass
D speed
Your answer
(1)
(Total for Question 1 = 1 mark)
2 A sports car accelerates from 10 ms−1 to 40 ms−1 in 5.0 s. Which line in the table
below gives the correct values for distance travelled, average speed and
acceleration during the 5.0 s?
Distance/m Average speed/ms−1 Acceleration/ms−2
A 100 25 8
B 100 20 6
C 125 25 6
D 125 20 8
Your answer
(1)
(Total for Question 2 = 1 mark)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
1
Assessment 2.1
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Motion
3 A cable car at rest is suspended from a cable as shown below. The tension in
the cable is T and the weight of the cable car is W.
Which of the equations below is correct?
A 2T = W
B 2T sin (80°) = W
C 2T cos (80°) = W
D 2T + W = 0
Your answer
(1)
(Total for Question 3 = 1 mark)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
2
Assessment 2.1
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Motion
4 A uniform metre ruler can be balanced horizontally by placing a 100 g mass on
the ruler 5.0 cm from one end and putting a pivot under the ruler at 30.0 cm from
the same end as shown below.
What is the mass of the metre ruler?
A 100 g
B 125 g
C 400 g
D There is not enough information to calculate the mass of the ruler.
Your answer
(1)
(Total for Question 4 = 1 mark)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
3
Assessment 2.1
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Motion
5 The diagram below shows a velocity–time graph for a vehicle of mass 2000 kg
over a 35 s time period.
(a) State the feature of the graph that represents the acceleration of the
vehicle.
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................
(b) State the feature of the graph that represents the displacement of the
vehicle.
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................
(c) (i) Calculate the acceleration during the first 10 s.
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................
(ii) Calculate the total displacement of the vehicle during the 35 s.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................
(ii) Calculate the braking force on the vehicle during the final 5 s.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 5 = 7 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
4
Assessment 2.1
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Motion
6 The diagram below shows a car towing a caravan at constant velocity along a
straight horizontal road. The car and caravan each have a mass of 1200 kg and
the total drag force on each vehicle is 1000 N.
(a) State the magnitude of the forward force from the car and explain your
answer.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(b) State the magnitude of the tension in the tow link. Justify your answer.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(c) Explain how the forces acting at the point where the tow link connects to the
car illustrate Newton’s third law of motion.
(3)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(d) The tow link suddenly breaks. Calculate the initial acceleration of the car.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 6 = 9 marks)
TOTAL FOR ASSESSMENT = 20 MARKS
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
5
Assessment 2.2
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Energy
1 Which of the following involves the greatest quantity of energy?
A A 50 kg child rising 20 m in a lift
B A 500 g projectile moving at 100 ms–1
C A 5.0 kg rock on a ledge at a height of 100 m above the ground
D The work done when a man pushes a car 50 m with an average force of
400 N
Your answer
(1)
(Total for Question 1 = 1 mark)
2 Which one of the following quantities is always conserved in a closed system?
A Kinetic energy
B Gravitational potential energy
C Work done
D Total energy
Your answer
(1)
(Total for Question 2 = 1 mark)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
1
Assessment 2.2
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Energy
3 A child of mass 50 kg runs at 5.0 ms–1 and then slides along an icy surface,
eventually coming to rest after sliding a distance of 20 m.
(a) Describe the energy transfers that take place as she comes to rest.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(b) Calculate her initial kinetic energy.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(c) Calculate the average frictional force acting on the child as she slows down.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(d) Discuss whether an adult, of greater mass than the child but running at the
same initial speed, would slide further or less far than the child.
(3)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 3 = 9 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
2
Assessment 2.2
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Energy
4 (a) State the law of conservation of energy.
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................
(b) Explain what is meant by ‘power’.
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................
(c) Calculate the energy transferred by each of the following (assume 100%
efficiency in each case):
(i) A wind turbine generating 25 kW for 1 hour
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(ii) A 10 000 W electric shower used for 10 minutes
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 4 = 6 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
3
Assessment 2.2
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Energy
5 The diagram below shows a man pulling a boat toward a jetty. As he pulls on
the rope he steps backwards so that the angle of the rope to the horizontal
remains constant and the boat moves forwards at constant velocity. The tension
in the rope is 200 N.
(a) State the distance moved by the boat when he moves back 2.0 m.
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................
(b) Calculate the work done on the boat as he moves back 2.0 m.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 5 = 3 marks)
TOTAL FOR ASSESSMENT = 20 MARKS
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
4
Assessment 2.3
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Momentum
1 Two birds are flying in a straight line directly towards one another. They each
have a mass of 2.0 kg and a speed of 5.0 ms−1. Which line of the table below
gives the total momentum and kinetic energy of the two birds?
Momentum/kg ms−1 Kinetic energy/J
A 50 10
B 10 50
C 0 50
D 0 10
Your answer
(1)
(Total for Question 1 = 1 mark)
2 A man of mass 80 kg steps forwards out of a stationary rowing boat. His initial
velocity is 1.0 and the boat begins to move backwards at 0.25 ms−1.
(a) State the law of conservation of momentum.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(b) Calculate the mass of the boat.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(c) State and explain any assumptions you made in order to answer part (b).
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 2 = 6 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
1
Assessment 2.3
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Momentum
3 Below is a simplified diagram of a jet engine.
(a) Explain, by referring to momentum, how the jet engine can generate a
forward thrust for the aircraft.
(3)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(b) When the aircraft is in steady flight, its momentum is constant. Explain how
the law of conservation of momentum applies even though the jet engine
continues to accelerate the air/exhaust gases.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 3 = 5 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
2
Assessment 2.3
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Momentum
4 The diagram below shows a girl jumping off a low wall. As she lands, she bends
her knees. Explain how this helps to protect her from injury.
(3)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 4 = 3 marks)
5 A man throws a sack of potatoes of mass 20 kg onto a stationary trolley of mass
40 kg. The trolley rolls forwards with an initial velocity of 0.40 ms−1. Calculate the
velocity of the sack of potatoes just before it landed on the trolley.
(3)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 5 = 3 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
3
Assessment 2.3
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Momentum
6 A rocket motor provides an impulse of 2.5 Ns to a rocket of mass 100 g.
What is the maximum velocity of the rocket?
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 6 = 2 marks)
TOTAL FOR ASSESSMENT = 20 MARKS
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
4
Assessment 3.1
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Electrical quantities
1 Which of the following rows gives the correct units for each of the electrical
quantities?
Resistance Current Charge Potential difference
A Ω I C A
B R I Q V
C Ω A C V
D R A Q Ω
Your answer
(1)
(Total for Question 1 = 1 mark)
2 Which of the following is a definition of electrical current?
A The energy transferred per unit charge in an electrical circuit
B The amount of electrical charge in a circuit
C The rate of flow of electrical charge in an electrical circuit
D The movement of charge around an electrical circuit
Your answer
(1)
(Total for Question 2 = 1 mark)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
1
Assessment 3.1
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Electrical quantities
3 The diagram below shows the variation of electrical resistivity with temperature
for three different metals.
(a) Explain why metals are good conductors of electricity.
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................................
(b) Explain the difference between ‘resistance’ and ‘resistivity’.
(4)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(c) Explain why the resistivity of a metal increases with temperature.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(d) Use the graph to calculate the resistance of an iron wire of length 2.0 m and
radius 0.50 mm at a temperature of 100 °C.
(4)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 3 = 11 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
2
Assessment 3.1
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Electrical quantities
4 Some materials exhibit superconductivity at very low temperatures.
(a) What is meant by superconductivity?
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................................
(b) State and explain one application of superconductors.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 4 = 3 marks)
5 The electrical circuit shown below was used to investigate the resistance of a
filament lamp.
(a) How can the resistance be calculated in this experiment?
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................................
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
3
Assessment 3.1
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Electrical quantities
(b) The graph below shows how the current varies with the potential difference
across the lamp.
(i) Use it to calculate the resistance of the lamp when it has a potential
difference of 5.0 V across it.
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................................
(ii) Explain why doubling the voltage across the lamp does not double the
current through it.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 5 = 4 marks)
TOTAL FOR ASSESSMENT = 20 MARKS
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
4
Assessment 3.2
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Complete electrical circuits
1 The diagram below shows three 2.0 resistors connected in three different
ways. For each combination (a) to (c) calculate the total resistance between
points A and B. Show how you obtain your answers.
(a)
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(b)
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(c)
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 1 = 5 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
1
Assessment 3.2
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Complete electrical circuits
2 A real cell has an emf of 6.0 V and an internal resistance of 0.50 .
(a) State and explain the reading that would be obtained if a high resistance
(perfect) voltmeter was connected across the terminals of this cell.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(b) Calculate the maximum current that could be drawn from this cell if it was
accidentally short-circuited (its terminals connected together by a wire of
negligible resistance).
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................
(c) The cell is now connected to a resistor of resistance 10 . Calculate the
power dissipated in this resistor.
(3)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 2 = 6 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
2
Assessment 3.2
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Complete electrical circuits
3 The diagram below shows a potential divider circuit. The battery has negligible
internal resistance.
(a) Calculate the reading that would be obtained if a high resistance (perfect)
voltmeter was connected across:
(i) AB
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................
(ii) BC
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................
(iii) AC
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................
(b) A second 200 resistor is connected in parallel with the first (across AB).
Calculate new values for:
(i) The potential difference across AB.
(3)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(ii) The potential difference across BC.
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 3 = 7 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
3
Assessment 3.2
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Complete electrical circuits
4 State and explain the magnitude of current flowing between A and B in the
diagram below. Each resistor has a resistance of 10 .
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 4 = 2 marks)
TOTAL FOR ASSESSMENT = 20 MARKS
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
4
Assessment 4.1
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Fluids
1 Which of the statements below about a floating object is correct?
A The volume of liquid displaced by the object is equal to the volume of the
object.
B The density of the object is greater than the density of the liquid.
C The mass of liquid displaced is equal to the upthrust on the object.
D The weight of the liquid displaced is equal to the weight of the object.
Your answer
(1)
(Total for Question 1 = 1 mark)
2 Stoke’s law for drag on a small sphere falling slowly through a viscous fluid is
F = 6πηrv. Which of the following is not an acceptable unit for viscosity, η?
A kgm−1s−1
B Ns
C Pa s
D Ns m−2
Your answer
(1)
(Total for Question 2 = 1 mark)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
1
Assessment 4.1
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Fluids
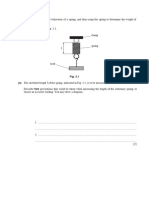
3 A student intends to carry out a falling ball method to determine the viscosity of
a viscous fluid. She sets up her apparatus as shown in the diagram below and
records the times for the ball to fall through each 5.0 cm distance.
(a) Sketch a graph to show how you would expect the velocity of the falling ball
bearing to change from the moment of release (at the surface) until it
reaches the bottom of the tube. Label the region in which the ball is falling at
terminal velocity.
(3)
(b) Explain in terms of the forces acting on the falling ball bearing why it
reaches a terminal velocity.
(3)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(c) How can she tell from her measurements when the ball has reached
terminal velocity?
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................................
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
2
Assessment 4.1
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Fluids
(d) She will also need to measure the diameter of the ball bearing. Suggest a
suitable measuring device in order to measure this accurately.
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................................
(e) In her experiment, the time taken to fall 5.0 cm at terminal velocity was
4.00 s and the diameter of the ball was 1.60 mm. The density of steel is
8000 kg m−3. Calculate the viscosity of the fluid.
(3)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(f) What must be assumed about the nature of the fluid flow in order to answer
part (e)?
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 3 = 12 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
3
Assessment 4.1
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Fluids
4 The table below gives the densities of some common materials.
Material Density/kg m−3
Air (atm. pressure and temp.) 1.2
Water 1000
Zinc 7140
Copper 8920
(a) Estimate the mass of air in your physics laboratory.
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................................
(b) Calculate the mass and weight of 500 cm3 of water.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(c) Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc. In a particular type of brass the ratio by
mass of copper to zinc is 90:10. Calculate the density of this brass alloy.
(3)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 4 = 6 marks)
TOTAL FOR ASSESSMENT = 20 MARKS
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
4
Assessment 4.2
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Material properties
1 Two cables, X and Y, are made of the same type of steel but differ in length and
cross-section. Cable X has length l and diameter d and cable Y has length
d
2l and diameter . Which of the following statements is correct?
2
A The two cables will break with the same force.
B The two cables will break with the same stress.
C The two cables will break with the same extension.
D The two cables will break with the same load.
Your answer
(1)
(Total for Question 1 = 1 mark)
2 A steel spring which obeys Hooke’s law extends by an amount e when a load W
is suspended from it. Two identical springs are connected in series and the
same load is suspended from them. By how much does this system of two
springs extend?
e
A
2
B e
C 2e
D It is not possible to say because the springs might have passed their limit of
proportionality.
Your answer
(1)
(Total for Question 2 = 1 mark)
3 Which of the following is equal to the area under a stress versus strain graph?
A Breaking stress
B Work done
C Plastic deformation
D Energy per unit volume
Your answer
(1)
(Total for Question 3 = 1 mark)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
1
Assessment 4.2
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Material properties
4 The Young modulus is a measure of:
A Stiffness
B Hardness
C Strength
D Ductility
Your answer
(1)
(Total for Question 4 = 1 mark)
5 The diagram below shows a stress–strain graph for a metal wire.
(a) Explain the difference between elastic and plastic deformation and identify a
region on the stress versus strain graph in which you would expect this
metal to exhibit each type of behaviour.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
2
Assessment 4.2
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Material properties
(b) Take measurements from the graph to estimate:
(i) The Young modulus.
(3)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(ii) The breaking stress.
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(iii) Explain how it is possible for the strain to increase while the stress
falls.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 5 = 8 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
3
Assessment 4.2
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Material properties
6 The diagram below shows a load against extension graph for a car suspension
system.
(a) How can you tell from the graph that the suspension system obeys
Hooke’s law?
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(b) Calculate the spring constant for the suspension system.
(3)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(c) Calculate the energy stored in the springs when there is a load of 2500 N in
the vehicle.
(3)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 6 = 8 marks)
TOTAL FOR ASSESSMENT = 20 MARKS
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
4
Assessment 5.1
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Basic waves
1 The speed of sound at sea level is 340 ms−1. Humans can hear sounds in the
range 20 Hz to 20 000 kHz.
(a) Calculate the wavelengths of sounds at 20 Hz and 20 000 kHz.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(b) A gun is fired from a ship lying 400 m from some cliffs. A sailor standing
close to the gun hears the gun fire and hears the echo from the cliffs a short
time later. Calculate the time between these two sounds being heard.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 1 = 4 marks)
2 Explain why it is impossible to hear an explosion in space but it is possible to
see it.
(4)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 2 = 4 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
1
Assessment 5.1
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Basic waves
3 A microphone is connected to an oscilloscope. The diagram below shows an
oscilloscope trace obtained when the microphone detects sound from a
loudspeaker connected to a signal generator. The oscilloscope settings are
0.2 V cm−1 (y-axis) and 2.0 ms−1 cm (x-axis).
(a) What is the amplitude of this signal?
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................................
(b) What is the frequency of this signal?
(3)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 3 = 4 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
2
Assessment 5.1
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Basic waves
4 When an earthquake occurs P-waves (longitudinal) and S-waves (transverse)
are created at the epicentre of the quake and travel outwards in all directions at
different speeds. The P-waves have a speed of about 5.0 kms−1 and the S-
waves have a speed of about 3.5 kms−1. Seismic stations detect both types of
wave and measure the time interval between the arrival of the P-waves and
then the arrival of the S-waves.
(a) Use diagrams to explain the difference between longitudinal and transverse
waves.
(4)
(b) Calculate the time interval between the arrival of P- and S-waves at a
seismic station 200 km from the epicentre of the earthquake.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(c) Another station measures a time interval of 72 s between the arrival of the
P-waves and the S-waves. How far is this station from the epicentre of the
earthquake?
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 4 = 8 marks)
= 20 MARKS
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
3
Assessment 5.2
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 The behaviour of waves
1 The diagram below shows two sound waves displayed on an oscilloscope
screen. Which of the following gives the phase difference in degrees between
the two signals?
A 60°
B 90°
C 120°
D 180°
Your answer
(1)
(Total for Question 1 = 1 mark)
2 The diagram below shows an experimental set-up used by a teacher to
demonstrate superposition effects. The two loudspeakers, S1 and S2, are
connected to the same signal generator so that they emit sound waves in phase
and of the same frequency and amplitude. The teacher moves a microphone
(at M) along line AB and displays the signal from the microphone on the
oscilloscope screen. The signal generator is set to a frequency of 680 Hz and
the speed of sound in the laboratory is 340 ms–1.
(a) Explain why the speakers are coherent sources.
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................................
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
1
Assessment 5.2
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 The behaviour of waves
(b) (i) State the value of the path difference in metres for sounds reaching the
microphone when it is at M, as shown in the diagram.
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................................
(ii) Calculate the phase difference between the waves from S1 and S2 at M.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(iii) What do you conclude about the amplitude of sound at M? Explain your
answer.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(c) Describe and explain how the amplitude of the trace on the oscilloscope
would change as the teacher moved the microphone from M to B.
(5)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 2 = 11 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
2
Assessment 5.2
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 The behaviour of waves
3 Microwaves inside a microwave oven can set up patterns of standing waves.
(a) Explain what is meant by a ‘standing wave’ and suggest how these might be
formed inside a microwave oven.
(3)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(b) When food is cooked in a microwave oven it is placed on a rotating plate.
Why is it important to rotate the food during cooking?
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 3 = 5 marks)
4 Which of the following statements about waves is incorrect?
A Sound waves can reflect and refract but they cannot be polarised.
B Low frequency sounds diffract more than high frequency sounds.
C All electromagnetic waves travel at the same speed in a vacuum.
D It is impossible to set up a standing wave pattern with visible light.
Your answer
(1)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
3
Assessment 5.2
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 The behaviour of waves
5 A vertical polarising filter is set up in front of a source of unpolarised white light.
A second polarising filter is placed perpendicular to the first and slowly rotated
through 180°. Sketch a graph to show how the intensity of light transmitted
through the two filters varies with angle from 0° to 180°.
(2)
(Total for Question 5 = 2 marks)
TOTAL FOR ASSESSMENT = 20 MARKS
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
4
Assessment 5.3
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Optics
1 Which of the following optical devices is not based on refraction of light?
A Microscope
B Periscope
C Telescope
D Camera
Your answer
(1)
(Total for Question 1 = 1 mark)
2 Which line of the table below states what happens to the speed, wavelength and
frequency of red light as it passes from glass into air?
Speed Wavelength Frequency
A reduces increases increases
B reduces reduces increases
C increases increases stays the same
D increases reduces stays the same
Your answer
(1)
(Total for Question 2 = 1 mark)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
1
Assessment 5.3
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Optics
3 The diagram below shows a ray of red light approaching a rectangular glass
block. The refractive index of this type of glass for red light is 1.513 and the
speed of red light in air is 3.00 108 ms−1.
(a) Copy the diagram and complete it to show the path of the ray of red light as
it passes through the block of glass and exits on the far side.
(2)
(b) Calculate the angle of refraction as the ray enters the glass.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(c) Calculate the incident and refracted angles at the far side of the block as the
ray exits the block. Comment on your answer.
(3)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(d) Calculate the speed of red light in glass.
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................................
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
2
Assessment 5.3
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Optics
(e) Blue light travels more slowly in glass than red light. How would this affect
the angles calculated in parts (b) and (c) above?
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 3 = 10 marks)
4 A small camera uses a thin converging lens to focus images onto a light
sensitive detector inside the camera. When the camera focuses on a distant
scene the distance from the lens to the detector is 4.0 cm.
(a) Calculate the power of the lens in dioptres.
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................................
(b) The camera focuses on objects at different distances by changing the
distance between the lens and the detector. How far must the lens be able
to move if it can focus on objects at any distance between 2.0 m and
infinity?
(3)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 4 = 4 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
3
Assessment 5.3
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Optics
5 The diagram below shows a ray of red light travelling along an optical fibre. This
particular fibre has a central core of refractive index 1.51 and a surrounding
cladding of refractive index 1.49 (for red light).
(a) Explain why the refractive index of the cladding must be less than the
refractive index of the core.
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................................
(b) Calculate the maximum value of the incident angle at the core cladding
boundary at which the ray will remain in the core. State the name of this
angle.
(3)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
TOTAL FOR ASSESSMENT = 20 MARKS
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
4
Assessment 5.4
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Quantum physics
1 Which of the following experiments provides evidence for the particle nature of
light?
A The diffraction of electrons as they pass through a layer of graphite
B The diffraction orders formed when light passes through a diffraction grating
C The ejection of photoelectrons from zinc when ultraviolet light falls on it
D The interference pattern formed in Young’s double slit experiment
Your answer
(1)
(Total for Question 1 = 1 mark)
2 Which of the following characteristics of the photoelectric effect cannot be
explained by the wave theory of light?
A The rate of transfer of energy from light to the metal surface is proportional
to the intensity of the light source.
B Increasing the intensity of light above the threshold frequency increases the
rate of emission of photoelectrons.
C Increasing the intensity of light below the threshold frequency does not
result in the emission of photoelectrons.
D The intensity of the light can be varied independently of its frequency.
Your answer
(1)
(Total for Question 2 = 1 mark)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
1
Assessment 5.4
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Quantum physics
3 The table below gives the photoelectric work functions for several different
metals. The Planck constant h = 6.6 10−34 Js. The magnitude of charge on an
electron e = 1.6 10−19 C.
Metal Work function/eV
Potassium 2.2
Zinc 4.2
Iron 4.5
Silver 4.7
(a) Explain what is meant by the work function.
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................................
(b) Convert the work function for zinc to J.
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................................
(c) Which of the metals above has the highest threshold frequency? Explain
your answer.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
2
Assessment 5.4
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Quantum physics
(d) The diagram below shows an experimental arrangement used to measure
the stopping voltage for a photocell. This particular cell uses potassium as
the emitter and is illuminated by a source of yellow light of wavelength
590 nm.
(i) Calculate the energy of a photon of light of wavelength 420 nm. Give
your answer in both J and eV.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(ii) Calculate the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons emitted from
potassium by light of wavelength 420 nm.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(iii) Calculate the stopping voltage for this experiment.
(1)
..............................................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 3 = 9 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
3
Assessment 5.4
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Quantum physics
4 The diagram below shows an experimental arrangement used to demonstrate
the diffraction of electrons.
(a) Sketch and describe the pattern seen on the fluorescent screen.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(b) State and explain how the pattern would change if the accelerating voltage
was increased.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 4 = 4 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
4
Assessment 5.4
EDEXCEL Physics Teacher Resource Pack 1 Quantum physics
5 The energy of the nth level of the hydrogen atom is given by the equation:
13.6 eV
En =
n2
(a) Calculate the energies of the n = 1 and n = 3 levels.
(2)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(b) Calculate the wavelength of the spectral line emitted by hydrogen when
electrons jump from the n = 3 level down to the n = 1 level.
(3)
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................
(Total for Question 5 = 5 marks)
TOTAL FOR ASSESSMENT = 20 MARKS
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015
This document may have been altered from the original
5
You might also like
- A Level Physics PracticalDocument9 pagesA Level Physics PracticalKelvin Yeung100% (1)
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2021Document15 pagesMark Scheme (Results) January 2021hassbanasghar39No ratings yet
- Edexcel As A Level Physics Answers (2015)Document34 pagesEdexcel As A Level Physics Answers (2015)AbdulRahman Mustafa50% (4)
- Topic Test Oxfordaqa Int A Level Physics Circular and Periodic MotionDocument14 pagesTopic Test Oxfordaqa Int A Level Physics Circular and Periodic Motionandhi soesiloNo ratings yet
- As Chemistry Answer BookDocument30 pagesAs Chemistry Answer Booksaviochow80% (5)
- International A Level Physics Example Responses PH04 Unit4Document53 pagesInternational A Level Physics Example Responses PH04 Unit4andhi soesiloNo ratings yet
- 8FM0-01 As Core Pure Mathematics October 2020 Examination Paper PDF 1Document28 pages8FM0-01 As Core Pure Mathematics October 2020 Examination Paper PDF 1Rizan RazakNo ratings yet
- IAL Physics Unit 3 NoteDocument22 pagesIAL Physics Unit 3 NoteÅzmâñ KhäñNo ratings yet
- Physics Unit 1 WPH11 01 MS June 21Document15 pagesPhysics Unit 1 WPH11 01 MS June 21Spam Spam50% (2)
- A-level Physics exam questionsDocument86 pagesA-level Physics exam questionsMoses Junior100% (1)
- 4.1 - Further MechanicsDocument28 pages4.1 - Further MechanicsEmperor Saladin100% (1)
- CIE AS-LEVEL CHEMISTRY PRACTICAL NOTESDocument6 pagesCIE AS-LEVEL CHEMISTRY PRACTICAL NOTESNandish ShahNo ratings yet
- WCH11 01 Que 20190521 PDFDocument28 pagesWCH11 01 Que 20190521 PDFPakistan English AcademyNo ratings yet
- wph11 01 Oct19Document28 pageswph11 01 Oct19DhanBahadur100% (1)
- Physics: Pearson EdexcelDocument32 pagesPhysics: Pearson EdexcelApsara WijemuniNo ratings yet
- Wma11 01 Que 20220513Document32 pagesWma11 01 Que 20220513Rehan Ragib100% (3)
- 3-Year SoW End of Term 5 Higher TestDocument10 pages3-Year SoW End of Term 5 Higher Testlucas50% (2)
- Physics 9702 A Level Tips For ExamsDocument4 pagesPhysics 9702 A Level Tips For Examsforum4physics75% (12)
- Language Paper 2 Mark Scheme PDFDocument21 pagesLanguage Paper 2 Mark Scheme PDFEbony Butler0% (2)
- Ecr As-Al Physics 9702 p3 v1Document42 pagesEcr As-Al Physics 9702 p3 v1AliMukhtarNo ratings yet
- IAL Edexcel Pure Maths 3 Jan 20Document32 pagesIAL Edexcel Pure Maths 3 Jan 20Mohamed Said DawNo ratings yet
- A Level Physics Board ComparisonDocument4 pagesA Level Physics Board ComparisonRussell Johnson100% (2)
- A2 Chemistry Answer BookDocument85 pagesA2 Chemistry Answer BookHarrys Oustapasidis100% (3)
- IAS Chemistry SB1 Answers Topic1Document5 pagesIAS Chemistry SB1 Answers Topic1Loh Jun XianNo ratings yet
- AS Physics at .: Transition Booklet From iGCSE Physics To AS PhysicsDocument42 pagesAS Physics at .: Transition Booklet From iGCSE Physics To AS PhysicsSalmuel SmithNo ratings yet
- Physics: Pearson EdexcelDocument16 pagesPhysics: Pearson EdexcelEffendi Jabid KamalNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 May19 Till Jan21Document299 pagesUnit 1 May19 Till Jan21Wael TareqNo ratings yet
- Edexcel A Level Bk2 Physics Answers FINAL PDFDocument39 pagesEdexcel A Level Bk2 Physics Answers FINAL PDFNasrin SultanaNo ratings yet
- Hasan Sayginel: Edexcel IAL Physics Unit 6Document55 pagesHasan Sayginel: Edexcel IAL Physics Unit 6Thangavel SarujanNo ratings yet
- As Level Physics Revision Guide For OCRDocument44 pagesAs Level Physics Revision Guide For OCRThomas Roe100% (1)
- AQA A-Level Applied Physics Chapter 1 Rotational DynamicsDocument21 pagesAQA A-Level Applied Physics Chapter 1 Rotational DynamicsJ3TL10% (1)
- Examiner Tips For ASA Level Chemistry 9701 FINALDocument6 pagesExaminer Tips For ASA Level Chemistry 9701 FINALFred H Halder67% (3)
- 2022 January Chemistry Unit 1 - SolvedDocument24 pages2022 January Chemistry Unit 1 - SolvedSidra SaifNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2019: Pearson Edexcel GCE Further Mathematics Further Pure 1 Paper 6667 - 01Document19 pagesMark Scheme (Results) Summer 2019: Pearson Edexcel GCE Further Mathematics Further Pure 1 Paper 6667 - 01Rahyan AshrafNo ratings yet
- Topic Test Oxfordaqa Int As Level Physics Particles Radiation and RadioactivityDocument9 pagesTopic Test Oxfordaqa Int As Level Physics Particles Radiation and Radioactivityandhi soesiloNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Physics A2 Answers Student S Book PDFDocument12 pagesEdexcel Physics A2 Answers Student S Book PDFWaqasKhan100% (1)
- Physics 1P - Specimen PaperDocument28 pagesPhysics 1P - Specimen Papersuru suru50% (2)
- AS Physics: Formula Sheet (Unit 1)Document1 pageAS Physics: Formula Sheet (Unit 1)Dina Lahham83% (6)
- Physics A2 Unit-4 Strong Interaction Particle ProductionDocument8 pagesPhysics A2 Unit-4 Strong Interaction Particle ProductionMer CyNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Yr13 Particles Qs Set 2Document5 pagesKami Export - Yr13 Particles Qs Set 2mhammouri2006No ratings yet
- Topic 3 Waves and Particle Nature of Light Topic 3D Quantum PhysicsDocument5 pagesTopic 3 Waves and Particle Nature of Light Topic 3D Quantum PhysicsLiang LuNo ratings yet
- Working As A Physicist Units and EquationsDocument13 pagesWorking As A Physicist Units and EquationsIlayda OzmerterNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Forces and Motion HDocument17 pagesTopic 5 Forces and Motion HHerry CenNo ratings yet
- October Half Term Revision 2020 (Edexcel)Document27 pagesOctober Half Term Revision 2020 (Edexcel)turboNo ratings yet
- AS PHYSICS NEWTON'S LAW EXAMDocument10 pagesAS PHYSICS NEWTON'S LAW EXAMnobodyNo ratings yet
- IAL Physics SB2 Assessment 5ADocument3 pagesIAL Physics SB2 Assessment 5AsalmaNo ratings yet
- 6.1 The Nucleus, Radioactive Decay and Using RadiationDocument42 pages6.1 The Nucleus, Radioactive Decay and Using RadiationpansehappeNo ratings yet
- PeriodicityDocument28 pagesPeriodicitylinjiachen932No ratings yet
- 2 Orbital Radius Time Period 2 × ×: EquationsDocument19 pages2 Orbital Radius Time Period 2 × ×: EquationsKiron SheiqNo ratings yet
- As Physics: Nature of LightDocument20 pagesAs Physics: Nature of LightnobodyNo ratings yet
- 7.2 StarsDocument6 pages7.2 StarsNirmani RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Energy Changesina SystemDocument74 pagesEnergy Changesina SystemCally ChewNo ratings yet
- Q1. The Diagram Below Shows Part of An Energy Level Diagram For A Hydrogen AtomDocument8 pagesQ1. The Diagram Below Shows Part of An Energy Level Diagram For A Hydrogen AtomTony CliftonNo ratings yet
- DP1 Phy P2 SL QPDocument14 pagesDP1 Phy P2 SL QPZianNo ratings yet
- L of The Spring, Indicated in Fig. 3.1, Is To Be MeasuredDocument4 pagesL of The Spring, Indicated in Fig. 3.1, Is To Be MeasuredzeeshanNo ratings yet
- Speed of Sound InvestigationDocument27 pagesSpeed of Sound Investigationalma rejiNo ratings yet
- Oct Mock RevisionDocument16 pagesOct Mock RevisionAdamNo ratings yet
- IB Atomic PhyDocument16 pagesIB Atomic PhyImran ZafarNo ratings yet
- A Level Pracice - Atomic StructureDocument8 pagesA Level Pracice - Atomic StructureXiyue ChenNo ratings yet
- Year 10 EOT3 Revison Booklet With AnswerDocument99 pagesYear 10 EOT3 Revison Booklet With AnswerAdamNo ratings yet
- The Sea Eats The Land at Home - CIE LiteratureDocument7 pagesThe Sea Eats The Land at Home - CIE LiteratureMarinos EliadesNo ratings yet
- London Snow - CIE LiteratureDocument8 pagesLondon Snow - CIE LiteratureMarinos EliadesNo ratings yet
- Afternoon With Irish Cows - CIE LiteratureDocument7 pagesAfternoon With Irish Cows - CIE LiteratureMarinos EliadesNo ratings yet
- Guidance On School Shoes 150720Document13 pagesGuidance On School Shoes 150720Marinos EliadesNo ratings yet
- You Will Know When You Get There - CIE LiteratureDocument8 pagesYou Will Know When You Get There - CIE LiteratureMarinos EliadesNo ratings yet
- In Praise of Creation - CIE LiteratureDocument8 pagesIn Praise of Creation - CIE LiteratureMarinos EliadesNo ratings yet
- Levels of DifficultyDocument1 pageLevels of DifficultyMarinos EliadesNo ratings yet
- Hamilton 2003 2009 PDFDocument43 pagesHamilton 2003 2009 PDFMarinos Eliades100% (1)
- The Caged Skylark - CIE LiteratureDocument7 pagesThe Caged Skylark - CIE LiteratureMarinos EliadesNo ratings yet
- Properties of Waves, Including Light & Sound: Your NotesDocument56 pagesProperties of Waves, Including Light & Sound: Your NotesMarinos Eliades100% (1)
- Hamilton 2010 2014 PDFDocument38 pagesHamilton 2010 2014 PDFMarinos Eliades100% (1)
- Intermediate Mathematical Challenge: Past Papers and Solutions 1999-2004Document48 pagesIntermediate Mathematical Challenge: Past Papers and Solutions 1999-2004Marinos EliadesNo ratings yet
- Ode To MelancholyDocument16 pagesOde To MelancholyMarinos EliadesNo ratings yet
- B M O B M O: Ritish Athematical Lympiad Ritish Athematical LympiadDocument65 pagesB M O B M O: Ritish Athematical Lympiad Ritish Athematical LympiadeduhubNo ratings yet
- Charged particles in magnetic fieldsDocument5 pagesCharged particles in magnetic fieldsMarinos EliadesNo ratings yet
- Spec QuestionsDocument11 pagesSpec QuestionsMarinos EliadesNo ratings yet
- January 2010 QP - Unit 1 Edexcel Physics A-LevelDocument23 pagesJanuary 2010 QP - Unit 1 Edexcel Physics A-Levelpraveen alwisNo ratings yet
- The Boy in The Striped PajamasDocument112 pagesThe Boy in The Striped PajamasMarinos EliadesNo ratings yet
- The Caged Skylark - CIE LiteratureDocument7 pagesThe Caged Skylark - CIE LiteratureMarinos EliadesNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Literature Poetry (Full Poems)Document16 pagesIGCSE Literature Poetry (Full Poems)Marinos Eliades100% (2)
- Cetacean - CIE LiteratureDocument7 pagesCetacean - CIE LiteratureMarinos EliadesNo ratings yet
- The Latter HuntDocument1 pageThe Latter HuntMarinos EliadesNo ratings yet
- The Poplar-Field - CIE LiteratureDocument8 pagesThe Poplar-Field - CIE LiteratureMarinos EliadesNo ratings yet
- PrepScholar Sat Practice Test 2 Essay PDFDocument4 pagesPrepScholar Sat Practice Test 2 Essay PDFDhrubajyoti GhoshNo ratings yet
- The Latter Hunt - EssayDocument1 pageThe Latter Hunt - EssayMarinos EliadesNo ratings yet
- The Lake VocabDocument1 pageThe Lake VocabMarinos EliadesNo ratings yet
- Homage BriefDocument1 pageHomage BriefMarinos EliadesNo ratings yet
- Scoring Sat Practice Test 1 PDFDocument9 pagesScoring Sat Practice Test 1 PDFbernardNo ratings yet
- Sat Practice Test 2 AnswersDocument42 pagesSat Practice Test 2 AnswersRamona GhitaNo ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics ExamDocument4 pagesProbability and Statistics ExamLeul SolomonNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument2 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentSwarnim KumbhareNo ratings yet
- FernDocument29 pagesFernMazlina NinaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document15 pagesLecture 2ZUHAL TUGRULNo ratings yet
- The Construction of Self-Made Freaks: Interviews with the Vampire WomanDocument68 pagesThe Construction of Self-Made Freaks: Interviews with the Vampire WomanAdriano LeoneNo ratings yet
- Eltorai, Ibrahim M A Spotlight On The History of Ancient EgyptianDocument215 pagesEltorai, Ibrahim M A Spotlight On The History of Ancient EgyptianJonas PsontomfanceNo ratings yet
- The Impact of New Normal To The Gadget Store OwnersDocument28 pagesThe Impact of New Normal To The Gadget Store OwnersKatricia Elaine VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Lc60 70le650ua PWB UnitDocument30 pagesLc60 70le650ua PWB UnitLeonel F. CamarilloNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Cultural Issues and ValuesDocument3 pagesUnit 1 Cultural Issues and ValuesACHRAF DOUKARNENo ratings yet
- CAMBRIDGE IGCSE (0478-0984) 3.3 Secondary StorageDocument10 pagesCAMBRIDGE IGCSE (0478-0984) 3.3 Secondary Storageangle5858zhaoNo ratings yet
- Plant Pathology Curriculum Revised for BSc, MSc and PhD DegreesDocument90 pagesPlant Pathology Curriculum Revised for BSc, MSc and PhD Degreesjahangir khanNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument19 pagesUntitledSmiles PrintingNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Ar. Sanjay PuriDocument15 pagesPresentation On Ar. Sanjay PuriAAYASHREE SHRESTHANo ratings yet
- Calmet Industrial Accreditation for Dimensional Inspection and Mechanical TestingDocument3 pagesCalmet Industrial Accreditation for Dimensional Inspection and Mechanical TestingFernando MarNo ratings yet
- CSC415 LAB ASSIGNMENT 1 TOPIC 2-5Document5 pagesCSC415 LAB ASSIGNMENT 1 TOPIC 2-5Amir AimanNo ratings yet
- 3rd Year Exam Schedule RegularDocument3 pages3rd Year Exam Schedule RegularHACHALU FAYENo ratings yet
- Toxicology Conversion Chart for PPM, PPB, mg/l and Other UnitsDocument2 pagesToxicology Conversion Chart for PPM, PPB, mg/l and Other UnitsWilliam ThompsonNo ratings yet
- PT SURYA CITRA INTI SEMESTA PROJECT REFERENCE LISTDocument1 pagePT SURYA CITRA INTI SEMESTA PROJECT REFERENCE LISTAgus RiyanaNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 VocabularyDocument2 pagesUnit 7 VocabularyNy MenghongNo ratings yet
- English written preparation for Dhaka University admission test (DUDocument7 pagesEnglish written preparation for Dhaka University admission test (DUShanian Ahmed100% (3)
- RatioLog and ProportionDocument6 pagesRatioLog and ProportionshlokNo ratings yet
- Compare formal and informal essay stylesDocument1 pageCompare formal and informal essay stylesLyka Nicole DoradoNo ratings yet
- Branches of Forensic ScienceDocument4 pagesBranches of Forensic ScienceIan owisoNo ratings yet
- Kajian Pengaruh Variasi Penambahan Bahan Accelerator Terhadap Parameter Beton Memadat Mandiri Dan Kuat Tekan Beton Mutu TinggiDocument7 pagesKajian Pengaruh Variasi Penambahan Bahan Accelerator Terhadap Parameter Beton Memadat Mandiri Dan Kuat Tekan Beton Mutu TinggiHilda NurhelfitrianingsihNo ratings yet
- MSCCH 504Document309 pagesMSCCH 504Harshal YadavNo ratings yet
- Wooldridge ExampleDocument4 pagesWooldridge Examplejomarta01No ratings yet
- Mind Map - Diffraction: (sin∝) 2 = m λƒ = n λƒDocument7 pagesMind Map - Diffraction: (sin∝) 2 = m λƒ = n λƒIlmi MunirahNo ratings yet
- 71 International Astronautical Congress (Iac) - The Cyberspace Edition, 12-14 October 2020Document8 pages71 International Astronautical Congress (Iac) - The Cyberspace Edition, 12-14 October 2020John DoeNo ratings yet
- Method Water QualityDocument8 pagesMethod Water Qualityazilah harisNo ratings yet
- Talking About ProfessionsDocument17 pagesTalking About ProfessionsenglishcommunityworkNo ratings yet