Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4th Class Hand Note 20.10.21 DA
Uploaded by
gtgtdfgfdg0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pages4th Class Hand Note 20.10.21 DA
Uploaded by
gtgtdfgfdgCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
4th class:
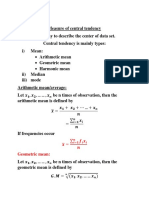
Median and mode:
Median:
Median is the value of a ranked or ordered
observation which divides the total observation into
two parts of equal size.
5, 9,4,13,10,22,2,3,11; n=9
2,3,4,5,9(median),10,11,13,22
𝑵+𝟏 𝟗+𝟏
= = 𝟓𝒕𝒉
𝟐 𝟐
2,3,4,5,9,10,11,13; n=8
Median=(5+9)/2=7
𝑁 𝑁
[ 𝑡ℎ 𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑚 + ( + 1) 𝑡ℎ 𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑚] /2
2 2
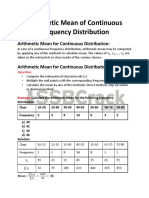
Calculating median for group data:
𝑵
− 𝒇𝒄
𝑴𝒆 = 𝑳𝟏 + 𝟐 .𝒄
𝒇𝒎
Where 𝑳𝟏 = 𝒍𝒐𝒘𝒆𝒓 𝒍𝒊𝒎𝒊𝒕 𝒐𝒇 𝒕𝒉𝒆 𝒎𝒆𝒅𝒊𝒂𝒏 𝒄𝒍𝒂𝒔𝒔
N=total number of observations
𝒇𝒄 =cumulative frequency of the pre-median class
𝒇𝒎 =frequency of the median class
C=class interval
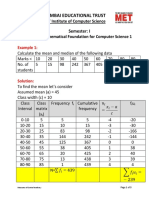
Problem: Calculate median from the following frequency
distribution:
Marks No. of students
0-10 5
10-20 7
20-30 13
30-40 15
40-50 8
50-60 2
Solution:
Marks No. of students(fi) Cumulative frequency
0-10 5 5
10-20 7 12
20-30 13 25
30-40 15 40
40-50 8 48
50-60 2 50
Total N=50
Here N=50; N/2=50/2=25
So, (20-30) is the median class because N/2=50/2=25th observation lies
in this class.
𝑵
− 𝒇𝒄
𝑴𝒆 = 𝑳𝟏 + 𝟐 .𝒄
𝒇𝒎
𝟐𝟓 − 𝟏𝟐
= 𝟐𝟎 + . 𝟏𝟎 = 𝟑𝟎
𝟏𝟑
Mode: mode is the value of a set of observation which
occurs most frequently.
7,10,15,15,17,17,17,17,19,20,25
Calculating mode for group data:
∇1
𝑀𝑜 = 𝐿1 + .𝑐
∇1 + ∇2
Where
𝐿1 =lower limit of the modal class
∇1 =difference between the frequencies of modal class
and pre-modal class
∇2 = difference between the frequencies of modal class
and post-modal class
C=class interval
Problem: Calculate mode from the following frequency
distribution:
Marks No. of students
0-10 5
10-20 7
20-30 13
30-40(modal class) 15
40-50 8
50-60 2
Here (30-40) is the modal class because maximum
frequency 15 occurs in this class.
∇1
𝑀𝑜 = 𝐿1 + .𝑐
∇1 + ∇2
15 − 13
= 30 + . 10 = 32.22
(15 − 13) + (15 − 8)
Next class: Quartiles, Deciles and percentiles
You might also like
- Class Test-1: Date:1-11-21 Syllabus: Up To Percentile Extra ClassDocument6 pagesClass Test-1: Date:1-11-21 Syllabus: Up To Percentile Extra ClassgtgtdfgfdgNo ratings yet
- Mean Median ModeDocument32 pagesMean Median ModeShiella Mae Baltazar BulauitanNo ratings yet
- Unit-V Basic Statistics and Probability: Presentation - Three Forms - Histogram, Bar Chart, Frequency PolygonDocument6 pagesUnit-V Basic Statistics and Probability: Presentation - Three Forms - Histogram, Bar Chart, Frequency PolygonVenkatesh WaranNo ratings yet
- Answer: The Mean Daily Wage Is Rs.145.2Document7 pagesAnswer: The Mean Daily Wage Is Rs.145.2Asmita DebnathNo ratings yet
- Mean Median ModeDocument29 pagesMean Median ModeJc LanuzaNo ratings yet
- Mean/MedianDocument5 pagesMean/MediangkjhkjhNo ratings yet
- Mumbai Educational Trust: MET Institute of Computer ScienceDocument368 pagesMumbai Educational Trust: MET Institute of Computer ScienceKavita KhandagaleNo ratings yet
- Caiib Abm Statistics Unit 3Document14 pagesCaiib Abm Statistics Unit 3vasanthi_cyberNo ratings yet
- Exercise 13.1 Page No: 157: NCERT Exemplar Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 13-Statistics and ProbabilityDocument19 pagesExercise 13.1 Page No: 157: NCERT Exemplar Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 13-Statistics and ProbabilitySaryajitNo ratings yet
- Statistics Class 11 CommerceDocument10 pagesStatistics Class 11 Commerce1vikaschaudhari4848No ratings yet
- 4 Measures of Central TendencyDocument3 pages4 Measures of Central TendencyJoseph HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Slides - B. Stat - I, Lecture 6 - Chap 3, Session 2, Median, ModeDocument22 pagesSlides - B. Stat - I, Lecture 6 - Chap 3, Session 2, Median, ModeKim NamjoonneNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic Mean PDFDocument29 pagesArithmetic Mean PDFDivya Gothi100% (1)
- StatisticsDocument24 pagesStatisticsthinkiitNo ratings yet
- Grouped Data Calculation: Mean, Median and Mode First Quartile, Third Quartile and Interquantile RangeDocument14 pagesGrouped Data Calculation: Mean, Median and Mode First Quartile, Third Quartile and Interquantile Rangezaihans79No ratings yet
- Bio StatisticsDocument110 pagesBio StatisticsPrtap Kumar PatraNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument26 pagesMeasures of Central Tendencydegraciajaylace6No ratings yet
- Grouped Data Calculation PDFDocument14 pagesGrouped Data Calculation PDFNuelle NefielNo ratings yet
- MCT UngroupedDocument25 pagesMCT UngroupedMikee Amanda Eunice GraydaNo ratings yet
- Measures Fo LocationDocument45 pagesMeasures Fo LocationMd Sabbir Ahmed EkhonNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic Mean of Continuous Frequency DistributionDocument2 pagesArithmetic Mean of Continuous Frequency DistributionSwapnil KhandareNo ratings yet
- Chapter: Measures of Central Tendency: ObjectivesDocument26 pagesChapter: Measures of Central Tendency: ObjectivesHasan RabyNo ratings yet
- Reviewer MathDocument18 pagesReviewer MathYAGI, Miyuki F.No ratings yet
- Business Statistics NotesDocument34 pagesBusiness Statistics NotesMartin KobimboNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency and Other Positional MeasuresDocument13 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency and Other Positional Measuresbv123bvNo ratings yet
- Statistics, mg4Document58 pagesStatistics, mg4Himanshu ChawlaNo ratings yet
- MedianDocument42 pagesMedianIndu MalikNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability - Solved Assignments - Semester Spring 2010Document33 pagesStatistics and Probability - Solved Assignments - Semester Spring 2010Muhammad UmairNo ratings yet
- Descriptive StatisticsDocument21 pagesDescriptive StatisticsComp105Jyot KalathiyaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory #4Document3 pagesLaboratory #4CHARLOTTE PINEDANo ratings yet
- Direct SeriesDocument22 pagesDirect SeriesSahil SethiNo ratings yet
- Median. ModeDocument23 pagesMedian. ModeMayank MajokaNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 14 - Statistics Exercise 14.3Document10 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 14 - Statistics Exercise 14.3beenickymauryaNo ratings yet
- Stat & ProbabilityDocument67 pagesStat & Probabilityanna luna berryNo ratings yet
- Median, ModeDocument44 pagesMedian, ModeSanjay SNo ratings yet
- GRADE 10 LAS 2 - MELC 1b - 4TH QUARTERDocument11 pagesGRADE 10 LAS 2 - MELC 1b - 4TH QUARTERnorlie caneteNo ratings yet
- DTB Assignment Central TendencyDocument4 pagesDTB Assignment Central Tendencyanushka2083No ratings yet
- Mean Median and Mode For Group DataDocument8 pagesMean Median and Mode For Group DataSyed Tauqeer Ahmed HashmiNo ratings yet
- CH - 13 MathsDocument3 pagesCH - 13 Mathskilemas494No ratings yet
- Mean, Median, Mode: Prepared By: Chris Eve B. RosalesDocument30 pagesMean, Median, Mode: Prepared By: Chris Eve B. RosalesRizel Durango-BarriosNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document108 pagesModule 1p4544468No ratings yet
- Mean Mode MedianDocument17 pagesMean Mode MedianzenneyNo ratings yet
- Find Mean, Median, Modal Class From Grouped DataDocument14 pagesFind Mean, Median, Modal Class From Grouped DatacrazyAss GamerNo ratings yet
- 4-Frequency DistributionDocument33 pages4-Frequency DistributionZoren Divina BorretaNo ratings yet
- Measuresofcentraltendency PDFDocument30 pagesMeasuresofcentraltendency PDFEthel OlivarNo ratings yet
- Pakka Measuresofcentraltendencymeanmedianmode 140706130428 Phpapp01Document30 pagesPakka Measuresofcentraltendencymeanmedianmode 140706130428 Phpapp01pradeepNo ratings yet
- Average Is A Calculated Value, Obtained by Adding Values and Dividing The Sum by The Number of ValuesDocument24 pagesAverage Is A Calculated Value, Obtained by Adding Values and Dividing The Sum by The Number of ValuesdiptidevNo ratings yet
- BBA (N) - 103 Central TendencyDocument20 pagesBBA (N) - 103 Central TendencyPratyum PradhanNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics Assign Men TiDocument6 pagesBusiness Statistics Assign Men TiYograj Rajput100% (1)
- 18bge14a U4Document16 pages18bge14a U4Deepak karhana?No ratings yet
- For Chapter 2, Statistical Techniques in Business & EconomicsDocument61 pagesFor Chapter 2, Statistical Techniques in Business & EconomicsVic SzeNo ratings yet
- Median and ModeDocument24 pagesMedian and Modemayra kshyapNo ratings yet
- Data AnalysisDocument29 pagesData AnalysislalravikantNo ratings yet
- Arithematic Mean - Continuous SeriesDocument4 pagesArithematic Mean - Continuous SeriesBadrinath IllurNo ratings yet
- Raghav Classes, Karan Celista, Balewadi: Worksheet 1: StatisticsDocument3 pagesRaghav Classes, Karan Celista, Balewadi: Worksheet 1: StatisticsRicha BhargavaNo ratings yet
- Solved Practice Questions Lecture 23-25Document5 pagesSolved Practice Questions Lecture 23-25Fun NNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument11 pagesMeasures of Central TendencyMartin KobimboNo ratings yet
- Applications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandApplications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Introductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)From EverandIntroductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)No ratings yet
- Course Outline - CSE 211 - Computer Architecture - 193 DCDocument5 pagesCourse Outline - CSE 211 - Computer Architecture - 193 DCgtgtdfgfdgNo ratings yet
- 1st Class Hand Note 11.10.21 DADocument2 pages1st Class Hand Note 11.10.21 DAgtgtdfgfdgNo ratings yet
- 3rd Class Hand Note 18.10.21 DADocument5 pages3rd Class Hand Note 18.10.21 DAgtgtdfgfdgNo ratings yet
- 2nd Class Hand Note 13.10.21 DADocument4 pages2nd Class Hand Note 13.10.21 DAgtgtdfgfdgNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Applications of HCIDocument19 pagesLecture 2 - Applications of HCIgtgtdfgfdgNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Domains of HCIDocument21 pagesLecture 3 - Domains of HCIgtgtdfgfdgNo ratings yet
- Course Outline of CSE 321 - Fall 2021Document5 pagesCourse Outline of CSE 321 - Fall 2021gtgtdfgfdgNo ratings yet
- Water Cooled Centrifugal Chiller (150-3000RT)Document49 pagesWater Cooled Centrifugal Chiller (150-3000RT)remigius yudhiNo ratings yet
- Transformative Change at PPLDocument24 pagesTransformative Change at PPLAli A. KhokhArNo ratings yet
- Centurion Bank of PunjabDocument7 pagesCenturion Bank of Punjabbaggamraasi1234No ratings yet
- Managerial Economics - 1Document36 pagesManagerial Economics - 1Deepi SinghNo ratings yet
- The Van Conversion Bible - The Ultimate Guide To Converting A CampervanDocument170 pagesThe Van Conversion Bible - The Ultimate Guide To Converting A CampervanPil100% (3)
- AutoCAD Civil 3D Performance Optimization 2Document5 pagesAutoCAD Civil 3D Performance Optimization 2Renukadevi RptNo ratings yet
- Modeling Cover Letter No ExperienceDocument7 pagesModeling Cover Letter No Experienceimpalayhf100% (1)
- Title To The ProjectDocument14 pagesTitle To The ProjectJatinChadhaNo ratings yet
- Cyber Cafe Audience Profiling Nielsen 2009Document17 pagesCyber Cafe Audience Profiling Nielsen 2009mahi46452No ratings yet
- Roundup WG Bula MonsantoDocument16 pagesRoundup WG Bula MonsantodandanyddNo ratings yet
- 9a Grundfos 50Hz Catalogue-1322Document48 pages9a Grundfos 50Hz Catalogue-1322ZainalNo ratings yet
- In Coming MailDocument4 pagesIn Coming Mailpoetoet100% (1)
- BreakwatersDocument15 pagesBreakwatershima sagarNo ratings yet
- Analytical Profiles Drug Substances and Excipien T S: Harry G. BrittainDocument693 pagesAnalytical Profiles Drug Substances and Excipien T S: Harry G. BrittainNguyen TriNo ratings yet
- New Form 2550 M Monthly VAT Return P 1 2 1Document3 pagesNew Form 2550 M Monthly VAT Return P 1 2 1The ApprenticeNo ratings yet
- Memorandum of AgreementDocument6 pagesMemorandum of AgreementJomar JaymeNo ratings yet
- SAN MIGUEL CORPORATION, ANGEL G. ROA and MELINDA MACARAIG, vs. NATIONAL LABOR RELATIONS COMMISSION (Second Division), LABOR ARBITER EDUARDO J. CARPIO, ILAW AT BUKLOD NG MANGGAGAWA (IBM), ET ALDocument6 pagesSAN MIGUEL CORPORATION, ANGEL G. ROA and MELINDA MACARAIG, vs. NATIONAL LABOR RELATIONS COMMISSION (Second Division), LABOR ARBITER EDUARDO J. CARPIO, ILAW AT BUKLOD NG MANGGAGAWA (IBM), ET ALLaila Ismael SalisaNo ratings yet
- Poverty Eradication Cluster HLPF Position Paper With Case StudiesDocument4 pagesPoverty Eradication Cluster HLPF Position Paper With Case StudiesJohn Paul Demonteverde ElepNo ratings yet
- BW-Africa 2023 BrochureDocument12 pagesBW-Africa 2023 BrochureDanial DarimiNo ratings yet
- Chapter IDocument38 pagesChapter ITuyền PhạmNo ratings yet
- Octopus 900 Instructions For UseDocument18 pagesOctopus 900 Instructions For UseAli FadhilNo ratings yet
- Analisis Dan Perbandingan Jaringan Wifi Dengan Frekuensi 2.4 GHZ Dan 5 GHZ Dengan Metode QosDocument19 pagesAnalisis Dan Perbandingan Jaringan Wifi Dengan Frekuensi 2.4 GHZ Dan 5 GHZ Dengan Metode QosNoltujuh Nollapan (Congyang)No ratings yet
- Rectangular Wire Die Springs ISO-10243 Standard: Red Colour Heavy LoadDocument3 pagesRectangular Wire Die Springs ISO-10243 Standard: Red Colour Heavy LoadbashaNo ratings yet
- Review of Financial Statements and Its Analysis: Rheena B. Delos Santos BSBA-1A (FM2)Document12 pagesReview of Financial Statements and Its Analysis: Rheena B. Delos Santos BSBA-1A (FM2)RHIAN B.No ratings yet
- Successfully Allocating Risk and Negotiating A PPP ContractDocument12 pagesSuccessfully Allocating Risk and Negotiating A PPP ContractWilliam Tong100% (1)
- Chapter 01Document26 pagesChapter 01zwright172No ratings yet
- Taller Sobre Preposiciones y Vocabulario - Exhibición Comercial SergioDocument5 pagesTaller Sobre Preposiciones y Vocabulario - Exhibición Comercial SergioYovanny Peña Pinzon100% (2)
- 4 A Industrial RevolutionDocument41 pages4 A Industrial Revolutionabekhti2008No ratings yet
- Gist of FIEO ServicesDocument1 pageGist of FIEO Servicessanjay patraNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Detection and Identification Using YOLO in Image ProcessingDocument6 pagesVehicle Detection and Identification Using YOLO in Image ProcessingIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet