Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FIDP Earth Sci
Uploaded by
Chermie Grace BataraOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FIDP Earth Sci
Uploaded by
Chermie Grace BataraCopyright:
Available Formats
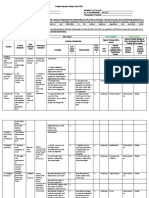
FLEXIBLE INSTRUCTION DELIVERY PLAN (FIDP) - EARTH SCIENCE
Grade: 11/12 Semester: 1st/2nd
Core Subject Title: Earth & Life Science No of Hours/ Semester: 80
Prerequisites if needed:
Core Subject Description: This learning area is designed to provide a general background for the understanding of Earth Science and Biology. It presents the history of the Earth through geologic time. It discusses the Earth’s
structure, composition, and processes. Issues, concerns, and problems pertaining to natural hazards are also included. It also deals with the basic principles and processes in the study of biology. It covers life processes and
interactions at the cellular, organism, population, and ecosystem levels.
Culminating Performance Standard: Conduct a survey to assess possible geological and hydrometeorological hazards that the community may experience.
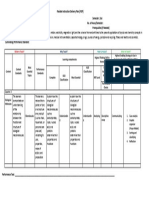
What to Teach? Why Teach? How To Assess? How to Teach?
Highest Enabling Strategy to Use in
Learning Competencies Highest Thinking Skill to Assess Developing the Highest Thingking Skill to
Content Most Essential Performance KUD KUD Flexible Assessment Enabling General Flexible Learning
Content Standards Topics Standards Complete Classific Most Essential Classific RBT Level Performance Strategy Strategies (FLS)
First Quarter
The learners
I. ORIGIN AND Conduct a survey to 1. state the different hypotheses K
demonstrate an assess the possible 2. describe the different hypotheses U
understanding of: geologic/ Hydro- 3. Recognize the uniqueness of Earth, Recognize the
meteorological being the only planet in the solar uniqueness of Earth,
1. the formation hazards that their system with properties necessary to being the only
A. Universe Universe and Online & Offline:
of the community may support life; planet in the solar Online & Offline:
and Solar Solar System U U Ana Essay (situational Communication
universe and the experience system with Document Analysis
System analysis)
solar properties
system; necessary to
support life.
4. explain the current advancements/ K
2. the subsystems 5. explain that the Earth consists of U Explain that the U Ana Online & Offline: Communication Online: Interactive
(geosphere, 6. show the contributions of K
B. Earth and Earth and Earth
hydrosphere, 7. identify the layers of the Earth K
Earth Systems Systems
atmosphere, 8. differentiate the layers of the Earth
U
and biosphere)
II. EARTH 1. the three main 1. classify rocks into igneous, Classify rocks into
MATERIALS categories of sedimentary, and metamorphic U igneous, U Ana Communication Online: Interactive
AND rocks sedimentary, and
Online: Kahoot and Game (discussion) via
PROCESSES metamorphic
Rock Profiling (PC)/ Kahoot
Minerals and Quiz Offline: Picture
Rocks Offline: Picture Analysis (4pics1word)
Analysis with Guide Questions
(Essay/Worksheet) and Discussion in
Modules
Online: Interactive
Online: Kahoot and Game (discussion) via
2. the origin and 2. identify common rock-forming Identify common Rock Profiling (PC)/ Kahoot
environment of Minerals and minerals using their physical and rock-forming Quiz Offline: Picture
formation of Rocks chemical properties minerals using their Offline: Picture Analysis (4pics1word)
common minerals physical and Analysis with Guide Questions
A. Minerals K K Rem Representation
and rocks chemical properties. (Essay/Worksheet) and Discussion in
and Rocks Modules
3. geologic 3. describe how rocks undergo
U
processes that weathering
occur on the 4. explain how the products of explain how the
surface of the weathering are carried away by products of Online: Buzz group
Earth such as erosion and deposited elsewhere weathering are Online & Offline:
article analysis
B. Exogenic Exogenic U carried away by U Ana Essay (situational Communication
weathering, Offline: concept
Processes Processes erosion and analysis)
erosion, mass mapping
wasting, and deposited elsewhere
sedimentation
5. make a report on how rocks and
(include the role U
soil move downslope due to the direct
of ocean basins in
action of gravity
the
4. geologic 6. describe where the Earth’s internal Describe where the Essay
processes that heat comes from. U Earth’s internal heat U Ana (Video Analysis) Communication Sharing of Thoughts
occur within the comes
Earth from.
describe how
Essay (Video
7. describe how magma is formed U magma is formed U Ana Communication Think-pair-share
analysis)
(magmatism) (magmatism)
8. describe what happens after the
magma is formed (plutonism and U
volcanism)
5. the folding and 9. describe the changes in mineral describe changes in
faulting of rocks components and texture of rocks due mineral components
C. Endogenic Endogenic to changes in pressure and and texture of rocks
temperature (metamorphism) due to changes in Essay (Video
Processes Processes U U Ana Communication Case Study
pressure and analysis)
temperature
(metamorphism)
10. compare and contrast the compare and
formation of the different types of contrast the
igneous rocks U formation of the U Ana Essay (Venn diagram) Communication Venn diagram
different types of
igneous rocks
11. describe how rocks behave under -
different types of stress such as U
compression, pulling apart, and
shearing
U
12. explain how the continents drift
13. cite evidence that support
K
continental drift
14. explain how the movement of explain how the
D. plates leads to the formation of folds movement of plates
Deformation of leads to the
Deformation 6. Plate Tectonics and faults U U Ana Written Report Communication Small Group Discussion
the Earth’s Crust formation of folds
of the Crust
and faults
U
15. explain how the seafloor spreads
16. describe the structure and
U
evolution of ocean basins
7. how the planet 17. describe how layers of rocks
earth evolved in the (stratified rocks) are formed describe how layers Group Report/ Online and Offline
U U Ana Communication
last 4.6 billion years of rocks (stratified presentation Jigsaw
(including the age rocks) are formed
of the earth, major 18. describe the different methods Online
geologic time describe the Picture Analysis
(relative and absolute dating) to Group Report
subdivisions, and different methods through Small Group
determine the age of stratified rocks (Analysis of
marker fossils) U (relative and U Ana Communication Discussion
absolute dating) to information)/
Offline
determine the age presentation
Picture analysis
of stratified rocks through worksheet
19. explain how relative and absolute Online
explain how relative Picture Analysis
dating were used to determine the Group Report
E. History of History of the and absolute dating through Small Group
subdivisions of geologic time (Analysis of
the Earth Earth U were used to U Ana Communication Discussion
determine the Information)/
Offline
subdivisions of presentation
Picture analysis
geologic time through worksheet
20. describe how marker fossils (also
known as guide fossils) are used to
define and identify subdivisions of the U
geologic time scale
describe how the
Earth’s history can Online and Offline
21. describe how the Earth’s history be interpreted from Worksheet/ Short
K K U Representation Constructing a Scaled
can be interpreted from the geologic the geologic time Response Essay
Geologic Time Table
time scale scale
III. NATURAL demonstrate an Geologic Conduct a survey to 1. describe the
HAZARDS, understanding Processes and assess the possible various hazards that
1. describe the various hazards that
MITIGATION, of: Hazards geologic/ may happen in the
may happen in the event of Online and Offline Online and Offline
AND Hydro- U event of U Ana Communication
earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and Case Study Analysis Situational Analysis
ADAPTATION 1. the different meteorological earthquakes,
landslides
hazards hazards that their volcanic eruptions,
caused by community may and landslides
geological experience 2. using hazard
processes maps, identify areas
2. using hazard maps, identify areas
(earthquakes, prone to hazards
prone to hazards brought about by Online and Offline Online and Offline
volcanic U brought about by U App Connections
earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and Case Study Analysis Hazard Map Analysis
eruptions, and earthquakes,
landslides
landslides) volcanic eruptions,
and landslides
3. give practical ways of coping with
geological hazards caused by
U
earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and
landslides
3. identify human Online Virtual Tool
4. identify human activities that speed activities that speed Online and Offline (using Google Maps)
K K U Representation
up or trigger landslides up or trigger Case Study Analysis Offline Gallery Walk
landslides (using Pictures)
5. suggest ways to help lessen the
occurrence of landslides in your U
community
2. the different Hydro- 4. describe the
hazards meteorological various hazards that
caused by Phenomena and 6. describe the various hazards that
may happen in the Online and Offline Online and Offline
hydro- Hazards may happen in the wake of tropical U U Ana Communication
wake of tropical Case Study Analysis Situational Analysis
meteorological cyclones, monsoons, floods, or ipo-ipo
cyclones, monsoons,
phenomena floods, or ipo-ipo
(tropical
cyclones, 5. using hazard
monsoons, floods maps, identify areas Online Hazard Map
7. using hazard maps, identify areas
and tornadoes or prone to hazards Analysis (using online
prone to hazards brought about by Online and Offline
ipo-ipo) U brought about by U App Connections app) Offline Hazard
tropical cyclones, monsoons, floods, Case Study Analysis
tropical cyclones, Map Analysis (using
or ipo-ipo worksheet)
monsoons, floods,
or ipo-ipo
8. give practical ways of coping with
hydro-meteorological hazards caused
U
by tropical cyclones, monsoons,
floods, or ipo-ipo
5. the different Marine and 6. describe how
Online Situational
hazards Coastal coastal processes Online and Offline
9. describe how coastal processes Analysis (through LMS)
caused by coastal Processes and result in coastal Collaborative
result in coastal erosion, submersion, U U Ana Communication Offline Situational
processes their Effects erosion, Writing and Story
and saltwater intrusion Analysis (through
(waves, tides, submersion, and Making
worksheet)
sea-level saltwater intrusion
7. identify areas in Online Hazard Map
changes, crustal
your community Online Analysis (using online
movement, and 10. identify areas in your community
prone to coastal Collaborative app)
storm surges) prone to coastal erosion, submersion, U U App Connections
erosion, Writing Offline Hazard Map
and saltwater intrusion
submersion, and Offline Story Making Analysis (using
saltwater intrusion worksheet)
11. give practical ways of coping with
coastal erosion, submersion, and U
saltwater intrusion
8. cite ways to
prevent or mitigate
12. cite ways to prevent or mitigate the impact of land
the impact of land development, development, waste
Online and Offline Online and Offline
waste disposal, and construction of U disposal, and U Eval Reasoning and Proof
Written Report Case Study Analysis
structures on control coastal construction of
processes structures on
control coastal
processes
Performance Task: The learners will construct an action plan containing a checklist of environmental concerns in a barangay and use these to create a series of mitigation measures for the community to address these environmental problems.
You might also like
- FIDP Earth and Life ScienceDocument10 pagesFIDP Earth and Life ScienceTeacher MelNo ratings yet
- Earth Sci Fidp (g11)Document8 pagesEarth Sci Fidp (g11)arvie lucesNo ratings yet
- The Learners Demonstr Ate An Understan Ding Of: The Learners Shall Be Able To: The LearnersDocument6 pagesThe Learners Demonstr Ate An Understan Ding Of: The Learners Shall Be Able To: The LearnersModelyn PerezNo ratings yet
- The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding Of: The Learners Shall Be Able To: The Learners: The LearnersDocument2 pagesThe Learners Demonstrate An Understanding Of: The Learners Shall Be Able To: The Learners: The LearnersFerdinand GarciaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map - g11 Earth and Life ScienceDocument8 pagesCurriculum Map - g11 Earth and Life ScienceJoke Jo100% (1)
- Earth and Life Science CIDAM 2019Document9 pagesEarth and Life Science CIDAM 2019Jantaloy0% (1)
- GEN PHYSICS 1 FIDP (Q1 and Q2)Document8 pagesGEN PHYSICS 1 FIDP (Q1 and Q2)Crisanta Ganado67% (3)
- Diary Curriculum Map Subject: Science Grade Level: 7 Teacher: Jeremieh Jan M.CorpuzDocument15 pagesDiary Curriculum Map Subject: Science Grade Level: 7 Teacher: Jeremieh Jan M.CorpuzDixie M AgregadoNo ratings yet
- 1st Sem Fidp Gen Chem EditedDocument6 pages1st Sem Fidp Gen Chem EditedMarielle Alystra100% (1)
- Science 10 - Curriculum MapDocument67 pagesScience 10 - Curriculum MapArjay BejisonNo ratings yet
- Fidp Earth Sci OnlyDocument5 pagesFidp Earth Sci Onlyjayson babaranNo ratings yet
- Mechanics and Free Fall - FIDPDocument4 pagesMechanics and Free Fall - FIDPAustin Capal Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan EARTH SCIENCEDocument5 pagesFlexible Instruction Delivery Plan EARTH SCIENCEREHANA ZAINUDINNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map G10 ScienceDocument7 pagesCurriculum Map G10 ScienceReynald AntasoNo ratings yet
- Disaster Readiness and Risk Reduction: CvcitcDocument13 pagesDisaster Readiness and Risk Reduction: CvcitcYzlle De Jesus EbreoNo ratings yet
- Q2 - Earth and Life ScienceDocument6 pagesQ2 - Earth and Life Sciencejessica ignacioNo ratings yet
- 7regsci Group5 4scaffoldDocument2 pages7regsci Group5 4scaffoldUwoonh EstraelNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science VIDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science VIJanice DomingoNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science ACID PlanDocument9 pagesEarth and Life Science ACID PlanHendrix Antonni Amante100% (3)
- Calendar of Lab ActivitiesDocument24 pagesCalendar of Lab ActivitiesMiss FaithNo ratings yet
- 2 Science 8 Curriculum MapDocument2 pages2 Science 8 Curriculum MapMayumie RelataNo ratings yet
- CM SCIENCE 9 3rd QuarterDocument7 pagesCM SCIENCE 9 3rd QuarterJenny Acosta Catacutan100% (1)
- Learning Plan For Peacscience8decDocument3 pagesLearning Plan For Peacscience8decMaam Elle CruzNo ratings yet
- Santiago Trillana Academy Inc.: Learning Plan in Science 10Document2 pagesSantiago Trillana Academy Inc.: Learning Plan in Science 10Glenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- Performance Task in Earth Science-2nd QuarterDocument2 pagesPerformance Task in Earth Science-2nd QuarterKarylle DeniseNo ratings yet
- Scaffold For TransferDocument3 pagesScaffold For TransferJogili Paragua100% (1)
- Sen. Gil Puyat National High School: Email AddDocument5 pagesSen. Gil Puyat National High School: Email AddRaymond BugagaoNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map: Northwestern Agusan Colleges Bayview Hill, Nasipit, Agusan Del NorteDocument2 pagesCurriculum Map: Northwestern Agusan Colleges Bayview Hill, Nasipit, Agusan Del Nortejoy100% (1)
- Curriculum Map: Archdiocesan Notre Dame School of Cotabato Notre Dame of Masiag, IncDocument5 pagesCurriculum Map: Archdiocesan Notre Dame School of Cotabato Notre Dame of Masiag, IncrichardsamranoNo ratings yet
- TOS Gen Physics 1 Second Quarter RAWDocument4 pagesTOS Gen Physics 1 Second Quarter RAWGenesis NgNo ratings yet
- Finaljunior Ecological RelationshipDocument8 pagesFinaljunior Ecological RelationshipBriansky HanNo ratings yet
- PEAC CIDAM Template 2019 Earth ScienceDocument10 pagesPEAC CIDAM Template 2019 Earth ScienceJaruay Celeridad100% (1)
- 2020-SAC SHS FIDP Final - Earth and Life ScienceDocument17 pages2020-SAC SHS FIDP Final - Earth and Life ScienceZerille Anne Inson Agregado100% (1)
- Subject: SCIENCE August-October: Grade Level: 10Document3 pagesSubject: SCIENCE August-October: Grade Level: 10Patrick BaleNo ratings yet
- KUD Class Ifi-Catio N RBT Level WW QA PCDocument2 pagesKUD Class Ifi-Catio N RBT Level WW QA PCFany Fabia100% (1)
- OBTL Chemistry I G12 STEMDocument8 pagesOBTL Chemistry I G12 STEMCelestial Lacambra50% (2)
- Quarter 1 Lesson 1Document3 pagesQuarter 1 Lesson 1Lester EstoquiaNo ratings yet
- Science 7 - Cur - Map.Document7 pagesScience 7 - Cur - Map.Marl Rina EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- CIDAM Group 1 Origin and Subsystem of The Earth (FINAL)Document12 pagesCIDAM Group 1 Origin and Subsystem of The Earth (FINAL)Venoc Hosmillo0% (1)
- Unit Unpacking Diagram Grade 9 Quarter 4 Araling Panlipunan: Mga Sektor NG EkonomiyaDocument1 pageUnit Unpacking Diagram Grade 9 Quarter 4 Araling Panlipunan: Mga Sektor NG EkonomiyaKrex AncenoNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map ScienceDocument3 pagesCurriculum Map ScienceJenefer Aguirre Roldan SonNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map SCIENCE 10Document5 pagesCurriculum Map SCIENCE 10Teacher MelNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Curriculum MapDocument2 pagesScience 10 Curriculum MapDxtr Talens100% (1)
- Q2 Module 14 Lesson 9 10Document8 pagesQ2 Module 14 Lesson 9 10RavenNo ratings yet
- FCAAM TemplateDocument4 pagesFCAAM TemplateCatherine Joy Zamora50% (2)
- Gen Phy 1 Quarter 1 Week 2Document5 pagesGen Phy 1 Quarter 1 Week 2Heidi Yutuc100% (2)
- DLL Physical ScienceDocument9 pagesDLL Physical ScienceTOt's VinNo ratings yet
- Q1 Sci8 CmapDocument12 pagesQ1 Sci8 CmapDevie Anne BiscarraNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map G7 ScienceDocument7 pagesCurriculum Map G7 ScienceReynald Antaso100% (1)
- SLRP TemplateDocument3 pagesSLRP TemplateWowie MarianoNo ratings yet
- School Form 8 (SF 8)Document2 pagesSchool Form 8 (SF 8)Geraldo N. QuillaoNo ratings yet
- Shs Daily Lesson in Earth ScienceDocument3 pagesShs Daily Lesson in Earth ScienceCherry MaeNo ratings yet
- GEN CHEMISTRY 1 FIDP (Q1 and Q2)Document11 pagesGEN CHEMISTRY 1 FIDP (Q1 and Q2)Crisanta Ganado100% (1)
- Subject: Science Grade Level: Grade 8 Teacher: Janine G. Ferrer StrandsDocument4 pagesSubject: Science Grade Level: Grade 8 Teacher: Janine G. Ferrer StrandsJanine Ginog Ferrer100% (1)
- DLL July 16 - 19Document3 pagesDLL July 16 - 19Ferna Joy LapinigNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map in Science 7Document1 pageCurriculum Map in Science 7Melerose Dela SernaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules - FIDPDocument1 pageBiomolecules - FIDPAustin Capal Dela Cruz0% (1)
- Earth and Life Science CIDAMDocument15 pagesEarth and Life Science CIDAMAngelicq RamirezNo ratings yet
- Flexible Instructional Delivery PlanDocument5 pagesFlexible Instructional Delivery PlanGerick Dave Monencillo Vender100% (2)
- 15200-Article Text-48581-2-10-20210505Document8 pages15200-Article Text-48581-2-10-20210505NadyaNo ratings yet
- CONTINGENCY PLAN FOR SUPER TYPHOON IN REGION 1 (Draft)Document21 pagesCONTINGENCY PLAN FOR SUPER TYPHOON IN REGION 1 (Draft)NFAR1 ORMNo ratings yet
- Sewerage and Drainage SystemDocument7 pagesSewerage and Drainage Systemanon_328698495No ratings yet
- Thermodynamic in Daily LifeDocument5 pagesThermodynamic in Daily Lifekhairilanuaryusof0% (1)
- MB4BMFMF 65 171818de in 43 VdiDocument3 pagesMB4BMFMF 65 171818de in 43 VdiyogiepNo ratings yet
- U.S. Bridge Failure Listing From Timothy G. Galarnyk CEO of Construction Risk ManagementDocument4 pagesU.S. Bridge Failure Listing From Timothy G. Galarnyk CEO of Construction Risk ManagementSandipan DharNo ratings yet
- DEN323E Week-11Document54 pagesDEN323E Week-11furkannt1453No ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Bangalore North Class - 6 Geography Lesson-2 Globe: Latitudes and Longitudes Question Bank Notebook Question/AnswersDocument3 pagesDelhi Public School Bangalore North Class - 6 Geography Lesson-2 Globe: Latitudes and Longitudes Question Bank Notebook Question/AnswersSumukh MullangiNo ratings yet
- Volvo BusDocument29 pagesVolvo BusGabriel Escarcena RoblesNo ratings yet
- Problems To ReviewDocument2 pagesProblems To ReviewANTHONETTE BERNABENo ratings yet
- Escape From MicroburstDocument4 pagesEscape From MicroburstRoger SacchelliNo ratings yet
- Autumn Grade 2 Comprehension WorksheetDocument2 pagesAutumn Grade 2 Comprehension WorksheetSaquib.MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Operations Manual: Part BDocument392 pagesOperations Manual: Part Bboban100% (1)
- NASA: 65776main Noaa NP MishapDocument113 pagesNASA: 65776main Noaa NP MishapNASAdocumentsNo ratings yet
- Quiz TrendsDocument7 pagesQuiz TrendsArlyn MoyaNo ratings yet
- Barometric PressureDocument3 pagesBarometric Pressureharsha919No ratings yet
- Hurricane Tracking Latitude-Longitude ActivityDocument3 pagesHurricane Tracking Latitude-Longitude ActivityJalyn WilkinsonNo ratings yet
- GSO&NGSODocument17 pagesGSO&NGSOintan yasminNo ratings yet
- Aviation Study - Regulation Miscellaneous Que. Paper - 2Document4 pagesAviation Study - Regulation Miscellaneous Que. Paper - 2parul sharmaNo ratings yet
- Heath's Montessori Learning Center IncDocument2 pagesHeath's Montessori Learning Center IncCris RealNo ratings yet
- Geography of Puerto Rico2Document3 pagesGeography of Puerto Rico2Jonnathan MoyaNo ratings yet
- MGD-GSP-OLV-DPR-024 - 02.10.2020 (Signed)Document3 pagesMGD-GSP-OLV-DPR-024 - 02.10.2020 (Signed)Mircea CaprarNo ratings yet
- Hovercraft To The RescueDocument3 pagesHovercraft To The Rescuehovpod6214No ratings yet
- Earthquake HazardsDocument32 pagesEarthquake HazardsJermer TabonesNo ratings yet
- Mid Rev SolDocument4 pagesMid Rev SolVishnu SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Acc Phu Case NCP HyperthermiaDocument1 pageAcc Phu Case NCP Hyperthermiamacy_bautistaNo ratings yet
- Custom KeysDocument91 pagesCustom KeyseliozuniNo ratings yet
- KarstsDocument1 pageKarstsRoman SionisNo ratings yet
- Schletter Product - Sheets Roof - Systems FixGrid18PlusDocument6 pagesSchletter Product - Sheets Roof - Systems FixGrid18Plusf789sgacanonNo ratings yet
- Memory Flash Card (MFC) Citation CJ4Document88 pagesMemory Flash Card (MFC) Citation CJ4João Paulo M. Pastana100% (3)