Professional Documents
Culture Documents
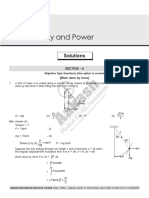
Practice 3.5 (p.133) : Normal Reaction From Lift N Man Tension in Cable T Lift
Uploaded by
Mavis LeeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Practice 3.5 (p.133) : Normal Reaction From Lift N Man Tension in Cable T Lift
Uploaded by
Mavis LeeCopyright:
Available Formats
2 Force and Motion Chapter 3 Force and Motion (I)
Practice 3.5 (p.133) 9 (a) normal reaction tension in
from lift N cable T
1 D
2 C man lift
3 C
weight mg
4 A force acting
weight Mg on lift by
5 When he pushes the platform, by Newton’s man N
third law, the platform also pushes him. He
(b) Take upwards as positive.
accelerates because of this pushing force from
Apply F = ma.
the platform.
(i) Consider the man.
6 The force acting on the ground by the tyres
N mg = ma (1)
points backwards. By Newton’s third law, the
By Newton’s third law,
ground exerts a forward force on the tyres.
N = N
This force pushes the car forwards.
Consider the lift.
7 When he pushes the ground in order to jump,
T Mg N = Ma
the normal reaction acting on him by the
T Mg N = Ma (2)
ground is larger than his weight.
(1) + (2),
This does not violate Newton’s third law since
T (m + M)g = (m + M)a
the two forces are not an action-and-reaction
T = (m + M)(a + g)
pair.
= (65 + 200)(0.6 + 9.81)
8 Take the direction to the right as positive.
= 2760 N
(a) Average force acting on B
The tension is 2760 N.
= ma = 1 3 = 3 N
(ii) Consider the man and the lift as
(b) The force acting on B by A and the force
one body.
acting on A by B forms a pair of action
T (m + M)g = (m + M)a
and reaction.
T = (m + M)(a + g)
Average force acting on A = 3 N
= (65 + 200)(0.6 + 9.81)
(c) Acceleration of A = = = 1 m = 2760 N
The tension is 2760 N.
s 2
The time of acceleration of A is the same
as that of B.
Velocity of A after collision
= u + at = 1.2 + (1)0.5 = 0.7 m s1
New Senior Secondary Physics at Work (Second Edition) 1
Oxford University Press 2015
You might also like
- How Steam Trap WorkDocument40 pagesHow Steam Trap Workdeny prasyamtyo100% (1)
- Ee Objective 1pdfDocument20 pagesEe Objective 1pdfKYLEBRIAN GOZARINNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Field Theory: "Our Thoughts and Feelings Have Electromagnetic Reality. Manifest Wisely."Document66 pagesElectromagnetic Field Theory: "Our Thoughts and Feelings Have Electromagnetic Reality. Manifest Wisely."Kavya Mamilla100% (1)
- MergedDocument520 pagesMergedPokemon trainnerNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Force and EnergyDocument45 pagesTopic 3 Force and EnergyAnthonyDomNo ratings yet
- 01 - SRV02 QUARC Integration - Instructor ManualDocument21 pages01 - SRV02 QUARC Integration - Instructor ManualFernando Her R0% (2)
- Nozzle CalculationDocument13 pagesNozzle Calculationaqilah liyanaNo ratings yet
- Revision Exercise 3: Concept Traps (p.137)Document8 pagesRevision Exercise 3: Concept Traps (p.137)4C 32 WONG SHU HANGNo ratings yet
- Practice 3.4 (p.126) : 2 Force and Motion Chapter 3 Force and Motion (I)Document2 pagesPractice 3.4 (p.126) : 2 Force and Motion Chapter 3 Force and Motion (I)Mavis LeeNo ratings yet
- Practice 3.4 (p.126) : 2 Force and Motion Chapter 3 Force and Motion (I)Document2 pagesPractice 3.4 (p.126) : 2 Force and Motion Chapter 3 Force and Motion (I)HU HNo ratings yet
- Physics, Chemistry and MathematicsDocument10 pagesPhysics, Chemistry and Mathematicsarchit jain123No ratings yet
- Unit HW Momentum Collisions Ans Key PDFDocument8 pagesUnit HW Momentum Collisions Ans Key PDFManansala LindsayNo ratings yet
- Low of Motion (S.C.Q.) EDocument67 pagesLow of Motion (S.C.Q.) Eraj100% (3)
- 36 Years Physics Pyq PWDocument316 pages36 Years Physics Pyq PWCat123No ratings yet
- Class 11 36 Pyq PW BiyoyoDocument153 pagesClass 11 36 Pyq PW Biyoyoavinandande24No ratings yet
- Practice 7.2 (p.280) : 2 Force and Motion Chapter 7 MomentumDocument2 pagesPractice 7.2 (p.280) : 2 Force and Motion Chapter 7 Momentum4C 32 WONG SHU HANGNo ratings yet
- Yo YoDocument3 pagesYo Yoitaiorr100% (1)
- Forces and Motion II: 5.1 The Important StuffDocument28 pagesForces and Motion II: 5.1 The Important StuffSclaffenNo ratings yet
- Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia: Mechanical Engineering Dynamics DAM 10903/ 20903 Kinetics of ParticleDocument16 pagesUniversiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia: Mechanical Engineering Dynamics DAM 10903/ 20903 Kinetics of ParticleAriff ShasteraNo ratings yet
- Final Revision Questions: RocketDocument229 pagesFinal Revision Questions: RocketDevashish RoyNo ratings yet
- A Level PhysicsDocument7 pagesA Level PhysicsshmaNo ratings yet
- Revision Exercise 9: Concept Traps (p.356)Document8 pagesRevision Exercise 9: Concept Traps (p.356)4C 32 WONG SHU HANGNo ratings yet
- 2ND SheetDocument2 pages2ND SheetGAMAGE SARANAPALANo ratings yet
- Dynamics of MotionDocument8 pagesDynamics of Motionjulianne sanchezNo ratings yet
- Campo Magnetico en Un ConductorDocument7 pagesCampo Magnetico en Un ConductorPEREDA UTRILLA MANUEL ALEXANDERNo ratings yet
- Dynamics: Newton's Laws of Motion: Phys101 Lectures 4 & 5Document27 pagesDynamics: Newton's Laws of Motion: Phys101 Lectures 4 & 5Phạm Bùi Quốc QuyềnNo ratings yet
- Law of MotionDocument19 pagesLaw of MotionEzhil MukilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Dynamics Checked PDFDocument24 pagesChapter 3 Dynamics Checked PDFWan WenNo ratings yet
- Revision Exercise 4: Cocept Traps (p.169)Document6 pagesRevision Exercise 4: Cocept Traps (p.169)4C 32 WONG SHU HANGNo ratings yet
- Physics Laws of MotionDocument9 pagesPhysics Laws of MotionLux SilverNo ratings yet
- Engineering Science: Dynamics (Newton's Second Law, Force, Inertia)Document39 pagesEngineering Science: Dynamics (Newton's Second Law, Force, Inertia)DRAGON LAMNo ratings yet
- F4 1920 Year-End Test MarkingDocument4 pagesF4 1920 Year-End Test Marking5B04 CHOW HOI LAMNo ratings yet
- (JEE Knockout) - NLM & Friction - 13th MarchDocument88 pages(JEE Knockout) - NLM & Friction - 13th Marchnitika agnihotriNo ratings yet
- Reinforcement Exercise Chapter 3Document3 pagesReinforcement Exercise Chapter 3Noratiqah Binti Mohd AminNo ratings yet
- Statics & Resolving Forces 1 MSDocument8 pagesStatics & Resolving Forces 1 MSAhmedNo ratings yet
- Lom TopicwiseDocument35 pagesLom Topicwisedd100% (1)
- Arihant Master The NCERT Physics Volume 1Document14 pagesArihant Master The NCERT Physics Volume 1zainrozindarNo ratings yet
- 11th - EM - JEE - J3 P+C+M 05 08 2023 - PAPER 1Document10 pages11th - EM - JEE - J3 P+C+M 05 08 2023 - PAPER 1ashmitaramoliya123No ratings yet
- Newton'S Laws of MotionDocument21 pagesNewton'S Laws of MotionRagheb IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Jan2005 PDFDocument4 pagesJan2005 PDFhenrykNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy and Power Advanced Practice Problems From Mechanics by DC PandeyDocument24 pagesWork, Energy and Power Advanced Practice Problems From Mechanics by DC PandeyChirag SinghNo ratings yet
- Physics SheetDocument4 pagesPhysics SheetPrisha KediaNo ratings yet
- 22 MPP 1 Work Power EnergyDocument13 pages22 MPP 1 Work Power EnergyAnshuman MohantyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13Document8 pagesLecture 13I190845 Samana NayyabNo ratings yet
- Practice 4.2 (p.166) : 2 Force and Motion Chapter 4 Force and Motion (II)Document2 pagesPractice 4.2 (p.166) : 2 Force and Motion Chapter 4 Force and Motion (II)4C 32 WONG SHU HANGNo ratings yet
- Position Distance From O / CM: A B C D EDocument22 pagesPosition Distance From O / CM: A B C D EVincent haNo ratings yet
- Mass Weight: QuantityDocument18 pagesMass Weight: QuantityraajNo ratings yet
- LAWS OF MOTION - Connected MotionDocument7 pagesLAWS OF MOTION - Connected MotionPrehaan ParikhNo ratings yet
- Assignment-24: Section-I Multiple Correct Answer Type 6 Q. (4 M (-1) ) 1Document5 pagesAssignment-24: Section-I Multiple Correct Answer Type 6 Q. (4 M (-1) ) 1ankitrajaj8083No ratings yet
- CH-5 Laws of MotionDocument23 pagesCH-5 Laws of MotionAkash GuptaNo ratings yet
- 11 Holiday HomeworkDocument199 pages11 Holiday Homeworksupriyarama413No ratings yet
- MC Web Mech2 9 2009 PDFDocument2 pagesMC Web Mech2 9 2009 PDFAshleyJaneFuentesNo ratings yet
- Newtons Laws Section 1 and 2..PDF CCDocument33 pagesNewtons Laws Section 1 and 2..PDF CCeoinmanganNo ratings yet
- Answer Tutorial 4Document3 pagesAnswer Tutorial 4Anas KamalNo ratings yet
- Physic Form 5 1Document5 pagesPhysic Form 5 1我是人I am a humanNo ratings yet
- Resonance NLM ExerciseDocument13 pagesResonance NLM ExerciseSujal SNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitled黃錞彥No ratings yet
- Test-1: Definition (WEP) Time: 90 Min Date:24-07-2021 Multi Choice Single Correct (+3,-1)Document5 pagesTest-1: Definition (WEP) Time: 90 Min Date:24-07-2021 Multi Choice Single Correct (+3,-1)AryanNo ratings yet
- Physics: A G Ma 2 A G Ma 2 A G Ma A G MaDocument11 pagesPhysics: A G Ma 2 A G Ma 2 A G Ma A G MaIhtisham Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- CLS JEEAD-18-19 XIII Phy Target-2 SET-1 Chapter-4 PDFDocument91 pagesCLS JEEAD-18-19 XIII Phy Target-2 SET-1 Chapter-4 PDFHarshit GuptaNo ratings yet
- LOM-03 - Subjective SolvedDocument13 pagesLOM-03 - Subjective SolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Newton's LawsDocument5 pagesNewton's LawsJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Newton's 2nd Law of Motion: Particle Motion in The PlaneDocument15 pagesNewton's 2nd Law of Motion: Particle Motion in The PlaneMuhammad Haris KhanNo ratings yet
- 0312 Scholarship Test Phy Paper-2Document8 pages0312 Scholarship Test Phy Paper-2tanmoymisra26No ratings yet
- 1415937280 - 4B10 - Exercise - E - 複本Document48 pages1415937280 - 4B10 - Exercise - E - 複本Mavis LeeNo ratings yet
- 6 Work, Energy and PowerDocument11 pages6 Work, Energy and PowerMavis LeeNo ratings yet
- Chem Ch17 Online VerDocument16 pagesChem Ch17 Online VerMavis LeeNo ratings yet
- Practice 9.1 (p.336) : 1 2 3 4 (D) Centripetal Acceleration of TomDocument1 pagePractice 9.1 (p.336) : 1 2 3 4 (D) Centripetal Acceleration of TomMavis LeeNo ratings yet
- Practice 5.1 (p.185) : F 600 N Acting On TheDocument1 pagePractice 5.1 (p.185) : F 600 N Acting On TheMavis LeeNo ratings yet
- Practice 20103 AnsDocument1 pagePractice 20103 AnsMavis LeeNo ratings yet
- Practice 7.1 (p.268) : 2 Force and Motion Chapter 7 MomentumDocument2 pagesPractice 7.1 (p.268) : 2 Force and Motion Chapter 7 MomentumMavis LeeNo ratings yet
- Practice 1.2 (p.12) : 2 Force and Motion Chapter 1 Motion (I)Document1 pagePractice 1.2 (p.12) : 2 Force and Motion Chapter 1 Motion (I)Mavis LeeNo ratings yet
- Practice 2.1 (p.57) : 2 Force and Motion Chapter 2 Motion (II)Document4 pagesPractice 2.1 (p.57) : 2 Force and Motion Chapter 2 Motion (II)Mavis LeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Motion Along A Straight Line PDFDocument21 pagesChapter 2 Motion Along A Straight Line PDFAnonymous UM3LWrUq6No ratings yet
- Ncert 11 Part A Practice Paper PhysicsDocument16 pagesNcert 11 Part A Practice Paper Physicskavyamanchanda102No ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Resistance of A Conductor: Prepared By: Engr. Tomashita P. ArenasDocument24 pagesFactors Affecting Resistance of A Conductor: Prepared By: Engr. Tomashita P. ArenasTomashita ArenasNo ratings yet
- Mech. Properties of FluidsDocument18 pagesMech. Properties of FluidsRakesh SNo ratings yet
- Alternating CurrentDocument35 pagesAlternating CurrentANSH TYAGINo ratings yet
- Revised Fee-From 2019 AprilDocument13 pagesRevised Fee-From 2019 AprildeepusvvpNo ratings yet
- Unit-IV Bridges Syllabus: AC Bridges Measurement of Inductance-Maxwell's Bridge, Anderson BridgeDocument27 pagesUnit-IV Bridges Syllabus: AC Bridges Measurement of Inductance-Maxwell's Bridge, Anderson BridgeSwami Naidu GummadiNo ratings yet
- Structural Dynamics Module 1 Assignment 1Document4 pagesStructural Dynamics Module 1 Assignment 1Arpit KumarNo ratings yet
- T8500CT0601EPR4 - TeSys Essential Guide 2013 LRDocument46 pagesT8500CT0601EPR4 - TeSys Essential Guide 2013 LRCbdtxd PcbtrNo ratings yet
- 6 ASTM C138 Density Yield Air ContentDocument4 pages6 ASTM C138 Density Yield Air Contentdidavaran tejaratNo ratings yet
- Index Kvar Panel Tray B B Light C: Capacitor Bank Panel Board Cable Tray Bus BarDocument19 pagesIndex Kvar Panel Tray B B Light C: Capacitor Bank Panel Board Cable Tray Bus BarprkshshrNo ratings yet
- 2016EME1076 Tutorial 1Document5 pages2016EME1076 Tutorial 1REan ANandNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work - FM 4 PhysicsDocument27 pagesScheme of Work - FM 4 PhysicsAnonymous aiinSGRwsNo ratings yet
- List of SymbolsDocument4 pagesList of Symbolstotoq51No ratings yet
- Xii Physics Experiment 1Document5 pagesXii Physics Experiment 1Solomon Peter SunilNo ratings yet
- Tech Article - Control Cable Lengths For ContactorsDocument8 pagesTech Article - Control Cable Lengths For ContactorsSandeep NairNo ratings yet
- Electrical ExerciseDocument16 pagesElectrical ExerciseChoa Pei ShuangNo ratings yet
- 1 Worksheet: Intermediate LevelDocument2 pages1 Worksheet: Intermediate LevelWawan RuswandiNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry Jee Main Selected 2Document2 pagesThermochemistry Jee Main Selected 2successvirenderNo ratings yet
- Physics - Ipe Important Questions 2023-24Document8 pagesPhysics - Ipe Important Questions 2023-24AbhijeetNo ratings yet
- MC 7 007 Ve003Document2 pagesMC 7 007 Ve003Leandro CiceroNo ratings yet
- Heat 2Document15 pagesHeat 2Dipesh BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- Boats and Stream NotesDocument5 pagesBoats and Stream Notesvarun gandhiNo ratings yet