Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Skeletal System (Bones)
Uploaded by
Erica Bobadilla0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views5 pagesThe document describes the main components and functions of the human skeletal system. It outlines the various bones grouped into axial (skull, vertebral column, ribs) and appendicular (upper and lower extremities attached by shoulder and pelvic girdles) bones. The bones are composed of cartilage and bone tissue and form through two processes - intramembranous and endochondral ossification. There are differences in male and female pelvic anatomy related to birthing capabilities. The skeletal system provides structure, protection, movement and mineral storage for the body.
Original Description:
Pictures
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document describes the main components and functions of the human skeletal system. It outlines the various bones grouped into axial (skull, vertebral column, ribs) and appendicular (upper and lower extremities attached by shoulder and pelvic girdles) bones. The bones are composed of cartilage and bone tissue and form through two processes - intramembranous and endochondral ossification. There are differences in male and female pelvic anatomy related to birthing capabilities. The skeletal system provides structure, protection, movement and mineral storage for the body.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views5 pagesSkeletal System (Bones)
Uploaded by
Erica BobadillaThe document describes the main components and functions of the human skeletal system. It outlines the various bones grouped into axial (skull, vertebral column, ribs) and appendicular (upper and lower extremities attached by shoulder and pelvic girdles) bones. The bones are composed of cartilage and bone tissue and form through two processes - intramembranous and endochondral ossification. There are differences in male and female pelvic anatomy related to birthing capabilities. The skeletal system provides structure, protection, movement and mineral storage for the body.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
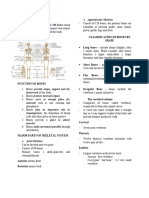
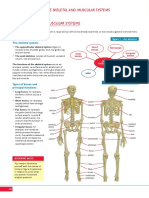
Lower Extremity Bones Upper Extremity Bones
Vertebral Column Sacrum
Pectoral Girdle: Scapula Pectoral Girdle: Clavicle
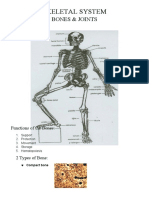
Skeletal System
A. FUNCTIONS Clavicle: Colar Bone
Scapula: Shoulder Blades
It provides supporting frameworks of body
It protects some viscera, brain, spinal cord, sense APPENDICULAR: Upper Extremities
organs, and the hemopoeitic system
Humerus, Radius, Ulna
It provides lever for muscle
Carpals, Metacarpals, Phalanges
It is Hemopoesis
It has storage of mineral like calcium and phosphorus APPENDICULAR: Pelvic Girdle (Coxae)
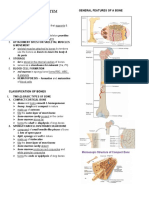
B. COMPOSITION: Cartilage & Bone Ilium, Ilia Crest, Ischum, Pubis, Accetabulum
FORMATION: APPENDICULAR: Lower Extremities
1. Intramembranous ossification Femur: Longest Bone
fibrous membranes of some part of fetal skeleton are Patella: Knee Cap
converted to bone. Tibia: Thicker
Fibula: Thinner
Ex. Some skull bone, clavicle, and lower jaw Tarsals, Metatarsals, Phalanges
2. Endochondral ossification D. JOINTS
- conversion of cartilage into bone. E. COMPARISON OF MALE AND FEMALE
SKELETON
Ex. Most bones of the skeletal system
1. The male skeleton is larger and heavier than female
C. DIVISIONS skeleton
2. The male pelvis is deep and funnel shaped with narrow
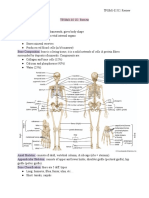
AXIAL: Hyoid Bone
public arch; female with wider and flaring pubic arch,
AXIAL: Skull female pelvis is shallow and broad.
Cranial Bones: Temporal, Parietal, Occipital, Frontal, F. GAIT – manner of walking
Ethmoid, Sphenoid
G. TYPES OF BONES
Facial Bones: Zygomatic Bone, Nasal Bone, Maxilla,
Mandible Short: Short bones are designated as those bones
that are as wide as they are long. Their primary
AXIAL: Vertebral Column
function is to provide support and stability with little
Cervical: C1-Atlas & C2-Axis to no movement (Carpals & Tarsals).
Thoracic: Th1-Th12 Long: Long bones are hard, dense bones that provide
Lumbar: L1-L5 strength, structure, and mobility.
Sacrum Flat: These bones are expanded into broad, flat
Coccyx: Tail Bone plates, as in the cranium (skull), the ilium (pelvis),
sternum and the rib cage, Scapula.
AXIAL: Ribs Irregular: Varies in shape & structure (Atlas, Axis,
Sternum: Breast Bone Hyoid, Zygomatic).
True Ribs: R1-R7 Sesamoid: A small independent bone or bony nodule
False Ribs: R8-R12 (Attached to sternum by Coastal developed in a tendon where it passes over an
Cartilage) angular structure, typically in the hands and feet. The
Floating Ribs: R11-R12 kneecap is a particularly large sesamoid bone.
APPENDICULAR: Pectoral Girdle
You might also like
- Lecture 3Document39 pagesLecture 3Anne XxNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument2 pagesSkeletal SystemKYLA LORENZ BALUMANo ratings yet
- Human BonesDocument39 pagesHuman Bonesmuhammad ijazNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document26 pagesUnit 4sivexgamingNo ratings yet
- 1-Upper LimbDocument37 pages1-Upper LimbArop AchierNo ratings yet
- Anatomical IntroductionDocument17 pagesAnatomical Introductionllazoozllbraa 7372No ratings yet
- Unit 4-6 Lesson Summarty Pe 1Document7 pagesUnit 4-6 Lesson Summarty Pe 1Vergel CallejaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4 Human MovementDocument18 pagesUNIT 4 Human Movementneoorivera6No ratings yet
- Skeletal System NOTADocument2 pagesSkeletal System NOTAVan PersieNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics ReviewerDocument12 pagesBiomechanics ReviewerJOHN EVAR LABASTILLANo ratings yet
- Interaction of Skeletal and Muscular SystemDocument43 pagesInteraction of Skeletal and Muscular SystemJezebel MolinoNo ratings yet
- Mod 1.2 Musculoskeletal System UpdatedDocument26 pagesMod 1.2 Musculoskeletal System UpdatedNandhkishoreNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3.1: Luminang, John Chris Bsmls 1B Anaphy Nov. 18, 2021Document13 pagesAssignment 3.1: Luminang, John Chris Bsmls 1B Anaphy Nov. 18, 2021John Chris LuminangNo ratings yet
- Core 2 PDHPE - Body in Motion Study NotesDocument43 pagesCore 2 PDHPE - Body in Motion Study Notesmarissa.makhNo ratings yet
- Elzatona Anatomy 2023Document9 pagesElzatona Anatomy 2023mahmoud ezzeldeenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 ANAPHY Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesChapter 6 ANAPHY Skeletal Systemrobh0026No ratings yet
- (Oct 1) THE SKELETAL SYSTEM PDFDocument7 pages(Oct 1) THE SKELETAL SYSTEM PDFBea GualbertoNo ratings yet
- Basic Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument37 pagesBasic Anatomy and PhysiologyIndu GNo ratings yet
- Presentacion Cuerpo Humano Organico Ilustrado Morado PastelDocument9 pagesPresentacion Cuerpo Humano Organico Ilustrado Morado PastelpaulagonzalezdiazNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument2 pagesSkeletal SystemMa Khristina S WongNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Wps Office1Document6 pagesSkeletal System Wps Office1Brent LorenzNo ratings yet
- L2 Reading 1Document62 pagesL2 Reading 1Milena RohenkohlNo ratings yet
- Bone ClassificationDocument5 pagesBone Classificationcharmcast9No ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesSkeletal SystemEdrea Aquino MendezNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Animal ScienceDocument16 pagesSkeletal System Animal Sciencealexenneth canilaNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesThe Skeletal Systemstar fireNo ratings yet
- Jo'rDocument124 pagesJo'rMade WidianantaraNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 3 (SkeletalSystem)Document2 pagesLECTURE 3 (SkeletalSystem)ALEXIS MOIRAH CALIGAGANNo ratings yet
- SkeletalDocument21 pagesSkeletalKeith HiadgeNo ratings yet
- Appendicular Skeletal SystemDocument4 pagesAppendicular Skeletal SystemSOFIA ALEXIS MALIÑANANo ratings yet
- Intro To Osteology (Oct 20, 2022)Document30 pagesIntro To Osteology (Oct 20, 2022)huzaifa arshadNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System (Use) - PESWDocument86 pagesSkeletal System (Use) - PESWAudrianna GaddyNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System: Femur, HumerusDocument21 pagesThe Skeletal System: Femur, HumerusLapitan Jared Anne S.No ratings yet
- Week 5 ExerciseDocument7 pagesWeek 5 ExerciseGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Chapter 7 - SkeletonDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Chapter 7 - Skeletonexpediant2No ratings yet
- Anatomy - Physiology of Animals - Skeletal System.Document3 pagesAnatomy - Physiology of Animals - Skeletal System.Erica MaeNo ratings yet
- Sports Science Study (Topics 1 - 6)Document39 pagesSports Science Study (Topics 1 - 6)Jayden OoiNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Skeletal Anatomy: (Typical)Document10 pagesSkeletal System Skeletal Anatomy: (Typical)anon_660872041No ratings yet
- Muscle and Skeletal FunctionDocument23 pagesMuscle and Skeletal FunctionLuan NguyenNo ratings yet
- 3 General OsteologyDocument90 pages3 General Osteologyvbh8222No ratings yet
- I. What Are The Different Components of The Skeletal System?Document6 pagesI. What Are The Different Components of The Skeletal System?Aria IsipNo ratings yet
- I. What Are The Different Components of The Skeletal System?Document6 pagesI. What Are The Different Components of The Skeletal System?Aria IsipNo ratings yet
- The Human Skeletal System: by Group 1 - Nurasmiati - Stevhani Febryaningsih - St. SyahiraDocument21 pagesThe Human Skeletal System: by Group 1 - Nurasmiati - Stevhani Febryaningsih - St. SyahiraVhani FebrianingsihNo ratings yet
- Anatomy From The DoctorDocument208 pagesAnatomy From The DoctorSweet manNo ratings yet
- BonesDocument9 pagesBonesKeith HiadgeNo ratings yet
- Rad14 PrelimDocument9 pagesRad14 PrelimShan CabelaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System QuestionsDocument44 pagesSkeletal System QuestionsSritama GhoshNo ratings yet
- Anatomy OSPEDocument17 pagesAnatomy OSPEjulietchiminyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - SKELETALSYSTEMDocument22 pagesChapter 5 - SKELETALSYSTEMGuenNo ratings yet
- ARMONIA ALEXA JOIE C. BSN 1B Manual Skeletal SystemDocument7 pagesARMONIA ALEXA JOIE C. BSN 1B Manual Skeletal SystemJohanna Marie GantalaoNo ratings yet
- Biology Review FebDocument16 pagesBiology Review FebSarahNo ratings yet
- Bio1 BSN 1 Skeletal SystemDocument29 pagesBio1 BSN 1 Skeletal SystemCamela Kim Domider TenorioNo ratings yet
- Bone AnatomyDocument1 pageBone AnatomyJustine Kay SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Skripta Za Usmeni Iz EngleskogDocument15 pagesSkripta Za Usmeni Iz EngleskogElizabetaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument3 pagesSkeletal SystemAIRENA RAIN TAMPOSNo ratings yet
- Axial SkeletonDocument10 pagesAxial SkeletonFrancisco LeaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument4 pagesSkeletal SystemHenry BuñagNo ratings yet
- C5 Skeletal NotesDocument10 pagesC5 Skeletal NotesJocelyn AlunanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument63 pagesAnatomy and Physiologykathleen.cuyaNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb RadiographyDocument122 pagesUpper Limb RadiographyBright KapambalalaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Epidemiology: Rockwood & Green's Fractures in Adults, 6th EditionDocument53 pagesOverview of Epidemiology: Rockwood & Green's Fractures in Adults, 6th EditionSilvia TacheNo ratings yet
- Frontal Bone& Frontal Sinus FractureDocument51 pagesFrontal Bone& Frontal Sinus Fracturetegegnegenet2No ratings yet
- BonesDocument2 pagesBonesAngie Espinoza UribeNo ratings yet
- Jadwal Operasi Elektif TGL 20 Maret 2023, XLDocument8 pagesJadwal Operasi Elektif TGL 20 Maret 2023, XLmuhammad arifNo ratings yet
- Surface Anatomy of Upper LimbDocument19 pagesSurface Anatomy of Upper Limbhussham100% (1)
- Materi Praktikum osteologi-RANGKA AKSIALISDocument20 pagesMateri Praktikum osteologi-RANGKA AKSIALISRudi SukrismanNo ratings yet
- Skeleton TaskDocument3 pagesSkeleton TaskKirstyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Review For Test 2Document4 pagesAnatomy Review For Test 2Sofia NNo ratings yet
- Awaji MCQsDocument172 pagesAwaji MCQsSomeshwar GuptNo ratings yet
- Chondrosarcoma 1Document74 pagesChondrosarcoma 1IceBearNo ratings yet
- 210921-303368305 MR Iqbal 56Y 21-Sep-2021 IMG-3014226035 MaleDocument1 page210921-303368305 MR Iqbal 56Y 21-Sep-2021 IMG-3014226035 MaleRizwan khanNo ratings yet
- 1 21 Projects Including All HeadingsDocument98 pages1 21 Projects Including All HeadingsAarti MehraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Surgical Appraches of The Temporal Bone PDFDocument251 pagesAnatomy and Surgical Appraches of The Temporal Bone PDFThamescracker28809100% (2)
- The Epidemiology of Fractures of The Scaphoid: Wrist and HandDocument6 pagesThe Epidemiology of Fractures of The Scaphoid: Wrist and HandantoanetaNo ratings yet
- Histogenesis of BoneDocument6 pagesHistogenesis of BoneAlya Putri KhairaniNo ratings yet
- Atlas Prophylaxis ResearchDocument8 pagesAtlas Prophylaxis ResearchitounosNo ratings yet
- lab6انسجة مترجمةDocument12 pageslab6انسجة مترجمةAzofNo ratings yet
- List of Skeletal Muscles of The Human Body - WikipediaDocument29 pagesList of Skeletal Muscles of The Human Body - WikipediaYoavNo ratings yet
- CH 5 AnswersDocument22 pagesCH 5 AnswersYhormmie Harjeinifujah100% (2)
- Shih 2018Document7 pagesShih 2018Genesis Cedeño GonzalezNo ratings yet
- TPJ3M1-02 U2: ReviewDocument11 pagesTPJ3M1-02 U2: ReviewLynn TrinhNo ratings yet
- What Is The Skeletal System?: Axial Skeleton AnatomyDocument2 pagesWhat Is The Skeletal System?: Axial Skeleton AnatomyJared RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Prelab 3 Bone Tissue and Axial Skeleton Winter 2020Document5 pagesPrelab 3 Bone Tissue and Axial Skeleton Winter 2020Mareline MendietaNo ratings yet
- Ao Spine KLDocument24 pagesAo Spine KLNikhil Khangar0% (1)
- Joints of Axial SkeletonDocument24 pagesJoints of Axial SkeletonPraney SlathiaNo ratings yet
- Ortho Nursing NotesDocument6 pagesOrtho Nursing NotesRAYANA UBASNo ratings yet
- Distal Radius Fracture Outcomes and RehabilitationDocument4 pagesDistal Radius Fracture Outcomes and Rehabilitationerfan khanNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy 7th Edition Martini Test BankDocument45 pagesHuman Anatomy 7th Edition Martini Test Banklaeliacaixpoyf100% (29)
- Biologi SelDocument105 pagesBiologi SelHekter Gunting KursiNo ratings yet
- Horse Care 101: How to Take Care of a Horse for BeginnersFrom EverandHorse Care 101: How to Take Care of a Horse for BeginnersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Lead with Your Heart: Lessons from a Life with HorsesFrom EverandLead with Your Heart: Lessons from a Life with HorsesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
- Project Solomon: The True Story of a Lonely Horse Who Found a Home--and Became a HeroFrom EverandProject Solomon: The True Story of a Lonely Horse Who Found a Home--and Became a HeroRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- The Power of the Herd: A Nonpredatory Approach to Social Intelligence, Leadership, and InnovationFrom EverandThe Power of the Herd: A Nonpredatory Approach to Social Intelligence, Leadership, and InnovationNo ratings yet
- The Winning Horseplayer: An Advanced Approach to Thoroughbred Handicapping and BettingFrom EverandThe Winning Horseplayer: An Advanced Approach to Thoroughbred Handicapping and BettingNo ratings yet
- The Faraway Horses: The Adventures and Wisdom of America's Most Renowned HorsemenFrom EverandThe Faraway Horses: The Adventures and Wisdom of America's Most Renowned HorsemenRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (49)
- The Equine Listenology Guide - Essential Horsemanship, Horse Body Language & Behaviour, Groundwork, In-hand Exercises & Riding Lessons to Develop Softness, Connection & Collection.From EverandThe Equine Listenology Guide - Essential Horsemanship, Horse Body Language & Behaviour, Groundwork, In-hand Exercises & Riding Lessons to Develop Softness, Connection & Collection.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Speak Your Horse's Language:: Communicating with the Driving HorseFrom EverandSpeak Your Horse's Language:: Communicating with the Driving HorseNo ratings yet
- How Long Can a Fly Fly?: 175 Answers to Possible and Impossible Questions about AnimalsFrom EverandHow Long Can a Fly Fly?: 175 Answers to Possible and Impossible Questions about AnimalsNo ratings yet
- Black Beauty (Illustrated): Classic of World LiteratureFrom EverandBlack Beauty (Illustrated): Classic of World LiteratureRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2429)
- Wild Horses of the Summer Sun: A Memoir of IcelandFrom EverandWild Horses of the Summer Sun: A Memoir of IcelandRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- Joey: How a Blind Rescue Horse Helped Others Learn to SeeFrom EverandJoey: How a Blind Rescue Horse Helped Others Learn to SeeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (23)
- Second-Chance Horses: True Stories of the Horses We Rescue and the Horses Who Rescue UsFrom EverandSecond-Chance Horses: True Stories of the Horses We Rescue and the Horses Who Rescue UsNo ratings yet
- Stable Relation: A Memoir of One Woman's Spirited Journey Home, by Way of the BarnFrom EverandStable Relation: A Memoir of One Woman's Spirited Journey Home, by Way of the BarnRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The USPC Guide to Longeing and Ground TrainingFrom EverandThe USPC Guide to Longeing and Ground TrainingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- The Tao Of Horses: Exploring How Horses Guide Us on Our Spiritual PathFrom EverandThe Tao Of Horses: Exploring How Horses Guide Us on Our Spiritual PathRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Everything Horse Care Book: A Complete Guide to the Well-being of Your HorseFrom EverandThe Everything Horse Care Book: A Complete Guide to the Well-being of Your HorseNo ratings yet
- Traditional Blacksmithing: The Fine Art of Horseshoeing and Wagon MakingFrom EverandTraditional Blacksmithing: The Fine Art of Horseshoeing and Wagon MakingNo ratings yet
- 101 Fun Facts and Trivia About Horses: All You Need To Know If You Are Crazy About HorsesFrom Everand101 Fun Facts and Trivia About Horses: All You Need To Know If You Are Crazy About HorsesNo ratings yet
- The Everything Horse Book: Buying, riding, and caring for your equine companionFrom EverandThe Everything Horse Book: Buying, riding, and caring for your equine companionRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)