Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic Use
Uploaded by
Mike EveretteOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic Use
Uploaded by
Mike EveretteCopyright:
Available Formats
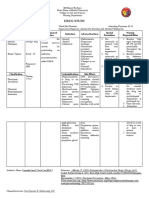
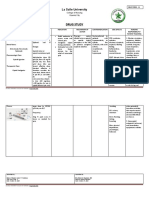
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATE: Medication
Michael Everette
STUDENT NAME______________________________________
Lorazepam, Diazepam, Alprazolam, Temazepam, Clonazepam
MEDICATION___________________________________________________________________________ REVIEW MODULE CHAPTER____________
CATEGORY CLASS__Benzodiazepine
_____________________________________________________________________
PURPOSE OF MEDICATION
Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic Use
Reduction of: Anxiety disorder and seizure - Anxiety & Anxiety disorders
- Skeletal muscle spasm & spasticty
disorder symptoms, and acute alcohol - Seicure Disorders, treats status epilepticus
withdrawal symptoms - Acute Alcohol withdrawal symptoms
- induction of anesthesia
Complications Medication Administration
- Drowsiness - Slurred Speech - Impaired recall of events, Overdose/ toxicity - Give Alprazolam orally
- Paradoxical reaction (confusion, anxiety) - Take oral benzo's with food if G.I.
- Hypotension, tachycardia, respiratory depression symptoms develop
- Withdrawal symptoms
- Give diazepam orally, rectally, IM or IV.
- Oral: Sedation, confusion, Parenteral: Possible Life-threatening sedation,
hypotension, respiratory depression, cardiac arrest - Administer IV Diazepam slowly & have
emergency resuscitation equipment
nearby
- Do not give emulsion form IM (IV only)
Contraindications/Precautions
- Pregnancy -Teratogenic
- Schedule IV controlled substances
- Glaucoma Nursing Interventions
- Coma, shock, neonates, labor / delivery (IV diazepam)
- Older adults & Children under 18 (alprazolam) - Monitor client to prevent falls & other
- Mental health disorders, Neuromuscular disorders, Chronic Respiratory Disorders
injury following administration
- Monitor vital signs
- Monitor for complications
- Reverse sedation with Flumazenil
- Provide airway & blood pressure
Interactions support as needed, for overdose
- When taken concurrently with other CNS depressants: Alcohol, opioids, - Taper over 1-2 weeks to prevent /
and other benzo's minimize withdrawal.
- Cimetidine (Tagamet): Increases benzo levels
- Kava-Kava, chamomile, and valerian increase the risk for sedation.
- Disulfiram (antabuse) & Fluoxetine (Prozac) increase alprazolam levels/
Client Education
- Instruct clients to use care with
ambulation, when driving, or when using
Evaluation of Medication Effectiveness hazardous equipment
- Advise client to stop use and inform
their provider, if complications arise.
- Instruct client to avoid increasing
prescribed dose
- Instruct client taper drug slowly to
prevent withdrawal
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES
You might also like
- Top 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)From EverandTop 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- SSRI (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor)Document1 pageSSRI (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor)Mike EveretteNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating Procedure Good Storage PracticeDocument2 pagesStandard Operating Procedure Good Storage PracticeDaniel Yves IV Paez100% (1)
- Parkinsons DrugDocument2 pagesParkinsons DrugChristine AllonarNo ratings yet
- CCCC CC C C!C CC C CCCC C C CC C C CCC C CCCC!C CC CC CC ! C C (CDocument4 pagesCCCC CC C C!C CC C CCCC C C CC C C CCC C CCCC!C CC CC CC ! C C (Cjanillle_burdeosNo ratings yet
- Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseDocument1 pageMedication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseJeffrey BurdNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Tofranil J Zoloft)Document2 pagesDrug Study (Tofranil J Zoloft)alteahmichaella.mintuNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MCL or TechDocument7 pagesDrug Study MCL or TechKyra Lalaine Angub CervantesNo ratings yet
- Substance Abuse: Related Learning ExperienceDocument7 pagesSubstance Abuse: Related Learning ExperienceDyanne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionDocument1 pageLui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionMagdayao Romamea100% (1)
- Drug Study 1 (Done)Document3 pagesDrug Study 1 (Done)Otaku MiyoNo ratings yet
- DiazepamDocument1 pageDiazepamIvanne Hisoler71% (7)
- Limos Drug-StudyDocument2 pagesLimos Drug-StudyClaire LimosNo ratings yet
- GROUP 2: Azuelo, Cano Pacheco, Inoc, Pareja, TejanoDocument5 pagesGROUP 2: Azuelo, Cano Pacheco, Inoc, Pareja, TejanoJesette KhoNo ratings yet
- BIPERIDENDocument3 pagesBIPERIDENDenise GabatoNo ratings yet
- Adult: IV/IM 5-10 MG, Drowsiness, Fatigue, Ataxia,: Injectable Form: ShockDocument1 pageAdult: IV/IM 5-10 MG, Drowsiness, Fatigue, Ataxia,: Injectable Form: ShockinfectionmanNo ratings yet
- Anti Anxiety Meds ONLYDocument5 pagesAnti Anxiety Meds ONLYphoenix180No ratings yet
- Morphine SulfateDocument1 pageMorphine SulfateyeshaellatapucayNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyHarland EstebanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FormatDocument2 pagesDrug Study FormatCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyryanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study by Ivy DecenaDocument6 pagesDrug Study by Ivy DecenaIvy Mae DecenaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MBDocument29 pagesDrug Study MBk4jggjtnz5No ratings yet
- Anti EpilepticsDocument23 pagesAnti EpilepticsSalman HabeebNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY TramadolDocument2 pagesDRUG-STUDY TramadolkitsimonmondinNo ratings yet
- I. Drug Study: Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument3 pagesI. Drug Study: Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Considerationscyn yana0723No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument22 pagesDrug StudyShenna RegaspiNo ratings yet
- Vhince Pisco BSN III NCM 117 - Drug StudyDocument3 pagesVhince Pisco BSN III NCM 117 - Drug StudyVhince Norben PiscoNo ratings yet
- De La Cruz DS - DIAZEPAMDocument2 pagesDe La Cruz DS - DIAZEPAMspain michaelisNo ratings yet
- Tramadol, Paracetamol, Calmoseptine, B12Document5 pagesTramadol, Paracetamol, Calmoseptine, B12Denise EspinosaNo ratings yet
- N-Methyl D Asparatate (NMDA) Receptor AntagonistDocument1 pageN-Methyl D Asparatate (NMDA) Receptor AntagonistMike EveretteNo ratings yet
- DRUGSTUDY3DIAZEDocument1 pageDRUGSTUDY3DIAZEEryn_Casaclang_6640No ratings yet
- ParacetamolDocument4 pagesParacetamolGermin CesaNo ratings yet
- MEDSDocument5 pagesMEDSSend FileNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: La Salle UniversityDocument3 pagesDrug Study: La Salle UniversityJb RosillosaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Phinma - University of Iloilo College of Allied Health SciencesDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Phinma - University of Iloilo College of Allied Health Scienceslhie cabanlitNo ratings yet
- Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseDocument1 pageMedication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseMike EveretteNo ratings yet
- DS DR RodasDocument7 pagesDS DR RodasChristian MarquezNo ratings yet
- Alprazolam BiperidinDocument6 pagesAlprazolam BiperidinFionah RetuyaNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia DSDocument2 pagesSchizophrenia DSCatungal RophineNo ratings yet
- All Other ClassificationsDocument6 pagesAll Other ClassificationsCorey100% (1)
- Drugs For Anxiety and InsomniaDocument10 pagesDrugs For Anxiety and InsomniaApple MaeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Module 4Document6 pagesDrug Study Module 4Hannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- Promethazine HCLDocument2 pagesPromethazine HCLIvanne Hisoler100% (8)
- Psychotropic Drugs.Document15 pagesPsychotropic Drugs.Xiaoqing SongNo ratings yet
- OrphenadrineDocument4 pagesOrphenadrineGermin CesaNo ratings yet
- Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseDocument1 pageMedication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseMike EveretteNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyJenny YenNo ratings yet
- Drug STUDY FOR TOMORROWDocument7 pagesDrug STUDY FOR TOMORROWRhandz Rhaven MaaghopNo ratings yet
- LevodopaDocument3 pagesLevodopaderic50% (2)
- Risperidone Drug StudyDocument2 pagesRisperidone Drug StudyLanzen DragneelNo ratings yet
- 014 Drug StudyDocument3 pages014 Drug StudyPatrickNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY LevetiracetamDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY LevetiracetamMaria Althea NajorraNo ratings yet
- CH19-25 PharmaDocument20 pagesCH19-25 Pharmakwon nanaNo ratings yet
- Risperidone Drug StudyDocument2 pagesRisperidone Drug StudyBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- Prescription Writing: Esha Ann FransonDocument9 pagesPrescription Writing: Esha Ann FransonAlosious JohnNo ratings yet
- Escitalopram 2018Document2 pagesEscitalopram 2018Anil JohnNo ratings yet
- Cabasis Drug StudyDocument3 pagesCabasis Drug StudyNick James CabasisNo ratings yet
- PharmaDocument20 pagesPharmaMary Roan RonatoNo ratings yet
- Medical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcFrom EverandMedical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcNo ratings yet
- Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseDocument1 pageMedication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseMike EveretteNo ratings yet
- HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors (Statins)Document1 pageHMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors (Statins)Mike EveretteNo ratings yet
- Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseDocument1 pageMedication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseMike EveretteNo ratings yet
- Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseDocument1 pageMedication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseMike EveretteNo ratings yet
- Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseDocument1 pageMedication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseMike EveretteNo ratings yet
- Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseDocument1 pageMedication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseMike EveretteNo ratings yet
- Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseDocument1 pageMedication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseMike EveretteNo ratings yet
- Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseDocument1 pageMedication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseMike EveretteNo ratings yet
- Beta 2 Adrenergic AgonistsDocument1 pageBeta 2 Adrenergic AgonistsMike EveretteNo ratings yet
- Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseDocument1 pageMedication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseMike EveretteNo ratings yet
- Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseDocument1 pageMedication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseMike EveretteNo ratings yet
- Phenothiazine (Used For Antiemetic)Document1 pagePhenothiazine (Used For Antiemetic)Mike EveretteNo ratings yet
- Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseDocument1 pageMedication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseMike EveretteNo ratings yet
- Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseDocument1 pageMedication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseMike EveretteNo ratings yet
- DK H 2310 001 ParDocument7 pagesDK H 2310 001 ParJagdish ChanderNo ratings yet
- List Besaran Diskon Maksimal Per Produk: NO Kode Produk Komposisi Kemasan HNADocument10 pagesList Besaran Diskon Maksimal Per Produk: NO Kode Produk Komposisi Kemasan HNAapotekerNo ratings yet
- Update PMDT GuidelineDocument53 pagesUpdate PMDT GuidelineTanto RusnantoNo ratings yet
- Drug Card MotrinDocument2 pagesDrug Card MotrinAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- PBF ObatDocument55 pagesPBF ObatAbdul Fahma FirmanaNo ratings yet
- Pharma - Fundamental Concepts of Pharmacology 1Document96 pagesPharma - Fundamental Concepts of Pharmacology 1gelean payodNo ratings yet
- Singhania University Rajasthan: (Yearly Programme)Document13 pagesSinghania University Rajasthan: (Yearly Programme)om vermaNo ratings yet
- Antiviral Drug Products Advisory Committee Meeting: NDA 21-266 Voriconazole Tablets NDA 21-267 Voriconazole For InjectionDocument51 pagesAntiviral Drug Products Advisory Committee Meeting: NDA 21-266 Voriconazole Tablets NDA 21-267 Voriconazole For InjectionNoura AlosaimiNo ratings yet
- Programa de Clases 2011-30 (10 Nov)Document100 pagesPrograma de Clases 2011-30 (10 Nov)Juan C Belen OrtizNo ratings yet
- HR Email Id of Pharmaceuticals CompanyDocument54 pagesHR Email Id of Pharmaceuticals CompanyTikoo AdityaNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Disorders and Carbamazepine PharmacokinetiDocument5 pagesBipolar Disorders and Carbamazepine PharmacokinetiAgr YuroNo ratings yet
- E5 Ethnic Factors in The Acceptability of Foreign Clinical DataDocument7 pagesE5 Ethnic Factors in The Acceptability of Foreign Clinical Data涂皇堯No ratings yet
- Pharmaceuticals Export Promotion Council of India: (Setup by Ministry of Commerce & Industry, Govt. of India)Document8 pagesPharmaceuticals Export Promotion Council of India: (Setup by Ministry of Commerce & Industry, Govt. of India)ZebaNo ratings yet
- Group 8 - Consumer Behavior - Team Cialis - Getting Ready To Market Case StudyDocument24 pagesGroup 8 - Consumer Behavior - Team Cialis - Getting Ready To Market Case StudyrizqighaniNo ratings yet
- Ship To Cust Ship-To Customer Name Billing Docu Billing Date SD Document CDocument24 pagesShip To Cust Ship-To Customer Name Billing Docu Billing Date SD Document CRao Arslan RajputNo ratings yet
- Group 3 - LowprazoleDocument68 pagesGroup 3 - LowprazoleAhmed AlaaNo ratings yet
- Update On Management of The Oral and Maxillofac - 2022 - Oral and MaxillofacialDocument8 pagesUpdate On Management of The Oral and Maxillofac - 2022 - Oral and MaxillofacialFadi Al HajjiNo ratings yet
- IPSF and SEPDocument29 pagesIPSF and SEPNabila AnjaniNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Propofol: CNS Depressants: AdditiveDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Propofol: CNS Depressants: AdditiveShara Lailanie A. AzisNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology For Dentists - 8791Document6 pagesPharmacology For Dentists - 8791asal bakhtyariNo ratings yet
- 2nd Contribution - Ouassou Et Al., 2021Document14 pages2nd Contribution - Ouassou Et Al., 2021Amine El BouzidiNo ratings yet
- Emergency Cart Content: Top TrayDocument2 pagesEmergency Cart Content: Top TrayJILL ANGELESNo ratings yet
- The Hospital Formulary: Bilal Hassan M.Phil PharmaceuticsDocument11 pagesThe Hospital Formulary: Bilal Hassan M.Phil PharmaceuticsShafaqat Ghani Shafaqat GhaniNo ratings yet
- (A) Introduction, Definition and Scope of PharmacologyDocument15 pages(A) Introduction, Definition and Scope of PharmacologyBabita kumariNo ratings yet
- NPPA On Dated 6 July 2017 - No Data Monopoly CasesDocument5 pagesNPPA On Dated 6 July 2017 - No Data Monopoly CasessppNo ratings yet
- MoH COVID 19 Protocol - V1.1 PDFDocument6 pagesMoH COVID 19 Protocol - V1.1 PDFHCX dghhqNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Medication Dosing GuildelinesDocument2 pagesPediatric Medication Dosing GuildelinesMuhammad ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - AtorvastatinDocument3 pagesDrug Study - AtorvastatinFlorence Grace MarceloNo ratings yet