Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exp 10. Ammonium Sulphate
Uploaded by
Debadrito RayOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exp 10. Ammonium Sulphate
Uploaded by
Debadrito RayCopyright:
Available Formats
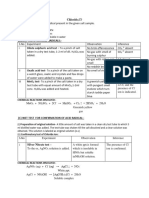
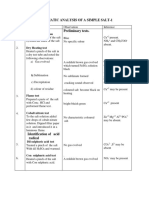
EXPERIMENT NO-3
AIM: To identify the acid radical and the basic radical present in the given salt sample.
(A) PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS: -
(i) Colour-White
(iii) Texture-Crystalline
(iv) Odour- Odourless
(v) Solubility-Soluble in water
(B) DRY TESTS FOR DETECTION OF ACID RADICALS: -
S.No Experiment Observation Inference
i Dilute sulphuric acid test - A pinch of salt was No brisk effervescence CO32- absent
taken in a clean dry test tube and 2-3 ml of dil.
H2SO4 was added. No gas with smell of SO32- absent
burning sulphur
No gas with rotten egg S 2- absent
smell
No reddish brown gas NO2- absent
ii Oxalic acid test- A small quantity of the salt was No smell of vinegar CH3COO- absent
taken on a watch glass and few drops of water
was added to make a paste.
iii MnO2 test-A pinch of the salt was taken in a No greenish yellow gas Cl- absent
clean dry test tube and a small quantity of with pungent smell
MnO2 and conc. H2SO4 was added, heated.
No reddish brown Br- absent
vapours
No deep violet vapours I - absent
iv Copper turning test- A small quantity of salt No dark brown gas NO3- absent
was taken in a clean dry test tube, 2-3 ml conc. evolved
H2SO4 was added and also a few copper chips
and the test tube was heated.
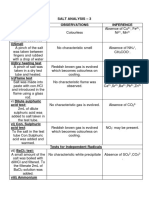
(C) WET TEST FOR CONFIRMATION OF ACID RADICAL:-
(i) Preparation of original solution- A little amount of salt was taken in a clean dry test tube to
which 5 ml distilled water was added. The test tube was shaken till the salt dissolved and a clear
solution was obtained. This solution is labeled as original solution (o.s)
Test for SO4 2-
Experiment Observation Inference
(i) BaCl2 test: To a part of the OS, 1-2 ml BaCl2 Thick white precipitation Presence of
solution was added. insoluble in mineral acids sulphate radical
confirmed
(ii) Lead acetate test: To the OS few drops of acetic acid Thick white precipitation Presence of
and lead acetate solution were added. insoluble in mineral acids sulphate radical
confirmed
CHEMICAL REACTIONS INVOLVED:-
2- -
(i) SO4 (aq) + BaCl2 (aq)→ BaSO4(white ppt, insoluble in mineral acids) + 2Cl
2- -
(ii) SO4 (aq)+ Pb(CH3COO)2 (aq)→PbSO4(white ppt,insoluble in mineral acids)+2CH3COO
(D) DRY TESTS FOR DETECTION OF BASIC RADICALS:-
S.No Experiment Observation Inference
(i) Flame test-A paste of salt with conc. HCl was No characteristic flame Inconclusive
taken in a loop made of platinum wire and colouration
introduced to the non- luminous flame.
(ii) NaOH bead test-To a pinch of salt taken in a A gas with ammoniacal ∙The evolving gas
clean dry test tube, 1or2 pellets of NaOH was smell evolved which is NH3.
added and heated give dense white ∙The presence of
fumes with dil. HCl NH 4 + indicated
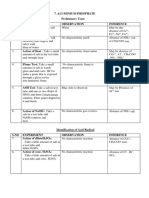
(E) TEST FOR GROUP ZERO: -
S.No Experiment Observation Inference
1. Nessler's reagent test-The solid salt was heated reddish-brown ppt. NH4+ confirmed
with conc. NaOH and the gas evolved was passed obtained
through Nessler's reagent.
CHEMICAL EQUATIONS INVOLVED:-
NH4+ + NaOH Na+ + H2O + NH3↑
NH3 + HCl NH4Cl
(white fumes)
2K2[HgI4] + NH3 + 3KOH H2N.HgO.HgI↓+ 7KI + 2H2O
(reddish-brown ppt)
(F) RESULT:-
(I) Acid radical= sulphate, SO42-
(ii) Basic radical= ammonium, NH4+
(iii) Salt= Ammonium Sulphate, (NH4)2SO4
You might also like
- Aluminium Sulphate 1Document2 pagesAluminium Sulphate 1Bimal Krishna Biswas60% (5)
- Lead NitrateDocument3 pagesLead NitrateSujinNo ratings yet
- SulphateDocument1 pageSulphateDarsh TodiNo ratings yet
- Iodide PDFDocument1 pageIodide PDFSujinNo ratings yet
- Ammonium BromideDocument2 pagesAmmonium BromideA KNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis Exp 2 To Exp 6 .PDF 22.05.23Document13 pagesSalt Analysis Exp 2 To Exp 6 .PDF 22.05.23nileshdasjeetestNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis I - Lead Acetate - (Ch3coo) 2pb-1Document28 pagesSalt Analysis I - Lead Acetate - (Ch3coo) 2pb-1YashikNo ratings yet
- AcetateDocument1 pageAcetateMr. InevitableNo ratings yet
- Carbonate, Sulphide, NitriteDocument3 pagesCarbonate, Sulphide, NitriteDarsh TodiNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis With EquationsDocument12 pagesSalt Analysis With Equationsabhikhya aryaNo ratings yet
- ChlorideDocument2 pagesChlorideMr. InevitableNo ratings yet
- Calcium AcetateDocument3 pagesCalcium AcetategreekyNo ratings yet
- 6 CaCO3Document3 pages6 CaCO3Abhi Suresh100% (3)
- Salt Analysis RecordDocument16 pagesSalt Analysis RecordAbhi SureshNo ratings yet
- Unknown Salt-4Document3 pagesUnknown Salt-4SANJAY BJNo ratings yet
- Calcium Acetate-1Document3 pagesCalcium Acetate-1Bimal Krishna BiswasNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis - Xii PDFDocument9 pagesSalt Analysis - Xii PDFहर्ष सैनी. कक्षा::बारहवीं 'द'No ratings yet
- Calcium NitrateDocument3 pagesCalcium NitrateiskypiskybruhNo ratings yet
- Systematic Analysis of Simple SalDocument22 pagesSystematic Analysis of Simple Sal11 M1 M.BHARATH RAJNo ratings yet
- Magnesium ChlorideDocument6 pagesMagnesium ChlorideiskypiskybruhNo ratings yet
- Term 2 Xi Chem Experiments 2021-22Document6 pagesTerm 2 Xi Chem Experiments 2021-22Tushar AngadiNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis 2Document3 pagesSalt Analysis 2Porkodi MNo ratings yet
- Ba CL 2Document2 pagesBa CL 2sabatsuhani74No ratings yet
- Wa0004.Document4 pagesWa0004.Arsh NeilNo ratings yet
- Barium ChlorideDocument5 pagesBarium ChlorideiskypiskybruhNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis Record BookDocument17 pagesSalt Analysis Record BookAashiya RNo ratings yet
- Term 2 Practicals Experiment No.1Document7 pagesTerm 2 Practicals Experiment No.1Ananya AryaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Practical: Experiment No. - 09Document6 pagesChemistry Practical: Experiment No. - 09chetan sharmaNo ratings yet
- Calcium NitrateDocument3 pagesCalcium NitrateanoopstudieNo ratings yet
- Nickel ChlorideDocument2 pagesNickel ChlorideanoopstudieNo ratings yet
- Aluminium Sulphate (Al2 (SO4) 3)Document3 pagesAluminium Sulphate (Al2 (SO4) 3)Rajesh MishraNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis I: Experiment Observations Inference Preliminary TestsDocument19 pagesSalt Analysis I: Experiment Observations Inference Preliminary TestsPreetam Kalyaan100% (1)
- Chemistry Salt Analysis (New) Exp. - 2 and 3Document8 pagesChemistry Salt Analysis (New) Exp. - 2 and 3Pritish KumarNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis-IiDocument4 pagesSalt Analysis-Iizuhair ahmadNo ratings yet
- Calcium No 3Document3 pagesCalcium No 3Ukkeshwaran SNo ratings yet
- Unknown Salt-3Document3 pagesUnknown Salt-3PES 21No ratings yet
- Salt Analysis 2Document2 pagesSalt Analysis 2MithunNo ratings yet
- Salt AnalysisDocument23 pagesSalt AnalysisflippodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Salt No - 1Document2 pagesSalt No - 1Santhosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Zinc AcetateDocument4 pagesZinc AcetateAbinaya chettiappanNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis - Aluminium SulphateDocument2 pagesSalt Analysis - Aluminium SulphatePriyanshee SongaraNo ratings yet
- Salt AnalysisDocument9 pagesSalt AnalysisAgent 47No ratings yet
- Lead Acetate SaltDocument5 pagesLead Acetate SaltiskypiskybruhNo ratings yet
- Zinc SulphateDocument4 pagesZinc SulphateAbinov Kumar KT100% (1)
- SALT - 03 (CaCl2)Document2 pagesSALT - 03 (CaCl2)Jeevan RaajNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis 1Document2 pagesSalt Analysis 1Siva KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Unknown Salt - 1Document2 pagesUnknown Salt - 1ranimos411No ratings yet
- Salt Analysis-Vi Aluminum SulphateDocument3 pagesSalt Analysis-Vi Aluminum SulphateNANNo ratings yet
- Unknown Salt 7Document3 pagesUnknown Salt 7SANJAY BJNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis - IIIDocument3 pagesSalt Analysis - IIIPorkodi MNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis Exp.Document4 pagesSalt Analysis Exp.Jems ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Expt 20 & 21Document4 pagesExpt 20 & 21Abhimanyu BhasinNo ratings yet
- AIM: To Identify The Given Salt For Acidic and Basic Radical - Experiment Observations Inference Colour: Smell: Dil. H SO TestDocument3 pagesAIM: To Identify The Given Salt For Acidic and Basic Radical - Experiment Observations Inference Colour: Smell: Dil. H SO TestnishchayNo ratings yet
- Calcium NitrateDocument3 pagesCalcium NitratenishchayNo ratings yet
- Aluminium PhosphateDocument3 pagesAluminium PhosphateanoopstudieNo ratings yet
- Practicals-Class Xi Salt AnalysisDocument12 pagesPracticals-Class Xi Salt AnalysisMariappan NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Experiment - Salt Analysis 12Document9 pagesExperiment - Salt Analysis 12Ayush MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis 1Document2 pagesSalt Analysis 1sowndharya.abigailNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis - Lead AcetateDocument2 pagesSalt Analysis - Lead AcetateSwarnabha BhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- MethodDocument4 pagesMethodDebadrito RayNo ratings yet
- Constructors ProgramsDocument2 pagesConstructors ProgramsDebadrito RayNo ratings yet
- Lesson 23Document4 pagesLesson 23Debadrito RayNo ratings yet
- CL10 GeogAssign Soil&NatVegSet1Document1 pageCL10 GeogAssign Soil&NatVegSet1Debadrito RayNo ratings yet
- 0 AgricultureDocument11 pages0 AgricultureDebadrito RayNo ratings yet
- Method Related ProgsDocument2 pagesMethod Related ProgsDebadrito RayNo ratings yet
- Ai2ts - Class 12Document1 pageAi2ts - Class 12Debadrito RayNo ratings yet
- Configuration Ofxa9h enDocument1 pageConfiguration Ofxa9h enDebadrito RayNo ratings yet
- String OutputDocument2 pagesString OutputDebadrito RayNo ratings yet
- Thought Pollution-Root Cause of All IllsDocument3 pagesThought Pollution-Root Cause of All IllsDebadrito RayNo ratings yet
- X, ICSE 19th OctoberDocument4 pagesX, ICSE 19th OctoberDebadrito RayNo ratings yet
- Geography Exam of Class XDocument4 pagesGeography Exam of Class XDebadrito RayNo ratings yet
- Global Iq Computer Education Centre P9, A. M. Bose Road, Kolkata-74 String Output Sheet Name: Date: A. Give The Output of The FollowingDocument2 pagesGlobal Iq Computer Education Centre P9, A. M. Bose Road, Kolkata-74 String Output Sheet Name: Date: A. Give The Output of The FollowingDebadrito RayNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Natural Vegetation (Pary-1) Class - X Session - 2020-2021 Day - 1Document19 pagesChapter - Natural Vegetation (Pary-1) Class - X Session - 2020-2021 Day - 1Debadrito RayNo ratings yet
- Computer Practical Examination Block Test 1 of Debadrito RayDocument5 pagesComputer Practical Examination Block Test 1 of Debadrito RayDebadrito RayNo ratings yet
- Kesp 103Document9 pagesKesp 103Satish Kumar ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Snapshots Eng TBDocument6 pagesSnapshots Eng TBfahima sunasaraNo ratings yet
- 11j Debadrito Ray 17 PhysicsDocument6 pages11j Debadrito Ray 17 PhysicsDebadrito RayNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Jan 31, 2022Document5 pagesAdobe Scan Jan 31, 2022Debadrito RayNo ratings yet
- BS 5911-120Document33 pagesBS 5911-120Niranjan GargNo ratings yet
- Hi-Macs - The - Europe - Colour - Book - LD 2018 PDFDocument31 pagesHi-Macs - The - Europe - Colour - Book - LD 2018 PDFandreeaNo ratings yet
- Alsiflex®-1260 Blankets - Technical Data Sheet - English PDFDocument2 pagesAlsiflex®-1260 Blankets - Technical Data Sheet - English PDFTanmay GorNo ratings yet
- Product Information Flyer: CIMSTAR® 10-700VLCDocument2 pagesProduct Information Flyer: CIMSTAR® 10-700VLCsobheysaidNo ratings yet
- Bioflex 2015 IN - (EN) PDFDocument4 pagesBioflex 2015 IN - (EN) PDFBijaya RaulaNo ratings yet
- Ryton R-4-200NA: Polyphenylene SulfideDocument3 pagesRyton R-4-200NA: Polyphenylene SulfideMatteo BaldiniNo ratings yet
- CVNG 2006 Cement 2022 RevisedDocument127 pagesCVNG 2006 Cement 2022 RevisedshayndellNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet For HDPEDocument1 pageData Sheet For HDPEShowkath AliNo ratings yet
- Separation of MixturesDocument25 pagesSeparation of MixturesYumie YamazukiNo ratings yet
- SS 212 Rehabilitation and Corrosion Protection of Sewers Using Geopolymer and Alkali-Activated Binder Mortar (V 2.0, CPDMS0031)Document22 pagesSS 212 Rehabilitation and Corrosion Protection of Sewers Using Geopolymer and Alkali-Activated Binder Mortar (V 2.0, CPDMS0031)Mohammed AlnahhalNo ratings yet
- Top 300 Companies of PakistanDocument8 pagesTop 300 Companies of PakistanadnanbwNo ratings yet
- CHM301 - Lab ManualDocument11 pagesCHM301 - Lab Manualsiti khadijahNo ratings yet
- Daily Manpower Report CPWDocument14 pagesDaily Manpower Report CPWVinod Kumar VermaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Papers, Questions, Answers, MCQ ... - CBSE Class 6 Science CH 4 - Sorting Material Into GroupsDocument3 pagesCBSE Papers, Questions, Answers, MCQ ... - CBSE Class 6 Science CH 4 - Sorting Material Into Groupssundar100% (1)
- GPC - Gel Permeation ChromatographyDocument13 pagesGPC - Gel Permeation Chromatographychiuchan888No ratings yet
- Chem Assignment Unit IDocument1 pageChem Assignment Unit ISumit NegiNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Behavior of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Reinforced 7075 Aluminum Alloy Composites Prepared by Mechanical Milling and Hot ExtrusionDocument9 pagesMechanical Behavior of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Reinforced 7075 Aluminum Alloy Composites Prepared by Mechanical Milling and Hot ExtrusionAdalberto G MirandaNo ratings yet
- Process For Technical NitrationDocument18 pagesProcess For Technical Nitrationmo ShahanawazNo ratings yet
- AlloysDocument7 pagesAlloysRAKIB AL MAHDINo ratings yet
- Brosur Furniture Labtech Indonesia Rev4Document20 pagesBrosur Furniture Labtech Indonesia Rev4bernhardNo ratings yet
- MT 2 4Document10 pagesMT 2 4Ramakrishna ReddyNo ratings yet
- Wood AshDocument5 pagesWood AshJohn loyd hernandezNo ratings yet
- Design of Free Standing Walls Feb 1984Document40 pagesDesign of Free Standing Walls Feb 1984Dale Stewart100% (4)
- What Is Shrinkage Cracks in Concrete - Types and Causes of Shrinkage CracksDocument3 pagesWhat Is Shrinkage Cracks in Concrete - Types and Causes of Shrinkage CracksJustin MusopoleNo ratings yet
- Loss On Ignition (L.O.I) : Concrete Technology (I) Lecture 3Document10 pagesLoss On Ignition (L.O.I) : Concrete Technology (I) Lecture 3Mahmoud HosnyNo ratings yet
- 02 Exercise5Document21 pages02 Exercise5AkashGauravNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen From Hydrogen Sulfide - Towards A More Sustainable Hydrogen EconomyDocument29 pagesHydrogen From Hydrogen Sulfide - Towards A More Sustainable Hydrogen EconomyNghiaNo ratings yet
- A Flair For SpringDocument8 pagesA Flair For SpringMonica MazzoniNo ratings yet
- Pavement Design SeminarDocument12 pagesPavement Design SeminarWayaya2009100% (3)
- EPDM Strips BrochureDocument1 pageEPDM Strips Brochurepolygomma Industries Pvt. LtdNo ratings yet