Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NPTEL Assignment 4 Directional
Uploaded by
AKSH0211Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NPTEL Assignment 4 Directional
Uploaded by
AKSH0211Copyright:
Available Formats
NPTEL Online Certification Courses
Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur
POWER SYSTEM PROTECTION
Assignment - 4
TYPE OF QUESTION: MCQ
Number of questions: 5 Total marks: 5 X 4 = 20
QUESTION 1:
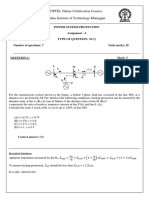
L M N
ES1 ES2
RLM RML RMN RNM
L1 L2 L3
220 kV, 50 Hz transmission system
For the transmission system shown above, line-to-line voltage and line current data measured by the
directional overcurrent relay RMN at bus M for two fault situations are provided in Table – I. Case-1 and case-
2 are two fault cases, phase-b-to-ground and phase-c-to-ground faults respectively, created one at a time in
line LM or MN. Identify the faulted line(s) for Case-1 and Case-2 respectively.
Table-I
For Case-1 For Case-2
Vab: 147.06∠71.740 kV Ia: 0.03∠-82.480 kA Vab: 210.35∠ 84.560 kV Ia: 0.05∠ -176.950 kA
Vbc: 141.76∠-14.63 kV Ib: 0.62∠-141.360 kA
0 Vbc: 156.52∠ -46.72 kV Ib: 0.06∠ 96.240 kA
0
Vca: 210.62∠-150.460 kV Ic: 0.09∠6.400 kA Vca: 159.05∠-143.130 kV Ic: 0.60∠ -85.630 kA
(A) LM, LM
(B) LM, MN
(C) MN, LM
(D) MN, MN
Correct answer: (C)
Detailed Solution:
With quadrature voltage directional relaying principle:
For fault case-1: Operating quantity is Ib and polarizing quantity is Vca
∠Ib – (∠Vca +900) = -80.90
So, Case-1 is a forward fault and the faulted line MN
For fault case2: Operating quantity is Ic and polarizing quantity is Vab
∠Ic – (∠Vab +900) = 99.80
So, case-2 is a fault in reverse direction and the faulted line LM
NPTEL Online Certification Courses
Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur
QUESTION 2:
L M N
ES1 ES2
RLM RML RMN RNM
L1 L2 L3
220 kV, 50 Hz transmission system
For the transmission system shown above, voltage and current data measured by the positive sequence
directional overcurrent relay RMN at bus M for two fault cases are provided in Table – II. Case-1 and case-2
are two cases, phase-b-to-ground and phase-c-to-ground faults respectively, created one at a time in line LM
or MN. Identify the faulted line(s) for Case-1 and Case-2 respectively.
Table-II
For Case-1 For Case-2
0
Va: 30.65∠88.27 kV 0
Ia: 0.70∠-172.73 kA Va: 115.25∠ 71.77 kV
0 Ia: 0.07∠ -94.570 kA
Vb: 30.09∠-29.890 kV Ib: 0.71∠65.140 kA Vb: 59.23∠-92.400 kV Ib: 0.65∠ -102.820 kA
Vc: 31.21∠-149.930 kV Ic: 0.68∠-54.380 kA Vc: 60.46∠-123.730 kV Ic: 0.72∠ 78.040 kA
(A) LM, LM
(B) LM, MN
(C) MN, LM
(D) MN, MN
Correct answer: (B)
Detailed Solution:
With positive sequence directional relaying principle:
For case-1: Operating quantity is I1 and polarizing quantity is V1
I1 and V1 for the situation are calculated as 0.70∠-1740 kA and 30.65∠89.480 kV respectively.
∠I1 – (∠V1) = 96.520
So, case-1 is a reverse fault and the faulted line LM
For fault case-2: Operating quantity is I1 and polarizing quantity is V1
V1 and I1 for the situation are calculated as 0.40∠-17.700 kA and 66.96∠72.090 kV respectively.
∠I1 – (∠V1) = -89.790
So, case-2 is a forward fault and the faulted line MN
NPTEL Online Certification Courses
Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur
QUESTION 3:
L M N
ES1 ES2
RLM RML RMN RNM
L1 L2 L3
220 kV, 50 Hz transmission system
For the transmission system shown above, voltage and current data measured by directional overcurrent relay
RMN at bus M for two fault cases are provided in Table – III. The relays use negative sequence approach for
direction information. Case-1 and case-2 are two cases, phase-b-to-ground and phase-c-to-ground faults
respectively, created one at a time in line LM or MN. Identify the faulted line(s) for case-1 and case-2
respectively.
Table-III
For Case-1 For Case-2
Va: 115.25∠ 71.770 kV Ia: 0.07∠ -94.570 kA Va: 116.53∠ 17.770 kV Ia: 0.3∠21.380 kA
Vb: 59.23∠-92.400 kV Ib: 0.65∠ -102.820 kA Vb: 136∠ -86.04 kV
0 Ib: 0.07∠-76.010 kA
Vc: 60.46∠-123.730 kV Ic: 0.72∠ 78.040 kA Vc: 124.93∠ 157.610 kV Ic: 0.09∠178.680 kA
(A) LM, LM
(B) LM, MN
(C) MN, LM
(D) MN, MN
Correct answer: (D)
Detailed Solution:
With negative sequence directional relaying principle:
For fault case-1: Operating quantity is I2 and polarizing quantity is -V2
I2 and V2 for the situation are calculated as 0.39∠173.100 kA and 48.30∠71.330 kV respectively.
∠I2 – (∠-V2) = -64.430
So, case-1 is a forward fault and the faulted line MN
For fault case-2: Operating quantity is I2 and polarizing quantity is -V2
I2 and V2 for the situation are calculated as 0.09∠11.600 kA and 9.68∠ -79.440 kV respectively.
∠I2 – (∠-V2) = -88.960
So, case-2 is also a forward fault and the faulted line MN
NPTEL Online Certification Courses
Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur
QUESTION 4:
L M N
ES1 ES2
RLM RML RMN RNM
L1 L2 L3
220 kV, 50 Hz transmission system
For the transmission system shown above, voltage and current data measured by the zero sequence directional
overcurrent relay RMN at bus M for a fault case are provided in Table – IV. Select the faulted line for the
situation and also determine the zero sequence current angle with respect to zero sequence voltage.
Table-IV
Va: 128.75∠49.350 kV Ia: 0.05∠ -176.950 kA
Vb: 128.71∠-60.210 kV Ib: 0.06∠ 96.240 kA
Vc: 43.42∠177.020 kV Ic: 0.60∠ -85.630 kA
(A) -850, LM
(B) -850, MN
(C) 850, LM
(D) 850, MN
Correct answer: (A)
Detailed Solution:
I0 and V0 for the situation are calculated as 0.18∠-91.390 kA and 35.03∠-6.430 kV respectively.
∠I0 – (∠V0) = -84.960
With zero sequence directional relaying principle:
Operating quantity is I0 and polarizing quantity is –V0
I0 and V0 for the situation are calculated as 0.39∠173.100 kA and 48.30∠71.330 kV respectively.
∠I0 – (∠-V0) = 95.040
So, the fault is in reverse direction and the faulted line LM
NPTEL Online Certification Courses
Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur
QUESTION 5:
L M N
ES1 ES2
RLM RML RMN RNM
L1 L2 L3
220 kV, 50 Hz transmission system
For the transmission system shown above, voltage and current data measured by the directional overcurrent
relay RMN at bus M for a high resistance fault situation are provided in Table – V. Determine the phase angle
of positive sequence current with respect to positive sequence voltage and identify the faulted line for the
situation using superimposed component based directional relaying principle.
Table-V
During prefault During fault
0 0
Va: 129.61∠100.95 kV Ia: 0.055∠130.68 kA Va: 115.20 ∠87.51 kV
0 Ia: 0.29∠90.910 kA
Vb: 129.40∠-18.030 kV Ib: 0.056∠11.290 kA Vb: 134.78∠-14.700 kV Ib: 0.06∠-2.900 kA
Vc: 131.51∠-138.460 kV Ic: 0.056∠-109.720 kA Vc: 125.64∠-132.350 kV Ic: 0.08∠-108.780 kA
(A) 10, LM
(B) 10, MN
(C) -10, LM
(D) -10, MN
Correct answer: (B)
Detailed Solution:
I1 and V1 for the fault situation are calculated as 0.14∠ 101.640 kA and 123.74∠100.660 kV respectively.
∠I1 – (∠V1) = 0.980
With superimposed component directional relaying principle:
Operating quantity is ∆V1 and polarizing quantity is ∆I1
∆V1 = V1fault - V1pre = 6.68∠-63.010 kV
∆I1 = I1fault - I1pre = 0.09∠84.390 kA
∠∆V1 – ∠∆I1 = -147.40
As superimposed component based directional relaying provides high sensitivity in fault direction
identification for high resistance fault, the fault is in forward direction i.e. in MN line
You might also like
- Answer Key To World English 3 Workbook Reading and Crossword Puzzle ExercisesDocument3 pagesAnswer Key To World English 3 Workbook Reading and Crossword Puzzle Exercisesjuanma2014375% (12)
- Mixing and Agitation 93851 - 10 ADocument19 pagesMixing and Agitation 93851 - 10 Aakarcz6731No ratings yet
- 1.O.C. & S.C. Tests On Single Phase TransformerDocument6 pages1.O.C. & S.C. Tests On Single Phase Transformerchandrakanth100% (3)
- Abb - Ret670Document42 pagesAbb - Ret670Sathya NarayananNo ratings yet
- Hydrogeological Survey and Eia Tor - Karuri BoreholeDocument3 pagesHydrogeological Survey and Eia Tor - Karuri BoreholeMutonga Kitheko100% (1)
- Electrical Circuits LabDocument64 pagesElectrical Circuits LabraveendrababupNo ratings yet
- Type 2 Co Ordination in LV SwitchgearDocument46 pagesType 2 Co Ordination in LV Switchgearkapil100% (4)
- ITMF 2013 07 2 Predl ENUDocument8 pagesITMF 2013 07 2 Predl ENUbcqbaoNo ratings yet
- Better Photography - April 2018 PDFDocument100 pagesBetter Photography - April 2018 PDFPeter100% (1)
- Innovativ and Liabl :: Professional Electronic Control Unit Diagnosis From BoschDocument28 pagesInnovativ and Liabl :: Professional Electronic Control Unit Diagnosis From BoschacairalexNo ratings yet
- Ch06 Allocating Resources To The ProjectDocument55 pagesCh06 Allocating Resources To The ProjectJosh ChamaNo ratings yet
- CT Doubt AnswersDocument4 pagesCT Doubt AnswerssathiyaseelanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Power Systems Transients - 20120920Document38 pagesIntroduction To Power Systems Transients - 20120920bubo28No ratings yet
- Network Analysis & Synthesis (Book)Document218 pagesNetwork Analysis & Synthesis (Book)hayatNo ratings yet
- Participate in Safe Food Handling Practices SITXFSA002 - PowerpointDocument71 pagesParticipate in Safe Food Handling Practices SITXFSA002 - PowerpointJuan Diego Pulgarín Henao100% (2)
- Conveyor Control Using Programmable Logic ControllerDocument7 pagesConveyor Control Using Programmable Logic ControllerWann RexroNo ratings yet
- On-Load Tests: Case Study: (30 Minutes)Document2 pagesOn-Load Tests: Case Study: (30 Minutes)Parameswararao Billa0% (1)
- Electric Vehicles PresentationDocument10 pagesElectric Vehicles PresentationVIBHU CHANDRANSH BHANOT100% (1)
- Week 1 MaterialsDocument101 pagesWeek 1 MaterialsAKSH0211No ratings yet
- NPTEL Assignment 10 RenewableDocument4 pagesNPTEL Assignment 10 RenewableAKSH0211No ratings yet
- End - Term - EE 313 PDFDocument3 pagesEnd - Term - EE 313 PDFHardik AmarwaniNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 11: Pakistan Navy Engineering College (NUST)Document8 pagesExperiment # 11: Pakistan Navy Engineering College (NUST)ovais123No ratings yet
- 3 ExperimentsDocument100 pages3 ExperimentsSaravanan T YNo ratings yet
- Simulation of A Three Phase Inverter: Name H Abdul Manan Reg. # 2015-EE-445 MarksDocument4 pagesSimulation of A Three Phase Inverter: Name H Abdul Manan Reg. # 2015-EE-445 MarksManan IFtikharNo ratings yet
- LAB MANUAL FOR 8 EXPERIMENTS DDocument52 pagesLAB MANUAL FOR 8 EXPERIMENTS D21je0575No ratings yet
- Pe Lab ManualDocument41 pagesPe Lab ManualGopalakrishna Murthy C RNo ratings yet
- M.M. Engineering College - Mullana: Laboratory Manual Practical Experiment Instruction SheetDocument3 pagesM.M. Engineering College - Mullana: Laboratory Manual Practical Experiment Instruction Sheetvj4249No ratings yet
- SPWMDocument21 pagesSPWMamilah qisthiNo ratings yet
- PS Lab Maual 7052 - MasterDocument70 pagesPS Lab Maual 7052 - MasterSunilNo ratings yet
- For Transformer DifferentialDocument2 pagesFor Transformer DifferentialVishnu ShankerNo ratings yet
- Ee694 Power Electronics Lab Manual PDFDocument24 pagesEe694 Power Electronics Lab Manual PDFSabeeh HasnainNo ratings yet
- Engr 2001-Circuits I Lab Laboratory Experiment 2 Voltage and Current Division Reference: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesEngr 2001-Circuits I Lab Laboratory Experiment 2 Voltage and Current Division Reference: ObjectiveJonathan MischNo ratings yet
- See 1302Document201 pagesSee 1302Xiao Wang QingNo ratings yet
- ArcCurrentRecoveryVoltageUHVtransmissionLine PDFDocument7 pagesArcCurrentRecoveryVoltageUHVtransmissionLine PDFYeissonSanabriaNo ratings yet
- Verification of KVL and KCLDocument3 pagesVerification of KVL and KCLVarun Vadluri80% (5)
- An Alternative To Reduce Medium-Voltage Transient Recovery Voltage PeaksDocument6 pagesAn Alternative To Reduce Medium-Voltage Transient Recovery Voltage PeaksHany NassimNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 01: To Verify Kirchhoff's Current Law and Kirchhoff's Voltage Law ForDocument56 pagesExperiment No. 01: To Verify Kirchhoff's Current Law and Kirchhoff's Voltage Law ForKaushik NNo ratings yet
- ECE 2201 Experiment 1 - 4Document13 pagesECE 2201 Experiment 1 - 4Deepak SharmaNo ratings yet
- PEE212 Tut Sheets 1-8 PDFDocument6 pagesPEE212 Tut Sheets 1-8 PDFArash GhumanNo ratings yet
- Transformer AssignmentDocument7 pagesTransformer AssignmentSiphesihle SkweyiyaNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Ferroresonance in 33 KV Distribution Network of PEA ThailandDocument4 pagesCase Study of Ferroresonance in 33 KV Distribution Network of PEA Thailandvoravuth srisomboonsukNo ratings yet
- Parallel Operation of Two Single Phase Transformers: Experiment No: 05Document31 pagesParallel Operation of Two Single Phase Transformers: Experiment No: 05Bhanoth MohanNo ratings yet
- ADE PracticalDocument7 pagesADE PracticalLikith VaddadiNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines IIDocument61 pagesElectrical Machines IIPriya SurvacyNo ratings yet
- Exp07 PDFDocument4 pagesExp07 PDFAhmed AttallaNo ratings yet
- VtfailDocument12 pagesVtfailMohd AlghunimatNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 InelectDocument9 pagesLab 1 InelectRiid CantosNo ratings yet
- Ateneo de Zamboanga University: V V V V V VDocument4 pagesAteneo de Zamboanga University: V V V V V VMargret DequitoNo ratings yet
- Ism LabDocument67 pagesIsm LabpadmavathiNo ratings yet
- Government Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Power Electronics & DrivesDocument18 pagesGovernment Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Power Electronics & DrivesVK DNo ratings yet
- Government Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Power Electronics & DrivesDocument18 pagesGovernment Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Power Electronics & Drivesshashi kumarNo ratings yet
- Electrical Technology Lab: Lab Manual I, Ii SemesterDocument34 pagesElectrical Technology Lab: Lab Manual I, Ii SemesterM.R. FahimNo ratings yet
- EEE ExperimentsDocument27 pagesEEE Experimentspushpak chandra sekharNo ratings yet
- 220KV Line - 2 P444Document5 pages220KV Line - 2 P444JayamkondanNo ratings yet
- Zoom 16Document90 pagesZoom 16ATHAR IQBALNo ratings yet
- Report Lab 1Document15 pagesReport Lab 1Mohd Syamsul Ramli100% (1)
- TechnicalDocument3 pagesTechnicalShubham TomarNo ratings yet
- Parallel Operation of Two Single Phase Transformers: Experiment No: 05Document18 pagesParallel Operation of Two Single Phase Transformers: Experiment No: 05Bhanoth MohanNo ratings yet
- SEEA1501Document215 pagesSEEA1501Samsung TabletNo ratings yet
- E1YM400VS10: Voltage Monitoring in 3-And 1-Phase MainsDocument3 pagesE1YM400VS10: Voltage Monitoring in 3-And 1-Phase Mainsathanas08No ratings yet
- Superposition TheveninDocument4 pagesSuperposition TheveninrahulkrishnapagotiNo ratings yet
- In S Coords Ample CalcDocument36 pagesIn S Coords Ample CalcPankaj ThataiNo ratings yet
- Circuit LabDocument7 pagesCircuit LabBiftu ShibbireNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Reference Values:: Ref Ref, A/ B Nom A/bDocument7 pagesCalculation of Reference Values:: Ref Ref, A/ B Nom A/bTufail AlamNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Double Line Frequency For PWM Rectifier Using Instantaneous Power MethodDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Double Line Frequency For PWM Rectifier Using Instantaneous Power MethodNuradin JemalNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines - Ii Lab Manual Department of Electrical & Electronics EngineeringDocument45 pagesElectrical Machines - Ii Lab Manual Department of Electrical & Electronics EngineeringpragatinareshNo ratings yet
- Fault Location DetectrorDocument20 pagesFault Location DetectrorAung MyatNo ratings yet
- Pràctica 2 Marc Ribot Forns & Oriol Jutglar Soler M12Document19 pagesPràctica 2 Marc Ribot Forns & Oriol Jutglar Soler M12Marc Ribot FornsNo ratings yet
- NPTEL - Assignment - 11 - Travelling WaveDocument6 pagesNPTEL - Assignment - 11 - Travelling WaveAKSH0211No ratings yet
- NPTEL - Assignment - 7 - CT - CVT (Modified)Document4 pagesNPTEL - Assignment - 7 - CT - CVT (Modified)AKSH0211No ratings yet
- NPTEL Assignment 9 Line BusbarDocument5 pagesNPTEL Assignment 9 Line BusbarAKSH0211No ratings yet
- NPTEL Assignment 6 DistanceDocument7 pagesNPTEL Assignment 6 DistanceAKSH0211No ratings yet
- NPTEL Assignment 3 OvercurrentDocument8 pagesNPTEL Assignment 3 OvercurrentAKSH0211No ratings yet
- NPTEL Assignment 1Document10 pagesNPTEL Assignment 1AKSH0211No ratings yet
- NPTEL - Assignment - 2 - Phasor EstimationDocument10 pagesNPTEL - Assignment - 2 - Phasor EstimationAKSH0211No ratings yet
- NPTEL Assignment 0Document15 pagesNPTEL Assignment 0AKSH0211No ratings yet
- aPP123 PDFDocument1 pageaPP123 PDFAKSH0211No ratings yet
- 8 PDFDocument1 page8 PDFAKSH0211No ratings yet
- Google PDFDocument1 pageGoogle PDFAKSH0211No ratings yet
- 8 PDFDocument1 page8 PDFAKSH0211No ratings yet
- IPM GuidelinesDocument6 pagesIPM GuidelinesHittesh SolankiNo ratings yet
- Tree PruningDocument15 pagesTree Pruningrita44No ratings yet
- FSM Syllabus20071228 1Document3 pagesFSM Syllabus20071228 1Institute of Fengshui BaziNo ratings yet
- Principles of Business Grade 10 June 2021 Time: 1 1/2 Hrs. Paper 2 Answer ONLY 1 Question in Section I. Section IDocument3 pagesPrinciples of Business Grade 10 June 2021 Time: 1 1/2 Hrs. Paper 2 Answer ONLY 1 Question in Section I. Section Iapi-556426590No ratings yet
- Mitsubishi FanDocument2 pagesMitsubishi FanKyaw ZawNo ratings yet
- Information Technology Project Management: by Jack T. MarchewkaDocument44 pagesInformation Technology Project Management: by Jack T. Marchewkadeeps0705No ratings yet
- Usm 1Document47 pagesUsm 1Abhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Business CombinationsDocument18 pagesBusiness Combinationszubair afzalNo ratings yet
- s15 Miller Chap 8b LectureDocument19 pagess15 Miller Chap 8b LectureKartika FitriNo ratings yet
- Frequency Response For Control System Analysis - GATE Study Material in PDFDocument7 pagesFrequency Response For Control System Analysis - GATE Study Material in PDFNarendra AgrawalNo ratings yet
- JP Selecta IncubatorDocument5 pagesJP Selecta IncubatorAhmed AlkabodyNo ratings yet
- LS01 ServiceDocument53 pagesLS01 ServicehutandreiNo ratings yet
- #Angles Are in Degrees: EGR2313 HW SOLUTIONS (2021)Document4 pages#Angles Are in Degrees: EGR2313 HW SOLUTIONS (2021)SolomonNo ratings yet
- Footing - f1 - f2 - Da RC StructureDocument42 pagesFooting - f1 - f2 - Da RC StructureFrederickV.VelascoNo ratings yet
- Meriam Mfc4150 ManDocument40 pagesMeriam Mfc4150 Manwajahatrafiq6607No ratings yet
- Practical Cs Xii Mysql 2022-23 FinalDocument9 pagesPractical Cs Xii Mysql 2022-23 FinalHimanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- IIM L: 111iiiiiiiDocument54 pagesIIM L: 111iiiiiiiJavier GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Lec. 2Document22 pagesLec. 2محمدNo ratings yet
- Baxter - Heraeus Megafuge 1,2 - User ManualDocument13 pagesBaxter - Heraeus Megafuge 1,2 - User ManualMarcos ZanelliNo ratings yet
- Blake 2013Document337 pagesBlake 2013Tushar AmetaNo ratings yet
- IMC - BisleriDocument8 pagesIMC - BisleriVineetaNo ratings yet