Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NME 2102-Lecture2
Uploaded by
Stephen Visperas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views20 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views20 pagesNME 2102-Lecture2
Uploaded by
Stephen VisperasCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 20
NME 2102
Engineering Mechanics:
Statics of Rigid Bodies
Force Vectors and Equilibrium of
Particles
Course Outline:
1. Introduction to Mechanics; Vector Operations
2. Force Vectors and Equilibrium of Particles
3. Vector Cross and Dot Product
4. Moment of a Force
5. Couples; Moment of a Couple
6. Equivalent Force Systems in 2D and 3D
7. Dry Static Friction, Wedge and Belt Friction
8. Centroid; Center of Mass; and Center of Gravity
9. Distributed Loads and Hydrostatic Forces; Cables
10. Moment of Inertia; Mass Moment of Inertia
11. Beams; Shear and Bending Moment Diagrams
Grading System: Cumulative Averaging
1 2
Mid- term Average (M.A.) = (Average of MidtermQuizzes)+ (MidtermExam)
3 3
1 2
Tentative Final Average (T.F.A.) = (Average of Final Quizzes)+ (Final Exam)
3 3
1 2
Final Average (F.A.) = (Mid- term Average )+ (Tentative Final Average)
3 3
Passing Mark = 75% (Based 50 points)
Resultant of Three or More Concurrent Forces:
The determination of the resultant of three or
more concurrent forces that are not collinear requires
determining the sum of three or more vectors. There
are two ways of accomplishing the addition of three or
more vectors: graphically and analytically.
Graphically. Two vectors can be added to give a
resultant; this resultant in turn can be added to a third
vector, etc., until all the vectors have been added
together to give an overall resultant. These vectors
can be added in any order.
Analytically. The vectors can be resolved into
components that coincide with arbitrarily chosen axes.
The components of each vector with respect to these
axes can be added algebraically, and the resulting
additions will be the components of the overall
resultant vectors.
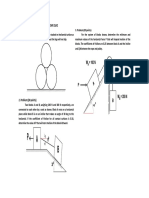
1. Problem:
Determine the resultant of the concurrent forces
shown in the figure below.
1. Solution:
1. Solution:
2. Problem:
The resultant of a certain system of forces has the X
and Y components shown in the figure. Determine the
components of this resultant to the T and N axes.
Answer: RN =500 lb; RT = 266 lb
2. Solution:
3. Problem:
The resultant of the concurrent forces shown in the
figure is 300 N pointing up along the Y axis. Compute
the values of F and θ required to give this resultant.
Answer: F =512 N up to the right at θx = 55.2°°
3. Solution:
3. Solution:
4. Problem:
The block shown in the figure below is acted upon by
its weight W = 200 lb, a horizontal force Q = 600 lb, and
the pressure P exerted by the inclined plane. The
resultant R of these forces is up and parallel to the
incline thereby sliding the block up it. Determine P and
R. Hint: Take one axis parallel to the incline.
Answer: R = 293 lb
1. Solution:
1. Solution:
5. Problem:
Two horses on opposite banks of a canal pull a barge
moving parallel to the banks by means of two
horizontal ropes. The tensions in these ropes are 200
lb and 240 lb while the angle between them is 60°°. Find
the resultant pull on the barge and the angle between
each of the ropes and the sides of the canal.
Answer: R = 382 lb; θ = 33°°; α = 27°°
References:
Engineering Mechanics by Jensen (S.I. Edition)
Engineering Mechanics by F. Singer 4th Edition
Engineering Mechanics by Hibbeler
You might also like
- Beams and Framed Structures: Structures and Solid Body MechanicsFrom EverandBeams and Framed Structures: Structures and Solid Body MechanicsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Module 1Document45 pagesModule 1MD SHAHRIARMAHMUDNo ratings yet
- Structural Mechanics Assignment HelpDocument29 pagesStructural Mechanics Assignment HelpMechanical Engineering Assignment HelpNo ratings yet
- JJ205 Engineering Mechanic Chapter 3 Jj205Document5 pagesJJ205 Engineering Mechanic Chapter 3 Jj205Ah TiangNo ratings yet
- Force Vectors, Vector Operations & Addition Coplanar ForcesDocument20 pagesForce Vectors, Vector Operations & Addition Coplanar ForcesMia RismaliaNo ratings yet
- Fem NotesDocument11 pagesFem NotesvenkiteshksNo ratings yet
- 02 Me1 PDFDocument5 pages02 Me1 PDFvat007No ratings yet
- Labreport Style Forces TableDocument4 pagesLabreport Style Forces TableMohammed ElnaggarNo ratings yet
- 05-Bar Elements in 2d SpaceDocument49 pages05-Bar Elements in 2d SpaceMohd NasimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-ADocument24 pagesChapter 2-AM Jamshaid TahiriNo ratings yet
- Node Nodal Degrees of Freedom: 1. The Definition of The Finite Element Method (FEM)Document32 pagesNode Nodal Degrees of Freedom: 1. The Definition of The Finite Element Method (FEM)KomarudinNo ratings yet
- 002.resultants of Force SystemsDocument9 pages002.resultants of Force SystemsIra James AbanesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document28 pagesChapter 3Muhammad TehreemNo ratings yet
- Elements of Continuum Elasticity: David M. Parks Mechanics and Materials II 2.002 February 25, 2004Document22 pagesElements of Continuum Elasticity: David M. Parks Mechanics and Materials II 2.002 February 25, 2004BalajeeNo ratings yet
- KR10203 Chapter 1Document64 pagesKR10203 Chapter 1RINA RINANo ratings yet
- 2.9 Analysing Forces in EquilibriumDocument27 pages2.9 Analysing Forces in EquilibriumeltytanNo ratings yet
- 01-ES202 - Topic1Document18 pages01-ES202 - Topic1Moguri OwowNo ratings yet
- ME1 Concurrent Forces and Static Equilibrium: ObjectivesDocument5 pagesME1 Concurrent Forces and Static Equilibrium: ObjectivesAhmed AbuNasserNo ratings yet
- Force VectorsDocument6 pagesForce VectorsH MNo ratings yet
- Rigid Body EQFMCSDocument63 pagesRigid Body EQFMCSNÏALNo ratings yet
- Force Vectors, Vector Operations & Addition of Forces 2D & 3DDocument51 pagesForce Vectors, Vector Operations & Addition of Forces 2D & 3DparklNo ratings yet
- IE C1 Statics of Rigid Bodies Part 2 Force VectorsDocument13 pagesIE C1 Statics of Rigid Bodies Part 2 Force VectorsBernadeth MontardeNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Frame and Grid ElementsDocument43 pagesModule 5 Frame and Grid ElementsKhaled AlzaabiNo ratings yet
- MM103 Lab 1 (s11199858)Document8 pagesMM103 Lab 1 (s11199858)Kirsten J100% (1)
- ALEVEL PHYSICS AQA Unit 2 Mechanics Materials and Waves NOTESDocument37 pagesALEVEL PHYSICS AQA Unit 2 Mechanics Materials and Waves NOTESJames ChongNo ratings yet
- Es 122-Student Assessment OnlyDocument8 pagesEs 122-Student Assessment OnlyronieNo ratings yet
- Force Vectors, Vector Operations & Addition Coplanar Forces: Today's ObjectiveDocument21 pagesForce Vectors, Vector Operations & Addition Coplanar Forces: Today's ObjectiveIsmailNo ratings yet
- ALEVEL PHYSICS AQA Unit 2 Mechanics Materials and Waves NOTESDocument37 pagesALEVEL PHYSICS AQA Unit 2 Mechanics Materials and Waves NOTESSam ShohetNo ratings yet
- MME2202 CourseReviewDocument5 pagesMME2202 CourseReviewMatt BrezinaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document150 pagesLecture 3Kedir ShiferawNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document89 pagesChapter 03KIÊN HOÀNG TRUNGNo ratings yet
- Me13A: Engineering Statics: CourseDocument71 pagesMe13A: Engineering Statics: CourseJenny Rose CadornaNo ratings yet
- Stress ResultantsDocument19 pagesStress ResultantsAmyRapaNo ratings yet
- Direct - Method Solved ExamplesDocument25 pagesDirect - Method Solved ExamplesHusnain100% (1)
- Mechanics: Study of What Happens To A "Thing" (The Technical Name Is "Body") When FORCES Are Applied To ItDocument39 pagesMechanics: Study of What Happens To A "Thing" (The Technical Name Is "Body") When FORCES Are Applied To Itdinosaur x-drakeNo ratings yet
- Statics Chapter 2Document18 pagesStatics Chapter 2Karl KronosNo ratings yet
- MSXR209 MechanicsDocument29 pagesMSXR209 MechanicspigcowdogNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document10 pagesModule 3Benson MataNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03aDocument80 pagesChapter 03aDamir KisoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Forces and EquilibriumDocument53 pagesChapter 2 Forces and EquilibriumvinoNo ratings yet
- CIVL 8/7117 Chapter 3 - Development of Truss Equations 1/77Document77 pagesCIVL 8/7117 Chapter 3 - Development of Truss Equations 1/77georgelennon68No ratings yet
- 10-Linear Strain Triangle and Other Types of 2d ElementsDocument31 pages10-Linear Strain Triangle and Other Types of 2d Elementskranthi142434No ratings yet
- Cse30301 2 2015Document44 pagesCse30301 2 2015王嵐No ratings yet
- Implementation of A Beam Element in FEA Using MATLAB: (Type The Document Subtitle)Document12 pagesImplementation of A Beam Element in FEA Using MATLAB: (Type The Document Subtitle)akankshag_13No ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument14 pagesPhysicsRalph CastilloNo ratings yet
- Mat Lab Beam DeflectionDocument15 pagesMat Lab Beam Deflectionriyyo2424No ratings yet
- Mekanika Teknik PDFDocument141 pagesMekanika Teknik PDFAnonymous dSFbLxc9No ratings yet
- Topic1 2to1 4Document35 pagesTopic1 2to1 4Sesha Sai KumarNo ratings yet
- Energy and Work: All External Work Supplied To A Real Structural System Is Stored or Dissipated As EnergyDocument16 pagesEnergy and Work: All External Work Supplied To A Real Structural System Is Stored or Dissipated As Energycomenzi8131No ratings yet
- Course Outline: - Week 1, January 4 and 6Document23 pagesCourse Outline: - Week 1, January 4 and 6Michael DemianNo ratings yet
- Physics 11 Word.Document23 pagesPhysics 11 Word.Michael John C UrpianoNo ratings yet
- Engineering MechanicsDocument80 pagesEngineering MechanicsVv4H100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Force System by TeddyDocument66 pagesChapter 2 Force System by Teddytewodros aliNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 FORCE VECTOR (Mechanic)Document41 pagesCHAPTER 2 FORCE VECTOR (Mechanic)Afiq NajmiNo ratings yet
- Dynamics: Principles of Linear Impulse and MomentumDocument17 pagesDynamics: Principles of Linear Impulse and MomentumVinot EsanNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes For Section 15-1Document19 pagesLecture Notes For Section 15-1JersonFerrerasPuaNo ratings yet
- Barron's Physics Practice Plus: 400+ Online Questions and Quick Study ReviewFrom EverandBarron's Physics Practice Plus: 400+ Online Questions and Quick Study ReviewNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies: Jervis James U DeeDocument12 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies: Jervis James U DeeStephen VisperasNo ratings yet
- RESISTANCEDocument3 pagesRESISTANCEStephen VisperasNo ratings yet
- Part 1. Multiple Choice: NME 2202 Engineering Data AnalysisDocument5 pagesPart 1. Multiple Choice: NME 2202 Engineering Data AnalysisStephen VisperasNo ratings yet
- Zge El01 Environmental Science Name/Group NameDocument2 pagesZge El01 Environmental Science Name/Group NameStephen VisperasNo ratings yet
- Case Study No. 1 Legal Structure and CapitalDocument4 pagesCase Study No. 1 Legal Structure and CapitalStephen VisperasNo ratings yet
- Exam No. 2 (Thermo)Document3 pagesExam No. 2 (Thermo)Stephen VisperasNo ratings yet
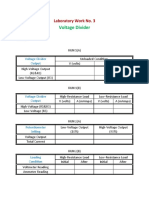
- Table For Laboratory Work No 3Document1 pageTable For Laboratory Work No 3Stephen VisperasNo ratings yet
- Zge El01 Environmental Science Name/Group Name: HeheDocument4 pagesZge El01 Environmental Science Name/Group Name: HeheStephen VisperasNo ratings yet
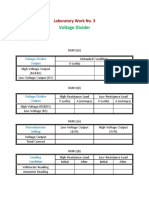
- Table For Laboratory Work No 3Document1 pageTable For Laboratory Work No 3Stephen VisperasNo ratings yet
- Zge El01 Environmental Science Name/Group Name: HeheDocument4 pagesZge El01 Environmental Science Name/Group Name: HeheStephen VisperasNo ratings yet
- Torsion: Torsion in Circular Shaft Torsion in Non-Circular ShaftDocument11 pagesTorsion: Torsion in Circular Shaft Torsion in Non-Circular ShaftStephen VisperasNo ratings yet
- Hypotheses Tests On The Difference in Means, Variances UnknownDocument10 pagesHypotheses Tests On The Difference in Means, Variances UnknownStephen VisperasNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical Cycles: (Water, Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sulfur)Document26 pagesBiogeochemical Cycles: (Water, Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sulfur)Stephen VisperasNo ratings yet
- Interdisciplinary Discipline - EnviscieDocument1 pageInterdisciplinary Discipline - EnviscieStephen VisperasNo ratings yet
- Statistical Inference of Two SampleDocument37 pagesStatistical Inference of Two SampleStephen VisperasNo ratings yet
- Act 1 - Environmental ScienceDocument3 pagesAct 1 - Environmental ScienceStephen VisperasNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical Cycles: (Water, Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sulfur)Document26 pagesBiogeochemical Cycles: (Water, Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sulfur)Stephen VisperasNo ratings yet
- Nme 2102 - Take Home QuizDocument1 pageNme 2102 - Take Home QuizStephen VisperasNo ratings yet
- ProfessionalismDocument22 pagesProfessionalismStephen VisperasNo ratings yet
- Project Planning (Project Quality Management)Document22 pagesProject Planning (Project Quality Management)Stephen VisperasNo ratings yet
- 1211: Philippine Electrical CodeDocument2 pages1211: Philippine Electrical CodeStephen VisperasNo ratings yet
- 1211: Philippine Electrical CodeDocument2 pages1211: Philippine Electrical CodeStephen VisperasNo ratings yet
- Statistical Inference For Two Samples: Chapter OutlineDocument83 pagesStatistical Inference For Two Samples: Chapter OutlineStephen VisperasNo ratings yet
- Nme 2102 - Take Home QuizDocument1 pageNme 2102 - Take Home QuizStephen VisperasNo ratings yet
- Hypotheses Tests On The Difference in Means, Variances UnknownDocument10 pagesHypotheses Tests On The Difference in Means, Variances UnknownStephen VisperasNo ratings yet
- Friction FactorDocument4 pagesFriction FactorStephen VisperasNo ratings yet
- Praveen Et Al-2018-Advanced Engineering MaterialsDocument22 pagesPraveen Et Al-2018-Advanced Engineering Materialscam nhung NguyenNo ratings yet
- Ch.1-Matter in Our Surroundings 9th SolvedDocument50 pagesCh.1-Matter in Our Surroundings 9th SolvedVikash SharmaNo ratings yet
- Direct Shear Box TestDocument4 pagesDirect Shear Box Testarid132No ratings yet
- Uplift Pressures by Khosla MethodDocument8 pagesUplift Pressures by Khosla MethodsamoonibrahimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document49 pagesChapter 3Mohnish Wadhwa0% (1)
- Numerical Unit1Document3 pagesNumerical Unit1Ayush DubeyNo ratings yet
- Secadores Sullair RN y OtrsoDocument268 pagesSecadores Sullair RN y Otrsoramiro alvarezNo ratings yet
- Me 423 - Computational Fluid Mechanics and Heat Transfer: Spring 2018/2019Document41 pagesMe 423 - Computational Fluid Mechanics and Heat Transfer: Spring 2018/2019HassanKMNo ratings yet
- Fired HeaterDocument77 pagesFired HeaterEslamSheblNo ratings yet
- Dissertation - Leong Dong Guo - 12631 - Ce PDFDocument103 pagesDissertation - Leong Dong Guo - 12631 - Ce PDFkmskskq100% (1)
- Lectures 1.1 - Review of Concepts PDFDocument10 pagesLectures 1.1 - Review of Concepts PDFHussain AliNo ratings yet
- الإجابة النموذجية لامتحان نصف الفصل مارس 20152015 - 5 - 9!8!27Document6 pagesالإجابة النموذجية لامتحان نصف الفصل مارس 20152015 - 5 - 9!8!27Amr RaghebNo ratings yet
- Session 1 All Ppts PDFDocument159 pagesSession 1 All Ppts PDF8273614328No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Well Testing (II) : Weibo Sui PH.D, Associate Professor College of Petroleum Engineering, CUPBDocument36 pagesChapter 5 Well Testing (II) : Weibo Sui PH.D, Associate Professor College of Petroleum Engineering, CUPBSanna JorgeNo ratings yet
- Exergy and Economic Analysis of Dual Pressure Waste Heat Recovery BoilerDocument8 pagesExergy and Economic Analysis of Dual Pressure Waste Heat Recovery BoilerÜmit GüneşNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibria Notes PDFDocument8 pagesChemical Equilibria Notes PDFdanielmahsa0% (1)
- Design 2Document28 pagesDesign 2Ken Jethro Mamaril CariñoNo ratings yet
- 2.3.2.A.SIM TensileTesting JerryDocument9 pages2.3.2.A.SIM TensileTesting JerryGerardo RoblescruzNo ratings yet
- MEO CLII Syllabus and FunctionsDocument24 pagesMEO CLII Syllabus and FunctionsBalraj Singh SandhuNo ratings yet
- Heat T CH 2-1Document67 pagesHeat T CH 2-1Fira tubeNo ratings yet
- Design of Shear Reinforcement in RCC Structures: Intended Learning Outcomes (ILO)Document16 pagesDesign of Shear Reinforcement in RCC Structures: Intended Learning Outcomes (ILO)anirbanpwd76No ratings yet
- CH 4 Bending StressesnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnDocument26 pagesCH 4 Bending StressesnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnndudescapeNo ratings yet
- Modelling of Secondary Petroleum Migration Using Invasion Percolation TechniquesDocument17 pagesModelling of Secondary Petroleum Migration Using Invasion Percolation TechniquesYash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Design of Dams and Bridges 1Document44 pagesDesign of Dams and Bridges 1Muralikrishna Baduru100% (1)
- BFC21103 Assignment No. 2 PDFDocument10 pagesBFC21103 Assignment No. 2 PDFKavi Maran100% (2)
- Part Number Description List Price PKG Qty.: Relief Valves Low Flow 1/8 NPT MDocument3 pagesPart Number Description List Price PKG Qty.: Relief Valves Low Flow 1/8 NPT MMuh IchsanudinNo ratings yet
- Continuous Beam Design With Moment Redistribution (ACI 318-11)Document34 pagesContinuous Beam Design With Moment Redistribution (ACI 318-11)MohammedNo ratings yet
- Overhead Contact System Steady State Ampacity Calculations Per AREMA Manual Chapter 33 and IEEE Std. 738Document2 pagesOverhead Contact System Steady State Ampacity Calculations Per AREMA Manual Chapter 33 and IEEE Std. 738Héctor VargasNo ratings yet
- Engg Mechanics Assignment and QuizDocument5 pagesEngg Mechanics Assignment and QuizYaagik GoelNo ratings yet
- Checklist For Process Engineering DeliverablesDocument1 pageChecklist For Process Engineering Deliverablesankur2061No ratings yet