Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Standard and Vertex Conversion
Uploaded by
Gabrielle M. GangadharOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Standard and Vertex Conversion
Uploaded by
Gabrielle M. GangadharCopyright:
Available Formats
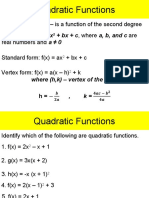
Converting Quadratic Equations between Standard and Vertex Form
Standard Form: y = ax2 + bx + c Vertex Form: y = a(x – h)2 + k
Convert from Standard Form to Vertex Form:
y = ax2 + bx = c y = a(x – h)2 + k
know a, b, c want a, h, k
a = a
= h
Solve for y = k
Substitute the values and rewrite.
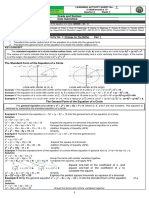
Example 1:
y = 8x2 – 16x + 27 We know a, b, c and want a, h, k
a=8 a is the coefficient of the x2 term
use the formula to find the value of h
substitute the value found for h into the
k = y = 8(1)2 – 16(1) + 27 = 8 – 16 + 27 = 19
original equation and solve for k
y = 8(x – 1)2 + 19
Example 2:
y = 5x2 – 40x + 67 We know a, b, c and want a, h, k
a=5 a is the coefficient of the x2 term
use the formula to find the value of h
k = y = 5(4)2 – 40(4) + 67 = 80 – 160 + 67 = –13 substitute the value found for h into the
original equation and solve for k
y = 5(x – 4)2 – 13
Practice: Convert the following quadratics from standard to vertex form.
1. y = 5x2 – 10x + 37 2. y = 7x2 + 28x + 19 3. y = -2x2 – 24x – 75
Convert from Vertex Form to Standard Form:
y = a(x – h)2 + k y = ax2 + bx = c
Example 1:
y = 5(x + 2)2 – 9
y = 5(x + 2)(x + 2) – 9 Rewrite (x + 2)2
y = 5(x2 + 4x + 4) – 9 Simplify (x + 2)(x + 2)
y = 5x2 + 20x + 20 – 9 Distribute the 5
y = 5x2 + 20x + 11 Combine Like Terms
Example 2:
y = –3(x – 4)2 + 7
y = –3(x – 4)(x – 4) + 7 Rewrite (x – 4)2
y = –3(x2 – 8x + 16) + 7 Simplify (x – 4)(x – 4)
y = –3x2 + 24x – 48 + 7 Distribute the –3
y = –3x2 + 24x – 41 Combine Like Terms
Practice: Convert the following quadratics from vertex to standard form.
1. y = ( x – 2)2 + 6 2. y = 3(x – 3)2 – 12 3. y = –2(x + 1)2 + 3
You might also like
- Quadratics Lecture NotesDocument13 pagesQuadratics Lecture NotesKaness Mathz100% (1)
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- Chap 3 Algebra Review PDFDocument46 pagesChap 3 Algebra Review PDFArah100% (1)
- Zoho Interview QuestionsDocument24 pagesZoho Interview Questionsjyowan100% (2)
- Quadratic EquationsDocument18 pagesQuadratic EquationsErwani KamaruddinNo ratings yet
- Quadratic FunctionsDocument2 pagesQuadratic FunctionsGrace Lamano100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Dm015 Indices 2021.2022Document30 pagesChapter 1 Dm015 Indices 2021.2022azizrafeeqNo ratings yet
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Add Maths Monthly Test March 2016Document10 pagesAdd Maths Monthly Test March 2016Armadaramor ShiNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet Q1 Math 9 LC5Document14 pagesActivity Sheet Q1 Math 9 LC5MATHUTO100% (1)
- Maths Revision Guide AnswersDocument20 pagesMaths Revision Guide Answerspriya100% (2)
- Math 9 Quarter 1Document34 pagesMath 9 Quarter 1Janinne Villa Del Rey100% (1)
- Grade 9 2nd Quarter Periodical Test SY 2022 2023 40 ITEMS FinalDocument3 pagesGrade 9 2nd Quarter Periodical Test SY 2022 2023 40 ITEMS FinalSAN JOSE LITEX SHS 342566100% (1)
- Basic Concepts of Functions: (Represents Real-Life Situations Using Rational Functions)Document33 pagesBasic Concepts of Functions: (Represents Real-Life Situations Using Rational Functions)Gerlie Jay-ann Ramos100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in Mathematics 9 August 8Document3 pagesLesson Plan in Mathematics 9 August 8Reynaldo Billones100% (2)
- Cavite State University: Daily Instruction Plan in Math 8Document5 pagesCavite State University: Daily Instruction Plan in Math 8Xofia RoceroNo ratings yet
- Math 9 ReviewerDocument23 pagesMath 9 ReviewerLorica John LuisNo ratings yet
- Translating Conic SectionsDocument15 pagesTranslating Conic SectionsNikhil KumarNo ratings yet
- Definition of Quadratic FunctionDocument12 pagesDefinition of Quadratic FunctionMary Ann CrizaldoNo ratings yet
- Csec Add Maths May 2018 PDFDocument33 pagesCsec Add Maths May 2018 PDFNatalie100% (1)
- Quadratic FunctionDocument13 pagesQuadratic FunctionJasmine Marie Padilla LimsonNo ratings yet
- DLP Cot 2 Quadratic FunctionsDocument10 pagesDLP Cot 2 Quadratic Functionskheza DelimanNo ratings yet
- Midterm Review Quadradtics pt2Document1 pageMidterm Review Quadradtics pt2Rishamjot KNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICSDocument11 pagesMATHEMATICSTEMIDIRE OLAYINKANo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Simultaneous EquationsDocument14 pagesChapter 4 Simultaneous EquationsAidil-Nur ZainalNo ratings yet
- What Does It Mean When You Have More, You See Less?: D L A F G K R ODocument7 pagesWhat Does It Mean When You Have More, You See Less?: D L A F G K R OMariel FerreraNo ratings yet
- Hand-Outs in MATH 9Document9 pagesHand-Outs in MATH 9Lee EspeletaNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Lesson 1 Quadratic EquationDocument15 pagesMath 9 Lesson 1 Quadratic EquationJosielyn ValladolidNo ratings yet
- Lessons 5-9 PDFDocument5 pagesLessons 5-9 PDFIbarra KakkiNo ratings yet
- Math 9-Q1-Week-6Document12 pagesMath 9-Q1-Week-6Pinky FaithNo ratings yet
- Problem 1 (14 Points 3 + 2 +4 + 5) : X FX XDocument2 pagesProblem 1 (14 Points 3 + 2 +4 + 5) : X FX Xiony971No ratings yet
- ExtractingtherootsDocument35 pagesExtractingtherootsPeter J. AgadaNo ratings yet
- Q1 W4 LAS4 Vertex FormDocument7 pagesQ1 W4 LAS4 Vertex FormCraig Dale B. GriponNo ratings yet
- Soalan 4-Circle and ElipseDocument6 pagesSoalan 4-Circle and ElipseHaooonNo ratings yet
- 7 Las m10 Week 7 Montad Nicanor Jr. S. EditedDocument4 pages7 Las m10 Week 7 Montad Nicanor Jr. S. EditedGemmhainne OrtizNo ratings yet
- Math Grade 9: Learning Activity Sheet Week 3 and 4 Quarter 1Document13 pagesMath Grade 9: Learning Activity Sheet Week 3 and 4 Quarter 1Sapanta, Junrel R.No ratings yet
- Math FT S1 G10 SGS 2023Document7 pagesMath FT S1 G10 SGS 2023noorlailyNo ratings yet
- Chap 6Document24 pagesChap 6Dawood MNo ratings yet
- D L A F G K R O: 6) 7) ? Is Quadratic EquationDocument7 pagesD L A F G K R O: 6) 7) ? Is Quadratic EquationMariel FerreraNo ratings yet
- DE Lec 1-9Document9 pagesDE Lec 1-9Cheat CodeNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Math Q1 M1Document12 pagesGrade 9 Math Q1 M1Renny Romero Luzada100% (2)
- Polynomial ExpressionsDocument39 pagesPolynomial ExpressionsZs TangNo ratings yet
- Convertions Between Different Forms of QuadraticsDocument10 pagesConvertions Between Different Forms of QuadraticsCharalampidis DimitrisNo ratings yet
- Nova Angelie C. Santos Jane P. Valencia Ed.D.: Eps I-MathematicsDocument9 pagesNova Angelie C. Santos Jane P. Valencia Ed.D.: Eps I-MathematicsIsrael Marquez100% (1)
- M49 AQuadratic SkillsDocument2 pagesM49 AQuadratic SkillsMohamed Sufian DamanhuriNo ratings yet
- The Graph of A Quadratic FunctionDocument30 pagesThe Graph of A Quadratic FunctionIr HeriawanNo ratings yet
- 1.14 MMC LessonDocument9 pages1.14 MMC LessondevikaNo ratings yet
- Quadratic FunctionsDocument14 pagesQuadratic FunctionsMicaelahNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Q1 Week 9Document12 pagesMath 9 Q1 Week 9Zion Conrad FuentesNo ratings yet
- Week 1 LessonsallDocument78 pagesWeek 1 LessonsallRaymund PesidasNo ratings yet
- Lines, Parabolas, and Systems 3.3 Quadratic Functions Example 1: Graphing A Quadratic FunctionDocument4 pagesLines, Parabolas, and Systems 3.3 Quadratic Functions Example 1: Graphing A Quadratic FunctionMathias MikeNo ratings yet
- Grade - 10 - Worksheet 8Document6 pagesGrade - 10 - Worksheet 8Zumygui JorgeNo ratings yet
- Equations and Inequalitites Extra PracticeDocument14 pagesEquations and Inequalitites Extra PracticeGuo HeqiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2:quadratic Expressions and Equations: M X + y - 3x + 5 7x - 3x - 2x + 3 5x - 4x + 7Document9 pagesChapter 2:quadratic Expressions and Equations: M X + y - 3x + 5 7x - 3x - 2x + 3 5x - 4x + 7Rita LauNo ratings yet
- Single Pure - DiscriminantDocument2 pagesSingle Pure - DiscriminantHead of Mathematics DepartmentNo ratings yet
- CombinepdfDocument34 pagesCombinepdfSoby K ThomasNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Transformations of Quadratic Functions: Essential QuestionDocument8 pages2.1 Transformations of Quadratic Functions: Essential QuestionMankaranNo ratings yet
- Exercise Chapter 2Document40 pagesExercise Chapter 2Samuel Sim Shien ShuangNo ratings yet
- Evaluating AE PPTDocument24 pagesEvaluating AE PPTJustin Paul VallinanNo ratings yet
- MH1811 Tutorial 1 - MC - 2020 - FN - Lmts - SolnDocument11 pagesMH1811 Tutorial 1 - MC - 2020 - FN - Lmts - SolnYachen WuNo ratings yet
- FunctionsDocument28 pagesFunctionsbruhwhatdoievenwritenaymore123No ratings yet
- III. Procedure: Daily Routine: Greetings: Exercise: Checking Of: A. Preparatory ActivityDocument7 pagesIII. Procedure: Daily Routine: Greetings: Exercise: Checking Of: A. Preparatory ActivityMariel FerreraNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Determining The Axis of Symmetry NewDocument12 pagesWeek 4 Determining The Axis of Symmetry NewSameer Ali MohamedNo ratings yet
- Preparatory Questions: T U S S M SDocument8 pagesPreparatory Questions: T U S S M STOM DAVISNo ratings yet
- Handout 2Document6 pagesHandout 2Marvin Yebes ArceNo ratings yet
- FindtheOriginalPrice 1Document2 pagesFindtheOriginalPrice 1Gabrielle M. GangadharNo ratings yet
- Geometric TransformationsDocument49 pagesGeometric TransformationsGabrielle M. GangadharNo ratings yet
- 2021 Coordinate Graphing 1 ST QuadrantDocument5 pages2021 Coordinate Graphing 1 ST QuadrantGabrielle M. GangadharNo ratings yet
- Algebra 1: Guided Notes Name - Period - Parts of A Quadratic GraphDocument2 pagesAlgebra 1: Guided Notes Name - Period - Parts of A Quadratic GraphGabrielle M. GangadharNo ratings yet
- Support Vector Machines (SVMS)Document2 pagesSupport Vector Machines (SVMS)Ankita SarkarNo ratings yet
- First-Order Resolution of A Perturbated Scale Factor For A Dust UniverseDocument2 pagesFirst-Order Resolution of A Perturbated Scale Factor For A Dust UniverseEric TrelutNo ratings yet
- High-Lights On Conic Sections Part 1 of 2Document13 pagesHigh-Lights On Conic Sections Part 1 of 2majji satishNo ratings yet
- Chapt 3 Number RepresentationDocument93 pagesChapt 3 Number Representationcreation portalNo ratings yet
- 81E-C VersionDocument12 pages81E-C VersionBhashyavi BossNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Extra PracticeDocument3 pages6.1 Extra PracticeAhmed hassanNo ratings yet
- Ramanujan - PaperDocument20 pagesRamanujan - PaperBudegaNo ratings yet
- W7 Second Order Linear Differential Equation Part 1 - ModuleDocument5 pagesW7 Second Order Linear Differential Equation Part 1 - ModuleRaison MichNo ratings yet
- 4 Graphing Functions The ParabolaDocument4 pages4 Graphing Functions The ParabolaNhlanhla HlátzNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Maths Pre Board 2023-24 (Navodaya Vidhyalaya Samiti) SolutionsDocument15 pagesClass Xii Maths Pre Board 2023-24 (Navodaya Vidhyalaya Samiti) Solutionsrsarthak227No ratings yet
- 3.5 Dividing PolynomialsDocument2 pages3.5 Dividing PolynomialsIrina StefaniaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-5Document251 pagesChapter 1-5Abdullah Ayub79% (24)
- Nichita, 2013Document12 pagesNichita, 2013Carlos Felipe Rubio RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Basic Mathematics and Logarithm - PYQ Practice SheetDocument6 pagesBasic Mathematics and Logarithm - PYQ Practice Sheetabhaysingh785124No ratings yet
- Galois Solutions PDFDocument20 pagesGalois Solutions PDFlaxmi mahtoNo ratings yet
- Vedic Math - Cube of 2 Digit NumbersDocument4 pagesVedic Math - Cube of 2 Digit NumbersAbhinab GogoiNo ratings yet
- A Level Further Mathematics For AQA Student Book 1 Scheme of WorkDocument21 pagesA Level Further Mathematics For AQA Student Book 1 Scheme of WorkAmirul Fahmi ZainalNo ratings yet
- JdjudjdDocument1 pageJdjudjdJulius BaniquedNo ratings yet
- S5 Eigenvalues and EigenvectorsDocument4 pagesS5 Eigenvalues and EigenvectorsrajeshmholmukheNo ratings yet
- Differential Geometry and Its Applications: A. PatákDocument4 pagesDifferential Geometry and Its Applications: A. PatákmiftahchoyNo ratings yet
- 3rd Update Pigeon Hole PrincipleDocument3 pages3rd Update Pigeon Hole PrincipleDương Minh ĐứcNo ratings yet
- MATH 241 Calculus IV (4) (Crosslisted As HNRS 241)Document2 pagesMATH 241 Calculus IV (4) (Crosslisted As HNRS 241)Cunxi HuangNo ratings yet
- Stability Analysis: U U C T X U U U UDocument1 pageStability Analysis: U U C T X U U U UnehaNo ratings yet
- Answer Key: 13 VXY (Date: 12-02-2012) Review Test-7 Paper-2Document18 pagesAnswer Key: 13 VXY (Date: 12-02-2012) Review Test-7 Paper-2vishal110085No ratings yet
- Syllabus - MCADocument3 pagesSyllabus - MCAtanvimital9No ratings yet