Professional Documents
Culture Documents
General Chemistry: - The Atom Nucleus
Uploaded by
Kristine0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageChemistry is the study of matter, its properties, and transformations, including energy changes. Matter can be classified based on its physical state as solid, liquid, gas, plasma, Bose-Einstein condensate, Fermionic condensate, or quark-gluon plasma. It can also be classified based on its composition as elements, compounds, or mixtures. Atoms are the basic units of matter and are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons. The nucleus contains protons and neutrons and is held together by the strong nuclear force.
Original Description:
Original Title
General Chemistry
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentChemistry is the study of matter, its properties, and transformations, including energy changes. Matter can be classified based on its physical state as solid, liquid, gas, plasma, Bose-Einstein condensate, Fermionic condensate, or quark-gluon plasma. It can also be classified based on its composition as elements, compounds, or mixtures. Atoms are the basic units of matter and are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons. The nucleus contains protons and neutrons and is held together by the strong nuclear force.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageGeneral Chemistry: - The Atom Nucleus
Uploaded by
KristineChemistry is the study of matter, its properties, and transformations, including energy changes. Matter can be classified based on its physical state as solid, liquid, gas, plasma, Bose-Einstein condensate, Fermionic condensate, or quark-gluon plasma. It can also be classified based on its composition as elements, compounds, or mixtures. Atoms are the basic units of matter and are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons. The nucleus contains protons and neutrons and is held together by the strong nuclear force.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
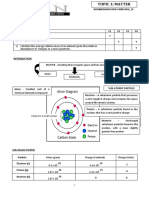
General Chemistry
Chemistry - study of matter and its The Atom
Composition properties and transformations - Composed of nucleons (protons & neutrons)
Including the energy changes accompanying it.
Nucleus
Properties of matter: - Made up of nucleons, held by strong force
1. Intensive Properties Neutrons acts as glue to lump protons together
○ Independent on the amt. of material
Ex. Temp, Freezing pt., conductivity Nuclide Notation
2. Extensive Properties
○ Dependent on the amt. of material
Ex. Mass, length, volume
Classification of Matter: X-A Example: C-12
Based on Physical states:
1. Solid
2. Liquid
Isotopes Same Atomic number (protons)
3. Gas
4. Plasma Diff. # of neutrons
- result of gas going thru ionization Isobars Same mass number
5. Bose-Einstein Condensate
- made under rare circumstances Diff. Atomic number
6. Fermionic Condensate Isotones Same Atomic number (neutrons)
- super-fluid phases formed @ low Temp
Diff. Atomic mass
7. Quark-Gluon Plasma
-Protons/neutrons formed of three quarks Isoelectronic Same # of electrons
Based on Composition:
Binding Energy
-energy required to separate an atom (p, n, e)
-quantified using Einstein's Equation
c - speed of light (3x108)
- mass defect
Mass of individual > Mass of an atom
(p, n, e) (binded)
Colloids - larger than solutes but smaller for
mixture to become heterogeneous.
- can be distinguished using Tyndall Effect. Constants kg
Mp #1
Mn #2
mc #3
NA #24
Ev -> J #23
c #28
General Chemistry Page 1
You might also like
- 1 - X Live Class Slides Atomic Structure and PropertiesDocument52 pages1 - X Live Class Slides Atomic Structure and Properties5796fpdfmrNo ratings yet
- 1819 Physical and Inorganic Summary PDFDocument60 pages1819 Physical and Inorganic Summary PDFAce PTNo ratings yet
- General Inorganic Chemistry Presentation For BSU Compre Handout 2Document118 pagesGeneral Inorganic Chemistry Presentation For BSU Compre Handout 2Ahe BeongNo ratings yet
- Chem 101 CH02 Ismail ANUDocument82 pagesChem 101 CH02 Ismail ANUameer jomaNo ratings yet
- Atoms: The Building Blocks of MatterDocument26 pagesAtoms: The Building Blocks of MatterReamtraxNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry DefinitionsDocument2 pagesIGCSE Chemistry DefinitionsoscarbecNo ratings yet
- Im 1482154379 PDFDocument23 pagesIm 1482154379 PDFramlakhanNo ratings yet
- (Gs Material Science) : Structure of Atom and Interatomic BondingDocument23 pages(Gs Material Science) : Structure of Atom and Interatomic BondingramlakhanNo ratings yet
- Chem1Chap2L5-Atoms and Electron ConfigurationDocument10 pagesChem1Chap2L5-Atoms and Electron ConfigurationPatrixiah Monicah Mareight BaronNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Science1Document6 pagesReviewer in Science1Cailin Loraine VibarNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Chemistry Study NotesDocument39 pagesYear 11 Chemistry Study NotesRaghav Jaitely100% (1)
- MATTER: ISOTOPES AND MASS SPECTROMETRYDocument35 pagesMATTER: ISOTOPES AND MASS SPECTROMETRYSupia NazmaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Chemistry BasicsDocument10 pagesNuclear Chemistry BasicsAlemkeng BrendaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Atomic Structure & Interatomic Bonding Atomic Structure (Freshman Chem.)Document6 pagesChapter 2: Atomic Structure & Interatomic Bonding Atomic Structure (Freshman Chem.)AruzhanNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics - Ii: Theory and Exercise BookletDocument25 pagesModern Physics - Ii: Theory and Exercise BookletJayeshNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: An OverviewDocument26 pagesAtomic Structure: An OverviewLuke DavisNo ratings yet
- Proton Physics: Structure and Properties of the ProtonDocument13 pagesProton Physics: Structure and Properties of the ProtonKhalid AhmedNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules and StoichiometryDocument28 pagesAtoms, Molecules and StoichiometryShima Senseii100% (1)
- Module 5 Nuclear PhysicsDocument24 pagesModule 5 Nuclear PhysicsZero EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure FundamentalsDocument40 pagesAtomic Structure FundamentalsShaina OrnopiaNo ratings yet
- Table of Physical ConstantsDocument1 pageTable of Physical ConstantsGarry Yan DiazNo ratings yet
- Algebra-Based Physics II: Dec. 3: Chap 31 Nuclear Physics and RadioactivityDocument24 pagesAlgebra-Based Physics II: Dec. 3: Chap 31 Nuclear Physics and RadioactivityazureusNo ratings yet
- File 2657Document6 pagesFile 2657Alexandra LupuNo ratings yet
- Intro To Nuclear Chemistry - NewDocument68 pagesIntro To Nuclear Chemistry - NewPink WandererNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 Atoms and Molecules STUDDocument22 pagesChapter2 Atoms and Molecules STUDCristian Menéndez FernándezNo ratings yet
- Topic:: STPM Term 1 ChemistryDocument47 pagesTopic:: STPM Term 1 ChemistryMenaga A/P IlangkovanNo ratings yet
- MSE 102 Ch02 - 1Document70 pagesMSE 102 Ch02 - 1Mohammed AlbkiliNo ratings yet
- Unit 01 Short Note-EMDocument9 pagesUnit 01 Short Note-EMShashiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lesson 2Document22 pagesChemistry Lesson 2Lili PinkNo ratings yet
- Nuclear ChemistryDocument12 pagesNuclear ChemistryAm AsdfghjklNo ratings yet
- Structure of The Atom: Sub-Atomic Particles Atomic Models Characteristics of AtomDocument1 pageStructure of The Atom: Sub-Atomic Particles Atomic Models Characteristics of AtomJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Elements, Compounds and the Development of the Atomic ModelDocument1 pageAtoms, Elements, Compounds and the Development of the Atomic ModelcallumNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 - Matter: Name: Lecturer: Subject: Class: Lesson No.: Topic: Day/TimeDocument30 pagesCHAPTER 1 - Matter: Name: Lecturer: Subject: Class: Lesson No.: Topic: Day/TimeLim Ru He能够No ratings yet
- CHM031L - Nuclear ChemistryDocument42 pagesCHM031L - Nuclear ChemistryKath CarmonaNo ratings yet
- Unless Otherwise Stated, All Images in This File Have Been Reproduced FromDocument19 pagesUnless Otherwise Stated, All Images in This File Have Been Reproduced FromLucille MelbourneNo ratings yet
- Transfer of Electrons Between Atoms With ADocument1 pageTransfer of Electrons Between Atoms With AameenallyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry FactsheetsDocument415 pagesChemistry FactsheetsAmbrose Aaron DavidNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Particle and Nuclear PhysicsDocument72 pagesIntroduction to Particle and Nuclear PhysicsShamsuzzaman SharifNo ratings yet
- CHEM 114 Nuclear Chem NotesDocument4 pagesCHEM 114 Nuclear Chem NotesPrincess PalerNo ratings yet
- NucleiDocument8 pagesNucleipoojanbhojan1No ratings yet
- Chemistry HL - Fast Facts - Second Edition - Pearson 2014Document16 pagesChemistry HL - Fast Facts - Second Edition - Pearson 2014Serena WilsonNo ratings yet
- Chemistry HL - FAST FACTS - Second Edition - Pearson 2014Document65 pagesChemistry HL - FAST FACTS - Second Edition - Pearson 2014sahilNo ratings yet
- UTAR Centre for Foundation Studies Group I and II Elements Physical and Chemical PropertiesDocument10 pagesUTAR Centre for Foundation Studies Group I and II Elements Physical and Chemical PropertiesHong Hong WongNo ratings yet
- Together When Positive Charges Repel Each Other?": - "Why Do Protons StayDocument23 pagesTogether When Positive Charges Repel Each Other?": - "Why Do Protons StayIvanah Mae AcloNo ratings yet
- 1 chapter 2-3原子结构Document119 pages1 chapter 2-3原子结构Pingping chenNo ratings yet
- Nuclear StructureDocument37 pagesNuclear StructureNaresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Modelos Nucleares 2023 Ver 2Document63 pagesModelos Nucleares 2023 Ver 2samuelNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument3 pagesCHEMISTRYSAN JOSE, KRIZZIA FAYE U.No ratings yet
- 3 - Atomic Structure - History of AtomDocument15 pages3 - Atomic Structure - History of AtomVimanan A/L S. VelangganiNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure NotesDocument6 pagesAtomic Structure NotesArti DeviNo ratings yet
- Chem 131 Final ReviewDocument13 pagesChem 131 Final ReviewShahd MuhamedNo ratings yet
- Nuclei For CBSE Physics Class XII Revision NotesDocument4 pagesNuclei For CBSE Physics Class XII Revision NotesKuldeep HoodaNo ratings yet
- RATIPDocument40 pagesRATIPphononsanchelaNo ratings yet
- 04 Structure of Atom CN (04-06-22) - MinDocument3 pages04 Structure of Atom CN (04-06-22) - Minnandukr.8083No ratings yet
- 3.1.1 Atomic Structure: AQA SpecDocument17 pages3.1.1 Atomic Structure: AQA SpecafshinNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 1Document7 pagesChemistry Unit 1Natasha Liliane LootNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Atomic Structure: Maulidia EkaputriDocument19 pagesChapter 2: Atomic Structure: Maulidia EkaputrilidiaepNo ratings yet
- The Stopping and Ranges of Ions in Matter: Handbook of Stopping Cross-Sections for Energetic Ions in All ElementsFrom EverandThe Stopping and Ranges of Ions in Matter: Handbook of Stopping Cross-Sections for Energetic Ions in All ElementsNo ratings yet
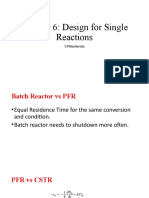
- Chapter 6: Design For Single Reactions: CpmonterolaDocument25 pagesChapter 6: Design For Single Reactions: CpmonterolaKristineNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Reactions in Series and Multiple ReactionsDocument10 pagesChapter 8 Reactions in Series and Multiple ReactionsKristineNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Design For Single Reactions: CpmonterolaDocument25 pagesChapter 6: Design For Single Reactions: CpmonterolaKristineNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Levenspiel: Reactors for Single ReactionsDocument24 pagesChapter 5 Levenspiel: Reactors for Single ReactionsKristineNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Levenspiel: Interpretation of Batch Reactor Data: CpmonterolaDocument40 pagesChapter 3 Levenspiel: Interpretation of Batch Reactor Data: CpmonterolaKristineNo ratings yet
- Selectivity, S & Conversion X for PFR vs CSTR Example 6.2 FoglerDocument7 pagesSelectivity, S & Conversion X for PFR vs CSTR Example 6.2 FoglerKristineNo ratings yet
- Fogler Chapter 4 Solutions and ExamplesDocument11 pagesFogler Chapter 4 Solutions and ExamplesKristineNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 FoglerDocument11 pagesChapter 1 FoglerKristineNo ratings yet
- Che171 1Document109 pagesChe171 1KristineNo ratings yet
- Pmma Conv-Look1Document77 pagesPmma Conv-Look1KristineNo ratings yet
- Catalysts: Removal of Hydrogen Sulfide From Various Industrial Gases: A Review of The Most Promising Adsorbing MaterialsDocument36 pagesCatalysts: Removal of Hydrogen Sulfide From Various Industrial Gases: A Review of The Most Promising Adsorbing MaterialsKristineNo ratings yet
- ChE ReviewerDocument82 pagesChE ReviewerKristineNo ratings yet
- ChE Past Board Exam QuestionsDocument18 pagesChE Past Board Exam QuestionsMi Casa100% (1)
- Health Protocol: Inclusive ofDocument3 pagesHealth Protocol: Inclusive ofKristineNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 5 AnswersDocument4 pagesWorksheet 5 AnswersKristineNo ratings yet
- ChE Day1 Questions (Objectives)Document4 pagesChE Day1 Questions (Objectives)Mhelvene100% (3)
- Solution To ChECal MRII BookDocument15 pagesSolution To ChECal MRII BookKristineNo ratings yet
- The Philippines in The Paper Global Value Chain: Technical ReportDocument65 pagesThe Philippines in The Paper Global Value Chain: Technical ReportKristineNo ratings yet
- Polymers 07 01379 PDFDocument10 pagesPolymers 07 01379 PDFKristineNo ratings yet
- TECHNOLOGICAL INSTITUTE OF THE PHILIPPINES ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY PROBLEM SETDocument1 pageTECHNOLOGICAL INSTITUTE OF THE PHILIPPINES ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY PROBLEM SETKaizerNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry MCQs With Answer KeyDocument11 pagesAnalytical Chemistry MCQs With Answer KeyMark Ryan Tripole84% (31)
- 1 s2.0 S187853521830008X Main1Document15 pages1 s2.0 S187853521830008X Main1KristineNo ratings yet
- Processes 07 00377 PDFDocument12 pagesProcesses 07 00377 PDFKaul PatrickNo ratings yet
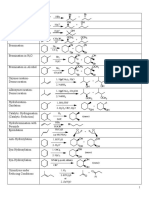
- Top Alkene and Alkyne ReactionsDocument11 pagesTop Alkene and Alkyne ReactionsKristineNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle Assessment Applied To Egg Packaging Made From Polystyrene and Recycled PaperDocument12 pagesLife Cycle Assessment Applied To Egg Packaging Made From Polystyrene and Recycled PaperKristineNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Development in Trust International Paper CorporationDocument11 pagesSustainable Development in Trust International Paper CorporationKristineNo ratings yet
- Resources PDFDocument23 pagesResources PDFKristineNo ratings yet
- Waste Paper For Recycling: Overview and Identification of Potentially Critical SubstancesDocument32 pagesWaste Paper For Recycling: Overview and Identification of Potentially Critical SubstancesKristineNo ratings yet
- Theoretical and Experimental Determination of Cell Constants of Planar-Interdigitated Electrolyte Conductivity SensorsDocument5 pagesTheoretical and Experimental Determination of Cell Constants of Planar-Interdigitated Electrolyte Conductivity SensorsKristineNo ratings yet
- Advanced Topics in Quantum Field Theory A Lecture Course by Shifman M.Document642 pagesAdvanced Topics in Quantum Field Theory A Lecture Course by Shifman M.Amos chenNo ratings yet
- Model Question: Third Semester M.Sc. (Physics)Document1 pageModel Question: Third Semester M.Sc. (Physics)Sagar RawalNo ratings yet
- Some Conceptual Problems in 1-Dimensional Schrodinger EquationDocument13 pagesSome Conceptual Problems in 1-Dimensional Schrodinger EquationkalshinokovNo ratings yet
- Practice Test H.2 Electrons, Periodicity, Nuclear: (PG 1 of 7)Document7 pagesPractice Test H.2 Electrons, Periodicity, Nuclear: (PG 1 of 7)ajgavinoNo ratings yet
- Oxo OGW16 C12ss Xq02 XxaannDocument7 pagesOxo OGW16 C12ss Xq02 XxaannAmanah Abdul-quddusNo ratings yet
- Topic 12.1 - The Interaction of Matter With Radiation - AHLDocument79 pagesTopic 12.1 - The Interaction of Matter With Radiation - AHLPaul Amezquita100% (1)
- Lecture 04 of Solid State PhysicsDocument29 pagesLecture 04 of Solid State PhysicsHena DianNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Force ExplainedDocument3 pagesElectrostatic Force ExplainedCarlton GrantNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics OperatorsDocument17 pagesQuantum Mechanics OperatorsAldeir De Los ReyesNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document2 pagesAssignment 3Stephen TanNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics TheoryDocument14 pagesNuclear Physics TheoryTanvir ShafalNo ratings yet
- Measuring Quantum States of LightDocument259 pagesMeasuring Quantum States of LightbrianjsmithNo ratings yet
- Relative Charge of An AtomDocument22 pagesRelative Charge of An AtomFatima M KhalifehNo ratings yet
- Neutrino Experiments and The Problem of Conservation of Leptonic ChargeDocument5 pagesNeutrino Experiments and The Problem of Conservation of Leptonic ChargeRicardo Miguel PedroNo ratings yet
- Molecular Orbital Calculations PDFDocument165 pagesMolecular Orbital Calculations PDFrakesh1521No ratings yet
- A Key To Nature's Secrets'Document11 pagesA Key To Nature's Secrets'Bruna LemesNo ratings yet
- Principles of NMR SpectrosDocument23 pagesPrinciples of NMR SpectrosSudha AtmakuriNo ratings yet
- Summative Test No. 1 Grade 8Document3 pagesSummative Test No. 1 Grade 8LENETTE ALAGONNo ratings yet
- QCCC SeminarDocument104 pagesQCCC SeminarJuan Garrapito Bermejo-VegaNo ratings yet
- Physics 465: Visualizing Traveling WavesDocument6 pagesPhysics 465: Visualizing Traveling WavesSteve SpicklemireNo ratings yet
- Rudram ChamakamDocument51 pagesRudram ChamakamBalakrishnan Rayirathil100% (2)
- Arnold Et Al. - 1991 - UnknownDocument12 pagesArnold Et Al. - 1991 - UnknowndielemandNo ratings yet
- Radiation Shielding Design For Medical Cyclotron: January 2013Document4 pagesRadiation Shielding Design For Medical Cyclotron: January 2013Samu SimamesaNo ratings yet
- E e e E: Opposite Properties. They Are Like + 1 and - 1 Same Magnitude But Different Signs. For Every Particle ThatDocument16 pagesE e e E: Opposite Properties. They Are Like + 1 and - 1 Same Magnitude But Different Signs. For Every Particle ThatPema WangmoNo ratings yet
- QuantumDocument54 pagesQuantumpashazade0% (1)
- S11 12PS-IIIa-1 How The Elements Found in The Universe WereDocument12 pagesS11 12PS-IIIa-1 How The Elements Found in The Universe WereMarArizala0% (2)
- The Quantum Handshake Explored PDFDocument27 pagesThe Quantum Handshake Explored PDFRichard BertemattiNo ratings yet
- Science Corner Production 3 @2021Document1 pageScience Corner Production 3 @2021Davies MasumbaNo ratings yet
- 02 Atomic Structure Que. Final EDocument31 pages02 Atomic Structure Que. Final EDIPESHNo ratings yet