Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Q3 - Science8 - Week 8 LAS 3
Uploaded by
zerleigh dream pagalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Q3 - Science8 - Week 8 LAS 3
Uploaded by
zerleigh dream pagalCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: ___________________________________________Grade & Section: _________________
Subject: Science 8 Teacher: __________________________________ Score: _____________
Lesson : Quarter 3 Week 8 LAS 3
Activity Title : Reactivity Series
Learning Target : Identify the relative reactivity of metals in a solution
Reference(s) : Science 8- Learners Module (MELCS S8MT-IIIi-j-12)
: https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/zrfmrj6/revision/1
LAS Writer : Christian Elaine P. Nabor
_______________________________________________________________________________
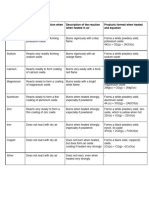
The reactivity series of metals is a chart listing metals in order of decreasing reactivity. In
general, the more reactive a metal is the more vigorously it reacts with other substances, easily it
loses electrons to form positive ions (cations).
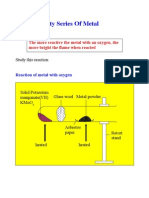
Reaction with oxygen (when heated
Metal Reaction with water Reaction with steam Reactivity
and at room temperature)
Reacts vigorously. Floats on the
Reacts vigorous when heated. Lilac flame surface. Moves and fizzes. Burns
Potassium Reaction too dangerous to Most
and white solid formed. Tarnishes when with a lilac flame. Heat is released.
(K) be attempted. reactive
freshly cut at room temperature Crackle as it disappears. Colourless
solution remains.
Reacts vigorously. Floats on the
Reacts vigorously when heated.
surface. Moves and fizzes. Melts to
Sodium Yellow/orange flame and white solid formed. Reaction too dangerous to
form a silvery ball. Heat is released. ⬆
(Na) Tarnishes when freshly cut at room be attempted.
Crackle as it disappears. Colourless
temperature
solution remains.
Reacts readily. Fizzes. Grey solid
Reacts vigorously with strong heating. Brick
Calcium rises then sink. Heat is released. Reaction too dangerous to
red flame and white solid formed. Slowly ⬆
(Ca) Grey solid disappears. Solution be attempted.
forms a surface oxide at room temperature
appears milky.
Reacts readily with strong heating. White Reacts on strong heating.
Magnesium Very slow reaction. A few bubbles
light and white solid formed. Slowly forms a White light and white solid ⬆
(Mg) of gas produced.
surface oxide at room temperature formed.
Reacts readily with strong heating as a Reacts as a powder on
Aluminum
powder. White solid formed. Slowly forms a No reaction strong heating. White solid ⬆
(Al)
surface oxide at room temperature formed.
Reacts steadily when heated forming a Reacts as a powder on
yellow solid which change to white on strong heating. Yellow solid
Zinc (Zn) No reaction ⬆
cooling. Slowly forms a surface oxide at forms which changes to
room temperature white on cooling.
Reacts readily when heated as iron filings.
Reacts as a powder on very
Orange sparks and black solid formed.
Iron (Fe) No reaction strong heating. Black solid ⬆
Slowly forms a surface oxide at room
formed.
temperature
Reacts on heating to form a black solid.
Copper Least
Slowly forms a surface oxide at room No reaction No reaction
(Cu) reactive
temperature
Activity: What am I?
Direction: Fill the missing letters in the box by analyzing the questions carefully.
T A S U 1. is the most reactive metal.
S I M 2. Floats on the surface when place on the water and it
melts to form a silvery ball.
A I U 3. Reacts vigorously with strong heating forming brick
red flames and white solids
Z 4. Shows no reaction on water but reacts steadily when
heated forming a yellow solid which change to white
P E R 5. It is the least reactive element
R O 6. Doesn’t show any reaction with water. But reacts on
heating to form a black solid and slowly forms a surface
oxide at room temperature.
X G N 7. Water is composed of 2 atoms of Hydrogen and what element?
L M U 8. When steamed, it reacts as a powder on strong heating forming a
a white solid
D U 9. Reacts vigorously when heated. Yellow/orange flame and white solid
formed. Tarnishes when freshly cut at room temperature
M N E I U 10. Very slow reaction. A few bubbles of gas produced when placed in
water.
You might also like
- Chemi Note Chapter 4 and 5Document10 pagesChemi Note Chapter 4 and 5derekNo ratings yet
- Lab#2 Physical Chemical Changes Worksheet HandoutDocument4 pagesLab#2 Physical Chemical Changes Worksheet HandoutLeslie wanyamaNo ratings yet
- Alkali Metals and Halogen 8th DCP PMCDocument2 pagesAlkali Metals and Halogen 8th DCP PMCRaoulNo ratings yet
- Activity Booklet Science 10th 2023Document21 pagesActivity Booklet Science 10th 2023krishangmaheshwari1No ratings yet
- Reaction of Alkali Metals With Water and OxygenDocument6 pagesReaction of Alkali Metals With Water and Oxygenみゆ マイクロ100% (1)
- Activity 4.1 Form 4Document3 pagesActivity 4.1 Form 4azrawrr83% (6)
- 9F Revision Q CardsDocument10 pages9F Revision Q CardsbanaliaNo ratings yet
- Alkali MetalsDocument7 pagesAlkali Metalsokguserfucker idontgiveashitNo ratings yet
- Chemistry C2 (GDW52) PDFDocument43 pagesChemistry C2 (GDW52) PDFBrain MasterNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Elements: Chemical PropertiesDocument15 pagesGroup 1 Elements: Chemical PropertiesIdris YatimNo ratings yet
- Results: Experiment 4.2 (A) : Reaction of Group 1 Elements With WaterDocument3 pagesResults: Experiment 4.2 (A) : Reaction of Group 1 Elements With WaterSyenny NgNo ratings yet
- 1.2. The Periodic Table (2020 - 05 - 09 13 - 54 - 55 UTC)Document3 pages1.2. The Periodic Table (2020 - 05 - 09 13 - 54 - 55 UTC)victoriaNo ratings yet
- 03 03 22Document1 page03 03 22roryNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Reactions IGCSEDocument9 pagesChemistry Reactions IGCSESasukeNo ratings yet
- OL Chemistry Notes - Periodic TableDocument2 pagesOL Chemistry Notes - Periodic Tablemanoirfan987No ratings yet
- Activity Series LabDocument6 pagesActivity Series LabJonathan_Khan7100% (4)
- Metals, Unit 9Document25 pagesMetals, Unit 9samikshakumar2009No ratings yet
- TLC Staining Procedure TLC Stain Recipe Stain Chemistry / Physics CommentsDocument3 pagesTLC Staining Procedure TLC Stain Recipe Stain Chemistry / Physics CommentsLara DiasNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form4 Chapter2 SPMDocument10 pagesChemistry Form4 Chapter2 SPMkaiqianNo ratings yet
- 2RMWB Expt 6 1 e AudioDocument22 pages2RMWB Expt 6 1 e AudioTaemoonchildNo ratings yet
- 9 Reactivity Series of MetalsDocument4 pages9 Reactivity Series of MetalsShee YingNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument5 pagesScienceLunaNo ratings yet
- 1c ANSWERS Chemical and Physical Reactions (2017)Document1 page1c ANSWERS Chemical and Physical Reactions (2017)Karina LeungNo ratings yet
- Reactivity of Metals: Learning GoalDocument36 pagesReactivity of Metals: Learning GoalRyanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5B Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument8 pagesExperiment 5B Types of Chemical ReactionsNicole ZhangNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical Reactions 6.2 and 6.3 NotesDocument2 pagesTypes of Chemical Reactions 6.2 and 6.3 NotesSimon TamNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes (Metals)Document4 pagesChemistry Notes (Metals)Teo Jia Ming Nickolas67% (3)
- Chemistry Practical Help For XiiDocument16 pagesChemistry Practical Help For XiiMehjabin Abdurrazaque50% (8)
- 1 Particle Theory&States of MatterDocument5 pages1 Particle Theory&States of Matter209garde10No ratings yet
- Chemistry - Part 5Document10 pagesChemistry - Part 5BALA GANESHNo ratings yet
- All in One SCIENCE - 10 - Activity - CH 1Document5 pagesAll in One SCIENCE - 10 - Activity - CH 1ShanthoshNo ratings yet
- GROUP II Elements Alkaline Earth MetalsDocument35 pagesGROUP II Elements Alkaline Earth MetalsSUIXIDENo ratings yet
- M7 Data and ObservationsDocument3 pagesM7 Data and ObservationsChen PamaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4, ChemistryDocument2 pagesChapter 4, ChemistryWilliam ChongNo ratings yet
- Functional Group Analysis (CAPE LAB)Document3 pagesFunctional Group Analysis (CAPE LAB)AmeliaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document6 pagesUnit 2Thu ReinNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Revision NotesDocument5 pagesChemistry Revision NotesShi Kai TengNo ratings yet
- MetalsDocument33 pagesMetalsaahanag10No ratings yet
- Group7 TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS LABDocument5 pagesGroup7 TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS LABPumpkin SpiceNo ratings yet
- Class Note - 2016 PDFDocument291 pagesClass Note - 2016 PDFMaousam NayakNo ratings yet
- Results and Observations: Title: Table Showing The Observations When Heating Ammonium Dichromate, Copper (I) Carbonate, Lead (I Nitrate and IodineDocument4 pagesResults and Observations: Title: Table Showing The Observations When Heating Ammonium Dichromate, Copper (I) Carbonate, Lead (I Nitrate and IodineHailey RagbirNo ratings yet
- 0 - Organic and Inorganic Tests For AS PDFDocument8 pages0 - Organic and Inorganic Tests For AS PDFAbed AymanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 ReportDocument6 pagesExperiment 2 ReportJunne TanNo ratings yet
- Teaching DiscussionsDocument16 pagesTeaching DiscussionsRenz Caballero EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Reactivity Series - Reactions of Metals Summaried Into A Table PDFDocument1 pageReactivity Series - Reactions of Metals Summaried Into A Table PDFVictoria KairooNo ratings yet
- Presentation 3Document7 pagesPresentation 3muhammad dawoodNo ratings yet
- 007 Activity ZoneDocument6 pages007 Activity ZoneTusharNo ratings yet
- Lab Vi. Chemical and Physical Properties and ChangesDocument4 pagesLab Vi. Chemical and Physical Properties and ChangesLiliana PerezNo ratings yet
- Comparative Chart - METALSDocument1 pageComparative Chart - METALSlynnNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument1 pageUntitled DocumentAlyssa PhillipsNo ratings yet
- Reaction of Metals With OxygenDocument9 pagesReaction of Metals With Oxygenmanery23No ratings yet
- 14.1 Matter & Thermal Energy (Press Read Only To Open)Document104 pages14.1 Matter & Thermal Energy (Press Read Only To Open)Abdullah Alqahtani100% (1)
- Science - Form 4 - Chapter 5Document12 pagesScience - Form 4 - Chapter 5Marcia PattersonNo ratings yet
- Solid State Class 1 (4th May 2022) Handout and Home WorkDocument89 pagesSolid State Class 1 (4th May 2022) Handout and Home WorkShivacharan HollaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 0620 Summary Moh - GamalDocument30 pagesChemistry 0620 Summary Moh - Gamalmya thet htar sweNo ratings yet
- Exp 4.1 For Group 1Document8 pagesExp 4.1 For Group 1Hajar Norasyikin Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- A. Sulfur and Iron Filling Sulfur Not Heat HeatedDocument4 pagesA. Sulfur and Iron Filling Sulfur Not Heat Heatedpeter vanderNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Attendance and ParticipationDocument2 pagesCertificate of Attendance and Participationzerleigh dream pagalNo ratings yet
- 2018-Secondary-School-Science-8-Practices-that-Affect-the-Digestive-System-LM (FINAL) 0c0Document23 pages2018-Secondary-School-Science-8-Practices-that-Affect-the-Digestive-System-LM (FINAL) 0c0zerleigh dream pagalNo ratings yet
- GR 8 Teaching Guide in ScienceDocument66 pagesGR 8 Teaching Guide in ScienceDecy Raye75% (8)
- SALNDocument2 pagesSALNzerleigh dream pagalNo ratings yet
- Science 8 q2 Mod1 Earthquakes and Faults v1 1Document22 pagesScience 8 q2 Mod1 Earthquakes and Faults v1 1zerleigh dream pagalNo ratings yet
- TOS-Grade 8Document4 pagesTOS-Grade 8zerleigh dream pagalNo ratings yet
- Passed 70-4 Baguio City Concept Maps On Hierarchical Taxonomic System of ClassificationDocument53 pagesPassed 70-4 Baguio City Concept Maps On Hierarchical Taxonomic System of Classificationzerleigh dream pagalNo ratings yet
- APEX Life ReproductionDocument104 pagesAPEX Life Reproductionzerleigh dream pagalNo ratings yet
- Caitlin King Punnett SquareDocument4 pagesCaitlin King Punnett Squarezerleigh dream pagalNo ratings yet
- Continuity of Life: Facilitator's Guide Presentation Plan Master Set of ResourcesDocument38 pagesContinuity of Life: Facilitator's Guide Presentation Plan Master Set of Resourceszerleigh dream pagalNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Development PlanDocument5 pagesLaboratory Development Planzerleigh dream pagal100% (1)
- DepEd Prescribed e SAT SY 2020 2021Document7 pagesDepEd Prescribed e SAT SY 2020 2021zerleigh dream pagalNo ratings yet
- Activity A. Direction: Select The Item/s From The WORD BANK To Complete The Statements Below. WriteDocument2 pagesActivity A. Direction: Select The Item/s From The WORD BANK To Complete The Statements Below. Writezerleigh dream pagalNo ratings yet
- Activity: A. Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerDocument1 pageActivity: A. Encircle The Letter of The Correct Answerzerleigh dream pagalNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 QUARTER 4 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT TOSDocument4 pagesGrade 8 QUARTER 4 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT TOSzerleigh dream pagalNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Science Summative TestDocument7 pagesGrade 8 Science Summative Testzerleigh dream pagal75% (4)
- Science8 Q2 WEEK3 LAS3Document1 pageScience8 Q2 WEEK3 LAS3zerleigh dream pagalNo ratings yet
- Science8 Q2 Week8 LAS3Document1 pageScience8 Q2 Week8 LAS3zerleigh dream pagalNo ratings yet
- Grade 7Document13 pagesGrade 7zerleigh dream pagalNo ratings yet
- Loctite 495Document3 pagesLoctite 495Rammstein GottNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 GasesDocument74 pagesChapter 5 GasesReem HamadNo ratings yet
- 6 - Materials - Metals and Non-Metals - Book Back AnswersDocument7 pages6 - Materials - Metals and Non-Metals - Book Back AnswersSOULSNIPER 15No ratings yet
- BOSTIK Patchfix Repair Mortar F5 Rev3Document3 pagesBOSTIK Patchfix Repair Mortar F5 Rev3Antonette Marie ElgarioNo ratings yet
- Product Bulletin - PHPADocument1 pageProduct Bulletin - PHPAEliz MelizaNo ratings yet
- 2 How Atoms Differ 2022Document3 pages2 How Atoms Differ 2022alexandraNo ratings yet
- Potentiostat: User ManualDocument28 pagesPotentiostat: User ManualKate AnagnostouNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mems EA C415: Dr. N.N. SharmaDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Mems EA C415: Dr. N.N. SharmaArjit GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Electrogravimetric MethodsDocument3 pagesElectrogravimetric MethodsEdna Lip AnerNo ratings yet
- CH312 - COD Experiment ReportDocument3 pagesCH312 - COD Experiment ReportNarelle IaumaNo ratings yet
- SMWW 3500-CaDocument2 pagesSMWW 3500-Calmb LaboratoriosNo ratings yet
- S.O.P 1Document7 pagesS.O.P 1vishvendanNo ratings yet
- College of Education Long Quiz # 1: MixturesDocument7 pagesCollege of Education Long Quiz # 1: MixturesClaudia Inoc100% (1)
- Radiation Curing Os CoatingsDocument9 pagesRadiation Curing Os CoatingsLangleyNo ratings yet
- Ritgen U. - Analytical Chemistry I-Springer (2023)Document308 pagesRitgen U. - Analytical Chemistry I-Springer (2023)Marios BeddaweNo ratings yet
- Biochem PrelimDocument42 pagesBiochem PrelimFaith RochaNo ratings yet
- M.pharm II SEM 04-12-2023 - CompressedDocument2 pagesM.pharm II SEM 04-12-2023 - Compressedsanthosh1121sasNo ratings yet
- Zinc Oxide Sorbents For The Removal of Hydrogen Sulfide From SyngasDocument10 pagesZinc Oxide Sorbents For The Removal of Hydrogen Sulfide From SyngasSuprio KamalNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document5 pagesPresentation 1Eziah Pearl Joy AlaveraNo ratings yet
- UCLFire TN 028 PDFDocument1 pageUCLFire TN 028 PDFperezismaelNo ratings yet
- Group B2 - Batch - Stirring RateDocument7 pagesGroup B2 - Batch - Stirring RateMimi Sharina HassanNo ratings yet
- Class-XI Chemistry Thermodynamics Worksheet DocumentDocument2 pagesClass-XI Chemistry Thermodynamics Worksheet DocumentSameer DahiyaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 Melc EngrDocument9 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 Melc EngrMarlon SuazoNo ratings yet
- 0620 s08 QP 3Document25 pages0620 s08 QP 3Varun PanickerNo ratings yet
- Authentication of Questioned Documents Using HPLCDocument19 pagesAuthentication of Questioned Documents Using HPLCab-azzehNo ratings yet
- Acetal (Polyoxymethylene) Chemical Compatibility ChartDocument15 pagesAcetal (Polyoxymethylene) Chemical Compatibility ChartAnbuchelvan CNo ratings yet
- Recycled Rubber - Vulcanized Crumb Particulate SpecificationDocument12 pagesRecycled Rubber - Vulcanized Crumb Particulate SpecificationDevesh Kumar PandeyNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Crash Reviewer PDFDocument11 pagesOrganic Chemistry Crash Reviewer PDFmaganda akoNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols & Ether - AnswersDocument6 pagesAlcohols, Phenols & Ether - AnswersK. RupaNo ratings yet
- Carbon Steel Chemical Compatibility ChartDocument17 pagesCarbon Steel Chemical Compatibility ChartOscar BernalNo ratings yet