Professional Documents
Culture Documents
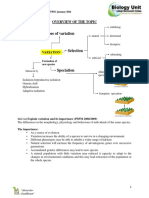
Genetic Diversity
Genetic Diversity
Uploaded by
Miss MeezOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Genetic Diversity
Genetic Diversity
Uploaded by
Miss MeezCopyright:
Available Formats
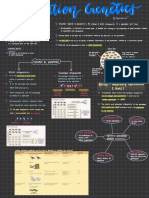
Increasing Genetic Diversity
Intro
Gene HOW
:
Genetic Diversity ? Genetic diversity can be increased by :
•
No of different alleles in a species or population a
↳ alternative version of a
gene
① Mutations : new alleles are created
•
T different alleles = In genetic diversity
-
-
different phenotypes some advantageous ,
some deleterious
•
Maintains ecological fitness of a population
•
t genetic diversity x able to adapt to
= a change in the ② Migration : new alleles may be brought into a population
environment a new population of the same species may migrate I interbreed w/
original population
Genetic Bottleneck leg European
.
Bison ) bring new & different alleles
Types of
Genetic Diversity
Occurs when size of population is ① Natural
dramatically
•
reduced disease or predator
.
"
② Directional
•
size of pop t -
-
gene pool small selection ③ stabilising
↳ no of diff alleles 11 Natural selection s ① Anatomical -
shorter I thicker ears
Surviving reproduce
members & new pop is based Random mutation ② Physiological oxidising fat
•
.
causes new alleles -
genetic diversity of a few individuals
-
on →
low genetic diversity -
Advantageous alleles causes posses or ③ Behavioural -
migration
to have an 9 reproductive success
The Founder Effect III. g Amish pop ) . -
Allele passed on
-
over many generations ,
new allele 4
Few members of a pop will leave habitat I start
frequency
•
.
in
a new
colony
•
Keg of alleles different to original pop .
'
In bacteria :
3) Stabilising selection
↳ rare alleles
may be common
°
Spontaneous mutation occurs •
Pop of this rat eapenie of -
If environmental conditions remain stable then individuals
t genetic diversity .
when penicillin used bacteria
,
nonresistant pop so freq of
. w/ phenotypes closest to mean are favoured
•
Occur due to :
① Migration would have advantage favourable allele is increased -
Eliminate phenotypes at the extremes
② New pop . becomes o
survive whilst the rest is killed
isolated a
survivor will multiply to build
Eg . Human Birth Weight
small pop of penicillin resistant bacteria
.
selected her
2) Directional Selection
M
this pop are able to survive in penicillin
peak T
"
:
.
-
mean
shifted in
-
narrower spread
Phenotypes at one extreme are selected for & those at the other extreme , direction or pop
having A resistance
are selected against
selected against
You might also like
- 8 Powerful Secrets To Anti-Aging - ProfDrPaul LingTaiDocument370 pages8 Powerful Secrets To Anti-Aging - ProfDrPaul LingTaiMikeNo ratings yet
- Patterns of InheritanceDocument99 pagesPatterns of InheritanceChirag Shah100% (1)
- Proteins Practice QuizDocument5 pagesProteins Practice Quizafaflotfi_155696459No ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Insulin Action and Insulin Resistance (Petersen y Shulman, 2018)Document91 pagesMechanisms of Insulin Action and Insulin Resistance (Petersen y Shulman, 2018)NICOLÁS ANDRÉS AYELEF PARRAGUEZNo ratings yet
- Look Good NakedDocument5 pagesLook Good NakedPedro Cabral Jr.No ratings yet
- Sensory Receptors (General and SepicalDocument33 pagesSensory Receptors (General and SepicalSambili Tonny50% (2)
- Kualitas Dna Hasil Isolasi Dari Beberapa Bagian Batang Rambut Untuk Bahan Analisis Dna ForensikDocument7 pagesKualitas Dna Hasil Isolasi Dari Beberapa Bagian Batang Rambut Untuk Bahan Analisis Dna ForensikFajrul AfifNo ratings yet
- Non Enzymatic BrowningDocument10 pagesNon Enzymatic Browninghurm350% (2)
- What Is Paper Chromatography? Principle and Procedure: Nature of The PaperDocument8 pagesWhat Is Paper Chromatography? Principle and Procedure: Nature of The PaperWiz Micheal SmithNo ratings yet
- Vilenkin Combinatorial MathematicsDocument206 pagesVilenkin Combinatorial MathematicsVasile MariusNo ratings yet
- Patel - 2010 - Music, Biological Evolution, and The BrainDocument37 pagesPatel - 2010 - Music, Biological Evolution, and The BrainMauricio SanchezNo ratings yet
- Note Topic3Document2 pagesNote Topic3Nurul AzminahNo ratings yet
- Populations GeneticsDocument8 pagesPopulations Geneticsjamshaid ibraheemNo ratings yet
- Diversity SpeciesDocument1 pageDiversity SpeciesSamica JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Heredity and Evolution - Shobhit NirwanDocument12 pagesHeredity and Evolution - Shobhit NirwanShivam Verma100% (1)
- The Mechanisms of Evolution:: Review: What Are The Basic Principles of Natural Selection?Document6 pagesThe Mechanisms of Evolution:: Review: What Are The Basic Principles of Natural Selection?brenden chapmanNo ratings yet
- General Ecology 2 NOTESDocument3 pagesGeneral Ecology 2 NOTESChristine Marie BudlaoNo ratings yet
- Sympa TricDocument6 pagesSympa Tricyunjay.k0215No ratings yet
- L5 - Population Genetics - 2021Document17 pagesL5 - Population Genetics - 2021Cynthia ChowNo ratings yet
- Calculating BiodiversityDocument3 pagesCalculating Biodiversitypia andrewNo ratings yet
- Mendelian Genetics Heredity Biology Lecture PowerPoint VCBCDocument24 pagesMendelian Genetics Heredity Biology Lecture PowerPoint VCBCMae MadronaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14 CoevolutionDocument68 pagesLecture 14 CoevolutionA.R.No ratings yet
- 24 Lecture Presentation 0Document39 pages24 Lecture Presentation 0stri47958No ratings yet
- Ess Sa PreparationDocument16 pagesEss Sa Preparationilgyu1207No ratings yet
- 8 Genetic InteractionDocument20 pages8 Genetic Interactionsadiewang0812No ratings yet
- C3 (Selection & Speciation)Document10 pagesC3 (Selection & Speciation)nurhasinahabrahimNo ratings yet
- Class 5Document31 pagesClass 5an23ms268No ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Evolution Devt of Evolutionary ThoughtDocument7 pagesMechanisms of Evolution Devt of Evolutionary ThoughtdizonfritzietheaNo ratings yet
- Padhle 10th - Heredity & EvolutionDocument21 pagesPadhle 10th - Heredity & EvolutionHarshit NegiNo ratings yet
- Genetic Diversity: As Basis For EvolutionDocument2 pagesGenetic Diversity: As Basis For EvolutionChetanNo ratings yet
- Selection and Evolution-Part 1Document177 pagesSelection and Evolution-Part 1amnaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer GeneticsDocument5 pagesReviewer GeneticsKryselle DianopraNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity ConservationDocument51 pagesBiodiversity ConservationFebryan RyanNo ratings yet
- Mendelian Genetics FinalDocument23 pagesMendelian Genetics FinalNJNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Population Genetics: Genetic VariationDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Population Genetics: Genetic VariationLance CarandangNo ratings yet
- GENETICS - 21.05.21 & 22.05.21 - MASE2 MergedDocument310 pagesGENETICS - 21.05.21 & 22.05.21 - MASE2 MergedHarshit VermaNo ratings yet
- S ENG POI COMPLETE 23 Dec GA SirDocument37 pagesS ENG POI COMPLETE 23 Dec GA SirDave JuneNo ratings yet
- Measuring Genetic Biodiversity Classification Adaptation To NicheDocument2 pagesMeasuring Genetic Biodiversity Classification Adaptation To NicheSarah LolyNo ratings yet
- Extensions and Modifications of Mendelian GeneticsDocument31 pagesExtensions and Modifications of Mendelian Geneticshanie100% (1)
- DarwinDocument77 pagesDarwinAakash NairNo ratings yet
- (BIO) Chapter 18 - InheritanceDocument19 pages(BIO) Chapter 18 - InheritanceMahi NoorNo ratings yet
- Gene Pool Total Number of A Certain Alleles Total Number of All Types of AllelesDocument3 pagesGene Pool Total Number of A Certain Alleles Total Number of All Types of AlleleskimNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of EvolutionDocument16 pagesMechanism of EvolutionLEGEND PLAYS CHANNELNo ratings yet
- Population GeneticsDocument37 pagesPopulation GeneticsSITI BAZILAH BINTI BILAK KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- 07 Quantitative InheritanceDocument2 pages07 Quantitative InheritanceBen AbellaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8-16 InheritanceDocument76 pagesLesson 8-16 Inheritancepranjalimalhotra21No ratings yet
- SpeciationDocument9 pagesSpeciationKeenisha KannanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 VariationDocument13 pagesChapter 14 VariationLisa AllisyaNo ratings yet
- Mendelian Genetics HeredityDocument19 pagesMendelian Genetics HeredityRahema VelmiNo ratings yet
- CommunitiesDocument15 pagesCommunitiesaloysius limNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity PPT NGEC 9 MTDocument50 pagesBiodiversity PPT NGEC 9 MTLyndon P. PastranaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2Document9 pagesGen Bio 2trinetteeecastroNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument1 pageConcept Mapapi-505212257No ratings yet
- Evolutionarty BiologyDocument3 pagesEvolutionarty BiologyNika MatammuNo ratings yet
- B15 Biodiversity and ConservationDocument1 pageB15 Biodiversity and ConservationAnkit AthreyaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5B - Ecological GeneticsDocument27 pagesLecture 5B - Ecological GeneticsNerey BalabatNo ratings yet
- Evolusi - Spesiasi (Asal Usul Spesies)Document39 pagesEvolusi - Spesiasi (Asal Usul Spesies)Olimpiade InfoNo ratings yet
- Evolution Mechanisms 17 18Document44 pagesEvolution Mechanisms 17 18GABRIEL AUDREY SOLONNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document6 pagesChapter 11blopsieNo ratings yet
- Science Form 2 ReviewerDocument5 pagesScience Form 2 ReviewerGertrude Reyes (Geri)No ratings yet
- Lect 3 Gene Segregation and Interaction PDFDocument10 pagesLect 3 Gene Segregation and Interaction PDFdhonaNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity ReviewDocument20 pagesBiodiversity ReviewMarcos J. MartinezNo ratings yet
- Plant Genetics and Molecular BiologyDocument30 pagesPlant Genetics and Molecular BiologyCeazar Ian PesimoNo ratings yet
- EvoRelationsSpecies StudentHO ActDocument14 pagesEvoRelationsSpecies StudentHO ActMARIA EMILIA PAZMI�O PALACIOSNo ratings yet
- Genetics & InheritanceDocument5 pagesGenetics & InheritanceClaraNo ratings yet
- Plant BreedingDocument39 pagesPlant BreedingCRISTY MAE JANDAYANNo ratings yet
- Evolution BioDocument37 pagesEvolution BioAdnan RizviNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11Document48 pagesLecture 11maximeNo ratings yet
- 06 Population 1Document12 pages06 Population 1GEOGINA HAZEL ROSALEA ANAK GHANA HILLIRY / UPMNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: MeiosisDocument8 pagesStudent Exploration: MeiosisAshtyn CurnowNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Iv Conceptual Background On Customers PerceptionDocument27 pagesChapter - Iv Conceptual Background On Customers PerceptionMatachi MagandaNo ratings yet
- Tok Resources enDocument13 pagesTok Resources enSemwezi EnockNo ratings yet
- Fairyland 4 Progress Test 7Document2 pagesFairyland 4 Progress Test 7ela.pryszczewskaNo ratings yet
- Insert CREP2 05402484001 V10 enDocument5 pagesInsert CREP2 05402484001 V10 enLabrsiabinamedika bintaroNo ratings yet
- Dermal Arteritis of The Nasal Philtrum in A Giant Schnauzer and Three Saint Bernard DogsDocument7 pagesDermal Arteritis of The Nasal Philtrum in A Giant Schnauzer and Three Saint Bernard DogsjenNo ratings yet
- Calip Advance - Scheda Tecnica ENG (Low-Res)Document6 pagesCalip Advance - Scheda Tecnica ENG (Low-Res)ahmed yahyaNo ratings yet
- Cause & Effect: Signal Words and PhrasesDocument43 pagesCause & Effect: Signal Words and PhrasesRenante PomasinNo ratings yet
- KlasifikasiDocument25 pagesKlasifikasiRunoff0% (1)
- Jasco Applications Book CD and PolarimetersDocument62 pagesJasco Applications Book CD and PolarimetersDan Pantoș100% (1)
- Biochemical Changes in Raw FoodDocument39 pagesBiochemical Changes in Raw FoodBinardo AdisenoNo ratings yet
- Best Practice & Research Clinical Obstetrics and GynaecologyDocument12 pagesBest Practice & Research Clinical Obstetrics and GynaecologyGrit WingsNo ratings yet
- Lab Practical Exam 2 InstructionsS21Document14 pagesLab Practical Exam 2 InstructionsS21jashanpreetNo ratings yet
- Effect of Nutrition in Edentulous Geriatric Patients: Review ArticleDocument6 pagesEffect of Nutrition in Edentulous Geriatric Patients: Review ArticleKrupali JainNo ratings yet
- 9 Cauliflower PDFDocument5 pages9 Cauliflower PDFIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- ShatkarmaDocument11 pagesShatkarmaNhà Khách Hải QuânNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Bangalore North (2018 - 19)Document3 pagesDelhi Public School Bangalore North (2018 - 19)Janaki KrishnanNo ratings yet
- The Hallmarks of CancerDocument7 pagesThe Hallmarks of Cancerari purnamayasaNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Treatment FAQsDocument4 pagesAerobic Treatment FAQsvince6111No ratings yet
- Read The Paragraphs Below and Underline The Topic SentenceDocument9 pagesRead The Paragraphs Below and Underline The Topic Sentencemarisa widyastuti100% (1)