Professional Documents
Culture Documents
List of Formulae: Measurements
Uploaded by
Vyom agarwalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
List of Formulae: Measurements
Uploaded by
Vyom agarwalCopyright:
Available Formats
List of formulae
Measurements
Mass 𝑀
1. Density = Volume ; ρ = 𝑉
2. For a Vernier caliper,
Value of one main scale division
Least count = Total no.of divisions on the vernier scale = 0.1mm
Total reading = main scale reading + Vernier scale reading
3. For a screw gauge,
Pitch of the screw
L.C. = Total no.of divisions on the circular scale = 0.01 mm
4. Total reading = Main scale reading + circular scale reading
5. Zero error for Vernier calipers and screw gauge
Positive zero error Z = r x L.C.
Negative zero error Z = - (n-r) x L.C.
Where, n is the total number of divisions on the Vernier scale or circular scale and r is
the Vernier scale division which coincides with any of the main scale division, when the
jaws are closed.
Corrected reading = total reading - Z
Motion
Total Distance 𝑠
1. Average Speed = ,v=𝑡
Total Time
Displacement s
2. Velocity = ,v=t
Time
Change in velocity v−u
3. Acceleration = ,a=
Time taken t
𝑌2−𝑦1
4. Gradient of a graph (slope) = 𝑥2−𝑥1
5. Speed = gradient of distance – time graph
6. Acceleration = gradient of speed – time graph
7. Distance = area under speed – time graph
Forces
1. Force = mass x acceleration, F= ma
2. W = mg
3. Momentum p = mv, where m is the mass and v is the velocity
4. Impulse J = Ft, where F is the force and t is time for which it acts.
5. Impulse J = change in momentum = mv-mu , m is the mass, v is the final velocity, u is the
initial velocity
Forces and matter
1. Pressure exerted by liquid column, P = hρg
h- height of the liquid column
ρ – density of the liquid
g – acceleration due to gravity
F1 F2
2. Pascal’s law : P1 = P2 or =
A1 A2
3. Hook’s law F= kx
F – force, k – Force constant, x – extension.
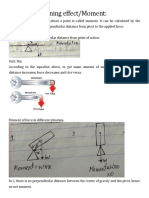
Turning effect of force
1. Moment of a force = Force x perpendicular distance from the pivot = f x d
2. Principle of moments,
If an object is in equilibrium, the clockwise moments = anticlockwise moments.
Energy
1
1. Kinetic energy = 2 m v2 ; m – mass and v- velocity
2. Gravitational potential energy = mgh ; m – mass, g- acceleration due to gravity,
h – object’s height above the ground level.
3. Work = force x displacement in the direction of force ; W = F x d
Work
4. Power = Time
useful energy output
5. Efficiency = x 100 %
Total energy input
************************************************
You might also like
- Quick Study Academic Physics 600dpiDocument6 pagesQuick Study Academic Physics 600dpiSunshineK95100% (8)
- O Level Physics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesO Level Physics Formula SheetYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- Applications of Circular MotionDocument3 pagesApplications of Circular Motionmonkey2rockz100% (2)
- ALEVEL PHYSICS AQA Unit 4 Fields and Further Mechanics NOTESDocument41 pagesALEVEL PHYSICS AQA Unit 4 Fields and Further Mechanics NOTESSam ShohetNo ratings yet
- 1 - Mechanics Revision NotesDocument5 pages1 - Mechanics Revision NotesHuaxiang HuangNo ratings yet
- Description of IcofoamDocument7 pagesDescription of Icofoamcypiii100% (6)
- Pump & Pump Piping PresentationDocument55 pagesPump & Pump Piping PresentationEduard Gonzalo Rojas Cervantes100% (1)
- Quick Revision For o Level PhysicsDocument28 pagesQuick Revision For o Level PhysicsRegie Sacil EspiñaNo ratings yet
- Sajc h2 Physics Summary Notes (All Topics)Document43 pagesSajc h2 Physics Summary Notes (All Topics)AjathShatruRajuNo ratings yet
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- AS Unit 1 Revision Note Physics IAL EdexcelDocument9 pagesAS Unit 1 Revision Note Physics IAL EdexcelMahbub Khan100% (1)
- Moment of InertiaDocument6 pagesMoment of Inertiarohan_nerlekar794100% (3)
- A Level FormulaeDocument1 pageA Level FormulaeVarun PanickerNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Physics Formula List PDFDocument7 pagesForm 4 Physics Formula List PDFTyron BongNo ratings yet
- Summary GenPhys IDocument11 pagesSummary GenPhys IAnthony David Altamirano De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Access Physics: Unit 1 - Motion, Energy and ForcesDocument7 pagesAccess Physics: Unit 1 - Motion, Energy and ForcesPezNo ratings yet
- Ryerson University Department of Physics Lab Report FOR Pcs 125 Section 05Document6 pagesRyerson University Department of Physics Lab Report FOR Pcs 125 Section 05Meet ShahNo ratings yet
- Physics FormulasDocument2 pagesPhysics FormulasSzraxNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Definations and EquationsDocument19 pagesMid Term Definations and Equationsellastella682008No ratings yet
- Physics Formulae List (IGCSE)Document6 pagesPhysics Formulae List (IGCSE)saimee77No ratings yet
- Topic-7 MechanicsDocument8 pagesTopic-7 MechanicsRoselyn BellezaNo ratings yet
- Important Terms/ Formulas For Aipmt: PhysicsDocument24 pagesImportant Terms/ Formulas For Aipmt: PhysicsDeusExMachinaNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS - EQUATIONS (1) KdksaklsDocument2 pagesPHYSICS - EQUATIONS (1) KdksaklsKry9No ratings yet
- Module 5 Advanced MechanicsDocument22 pagesModule 5 Advanced MechanicsVictor GuanNo ratings yet
- A2 Physics: Unit 4 Unit 5Document37 pagesA2 Physics: Unit 4 Unit 5Muhammad Shafnoon KabirNo ratings yet
- Physics Formulae 4NADocument5 pagesPhysics Formulae 4NAmuhdnurimann7No ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 - Applying Newton's Laws of Motion - R K ParidaDocument12 pagesChapter - 5 - Applying Newton's Laws of Motion - R K Paridaraunakrathor2005No ratings yet
- PHS 101.2Document35 pagesPHS 101.2Temitayo TaiwoNo ratings yet
- Basic Physics: Some Concepts For Geodesy: James R. Clynch, 2003Document10 pagesBasic Physics: Some Concepts For Geodesy: James R. Clynch, 2003Rendi Adi FebrianNo ratings yet
- The Simple PendulumDocument5 pagesThe Simple PendulumDexter TorringtonNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 A2 Physics Problems STEM-N ASICODocument11 pagesPhysics 1 A2 Physics Problems STEM-N ASICOChristian Paul A. AsicoNo ratings yet
- Physics Main Focus NotesDocument103 pagesPhysics Main Focus NotesAswithNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Mekaniks: English Swedish Symbol Units Units-Name ValueDocument10 pagesMechanics Mekaniks: English Swedish Symbol Units Units-Name ValueEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Compendium Book For IIT - MainsDocument28 pagesCompendium Book For IIT - MainsApex InstituteNo ratings yet
- Physics Q2M12Document4 pagesPhysics Q2M12Angel PicazoNo ratings yet
- Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesCheat SheetAnush UnanyanNo ratings yet
- Concepts in Theoretical Physics: Lecture 1: The Principle of Least ActionDocument19 pagesConcepts in Theoretical Physics: Lecture 1: The Principle of Least Actionsupremely334No ratings yet
- Experiment 12: Simple Harmonic Motion: I. About The ExperimentDocument6 pagesExperiment 12: Simple Harmonic Motion: I. About The ExperimentAnurag SharmaNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Physics Exam 2Document25 pagesPreliminary Physics Exam 2Dog DogNo ratings yet
- Physics Equations and Definitions SheetDocument6 pagesPhysics Equations and Definitions SheetOkkar AungNo ratings yet
- PHY2001 Formula SheetDocument5 pagesPHY2001 Formula SheetMario MelendezNo ratings yet
- ALEVEL PHYSICS AQA Unit 4 Fields and Further Mechanics NOTESDocument41 pagesALEVEL PHYSICS AQA Unit 4 Fields and Further Mechanics NOTESJames ChongNo ratings yet
- Kertas Trial Fizik Pahang k1 2021Document26 pagesKertas Trial Fizik Pahang k1 2021sbyteNo ratings yet
- Phy 311 Unit 2 - Chap 16-17Document25 pagesPhy 311 Unit 2 - Chap 16-17Alex William JohnNo ratings yet
- G12 Study GuideDocument25 pagesG12 Study GuideNiceannNo ratings yet
- PHY-251 Centripetal Force LabDocument7 pagesPHY-251 Centripetal Force LabRenzo Jose Canro CalderonNo ratings yet
- Hooke's Law and The Simple Harmonic Motion: ObjectiveDocument7 pagesHooke's Law and The Simple Harmonic Motion: ObjectiveMaisha Nusrat Tori 1612830643No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes For Physical Chemistry II Quantum Theory and SpectroscoptyDocument41 pagesLecture Notes For Physical Chemistry II Quantum Theory and Spectroscopty3334333No ratings yet
- GwgPartIII SupergravityDocument42 pagesGwgPartIII SupergravityrobotsheepboyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 CIRCULAR MOTIONDocument11 pagesLesson 7 CIRCULAR MOTIONDianna GwennNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics Notes 10 Oscillations and WavesDocument21 pages11 Physics Notes 10 Oscillations and WavesAkshay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Weekly Learning Activity Sheets General Physics 1 Grade 12, Quarter 2, Week 3Document6 pagesWeekly Learning Activity Sheets General Physics 1 Grade 12, Quarter 2, Week 3Shekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Physics P2 Cheat SheetDocument33 pagesPhysics P2 Cheat SheetfullnameisitNo ratings yet
- Revision Lectures M122 2023 HandoutDocument4 pagesRevision Lectures M122 2023 HandoutRiley CollinsNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Linear MomentumDocument3 pagesConservation of Linear MomentumAbed Alrahman Al SAYYEDNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Chapter 6 - Turning Effect of ForcesDocument12 pagesUnit 1 Chapter 6 - Turning Effect of ForcesFatimah AfzalNo ratings yet
- Calculative Methods or Formulas 1) Speed. Average Speed 2) VelocityDocument8 pagesCalculative Methods or Formulas 1) Speed. Average Speed 2) Velocityjyoti mishraNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula Y9Document5 pagesPhysics Formula Y9Lim MonyratanakNo ratings yet
- Handout - Physics - 101 - Kinematics (Complete)Document10 pagesHandout - Physics - 101 - Kinematics (Complete)Mary Grace AcostaNo ratings yet
- 7 3-LeptonsDocument1 page7 3-LeptonsVyom agarwalNo ratings yet
- ACT Science Book - (Student Response Sheet)Document6 pagesACT Science Book - (Student Response Sheet)Vyom agarwalNo ratings yet
- 7.3 Forces and Exchange ParticlesDocument1 page7.3 Forces and Exchange ParticlesVyom agarwalNo ratings yet
- ACT English Book (Part - 1) With SRSDocument68 pagesACT English Book (Part - 1) With SRSVyom agarwalNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument25 pagesCurrent ElectricityVyom agarwalNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits 4 QPDocument14 pagesElectric Circuits 4 QPVyom agarwalNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Effects 2 QPDocument13 pagesElectromagnetic Effects 2 QPVyom agarwalNo ratings yet
- Gr9 Phy Revision P4Document10 pagesGr9 Phy Revision P4Vyom agarwalNo ratings yet
- Atomic Stucture: Name - Date - ClassDocument2 pagesAtomic Stucture: Name - Date - ClassVyom agarwalNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Elements & Compounds 3 QPDocument10 pagesAtoms, Elements & Compounds 3 QPVyom agarwalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Periodic Table Group 1 - The Alkali Metals: The Learning Objectives For Today's LessonDocument5 pagesChemistry: Periodic Table Group 1 - The Alkali Metals: The Learning Objectives For Today's LessonVyom agarwalNo ratings yet
- A Student Is Determining The Mass of A Metre Rule by A Balancing MethodDocument6 pagesA Student Is Determining The Mass of A Metre Rule by A Balancing MethodVyom agarwalNo ratings yet
- Gr10 Momentum WorksheetDocument10 pagesGr10 Momentum WorksheetVyom agarwalNo ratings yet
- Enclosure A: User Defined Functions For ANSYS Fluent Define - Sdof - PropertiesDocument13 pagesEnclosure A: User Defined Functions For ANSYS Fluent Define - Sdof - PropertiesbentalebNo ratings yet
- Completion 8Document57 pagesCompletion 8Arvin AbbaspourNo ratings yet
- The Rube Goldberg MachineDocument10 pagesThe Rube Goldberg Machinejohnvincent34No ratings yet
- Fluid Flow Through Convergent - Divergent NozzleDocument2 pagesFluid Flow Through Convergent - Divergent NozzleHammadNo ratings yet
- Ground Effect (Aircraft)Document5 pagesGround Effect (Aircraft)Mohd Anuar50% (2)
- Simplified Procedure To Evaluate Head Losses in Drip Irrigation LateralsDocument8 pagesSimplified Procedure To Evaluate Head Losses in Drip Irrigation LateralsMen Keo RathaNo ratings yet
- Conclusion For PressureDocument1 pageConclusion For Pressurelimakupang_mat780% (1)
- Damped Oscillation SDocument4 pagesDamped Oscillation SAmaresh MishraNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis III - Range and Endurance - 2 Topics: Flight Dynamics-I Prof. E.G. Tulapurkara Chapter-7Document8 pagesPerformance Analysis III - Range and Endurance - 2 Topics: Flight Dynamics-I Prof. E.G. Tulapurkara Chapter-7Chegrani AhmedNo ratings yet
- Compressible Potential FlowDocument15 pagesCompressible Potential FlowChanoNo ratings yet
- Flowline To CGDF: Size 14" Wall Thickness 12.7 MMDocument2 pagesFlowline To CGDF: Size 14" Wall Thickness 12.7 MMNKNo ratings yet
- 01honors Physics - Direct and Inverse Relationships PDFDocument9 pages01honors Physics - Direct and Inverse Relationships PDFJaime Feliciano HernándezNo ratings yet
- 2 Conservation EquationsDocument45 pages2 Conservation EquationsLovelypreet Mann100% (1)
- PumpsDocument31 pagesPumpsOsamaNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument9 pages1 PDFalihasan12No ratings yet
- Balloon Pop Rube GoldbergDocument14 pagesBalloon Pop Rube Goldbergapi-235347993No ratings yet
- Goldstein 22 15 21 23Document9 pagesGoldstein 22 15 21 23Laura SáezNo ratings yet
- 1-D Kinematics Study GuideDocument2 pages1-D Kinematics Study GuideJaydeepNo ratings yet
- Sheet 5-Dynamic 2Document4 pagesSheet 5-Dynamic 2mmrhero8No ratings yet
- Small Perturbation TheoryDocument4 pagesSmall Perturbation TheoryviviyanissacNo ratings yet
- CS274: Computer Animation and Simulation: Rigid Body DynamicsDocument36 pagesCS274: Computer Animation and Simulation: Rigid Body DynamicsAyub MohamedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document53 pagesChapter 4DkkNo ratings yet
- CR 0701 CH 10Document13 pagesCR 0701 CH 10Rıfat BingülNo ratings yet
- Jain College of Engineering, Belagavi: Fluid Power Engineering (18ME55)Document17 pagesJain College of Engineering, Belagavi: Fluid Power Engineering (18ME55)Getresponsespatil 1No ratings yet
- Physics Gravitation ProjectDocument21 pagesPhysics Gravitation ProjectAdityaNo ratings yet
- Orval Hydraulic - Catalogue PDFDocument18 pagesOrval Hydraulic - Catalogue PDFtatiana hernandezNo ratings yet
- Rajaratnam 199012345Document5 pagesRajaratnam 199012345Asim MazumderNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Spalart-Allmaras Turbulence ModelDocument12 pagesUnderstanding The Spalart-Allmaras Turbulence ModelsanaNo ratings yet