Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Teaching Science in The Elementary Grades (Biology and Chemistry)
Uploaded by
Erika AguilarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Teaching Science in The Elementary Grades (Biology and Chemistry)
Uploaded by
Erika AguilarCopyright:
Available Formats
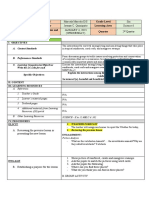
TEACHING SCIENCE
in the ELEMENTARY GRADES
(Biology and Chemistry)
MODULE 4
AGUILAR ERIKA M. BEED II-A
ACTIVATE
Activity A.1
Recall the best moments you had in your science class. What were you doing? What was your lesson?
Who was your teacher? What made it the best moment?
The best part is that by chance me and my partner did it right in the first time even we didn't knew how
we expected ourselves in the third category but mam took our flask up and showed the class that this is
how colour is supposed to be!! So a EUREKA moment! Needless to say we were helping our friends after
that without having the proper clue how we did it ourselves! One of my favourites is from bio lab. One
day lazily I was just seeing the specimens(preserved dead bodies of animals like frog fish earthworm etc.
and absentmindedly started singing really low but still somehow some saw it and he shouted — Sakshi is
talking to the specimens!! (embarrassing) Apart from this every experiment done ,every gossip told ,to
every broken appratus that we used to hide, to some of the flirty lab partners everything was fun and I
miss it a lot!
ANALYZE
Activity B.1
From the list below, circle the principles of constructivist teaching and learning.
Make it Meaningful 1. Engage the students in the discovery and examination of relevant and meaningful
problems.
Curriculum Organization. 2. Organize the curriculum into activities and broad primary concepts.
Seeing and understanding the world 3. Explore and value the students’ perspective.
Classroom Activities Challenge Student Assumptions 4. Encourage the students to investigate and
challenge their assumptions.
Diagnostic Assessment 5. Use assessment to diagnose and guide the student learning.
Benefits of using flexible groupings 6. The teacher uses multiple forms of assessment and flexible
groupings.
Constructivism is a learning theory 7. Knowledge is shaped by experience.
Constructivism is a learning theory 8. Learning is a personal interpretation of the world.
Kinesthetic learners 9. Learning is solely by doing.
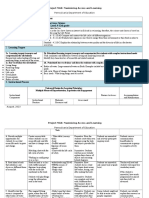
Activity B.2
How does a constructivist classroom look like compared to a traditional classroom? Characterize a
constructivist classroom by completing the list of features in the second column.
Traditional Classroom Constructivist Classroom
Adhere to fixed curriculum Strict adherence to fixed curriculum is highly valued.
Pursuit of student questions and interests is valued.
Teachers have a dialogue with students, helping
students construct their own knowledge. Teacher's role
is directive, rooted in authority.
Textbooks and Workbook Materials include primary sources of material and
manipulative materials.
The instructor gives and the students receive Learning interaction building on what students already
know
Knowledge is inert Knowledge is seen as dynamic, ever changing with our
experiences.
Assessment via paper-and-pen test Assessment via student works observation point of
view, tests.
The instructor assumes authoritative role Instructor interacts/ negotiates with student
The students work individually Knowledge is dynamic/change with experiences.
Students work in groups source
APPLY
Activity D.1
Try out your knowledge and understanding of constructivist teaching strategies by selecting appropriate
strategies that will complete the table of alignment below. Make sure that the teaching strategies match
the target topic and competencies.
Topics Competencies Constructivist Teaching Strategies
Characteristics of solids, liquids, and Describe the different objects based Solids have a definite shape and
gases. on their characteristics (e.g., shape, volume. Liquids have a definite
weight, volume, ease of flow) volume, but take the shape of the
container. Gases have no definite
shape or volume.
Human sense organs Enumerate healthful habits to The human sense organs contain
protect the sense organs receptors that relay information
through sensory neurons to the
appropriate places within the
nervous system. Each sense organ
contains different receptors.
Animal Describe animals in their immediate The environment in which an animal
surroundings lives is referred to as its habitat. A
habitat includes both biotic (living)
and abiotic (non-living) components
of the animal's environment.
Plants Describe ways of caring and proper Stick your finger in the soil up to
handling of plants your 2nd knuckle to see how wet it
is; if your finger comes back dry, you
need to water your plant.
Always use warm water for your
plants, as cold water can shock the
roots and cause damage to the
plant.
Give your plants a deep watering
about once a month.
Ecosystems Explain the need to protect and Don't dump your trash overboard;
conserve estuaries and dispose of properly and recycle.
intertidal zones. Maintain your boats to reduce oil
leaks.
Keep your boat or motorized
watercraft out of sensitive areas like
seagrass beds.
Install and maintain marine
sanitation devices on your boat.
Use designated pumpout stations.
Humans Describe the changes that occur Their bodies increase in size and
during puberty shape during puberty. Their hips
become more rounded and they get
a more defined waist. The vulva,
vagina and nipples get bigger and
the breasts begin to develop,
sometimes unevenly.
Activity D.2
How would you like to be taught in science?
1. Ask your colleagues the same question and tabulate your answers.
• What are the challenges of online classroom management?
Online teaching platforms are equipped with different facilities to enable teachers and students to make
the best use of the learning environment. These classes are more flexible and convenient. It MIGHT
promote life-long learning and computer literacy as well. Additionally, you can save a lot of money by
participating in online classes.
HOWEVER, it is not without problems. It can be difficult for the instructors to monitor students' behavior
and check their contribution and progress. It may create a sense of isolation in my opinion. This image
tell the story:
" In an online course, no one can hear you scream. And that causes discomfort for some online students.
Studying alone with only the computer as your companion can be terrifying. There's no whispering in
the back of the room, no wise remarks from the peanut gallery, no commanding presence at the front of
the classroom pleading for everyone to listen
2. Find out patterns and themes.
• A theme is generated when similar issues and ideas expressed by participants within qualitative data
are brought together by the researcher into a single category or cluster.
• Thematic analysis is a method of analyzing qualitative data. It is usually applied to a set of texts, such
as interview transcripts. The researcher closely examines the data to identify common themes topics,
ideas and patterns of meaning that come up repeatedly.
3. Categorize your response as constructivist or non-constructivist teaching and
learning approaches.
• Constructivist teaching is based on the belief that learning occurs as learners are actively involved in a
process of meaning and knowledge construction rather than passively receiving information. Learners
are the makers of meaning and knowledge. Constructivist teaching fosters critical thinking and creates
motivated and independent learners. This report examines constructivist teaching and learning by
looking at the distinctive features of a constructivist programme, the qualities of a constructivist
teacher, and the organization of a constructivist classroom. A constructivist teacher and classroom differ
from a traditional classroom in a number of ways: the learners are interactive and student-centered;
and the teacher facilitates a process of learning in which students are encouraged to be responsible and
autonomous. Part One of this report provides a definition of an a rationale for constructivist teaching.
Part Two examines the characteristic features of a constructivist classroom interweaving the research
literature on constructivist teaching with the narrated experiences of a practising constructivist teacher.
Part Three presents a discussion of the professional development of a constructivist teacher. Part Four
considers implications of and possibilities for this research on constructivist teaching and suggests
recommendations for schools, colleges and school boards.
4. Come up with your personal definition of constructivist teaching.
• Constructivist teaching is based on the belief that learning occurs as learners are actively involved in a
process of meaning and knowledge construction rather than passively receiving information.
Constructivist teaching fosters critical thinking and creates motivated and independent learners.
EVALUATE
Write a brief reflection. Consider the following questions.
1. Are there downfalls in using constructivist teaching approach? Explain your answer.
One of the biggest disadvantages of constructivism is that the learner may be hampered by
contextualising learning in that, at least initially, they may not be able to form abstractions and transfer
knowledge and skills in new situations (Merrill, 1991) In other words, there is often, during the initial
stage.
2. When does constructivist teaching strategy work best?
• Consequences of constructivist theory are that: Students learn best when engaged in learning
experiences rather passively receiving information. Learning is inherently a social process because it is
embedded within a social context as students and teachers work together to build knowledge.
You might also like
- Module 4 Teaching ScienceDocument6 pagesModule 4 Teaching ScienceErika AguilarNo ratings yet
- COT2DLLDocument3 pagesCOT2DLLCecille Muñasque Dela Victoria100% (1)
- Curriculum Guide: Instructional PlanningDocument10 pagesCurriculum Guide: Instructional PlanningMerce Tojino ManigosNo ratings yet
- The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofDocument3 pagesThe Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofJeffrey Selpo BondadNo ratings yet
- Coyle CLIL Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesCoyle CLIL Lesson PlanEsther Simpson100% (2)
- Co2 RickyDocument3 pagesCo2 RickyRitz De Vera PuquizNo ratings yet
- Science 3 LP NOV. - DEC. 2019Document15 pagesScience 3 LP NOV. - DEC. 2019CAthh TherineeNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log Ready ReadyyDocument4 pagesDaily Lesson Log Ready ReadyyPrincess De VegaNo ratings yet
- DLP in Science 3 - 4 Q2 WK 3 ValidatedDocument12 pagesDLP in Science 3 - 4 Q2 WK 3 ValidatedSalve Serrano100% (1)
- Activity 2: General Biology 2 (Quarter IV-Week 3)Document4 pagesActivity 2: General Biology 2 (Quarter IV-Week 3)KatsumiJ AkiNo ratings yet
- Elm 570 - Benchmark Science Unit PlanDocument18 pagesElm 570 - Benchmark Science Unit Planapi-552613705No ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson PlanDencie CabarlesNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledAqila SalimNo ratings yet
- Living Orn and Their Surroundings - 8th Nov To 16th Nov 22 DLPDocument6 pagesLiving Orn and Their Surroundings - 8th Nov To 16th Nov 22 DLPManasa PriyankaNo ratings yet
- The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofDocument3 pagesThe Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofJeffrey Selpo Bondad100% (1)
- Instruction and Assessment - Unit Plan 2nd Grade ScienceDocument10 pagesInstruction and Assessment - Unit Plan 2nd Grade Scienceapi-607137850No ratings yet
- Co TeachingDocument8 pagesCo Teachingapi-508424314No ratings yet
- Hoelzel Educ 230 Lesson Plan 1Document6 pagesHoelzel Educ 230 Lesson Plan 1api-549300278No ratings yet
- DLL Science Math Filipino Mapeh4 q2 w5Document16 pagesDLL Science Math Filipino Mapeh4 q2 w5Jess Amiel D. TapangNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log: Types-Of-Biodiversity/30141Document7 pagesDaily Lesson Log: Types-Of-Biodiversity/30141Noreenzel Joy VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work Science Stage 7Document90 pagesScheme of Work Science Stage 7Arjun Srinivasan100% (1)
- COT 4 Science FinalDocument7 pagesCOT 4 Science FinalMLG F100% (1)
- DLL - Science 4 - Q2 - W4Document9 pagesDLL - Science 4 - Q2 - W4FredjayEdillonSalocotNo ratings yet
- Asle 1 - Writing Objectives (Constructive Alignment)Document8 pagesAsle 1 - Writing Objectives (Constructive Alignment)523002325No ratings yet
- Habitat Investigations: Year 1 - ScienceDocument29 pagesHabitat Investigations: Year 1 - ScienceThủy Đậu ThuNo ratings yet
- RPT SN Y1Document8 pagesRPT SN Y1K Vinmalar SaravananNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Sa GoogleDocument10 pagesLesson Plan Sa GoogleRegie G. GalangNo ratings yet
- Class 6 Lesson Plan LivingDocument10 pagesClass 6 Lesson Plan LivingHIRAL SOLANKINo ratings yet
- S7LT IIh 10 - ECOLOGICAL RELATIONSHIPS CAYMEDocument17 pagesS7LT IIh 10 - ECOLOGICAL RELATIONSHIPS CAYMEMonica P. Ramos100% (1)
- SDLP-DAY - Eco-Bio 1Document7 pagesSDLP-DAY - Eco-Bio 1Jessica SudioNo ratings yet
- Simplified Melc-Based Budget of Lesson in Science-4Document5 pagesSimplified Melc-Based Budget of Lesson in Science-4Beverly Jane Glino AzuraNo ratings yet
- About The Unit: Unit 7C Environment and Feeding RelationshipsDocument8 pagesAbout The Unit: Unit 7C Environment and Feeding RelationshipsAnonymous tc7XPINo ratings yet
- Stephanie Good & Cathy HarronDocument23 pagesStephanie Good & Cathy HarronShoy WNo ratings yet
- EED2601 Assignment 04Document12 pagesEED2601 Assignment 04wandywandy938No ratings yet
- Final Demo Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesFinal Demo Lesson PlanClenchtone CelizNo ratings yet
- DLL 9Document5 pagesDLL 9Jonathan TabbunNo ratings yet
- MharDocument9 pagesMharRhie VillarozaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Mapping Science 6 Prepared By: Kenneth Feliciano: Grade 6 - Matter First Quarter/First Grading PeriodDocument4 pagesCurriculum Mapping Science 6 Prepared By: Kenneth Feliciano: Grade 6 - Matter First Quarter/First Grading PeriodlouisNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and StabilityDocument8 pagesBiodiversity and StabilityChrisa C. TabiliranNo ratings yet
- Animals k-2 Fbtips Deep OceanDocument2 pagesAnimals k-2 Fbtips Deep OceanFox XinNo ratings yet
- Biotech8 DLL October 10Document4 pagesBiotech8 DLL October 10ART JOSHUA MARANo ratings yet
- Activity and Assessment Plan: Name: Grade Level NGSS Performance Expectation: 2-LS4-1Document5 pagesActivity and Assessment Plan: Name: Grade Level NGSS Performance Expectation: 2-LS4-1api-506353226No ratings yet
- Jenny 2fashlyn 2fryan CT Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesJenny 2fashlyn 2fryan CT Lesson Planapi-405892620No ratings yet
- W5-DLL 2-Els-Jan 4-5 2023Document12 pagesW5-DLL 2-Els-Jan 4-5 2023Anne RiveroNo ratings yet
- Updated COT 1-11-26-2021 - Manuel Santos Lesson ExemplarDocument6 pagesUpdated COT 1-11-26-2021 - Manuel Santos Lesson ExemplarMICHAEL ANORANo ratings yet
- DLP Science 6Document11 pagesDLP Science 6lndnslmnNo ratings yet
- Name: Instructor: Subject:: Activity 1Document2 pagesName: Instructor: Subject:: Activity 1JU LSNo ratings yet
- Standards-Aligned Unit Planning Process: 1. Unit Overview Content Area: Science Grade Level: 9-12th GradeDocument5 pagesStandards-Aligned Unit Planning Process: 1. Unit Overview Content Area: Science Grade Level: 9-12th Gradeapi-339285106No ratings yet
- 5E Lesson Plan: Topic: Grade Level: Logistics InformationDocument2 pages5E Lesson Plan: Topic: Grade Level: Logistics InformationTracy Johnson-GauffNo ratings yet
- DLP Science 6 Q2 W2 Day 5Document5 pagesDLP Science 6 Q2 W2 Day 5Rubie Jane Aranda100% (1)
- B7 Sci WK5 PDFDocument4 pagesB7 Sci WK5 PDFDerick DadzieNo ratings yet
- Gr0.Kpa Lesson1cDocument19 pagesGr0.Kpa Lesson1ceffiongpatience07No ratings yet
- Cmap Science 9Document3 pagesCmap Science 9Zharina Ann EstavilloNo ratings yet
- DLL Science 2Q WK5Document4 pagesDLL Science 2Q WK5MalynNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 4 - Q2 - W3Document8 pagesDLL - Science 4 - Q2 - W3Judy Mae LacsonNo ratings yet
- Field Study 1Document32 pagesField Study 1guillermo desaculaNo ratings yet
- Year 5 MYP End-of-Unit 1 ReflectionDocument2 pagesYear 5 MYP End-of-Unit 1 Reflectionmmoghrabi.hananNo ratings yet
- W5-DLL 2-Els-Jan 9 2023Document11 pagesW5-DLL 2-Els-Jan 9 2023Anne RiveroNo ratings yet
- Q2 DLL Science Sep 2-6Document4 pagesQ2 DLL Science Sep 2-6Florecita CabañogNo ratings yet
- Gravity and Friction-LpDocument7 pagesGravity and Friction-LpErika AguilarNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Soil Erosion-Lp-BeedDocument10 pagesFactors Affecting Soil Erosion-Lp-BeedErika AguilarNo ratings yet
- Examine The Characteristics of Rocks-LpDocument17 pagesExamine The Characteristics of Rocks-LpErika AguilarNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 5 I - Objectives A. Content StandardsDocument10 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 5 I - Objectives A. Content StandardsErika AguilarNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 4 Module 14Document3 pagesProf Ed 4 Module 14Erika AguilarNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Content & PedagogyDocument5 pagesModule 3 Content & PedagogyErika AguilarNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Teaching ProfessionDocument6 pagesModule 3 Teaching ProfessionErika AguilarNo ratings yet
- Teaching Science in The Elementary Grades (Biology & Chemistry) Module 1Document5 pagesTeaching Science in The Elementary Grades (Biology & Chemistry) Module 1Erika AguilarNo ratings yet
- Teaching Science in The Elementary Grades (Biology and Chemistry) MODULE 3Document5 pagesTeaching Science in The Elementary Grades (Biology and Chemistry) MODULE 3Erika AguilarNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Teaching MathematicsDocument8 pagesModule 3 Teaching MathematicsErika AguilarNo ratings yet
- 1939 - Hammer - Terrain Corrections For Gravimeter StationsDocument11 pages1939 - Hammer - Terrain Corrections For Gravimeter Stationslinapgeo09100% (1)
- Auditing BasicsDocument197 pagesAuditing BasicsMajanja AsheryNo ratings yet
- T HR El 20003 ST PDFDocument20 pagesT HR El 20003 ST PDFAngling Dharma100% (1)
- Differentiating Language Difference and Language Disorder - Information For Teachers Working With English Language Learners in The Schools PDFDocument23 pagesDifferentiating Language Difference and Language Disorder - Information For Teachers Working With English Language Learners in The Schools PDFIqra HassanNo ratings yet
- Iso 16232 10 2007 en PDFDocument8 pagesIso 16232 10 2007 en PDFyağmurNo ratings yet
- Wapda CSR 2013 Zone 3Document245 pagesWapda CSR 2013 Zone 3Naveed Shaheen91% (11)
- Test Bank Bank For Advanced Accounting 1 E by Bline 382235889 Test Bank Bank For Advanced Accounting 1 E by BlineDocument31 pagesTest Bank Bank For Advanced Accounting 1 E by Bline 382235889 Test Bank Bank For Advanced Accounting 1 E by BlineDe GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Climate Declaration: For White Corex PlasterboardDocument1 pageClimate Declaration: For White Corex PlasterboardAbdullah BeckerNo ratings yet
- Safe Motherhood Ao2016-0035 Quality Antenatal Care PDFDocument9 pagesSafe Motherhood Ao2016-0035 Quality Antenatal Care PDFGa B B OrlonganNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Math Lesson 22: Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials Learning GuideDocument4 pagesGrade 7 Math Lesson 22: Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials Learning GuideKez MaxNo ratings yet
- Alumni Homecoming ScriptDocument2 pagesAlumni Homecoming ScriptMeliza Casipit100% (1)
- The FlyDocument8 pagesThe FlyDrei Tiam Lacadin100% (1)
- Isp List MatiurDocument3 pagesIsp List Matiurmatiur7No ratings yet
- Soal PTS Vii BigDocument6 pagesSoal PTS Vii Bigdimas awe100% (1)
- Roles of Community Health NursingDocument2 pagesRoles of Community Health Nursingdy kimNo ratings yet
- AA1 Adventure Anthology One r14Document85 pagesAA1 Adventure Anthology One r14dachda100% (1)
- This Study Resource Was: MCV4U Exam ReviewDocument9 pagesThis Study Resource Was: MCV4U Exam ReviewNathan WaltonNo ratings yet
- თინათინ ზურაბიშვილი, თვისებრივი მეთოდებიDocument111 pagesთინათინ ზურაბიშვილი, თვისებრივი მეთოდებიNino LomaiaNo ratings yet
- Automatic Tools For High Availability in Postgresql: Camilo Andrés EcheverriDocument9 pagesAutomatic Tools For High Availability in Postgresql: Camilo Andrés EcheverriRegistro PersonalNo ratings yet
- Answer KeyDocument4 pagesAnswer KeyLouina YnciertoNo ratings yet
- Pemisah ZirconDocument10 pagesPemisah ZirconLorie Banka100% (1)
- Happiest Refugee Coursework 2013Document10 pagesHappiest Refugee Coursework 2013malcrowe100% (2)
- Dell Inspiron 5547 15Document7 pagesDell Inspiron 5547 15Kiti HowaitoNo ratings yet
- Store Docket - Wood PeckerDocument89 pagesStore Docket - Wood PeckerRakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Branch & Category Wise Opening & Closing Rank of JEE (Main) 2019Document46 pagesBranch & Category Wise Opening & Closing Rank of JEE (Main) 2019soni dwivediNo ratings yet
- Instructional Decision MakingDocument5 pagesInstructional Decision Makingapi-257693907No ratings yet
- Adel Lock ManualDocument1 pageAdel Lock Manual24245677843No ratings yet
- Manual Daily Calorie Log: MyfitnesspalDocument4 pagesManual Daily Calorie Log: MyfitnesspalAzariah Burnside100% (2)
- Root End Filling MaterialsDocument9 pagesRoot End Filling MaterialsRuchi ShahNo ratings yet