Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GIT Disorders: Friday, February 4, 2022 11:39 AM
Uploaded by
Sheryhan BayleOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GIT Disorders: Friday, February 4, 2022 11:39 AM
Uploaded by
Sheryhan BayleCopyright:
Available Formats
GIT Disorders
Friday, February 4, 2022 11:39 AM
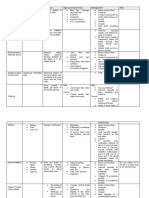
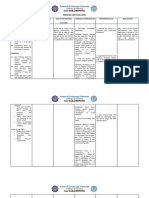
Git Disorders Define Risk Factors Surgical Management Clinical Findings Assessment Med Management
(post OP)
Conditions
affecting ORAL
CAVITY
Cleft Lip Congenital anomaly involving cleft in Family history Repair 3 mos. (rule of 10): Cleft upper lip - feed
(cheiloschisis) upper lip, may occur independently Cheiloplasty upright, large nipple
but frequently occurs together Exposure to certain holes, special lamb
substances during Maintain airway, avoid nipple
Can be unilateral (incomplete) or pregnancy prone
Bilateral (complete) Mouth breathing -
Elbow restraints, check q encourage early use of
2hr spoon and cup
Prevent crust formation Difficult sucking
on suture line (NSS, (breastfeeding may be
Hydrogen peroxide) more effective) - burp
frequently, allow to
Prevent pressure on swallow
suture line: avoid crying,
Logan's Bow, Analgesic
Cleft Palate Congenital anomaly involving cleft in Having diabetes Repair 2 yrs. Aspiration pneumonia
(palatoschisis) palate (palatoplasty)
Being obese during Altered speech
Repair: Cheiloplasty pregnancy Protect site: no straws,
Rule of 10: 10wks, 10 lbs, Hgb of 10 toothbrush, hard Recurrent otitis media
Dental development -
Side lying promotes parent infant
bonding
Liquid diet, no milk-> soft
Analgesic
Oral cancer Uncommon, highest amongst males Excessive sun Ulcers irregular borders Position:
over 40 yrs. Old exposure Mouth irrigation:
Leukoplakia
Appears as growth/sore in the mouth Tobacco, Alcohol Nutritional support: Tube
does not go away Difficulty chewing, feedings
Human dysphagia Monitor for facial nerve
Cancers of the lips, tongue, cheeks, Papillomavirus damage
floor of the mouth, hard and soft (HPV) Unexplained bleeding in
palate, sinuses, and pharynx (throat) the mouth Post radiation/chemotherapy
care
Unexplained numbness,
loss of feeling, or
pain/tenderness in any
area of face, mouth,
neck
Hoarseness, chronic
sore throat or change in
voice
Ear pain
Change in way your
teeth/dentures fit
together
Dramatic weight loss
Dx: positive cytology
test
Esophageal Define Therapeutic Medications Nursing Intervention Assessment Diagnostic procedures
Disorders Procedures
GERD, Reflux of the gastric Surgery (Nissen ANTACIDS: Educate: Pyrosis (heartburn) Barium swallow, UGI
Chalasia contents into esophagus Fundoplication) - -Aluminum H. (Mylanta, Diet - High protein, low Regurgitation Endoscopy
(Gastro - - Incompetent LES Laparoscopy Amphogel): Const. fat Nausea Esophageal manometry
stomach, -Magnesium: MOM: diarrhea - Small frequent A recurring sour/bitter - Monitor pressure of
Esophageal - Barrett's esophagus -Aluminum/Magnesium: Maalox, feedings (infants: taste in the mouth muscle contractions in
esophagus, Gaviscon thicken w/ rice the lower part of the
Reflux - to -Sodium Preps: Tums meal), upright Causes: esophagus while
Wednesday - GIT Page 1
Reflux - to -Sodium Preps: Tums meal), upright Causes: esophagus while
flow back) - 1 to 3 hrs. PC and bedtime after meal, avoid - Weakness swallowing
(acid highest) eating before - Increase ABD - NPO before test
- At least 1 hour from other going to bed pressure: obesity,
meds - No alcohol, tight clothing,
- Chew tab carbonated, pregnancy
-H2 Block: caffeinated, acidic Relaxation of LES:
Ranitidine (Zantac), Famotidine fruits - Smoking,
(Pepcid), Nizatidine (Acid) and Lifestyle: avoid tight- caffeine, alcohol
cimetidine (Tagamet) fitting clothing, lose - Drugs (nitrates,
-Proton Pump Inhibitor: weight, no smoking, calcium channel
Pantoprazole (Protonix), elevated HOB (6 to 8 in): blockers, Valium)
Omeprazole (Prilosec), blocks - Foods (fatty,
Lansoprazole (Prevacid) citrus, tomatoes,
spicy)
Hiatal Hernia Protruding of stomach out Antacids, H2 blockers, Analgesics Medications Substernal pain Upper GI series
of the diaphragm Dysphagia
- Small frequent, head Avoid HIATAL
Types: elevation Hot and spicy
Sliding: portion of stomach Ingestion of large meals
slips into thoracic cavity Apparel that constrictive
Twisting/bending/lifting
Paraoesophageal: fundus Alcohol
rolls out of stomach and Limit carbonated
forms a pocket beverages
Surgery
Esophageal Begins in the cells that line Radiation Post operations: Dysphagia Barium swallow
Cancer the inside of the esophagus Choking, Hoarseness,
Surgery: Semi-Fowler's cough Esophagoscopy w/ biopsy
Esophageal cancer can Esophagectomy: graft NGT/Gastrostomy care
occur anywhere along the High-calorie, high-
esophagus Esophagogastrostomy protein diet
Post radiation care
More men than women get
esophageal cancer
More common in men
between 50-70 years old
Risk factors:
- Smoking, alcohol,
poor oral hygiene,
achalasia
- Barrett's esophagus
Esophageal Dilated veins exist in the Saline lavage, Drugs: propranolol Avoid alcohol EGD
Varices distal esophagus esophagogastric Vasopressin Eat a healthy diet Endoscopic banding
balloon tamponade, Vit K Maintain a healthy Emergency (TIPS) -
Can rupture and cause BT, ligations and Octreotide IV weight Transjugular intrahepatic
massive bleeding sclerotherapy Monitor VS and Hgb Use chemical sparingly portosystemic shunting
Mouth care and carefully CBC, PT, liver function test
Causes:
Severe liver scarring
(cirrhosis)
Blood clot (thrombosis)
Alcoholism
Wednesday - GIT Page 2
You might also like
- Emergency Causes Signs and Symtomps Management NoteDocument5 pagesEmergency Causes Signs and Symtomps Management NoteAna Victoria JiménezNo ratings yet
- Cleft Lip and Cleft PalateDocument16 pagesCleft Lip and Cleft Palatemacuka08100% (3)
- Common Acquired and Congenital AnomaliesDocument5 pagesCommon Acquired and Congenital AnomaliesDang SaplanNo ratings yet
- LABIOPALATOSCHIZISDocument25 pagesLABIOPALATOSCHIZISEya Prepti SerraNo ratings yet
- Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors:: I. Schematic DiagramDocument1 pagePredisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors:: I. Schematic DiagramEileen CeloricoNo ratings yet
- Cleft, Hirschsprung, Imperforate AnusDocument3 pagesCleft, Hirschsprung, Imperforate AnusMyraflor CaroNo ratings yet
- System Disorder CP CLDocument1 pageSystem Disorder CP CLSariahNo ratings yet
- CORNELL NOTE Physical and Developmental Disorders in NewbornDocument4 pagesCORNELL NOTE Physical and Developmental Disorders in NewbornMargareth DandanNo ratings yet
- PhysicalAssessment-Geriatrics Older AdultsDocument12 pagesPhysicalAssessment-Geriatrics Older AdultsrectopaduaiiNo ratings yet
- Bubblehe FormDocument2 pagesBubblehe FormzycharcabreraNo ratings yet
- ENT - Diseases of The Oral Cavity and PharynxDocument6 pagesENT - Diseases of The Oral Cavity and PharynxChristian LantanoNo ratings yet
- Head and Neck Cancer GuideDocument6 pagesHead and Neck Cancer GuideMari FeNo ratings yet
- Cleft Lip and PalateDocument27 pagesCleft Lip and PalatejolibeecaldonaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Postpartum PatientDocument4 pagesAssessment of The Postpartum PatientJanice SnellNo ratings yet
- Common Acquired and Congenital Anomalies (Infangy) Congenital Anomalies Signs and SymptomsDocument5 pagesCommon Acquired and Congenital Anomalies (Infangy) Congenital Anomalies Signs and SymptomsShermina JalaniNo ratings yet
- Etiology of Malocclusion Classification Syndromes Parafunctional HabitsDocument35 pagesEtiology of Malocclusion Classification Syndromes Parafunctional HabitsayeshaNo ratings yet
- Childhood Autism: (Kanner's Syndrome, Early Infantile Syndrome)Document23 pagesChildhood Autism: (Kanner's Syndrome, Early Infantile Syndrome)Mereesha K MoideenNo ratings yet
- Obh 5 PDFDocument7 pagesObh 5 PDFFajrul AkmalNo ratings yet
- Symptoms Differential ChartsDocument52 pagesSymptoms Differential ChartsXiaxin Liu100% (2)
- Disturbances in Ingestion: Cleft Lip and Cleft Palate 1. Cleft Lip/cleft PalateDocument15 pagesDisturbances in Ingestion: Cleft Lip and Cleft Palate 1. Cleft Lip/cleft PalatehahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Table of Gi DiseasesDocument15 pagesTable of Gi Diseasesrosa sumnerNo ratings yet
- Waiters Newborn Care PDFDocument1 pageWaiters Newborn Care PDFmp1757No ratings yet
- Ent Diseases of The Oral and Pharynx Dr. UyDocument7 pagesEnt Diseases of The Oral and Pharynx Dr. UyAileen EmyNo ratings yet
- Group 3 - BSN 2BDocument16 pagesGroup 3 - BSN 2BJan Clarisse RamosNo ratings yet
- Cariology-The Susceptible Tooth 9Document106 pagesCariology-The Susceptible Tooth 9Vincent De AsisNo ratings yet
- Ear DisorderDocument61 pagesEar DisorderSakthi DeviNo ratings yet
- 4 - Assessing EarDocument7 pages4 - Assessing EarFrancine Julia MorilloNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Oral Mucous Membrane ImpairmentDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Oral Mucous Membrane ImpairmentJesabel DocdocanNo ratings yet
- 65 Year Old Man with Severe Ear Pain and SwellingDocument9 pages65 Year Old Man with Severe Ear Pain and SwellingJoe RealNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Complete Placenta PreviaDocument16 pagesCase Study On Complete Placenta PreviaAlphine DalgoNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing Module 19Document4 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Module 19weissNo ratings yet
- Commonly Occuring Oral Habits in ChildrenDocument43 pagesCommonly Occuring Oral Habits in ChildrenJustforkiddslaserdental ChNo ratings yet
- MacarambonFD PowerpointPresentation (ENG120)Document11 pagesMacarambonFD PowerpointPresentation (ENG120)Umar MacarambonNo ratings yet
- Apolonio, JC - Postpartum Assessment ActivityDocument3 pagesApolonio, JC - Postpartum Assessment ActivityJustin ApolonioNo ratings yet
- Baby Care HandbookDocument4 pagesBaby Care HandbookSreekanthNo ratings yet
- Tsang Int Detintsry 2009Document12 pagesTsang Int Detintsry 2009Robbie WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Concepto Castillo MoralesDocument7 pagesConcepto Castillo MoralesOdontoEspecialNo ratings yet
- Ent Guidelines New 020616Document15 pagesEnt Guidelines New 020616Osasere EwekaNo ratings yet
- Health Problems Common in PRESCHOOLDocument15 pagesHealth Problems Common in PRESCHOOLJanelle Lois EscolanoNo ratings yet
- Ateneo de Zamboanga University: Case Study (HOSPITAL)Document7 pagesAteneo de Zamboanga University: Case Study (HOSPITAL)Lyka SaysonNo ratings yet
- Voice and Speech DisordersDocument2 pagesVoice and Speech DisordersVishal Gaurav100% (1)
- Paskay JAOSm-A12 Prf1Document8 pagesPaskay JAOSm-A12 Prf1cintaNo ratings yet
- Patient Swallow ScreenDocument1 pagePatient Swallow ScreenLUCASNo ratings yet
- Interceptive OrthodonticsDocument17 pagesInterceptive OrthodonticsMeiz JaleelNo ratings yet
- CORNELL NOTE Postpartum ComplicationsDocument3 pagesCORNELL NOTE Postpartum ComplicationsMargareth DandanNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Neurological AssessmentDocument4 pagesAbdominal Neurological AssessmentMonica Angelique SalayoNo ratings yet
- GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS Cleft Palate - Esophageal Atresia - Oral MoniliasisDocument7 pagesGASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS Cleft Palate - Esophageal Atresia - Oral MoniliasisMikasa AckermanNo ratings yet
- Generic Name:: M@Bile ScanneDocument1 pageGeneric Name:: M@Bile ScanneWinnie AriolaNo ratings yet
- Upper Gastrointestinal Congenital MalformationsDocument8 pagesUpper Gastrointestinal Congenital Malformationsaasingh7800No ratings yet
- Final Year Clinicals: Malocclusions and Etiology (Graber)Document31 pagesFinal Year Clinicals: Malocclusions and Etiology (Graber)Sruthy NairNo ratings yet
- ASHA ClinicalSwallowingEval PDFDocument7 pagesASHA ClinicalSwallowingEval PDFAnonymous BRS5mD6aNo ratings yet
- Stage II of LaborDocument2 pagesStage II of LaborJharaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory PathophysiologiesDocument1 pageRespiratory PathophysiologiesTori IkeharaNo ratings yet
- CORNELL NOTE High Risk New BornDocument3 pagesCORNELL NOTE High Risk New BornMargareth DandanNo ratings yet
- Common Health Problems InfancyDocument147 pagesCommon Health Problems Infancymark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Intrapartum Complications: Kristen AzusanoDocument3 pagesIntrapartum Complications: Kristen AzusanokirbsNo ratings yet
- Snoring, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandSnoring, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Ranula Cyst, (Salivary Cyst) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandRanula Cyst, (Salivary Cyst) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Dysphonia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Dysphonia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Notes on Diseases of Swine, Sheep, Poultry and the Dog: Cause, Symptoms and TreatmentsFrom EverandNotes on Diseases of Swine, Sheep, Poultry and the Dog: Cause, Symptoms and TreatmentsNo ratings yet
- Responses To Altered PerceptionDocument1 pageResponses To Altered PerceptionSheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- BATESDocument9 pagesBATESSheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- Week 3 4 Objs POA Level 4 DutyDocument4 pagesWeek 3 4 Objs POA Level 4 DutySheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Nursing Care PlanDocument24 pagesNasopharyngeal Carcinoma Nursing Care PlanSheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Hemorrhagic Stroke PatientDocument40 pagesNursing Care of Hemorrhagic Stroke PatientSheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument1 pageNew Microsoft Word DocumentSheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Week 4Document4 pagesDRUG STUDY Week 4Sheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- DefinitionsDocument1 pageDefinitionsSheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- Jelly BaseDocument1 pageJelly BaseSheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document7 pagesModule 2Sheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- Guevara Camille Chloe B. CaseDocument1 pageGuevara Camille Chloe B. CaseSheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- Guevara Camille Chloe B. CaseDocument1 pageGuevara Camille Chloe B. CaseSheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- Case of TuberculosisDocument6 pagesCase of TuberculosisSheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- Plan of ActivitiesDocument2 pagesPlan of ActivitiesSheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- Nursing Student's Clinical Experience ReportDocument12 pagesNursing Student's Clinical Experience ReportSheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario Post Cataract SurgeryDocument1 pageCase Scenario Post Cataract SurgerySheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- Cataract NCPDocument1 pageCataract NCPSheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- GIT disorders and oral cavity conditionsDocument4 pagesGIT disorders and oral cavity conditionsSheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- GIT disorders and oral cavity conditionsDocument4 pagesGIT disorders and oral cavity conditionsSheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of ChloramphenicolDocument3 pagesDrug Study of Chloramphenicolcasimir1128No ratings yet
- GIT Disorders: Friday, February 4, 2022 11:39 AMDocument2 pagesGIT Disorders: Friday, February 4, 2022 11:39 AMSheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- Neuro Week 1Document6 pagesNeuro Week 1Sheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- Neuro Week 1Document6 pagesNeuro Week 1Sheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- Code 1Document1 pageCode 1Sheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- Manalo Rle Week 4Document13 pagesManalo Rle Week 4Sheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario Post Cataract SurgeryDocument1 pageCase Scenario Post Cataract SurgerySheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- Case of TuberculosisDocument6 pagesCase of TuberculosisSheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- Awts GegeDocument2 pagesAwts GegeSheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- Nursing Student's Clinical Experience ReportDocument12 pagesNursing Student's Clinical Experience ReportSheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- WEEK 8. - Gen Math-PortfolioDocument12 pagesWEEK 8. - Gen Math-PortfolioOreo ProductionsNo ratings yet
- Technical Description: BoilerDocument151 pagesTechnical Description: BoilerÍcaro VianaNo ratings yet
- BCRW Course - Answer-Booklet PDFDocument18 pagesBCRW Course - Answer-Booklet PDFSarah ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Daily Assessment RecordDocument4 pagesDaily Assessment Recordapi-342236522100% (2)
- PrintDocument18 pagesPrintHookandcrookNo ratings yet
- Class Opening Preparations Status ReportDocument3 pagesClass Opening Preparations Status ReportMaria Theresa Buscato86% (7)
- 8.4 Example: Swiss Market Index (SMI) : 188 8 Models of VolatilityDocument3 pages8.4 Example: Swiss Market Index (SMI) : 188 8 Models of VolatilityNickesh ShahNo ratings yet
- Klein & Kulick Scandolous ActsDocument20 pagesKlein & Kulick Scandolous ActsClaudia Costa GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Simulia Abaqus Standard DatasheetDocument3 pagesSimulia Abaqus Standard Datasheetuser923019231831No ratings yet
- PAPERBOARD QUALITYDocument8 pagesPAPERBOARD QUALITYaurelia carinaNo ratings yet
- Copy Resit APLC MiniAssignmentDocument5 pagesCopy Resit APLC MiniAssignmentChong yaoNo ratings yet
- United Airlines Case Study: Using Marketing to Address External ChallengesDocument4 pagesUnited Airlines Case Study: Using Marketing to Address External ChallengesSakshiGuptaNo ratings yet
- Phaseo Abl7 Abl8 Abl8rps24100Document9 pagesPhaseo Abl7 Abl8 Abl8rps24100Magda DiazNo ratings yet
- Building Primitive Traps & SnaresDocument101 pagesBuilding Primitive Traps & SnaresJoseph Madr90% (10)
- $R6RN116Document20 pages$R6RN116chinmay gulhaneNo ratings yet
- Operating Manual: Please Read These Operating Instructions Before Using Your FreedomchairDocument24 pagesOperating Manual: Please Read These Operating Instructions Before Using Your FreedomchairNETHYA SHARMANo ratings yet
- EPISIOTOMYDocument17 pagesEPISIOTOMYKaye Arriane TenorioNo ratings yet
- 266 009-336Document327 pages266 009-336AlinaE.BarbuNo ratings yet
- Stages of Intimate RelationshipsDocument4 pagesStages of Intimate RelationshipsKrystalline ParkNo ratings yet
- C-Dot Max-XlDocument39 pagesC-Dot Max-XlGourav Roy100% (3)
- Travis Walton Part 1 MUFON Case FileDocument346 pagesTravis Walton Part 1 MUFON Case FileClaudio Silva100% (1)
- Presepsi Khalayak Terhadap Program Acara Televise Reality Show "Jika Aku Menjadi" Di Trans TVDocument128 pagesPresepsi Khalayak Terhadap Program Acara Televise Reality Show "Jika Aku Menjadi" Di Trans TVAngga DianNo ratings yet
- LNG Vaporizers Using Various Refrigerants As Intermediate FluidDocument15 pagesLNG Vaporizers Using Various Refrigerants As Intermediate FluidFrandhoni UtomoNo ratings yet
- Tirfor: Lifting and Pulling Machines With Unlimited Wire RopeDocument26 pagesTirfor: Lifting and Pulling Machines With Unlimited Wire RopeGreg ArabazNo ratings yet
- GKInvest Market ReviewDocument66 pagesGKInvest Market ReviewjhonxracNo ratings yet
- Ek Pardesi Mera Dil Le Gaya Lyrics English Translation - Lyrics GemDocument1 pageEk Pardesi Mera Dil Le Gaya Lyrics English Translation - Lyrics Gemmahsa.molaiepanahNo ratings yet
- LogDocument119 pagesLogcild MonintjaNo ratings yet
- Proposed Panel Antenna: Globe Telecom ProprietaryDocument2 pagesProposed Panel Antenna: Globe Telecom ProprietaryJason QuibanNo ratings yet
- Komatsud65ex 16dozerbulldozerservicerepairmanualsn80001andup 200727063646Document26 pagesKomatsud65ex 16dozerbulldozerservicerepairmanualsn80001andup 200727063646juan santa cruzNo ratings yet
- ACL GRC Risk Manager - Usage Guide V1.1Document28 pagesACL GRC Risk Manager - Usage Guide V1.1Rohit ShettyNo ratings yet