Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Skeletal System NOTA
Uploaded by
Van PersieCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Skeletal System NOTA
Uploaded by
Van PersieCopyright:
Available Formats
Skeletal System
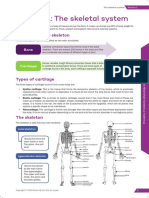
-Skeleton is a structure of living tissue that grows, repairs, and renews itself. The bones within it
are dynamic and complex organs that serve a number of important functions, including some
necessary to maintain homeostasis.
Function of the Skeletal System
-The skeletal system is the body system composed of bones and cartilage and performs the
following critical functions for the human body:
supports the body
Example: Simply by looking at a person, you can see how the bones support, facilitate
movement, and protect the human body.
facilitates movement
protects internal organs
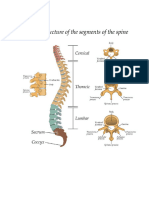
By covering or surrounding them. For example, your ribs protect your lungs and heart,
the bones of your vertebral column (spine) protect your spinal cord, and the bones of your
cranium (skull) protect your brain
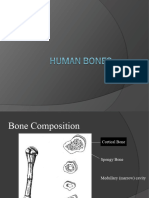
produces blood cells
There are two types of bone marrow: yellow marrow and red marrow. Yellow marrow
contains adipose tissue.
Red marrow is where hematopoiesis—the production of blood cells—takes place. Red
blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets are all produced in the red marrow.
stores and releases minerals and fat
Acts as a reservoir for a number of minerals important to the functioning of the body,
especially calcium, and phosphorus
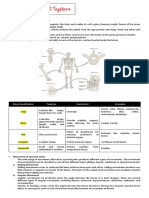
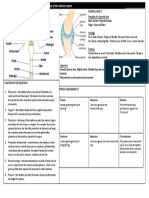
Bone Classification
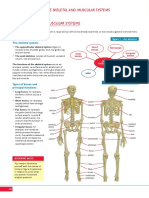
The 206 bones that compose the adult skeleton are divided into five categories based on their
shapes. Their shapes and their functions are related such that each categorical shape of bone has
a distinct function.
Bone Classifications (Table 1)
Bone
classification Features Function(s) Examples
Femur, tibia, fibula,
Cylinder-like shape, metatarsals ,humerus ,
Long Leverage
longer than it is wide ulna, radius, metacarpals,
phalanges
Cube-like shape, Provide stability,
approximately equal in support, while
Short Carpals, tarsals
length, width, and allowing for some
thickness motion
Points of attachment
for muscles; Sternum, ribs, scapulae,
Flat Thin and curved
protectors of internal cranial bones
organs
Protect internal
Irregular Complex shape Vertebrae, facial bones
organs
Small and round; Protect tendons from
Sesamoid Patellae
embedded in tendons compressive forces
Bones can be classified according to their shapes. Long bones, such as the femur, are longer than
they are wide. Short bones, such as the carpals, are approximately equal in length, width, and
thickness. Flat bones are thin, but are often curved, such as the ribs. Irregular bones such as those
of the face have no characteristic shape. Sesamoid bones, such as the patellae, are small and
round, and are located in tendons.
You might also like
- Bone ClassificationDocument5 pagesBone Classificationcharmcast9No ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology: Functions of the Skeletal and Muscular SystemsDocument43 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology: Functions of the Skeletal and Muscular SystemsJezebel MolinoNo ratings yet
- Unit 4-6 Lesson Summarty Pe 1Document7 pagesUnit 4-6 Lesson Summarty Pe 1Vergel CallejaNo ratings yet
- BONES Pointers MIDTERMDocument6 pagesBONES Pointers MIDTERMRumochiiNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document26 pagesUnit 4sivexgamingNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System QuestionsDocument44 pagesSkeletal System QuestionsSritama GhoshNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology: Study of the Human BodyDocument37 pagesAnatomy & Physiology: Study of the Human BodyIndu GNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Wps Office1Document6 pagesSkeletal System Wps Office1Brent LorenzNo ratings yet
- UNIT-4-Human-movementDocument18 pagesUNIT-4-Human-movementneoorivera6No ratings yet
- Bone AnatomyDocument1 pageBone AnatomyJustine Kay SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument2 pagesSkeletal SystemKYLA LORENZ BALUMANo ratings yet
- Muscle and Skeletal FunctionDocument23 pagesMuscle and Skeletal FunctionLuan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System: Christine Bas Sweet Audrey Gwen SamsonDocument39 pagesSkeletal System: Christine Bas Sweet Audrey Gwen SamsonDanielle Kate MadridNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3.1: Luminang, John Chris Bsmls 1B Anaphy Nov. 18, 2021Document13 pagesAssignment 3.1: Luminang, John Chris Bsmls 1B Anaphy Nov. 18, 2021John Chris LuminangNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System (Bones)Document5 pagesSkeletal System (Bones)Erica BobadillaNo ratings yet
- Mehak General Physiology Activity - Integumentary LabDocument7 pagesMehak General Physiology Activity - Integumentary LabMehak DhaliwalNo ratings yet
- The Human Skeletal System: by Group 1 - Nurasmiati - Stevhani Febryaningsih - St. SyahiraDocument21 pagesThe Human Skeletal System: by Group 1 - Nurasmiati - Stevhani Febryaningsih - St. SyahiraVhani FebrianingsihNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Skeletal Anatomy: (Typical)Document10 pagesSkeletal System Skeletal Anatomy: (Typical)anon_660872041No ratings yet
- The Musculoskeletal SystemDocument3 pagesThe Musculoskeletal SystemCUARTERO, SHERYL ANNENo ratings yet
- Ch. 6 - Osseous Tissue Bone StructureDocument54 pagesCh. 6 - Osseous Tissue Bone StructureHilary OliverioNo ratings yet
- Types of BonesDocument2 pagesTypes of BonesJess MCDNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Skeletal SystemDocument2 pagesTopic 5 Skeletal SystemKandy Anne Castillo AbuanNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System: Femur, HumerusDocument21 pagesThe Skeletal System: Femur, HumerusLapitan Jared Anne S.No ratings yet
- L2 Reading 1Document62 pagesL2 Reading 1Milena RohenkohlNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of the Skeletal SystemDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of the Skeletal SystemFrancine Dominique CollantesNo ratings yet
- Bone StructuresDocument11 pagesBone StructuresLomaynah Dimatingcal, RPhNo ratings yet
- VisibleBody - Types of Bones Ebook - 2018Document17 pagesVisibleBody - Types of Bones Ebook - 2018AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 The Skeletal SystemDocument22 pagesChapter 5 The Skeletal SystemJUSTINE MAE MANTILLANo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 ANAPHY Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesChapter 6 ANAPHY Skeletal Systemrobh0026No ratings yet
- Human BonesDocument39 pagesHuman Bonesmuhammad ijazNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument13 pagesSkeletal Systemariolajose5No ratings yet
- The Skeletal and Muscular SystemDocument22 pagesThe Skeletal and Muscular SystemHannah Nicole AlicayaNo ratings yet
- Midterms AnaphyDocument3 pagesMidterms AnaphyMaricar Aquino EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument66 pagesChapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology21- VARNIKA DALALNo ratings yet
- Types of Bones Powerpoint Ver 1Document16 pagesTypes of Bones Powerpoint Ver 1mrejcrewsNo ratings yet
- Principles of Anatomy and Physiology in SportDocument20 pagesPrinciples of Anatomy and Physiology in SportRachelHatcher123No ratings yet
- Intro To Osteology (Oct 20, 2022)Document30 pagesIntro To Osteology (Oct 20, 2022)huzaifa arshadNo ratings yet
- Label the Skeletal System and Describe its FunctionsDocument4 pagesLabel the Skeletal System and Describe its FunctionsLucía ChabletNo ratings yet
- Core 2 PDHPE - Body in Motion Study NotesDocument43 pagesCore 2 PDHPE - Body in Motion Study Notesmarissa.makhNo ratings yet
- Sports Science Study (Topics 1 - 6)Document39 pagesSports Science Study (Topics 1 - 6)Jayden OoiNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument24 pagesSkeletal Systemrheanna0076No ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument44 pagesSkeletal SystemRobi SariegoNo ratings yet
- Locomotion and SupportDocument54 pagesLocomotion and SupportiQalyana100% (1)
- Unit 2-4 Anatomy and Human Physiology NotesDocument90 pagesUnit 2-4 Anatomy and Human Physiology NotesAbi .JNo ratings yet
- Types of BonesDocument3 pagesTypes of Bonesfrank menshaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System: Group 1: 1. Cheryl 2. Samuel 3. DEI 4. Satria 5. MerlynDocument5 pagesSkeletal System: Group 1: 1. Cheryl 2. Samuel 3. DEI 4. Satria 5. MerlynMikhael SatriaNo ratings yet
- Mata Kuliah Anatomi Dan Fisiologi "Sistem Gerak"Document50 pagesMata Kuliah Anatomi Dan Fisiologi "Sistem Gerak"Fardian AkbarNo ratings yet
- 4-The Skeletal SystemDocument46 pages4-The Skeletal SystemSimco plusNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System ExplainedDocument6 pagesThe Skeletal System Explainedstar fireNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System: Dr. Mona Liza N. Valencia, PTRPDocument33 pagesThe Skeletal System: Dr. Mona Liza N. Valencia, PTRPAccount ExtraNo ratings yet
- Locomotion Handout 2023Document7 pagesLocomotion Handout 2023rheanna0076No ratings yet
- Rad14 PrelimDocument9 pagesRad14 PrelimShan CabelaNo ratings yet
- WEEK 6 TRANS AnaphyDocument13 pagesWEEK 6 TRANS AnaphygazzyngsalvadorNo ratings yet
- Presentation 14 Skeletal SystemDocument14 pagesPresentation 14 Skeletal SystemJeff Bryan Arellano HimorNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System PowerPointDocument50 pagesSkeletal System PowerPointEly QuijanoNo ratings yet
- Presentacion Cuerpo Humano Organico Ilustrado Morado PastelDocument9 pagesPresentacion Cuerpo Humano Organico Ilustrado Morado PastelpaulagonzalezdiazNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System - KODocument1 pageSkeletal System - KOGift Munyinda (G-Man)No ratings yet
- Week 10 Bio 11 Skeletal SystemDocument46 pagesWeek 10 Bio 11 Skeletal SystemDyah AnggraeniNo ratings yet
- SL REVISION Topic 1 & 2Document27 pagesSL REVISION Topic 1 & 2Muffaddal MustafaNo ratings yet
- Find Out How in Demand' Your Idea Is: StudyDocument3 pagesFind Out How in Demand' Your Idea Is: StudyVan PersieNo ratings yet
- Thinking Like A ChampionDocument1 pageThinking Like A ChampionVan PersieNo ratings yet
- Psychology Skills TrainingDocument17 pagesPsychology Skills TrainingVan PersieNo ratings yet
- Malaysia tourism challenges webinarDocument1 pageMalaysia tourism challenges webinarVan PersieNo ratings yet
- Performance Profiling: G Games T TrainingDocument1 pagePerformance Profiling: G Games T TrainingVan PersieNo ratings yet
- Self-Confidence For Netball ShootingDocument3 pagesSelf-Confidence For Netball ShootingVan PersieNo ratings yet
- Sport Imagery Activities Form: (Tick Appropriate Box)Document7 pagesSport Imagery Activities Form: (Tick Appropriate Box)Van PersieNo ratings yet
- TQG Proven Success RoadmapDocument1 pageTQG Proven Success RoadmapVan PersieNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need To Know About SquattingDocument10 pagesEverything You Need To Know About Squattingנתנאל מושקוביץNo ratings yet
- Test of Performance Strategies For Muay ThaiCSDocument2 pagesTest of Performance Strategies For Muay ThaiCSVan PersieNo ratings yet
- My BibDocument3 pagesMy BibVan PersieNo ratings yet
- Unit SpaceDocument7 pagesUnit SpaceEnglish DepNo ratings yet
- Interpreting SNT TC 1A PDF 2Document1 pageInterpreting SNT TC 1A PDF 2Jagannath SahuNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Essentials A Personal Approach 1st Edition Schiff Test BankDocument35 pagesNutrition Essentials A Personal Approach 1st Edition Schiff Test Bankwonders.stufferlx27100% (25)
- Calibrating Waterjets: An Experiment to Determine Flow RatesDocument5 pagesCalibrating Waterjets: An Experiment to Determine Flow Ratespacoto livingstoneNo ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics Tutorial for EQT 272Document2 pagesProbability and Statistics Tutorial for EQT 272Jared KuyislNo ratings yet
- Math6 q1 Mod5 AdditionofDecimals v4-SIGNEDDocument34 pagesMath6 q1 Mod5 AdditionofDecimals v4-SIGNEDARRIANE JOY TOLEDONo ratings yet
- Assessment of Crude Oil Blends PDFDocument6 pagesAssessment of Crude Oil Blends PDFDanivian HigginsNo ratings yet
- Power AdministrationDocument17 pagesPower AdministrationWaseem KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document25 pagesUnit 1ragavaharish463No ratings yet
- Concept Paper (R)Document7 pagesConcept Paper (R)Joseph EneroNo ratings yet
- Defining Public HealthDocument36 pagesDefining Public Healthv.shivakumarNo ratings yet
- Design Brief On MEP Systems PDFDocument21 pagesDesign Brief On MEP Systems PDFAdhikari ThushanNo ratings yet
- Literacy Day in IndiaDocument10 pagesLiteracy Day in IndiaThe United IndianNo ratings yet
- Phonons 1-D Linear Chain of AtomsDocument12 pagesPhonons 1-D Linear Chain of Atomsمؤيد العليNo ratings yet
- PoisonedfoodDocument10 pagesPoisonedfoodMare JNo ratings yet
- API 5L 46thDocument35 pagesAPI 5L 46thInam Ul Haq KhanNo ratings yet
- BC846WDocument8 pagesBC846WBrunoNo ratings yet
- Sanei SK1-31 Technical ManualDocument60 pagesSanei SK1-31 Technical Manualcompu sanaNo ratings yet
- D4643Document5 pagesD4643Ruddy EspejoNo ratings yet
- ATEC Smart Brochure - ItalyDocument6 pagesATEC Smart Brochure - ItalyArun Kumar PancharajNo ratings yet
- TOPNOTCH DIGITAL HANDOUT - BIOCHEMISTRY Juan Dela CruzDocument2 pagesTOPNOTCH DIGITAL HANDOUT - BIOCHEMISTRY Juan Dela CruzJoy Fucanan100% (1)
- Vol 5, No 2 November, Pp. 99-111 P-ISSN 2549-4880, E-ISSN 2614-1310 Journal DOI: WebsiteDocument11 pagesVol 5, No 2 November, Pp. 99-111 P-ISSN 2549-4880, E-ISSN 2614-1310 Journal DOI: WebsiteSyarah RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Phrasal Verbs ListDocument85 pagesPhrasal Verbs ListVirginia E. C.No ratings yet
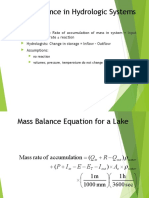
- Lecture 12 - Mass Balance ApproachDocument18 pagesLecture 12 - Mass Balance ApproachAshhad ShafiqueNo ratings yet
- Confidential UniTM Mara Materials TestDocument2 pagesConfidential UniTM Mara Materials TestDEBRA DEIRDRE S. ONONG DEBRA DEIRDRE S. ONONGNo ratings yet
- 08 - Marian-Avram Vincze, Horatiu-Stefan GrifDocument4 pages08 - Marian-Avram Vincze, Horatiu-Stefan GrifBudiandra Yusuf MahendraNo ratings yet
- Properties and Reactions of Acids and BasesDocument46 pagesProperties and Reactions of Acids and Basesaliefyan4769No ratings yet
- QC OF SUPPOSITORIESDocument23 pagesQC OF SUPPOSITORIESHassan kamalNo ratings yet
- Budget of Work English 7: Quarter Competencies No. of Sessions First QuarterDocument3 pagesBudget of Work English 7: Quarter Competencies No. of Sessions First QuarterEllane Jean DeniegaNo ratings yet
- SE-409 Aluminium Enclosure SE-409-0-0-A-0-11284: RevisionDocument1 pageSE-409 Aluminium Enclosure SE-409-0-0-A-0-11284: RevisionAhmet MehmetNo ratings yet
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindFrom EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- This Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyFrom EverandThis Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueFrom EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- The Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineFrom EverandThe Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (17)
- Superlative: The Biology of ExtremesFrom EverandSuperlative: The Biology of ExtremesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (51)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomFrom EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (215)
- Eels: An Exploration, from New Zealand to the Sargasso, of the World's Most Mysterious FishFrom EverandEels: An Exploration, from New Zealand to the Sargasso, of the World's Most Mysterious FishRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (30)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (515)
- Human Errors: A Panorama of Our Glitches, from Pointless Bones to Broken GenesFrom EverandHuman Errors: A Panorama of Our Glitches, from Pointless Bones to Broken GenesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (56)
- Darwin's Dangerous Idea: Evolution and the Meaning of LifeFrom EverandDarwin's Dangerous Idea: Evolution and the Meaning of LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (523)
- The Mind & The Brain: Neuroplasticity and the Power of Mental ForceFrom EverandThe Mind & The Brain: Neuroplasticity and the Power of Mental ForceNo ratings yet
- The Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceFrom EverandThe Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (632)