Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FP Molarmass Formula 13-70 Soln
Uploaded by
Bryan Philip BejeranoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FP Molarmass Formula 13-70 Soln
Uploaded by
Bryan Philip BejeranoCopyright:
Available Formats
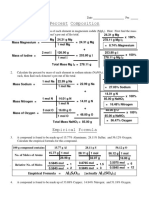
Freezing Point Depression, Molar Mass, Percentage Composition
Problem 13-70
Nicotinamide is a water-soluble vitamin important in metabolism. A deficiency in this vitamin results
in the debilitating condition known as pellagra. Nicotinamide is 59.0% C, 5.0% H, 22.9% N, 13.1% O,
by mass. Addition of 3.88 g of nicotinamide to 30.0 mL nitrobenzene, C6H5NO2 (d = 1.204 g/mL),
lowers the freezing point from 5.7 to -1.4 °C. What is the molecular formula of this compound?
Solution:
This problem combines the determination of the empirical and molecular formula with the colligative
property of freezing point depression.
Start with calculating the molar mass of Nicotinamide:
K nitrobenzene
f = 8.1 °C m (Table 13.2)
Tfpo = 5.7°C Tfpsoln = −1.4°C ∆T = −7.1°C
∆T 7.1°C
∆T = −iK f c c= =− = 0.8765 m
−iK f (1)(8.1 °C m)
The molar quantity of nicotinamide can be calculated from the molal concentration
and the mass of nitrobenzene (solvent) used to make the solution.
msolvent = 30.0 mL × 1.204 mL
g
= 36.12 g = 0.03612 kg
nnicotinamide = 0.8765 m × 0.03612 kg = 0.03166 mol nicotinamide
This quantity is represented by 3.88 g of nicotinamide so the molar mass is
3.88 g
M= = 122.5 mol
g
0.03166 mol
Now work on the empirical formula from the microanalysis:
Assume 100 g of nicotinamide
nC = 59.0 g C g = 4.913 mol C 6.0 mol C
12.01 mol
nH = 5.0 g H g = 4.960 mol H normalize to 1 O 6.06 mol H
1.008 mol
nN = 22.9 g N g = 1.635 mol N 2.00 mol N
14.007 mol
nO = 13.1 g O g = 0.8188 mol O 1.0 mol O
16.00 mol
Empirical Formula = C6 H 6 N 2 O (122.1 g/mol)
which is the same as the molecular formula
You might also like
- Lecture 5, The Mole: What Is A Mole?Document38 pagesLecture 5, The Mole: What Is A Mole?JohnNo ratings yet
- Science (10) Reviewer - 1st MonthlyDocument4 pagesScience (10) Reviewer - 1st MonthlymaeNo ratings yet
- Rpactice ExamDocument6 pagesRpactice Examnaloma.juliacamilleNo ratings yet
- %W/W M M ×100 % 7.60 G ×100 % 8.705612829 %: Assignment 2Document13 pages%W/W M M ×100 % 7.60 G ×100 % 8.705612829 %: Assignment 2Poison PinkNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 AnswersDocument5 pagesTopic 3 AnswersHarani ThillainathanNo ratings yet
- Module 4 StoichiometryDocument41 pagesModule 4 StoichiometryMariane CarandangNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Problem SetsDocument8 pagesChemistry Problem SetsMacky DacilloNo ratings yet
- Questions Chapter 3Document9 pagesQuestions Chapter 3hadassahhadidNo ratings yet
- Gibbs y MezclasDocument5 pagesGibbs y MezclasRodrigo GarciaNo ratings yet
- 3.chapter Three - Suggested ProblemsDocument10 pages3.chapter Three - Suggested ProblemsAbdulrahman AlrefaieNo ratings yet
- Chem Assignment 2Document13 pagesChem Assignment 2Rachna LalNo ratings yet
- Report 4Document3 pagesReport 4burucgmiciNo ratings yet
- Act 8 4 Molecular Form HydratKEYDocument2 pagesAct 8 4 Molecular Form HydratKEYEthanNo ratings yet
- Pset 3 6Q ADocument3 pagesPset 3 6Q AywkimbNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry: Stoichiometry Is The Calculation of Reactants and Products in Chemical Reactions (Wikipedia, 2019)Document47 pagesStoichiometry: Stoichiometry Is The Calculation of Reactants and Products in Chemical Reactions (Wikipedia, 2019)Dasilva PermataNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 - Concentrations (LEC)Document11 pagesAssignment 2 - Concentrations (LEC)Poison PinkNo ratings yet
- Concentration of SolutionDocument3 pagesConcentration of SolutionJoon Bok NamleeNo ratings yet
- Activity in General Chemistry II: Thermochemistry Problem SolvingDocument5 pagesActivity in General Chemistry II: Thermochemistry Problem SolvingGheerah PantojaNo ratings yet
- 1 2Document65 pages1 2AQEESHA NUWAIRA BINTI USMAN BN21110154No ratings yet
- Review Session Prelim To FinalsDocument4 pagesReview Session Prelim To FinalsjaporlanteNo ratings yet
- 4.13 ReviewDocument3 pages4.13 ReviewVansh PatelNo ratings yet
- Chemlec Assignment 3.Document4 pagesChemlec Assignment 3.ElleNo ratings yet
- 5.2X10 F.U. Nacl: CH 8 Review Handout. Show All WorkDocument6 pages5.2X10 F.U. Nacl: CH 8 Review Handout. Show All WorkJessa BrackettNo ratings yet
- Empirical Molecular Formulas WKST KEY PDFDocument3 pagesEmpirical Molecular Formulas WKST KEY PDFMisbah TufailNo ratings yet
- Ecuaciones Quimica 123Document4 pagesEcuaciones Quimica 123Ruben Rodriguez ValverdeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Properties of Solutions Exercise 1Document26 pagesChapter 13 Properties of Solutions Exercise 1janeNo ratings yet
- Comb Analysis Ch3!91!92 93Document2 pagesComb Analysis Ch3!91!92 93biniamkiros09No ratings yet
- Lesson 10 Chemical Composition FinalDocument5 pagesLesson 10 Chemical Composition Finalnarutouzumakiabc9No ratings yet
- A2 Answer KeysDocument11 pagesA2 Answer KeysJose Emanuel AquinoNo ratings yet
- 解答 20221124Document2 pages解答 20221124Denny LuNo ratings yet
- A Solution Contains 5 G of Urea (M2 60.05) Per 100 G of Water. What Will Be The Vapor Pressure of This Solution at 25Document21 pagesA Solution Contains 5 G of Urea (M2 60.05) Per 100 G of Water. What Will Be The Vapor Pressure of This Solution at 25Marianne Camille de Guzman100% (1)
- Tutorial 2 - Mole Concept Semester 2 2017-8 SolutionDocument4 pagesTutorial 2 - Mole Concept Semester 2 2017-8 SolutionMyeisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Solutions: Lecture NotesDocument14 pagesSolutions: Lecture NotesMisa AmaneNo ratings yet
- Userdata Paziras Chem101 Review 03ANSDocument3 pagesUserdata Paziras Chem101 Review 03ANSJerich Ivan PaalisboNo ratings yet
- Chap 7 Mole and Chemical CompositionDocument36 pagesChap 7 Mole and Chemical CompositionAnthony AraizaNo ratings yet
- Tugas RutinDocument15 pagesTugas RutinElvi ZurryyatiNo ratings yet
- Answer Key EmpiricalDocument6 pagesAnswer Key EmpiricalANGELYN SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Problem Set PCPDocument4 pagesProblem Set PCPJenny LlanesNo ratings yet
- Graded Problem SetDocument6 pagesGraded Problem SetLala LandNo ratings yet
- CLS JEEAD-18-19 XI Che Target-1 SET-2 Chapter-1Document32 pagesCLS JEEAD-18-19 XI Che Target-1 SET-2 Chapter-1vishavpreet yadavNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Handoutsworksheet Brinell ValencianoDocument8 pagesWeek 5 Handoutsworksheet Brinell ValencianoPortgas D. AceNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 Quarter 1 - Week 3a (Molecular Formula (Learning Activity Sheets) )Document4 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 Quarter 1 - Week 3a (Molecular Formula (Learning Activity Sheets) )Sachzelle MikaylaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial ChemDocument2 pagesTutorial ChemNurAin FatihahNo ratings yet
- REVIEW AgainDocument25 pagesREVIEW AgainFahmiNo ratings yet
- P 29-37 Imper Molec Form, %Document10 pagesP 29-37 Imper Molec Form, %molakathallanehareddyNo ratings yet
- C01 14SDocument49 pagesC01 14STiffany LiuNo ratings yet
- Problems: CHEM1020Document45 pagesProblems: CHEM1020Ahmed AliNo ratings yet
- Molar MassDocument16 pagesMolar Massmleitch12No ratings yet
- Answer Checkpoint Chapter 1Document4 pagesAnswer Checkpoint Chapter 1ALIS SUHAIRIN BT ABD GHANI BMNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three The Mole and Stoichiometry: Practice ExerciseDocument30 pagesChapter Three The Mole and Stoichiometry: Practice ExerciseRIKI MUHAMMADNo ratings yet
- 9 Ba 965Document80 pages9 Ba 965Mind NiramindNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY - Grade 9 - Revision NoteDocument36 pagesCHEMISTRY - Grade 9 - Revision Notebasleal tamiruNo ratings yet
- chm431 2020 ps12 2020 AnsDocument7 pageschm431 2020 ps12 2020 AnsDede RohayatiNo ratings yet
- Combustion Analysis Extra Problems KeyDocument2 pagesCombustion Analysis Extra Problems KeyJoselyna GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Combustion Analysis Extra Problems KeyDocument2 pagesCombustion Analysis Extra Problems KeyJoselyna GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Chap3lect 2020Document62 pagesChap3lect 2020Anonymous wt2BA7uNo ratings yet
- No. of Carbon-12 Atoms Atomic Mass (G) Mass of One Atom (G)Document20 pagesNo. of Carbon-12 Atoms Atomic Mass (G) Mass of One Atom (G)Prince SanjiNo ratings yet
- TR KIMIA - Yogi Sihite PDFDocument23 pagesTR KIMIA - Yogi Sihite PDFYogi SihiteNo ratings yet
- Stratospheric Chemistry: The Ozone LayerDocument38 pagesStratospheric Chemistry: The Ozone LayerBryan Philip BejeranoNo ratings yet
- Sorsogon National High School: Self-Directed Learning Activity Sheet in General Chemistry 2Document4 pagesSorsogon National High School: Self-Directed Learning Activity Sheet in General Chemistry 2Bryan Philip BejeranoNo ratings yet
- Self-Directed Learning Activity Sheet in General Chemistry 2Document4 pagesSelf-Directed Learning Activity Sheet in General Chemistry 2Bryan Philip BejeranoNo ratings yet
- Social Security System: Applicable Period Individual Payment Reference Number AmountDocument1 pageSocial Security System: Applicable Period Individual Payment Reference Number AmountBryan Philip BejeranoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry IiDocument2 pagesGeneral Chemistry IiBryan Philip BejeranoNo ratings yet
- General ChemistryDocument2 pagesGeneral ChemistryBryan Philip BejeranoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 1 Summative TestDocument2 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 1 Summative TestBryan Philip BejeranoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 (Summative Test No.1) : Mikylla D. Mendina 11-Curiosity April 15,2021Document6 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 (Summative Test No.1) : Mikylla D. Mendina 11-Curiosity April 15,2021Bryan Philip BejeranoNo ratings yet
- Has The Closest Boiling Point To That of ArgonDocument3 pagesHas The Closest Boiling Point To That of ArgonBryan Philip BejeranoNo ratings yet
- Mendina, Camille D 11-Stem CuriosityDocument4 pagesMendina, Camille D 11-Stem CuriosityBryan Philip BejeranoNo ratings yet
- Torrent Downloaded From Demonoid - Ph.Document1 pageTorrent Downloaded From Demonoid - Ph.Bryan Philip BejeranoNo ratings yet
- 15.1 250 KG/H of Air Saturated at 2°C Is Mixed With 50 KG/H of Air at 35°C and 80% RHDocument17 pages15.1 250 KG/H of Air Saturated at 2°C Is Mixed With 50 KG/H of Air at 35°C and 80% RHNathan EscobalNo ratings yet
- J Scitotenv 2020 142108Document26 pagesJ Scitotenv 2020 142108SHERLY KIMBERLY RAMOS JESUSNo ratings yet
- Ms 4 Ss A Introduction To PolymersDocument132 pagesMs 4 Ss A Introduction To Polymersbianca reyesNo ratings yet
- LNG PRDocument16 pagesLNG PRFakgNo ratings yet
- Using Physical and Chemical Properties To Manage Flammable Liquid Hazards Part Three of A Three Part SeriesDocument9 pagesUsing Physical and Chemical Properties To Manage Flammable Liquid Hazards Part Three of A Three Part SeriesAbdul AwanNo ratings yet
- Rheology ModifiersDocument35 pagesRheology Modifierssbttbs67% (3)
- Process Design Course DME Autumn 2009Document108 pagesProcess Design Course DME Autumn 2009Srikari MulaNo ratings yet
- High Temperature CorrosionDocument3 pagesHigh Temperature CorrosiontechzonesNo ratings yet
- 03 Naproxen SodiumDocument10 pages03 Naproxen SodiumSadi SamanNo ratings yet
- Small Scale Bio-LNG Plant - Comparison of Different Biogas UpgradingtechniquesDocument8 pagesSmall Scale Bio-LNG Plant - Comparison of Different Biogas UpgradingtechniquesPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Solving Problems in Food Engineering Springer 0387735135-233-239Document7 pagesSolving Problems in Food Engineering Springer 0387735135-233-239Bagner castillo garzonNo ratings yet
- Chemical Oceanography PDFDocument34 pagesChemical Oceanography PDFLia Kusumawati100% (1)
- Carga Nitrogeno NPK PDFDocument5 pagesCarga Nitrogeno NPK PDFhenry vega100% (1)
- Electrostatics Notes of Allen Kota BatchDocument143 pagesElectrostatics Notes of Allen Kota BatchAbhijeet ThakurNo ratings yet
- 1559024845Document29 pages1559024845habiba jamilNo ratings yet
- ESE - Miscellaneous Treatments of WaterDocument13 pagesESE - Miscellaneous Treatments of WaterRoshan NayakNo ratings yet
- Basics of Steam Turbine RollingDocument9 pagesBasics of Steam Turbine RollingLipika Ghosh BiswasNo ratings yet
- The Quantum RobinDocument3 pagesThe Quantum RobinpresuraNo ratings yet
- Basics of ElectrochemistryDocument36 pagesBasics of ElectrochemistryNaveed JanjuaNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen 2006 01 0434Document6 pagesHydrogen 2006 01 0434Rajesh VarmaNo ratings yet
- Precipitation in A Lead Calcium Tin AnodeDocument7 pagesPrecipitation in A Lead Calcium Tin AnodeDilfredo RuizNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 2 Types of Compounds Based On Their PropertiesDocument9 pagesScience: Quarter 2 Types of Compounds Based On Their PropertiesAriel Lomugdang PatricioNo ratings yet
- CHEM225 Organic Chemistry 1 Module Week 1-4Document17 pagesCHEM225 Organic Chemistry 1 Module Week 1-4Kezia CaratorNo ratings yet
- WWW Askiitians Com Revision Notes Class 9 Science Is Matter Around Us PureDocument17 pagesWWW Askiitians Com Revision Notes Class 9 Science Is Matter Around Us PureDeepak Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Full Download Test Bank For Foundations of Maternal Newborn and Womens Health Nursing 6th Edition by Murray PDF FreeDocument32 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Foundations of Maternal Newborn and Womens Health Nursing 6th Edition by Murray PDF FreeMichael Taylor100% (12)
- HMT 113401 Anna UnivDocument3 pagesHMT 113401 Anna Univsathiya_ramNo ratings yet
- Metals MCQ PDFDocument21 pagesMetals MCQ PDFMunshatia Islam MerryNo ratings yet
- Guidlines For Use and Care of Aminex Resin-Based ColumnsDocument32 pagesGuidlines For Use and Care of Aminex Resin-Based ColumnsSara Dolgun0% (1)
- Tutorial On Electrolysis and Faraday's Law.: Prepared by Lawrence KokDocument27 pagesTutorial On Electrolysis and Faraday's Law.: Prepared by Lawrence KokoscarbecNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01 (30-08-2022)Document12 pagesLecture 01 (30-08-2022)Harshil PatelNo ratings yet