Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Understanding Batteries & Cells
Uploaded by
ajmat140Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Understanding Batteries & Cells
Uploaded by
ajmat140Copyright:
Available Formats
A LEARNING REPORT ON THE BATTERIES &
CELLS
By
Karthikeyan.S
Karthikeyan SK https://www.linkedin.com/in/simplykarthik/ Page No: 1
List of Content
\
S.No Name of the Contents Page No
1 Cell 3
2 String 3
3 Connection 3
4 Working Principle of a cell 3
5 Classification of a cell 3
6 Battery 4
7 Classification of Battery 4
8 Component of Battery 4
9 Battery Vs Cell 5
10 Primary Battery 5
11 Secondary Battery 6
12 Primary Battery Vs Secondary Battery 7
Karthikeyan SK https://www.linkedin.com/in/simplykarthik/ Page No: 2
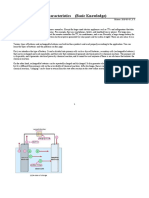
CELL:
A unit part consisting of two dissimilar electrodes immersed in an electrolyte;
1. One lead acid cell is 2 volts nominal
2. One nickel cadmium cell is 1.2 volts nominal
It is one module of energy-storing that stores chemical energy and transforms it into electrical when
connected to the circuitry.
STRING:
1. An energy storage system consisting of two or more series connected cells up to the required system
voltage.
CONNECTIONS:
1. Series connection of Cells: Add up the cell voltage, but the Amp-hour stays the same
2. Parallel connection of Cells: Sum the Capacity of each string (Watts or Amp Hours); the voltage
remains the same
3. Lead Acid: “125 Vdc” = 58-60 cells Typical Float = 130-134Vdc
4. Nickel Cadmium: “125 Vdc” = 90-96 cells Typical Float =130 -134 Vdc
WORKING PRINCIPLE OF A CELL:
The redox reaction occurs between the electrolyte and the electrodes and due to this reaction, the
electric current starts flowing through an external circuit.
CLASSIFICATION OF A CELL:
1. The cell is mainly classified into four types. They are the
• Wet cell
• Dry cell
• Reserve cell
• Fuel cell.
2. The wet cell uses a liquid electrolyte, and in the dry cell, the electrolyte is in the form of the
powder.
Karthikeyan SK https://www.linkedin.com/in/simplykarthik/ Page No: 3
BATTERY:
1. A battery is a device, which consists of a various voltaic cell.
2. Each voltaic cell consists of two half cells connected in series by a conductive electrolyte holding
anions and cat ions.
3. One half-cell includes electrolyte and the electrode to which anions move, i.e. the anode or negative
electrode; the other half-cell includes electrolyte and the electrode to which cat ions move, i.e. the
cathode or positive electrode.
4. In the redox reaction that powers the battery, reduction occurs to cations at the cathode, while
oxidation occurs to anions at the anode. The electrodes do not touch one another but are electrically
connected by the electrolyte.
CLASSIFICATION OF BATTERY:
BATTERY
CHEMICAL PHYSICAL BIOLOGICAL
PRIMARY SECONDARY
1. Chemical Batteries: These are the batteries which produce electricity by chemical reaction
2. Physical Batteries: These are the batteries which produce electricity by physical change
3. Biological Batteries: These are the batteries which produce electricity by biological reactions
COMPONENTS OF BATTERIES:
1. CONTAINER
• The Case need to be corrosive resistant and stable to chemical attack by electrolyte.
• It should have mechanical strength, be cheap and light.
2. SEPARATOR
• The separator must be chemically stable to the electrolyte and to the active materials at the
temperature of operation.
3. CURRENT COLLECTOR
• The current collector is usually a metal grid or sheet, to provide a conducting path through
the paste (active material) and thereby minimize the resistance of the battery.
• The current collector must be stable to chemical attack by both electrolyte and active
material, and this limits the choice of material.
4. ELECTROLYTE
• Selection of electrolyte is determined by the electrode reactions
Karthikeyan SK https://www.linkedin.com/in/simplykarthik/ Page No: 4
• Temperature has a large effect on electrolyte properties and both viscosity and resistance
increase by more an order of magnitude as the temperature drops from ambient to -30°C.
This largely accounts for the poorer performance of the battery at lower temperature
• The weight of the electrolyte is a major contribution to that of the complete battery.
5. ACTIVE MATERIALS
• The active materials in a battery are those that participate in the electrochemical
charge/discharge reaction. These materials include the electrolyte and the positive and
negative electrodes. As mentioned earlier, the electrolyte in a lead-acid battery is a dilute
solution of sulfuric acid (H2SO4).
BATTERY Vs CELL:
Basis for
Cell Battery
Comparison
Definition The single unit device which converts It is the collection of electrochemical cells
the chemical energy into electrical which either connects in series or in
energy parallel
Symbol
Types Dry Cell, Wet Cell, Reserve Cell and Primary battery and Secondary battery.
Fuel Cell.
Specification Light and compact Heavy
Power Supply power for a short time. Supply power for a long time.
Applications Clocks, lamp, radio, remote control Automobiles, inverter, emergency light
devices etc. etc.
Cost Cheap Costly
PRIMARY BATTERIES:
1. A Primary Battery is one of the simple and convenient sources of power for several portable
electronic and electrical devices like lights, cameras, watches, toys, radios etc.
2. As they cannot be recharged electrically, they are of “use it and when discharged, discard it” type.
3. Once these batteries are used they cannot be recharged as the devices are not easily reversible and
active materials may not return to their original forms.
4. Battery manufacturers recommend against recharge of primary cells.
5. Some of the examples for the disposable batteries are the normal AA, AAA batteries which we use
in wall clocks, television remote etc.
6. Other name for these batteries is disposable batteries.
Karthikeyan SK https://www.linkedin.com/in/simplykarthik/ Page No: 5
PRIMARY
BATTERY
Zinc-carbon Alkaline Lithium Cadmium
batteries batteries batteries batteries
SECONDARY BATTERIES:
1. Secondary batteries are also called as rechargeable batteries.
2. These batteries can be used and recharges simultaneously.
3. They are usually assembled with active materials with active in the discharged state.
4. Rechargeable batteries are recharged by applying electric current, which reverses the chemical
reactions that occur during discharge. Chargers are devices which supply the required current.
SECONDARY
BATTERY
NICKEL-METAL NICKEL LEAD
LITHIUM
HYDRIDE CADMIUM ACID
BATTERY
BATTERY BATTERY BATTERY
Karthikeyan SK https://www.linkedin.com/in/simplykarthik/ Page No: 6
PRIMARY BATTERY Vs SECONDARY BATTERY:
Karthikeyan SK https://www.linkedin.com/in/simplykarthik/ Page No: 7
You might also like
- Chapter No. 4- Automobile Electronics and Electrical SystemsDocument125 pagesChapter No. 4- Automobile Electronics and Electrical Systemsashwini yewaleNo ratings yet
- AEN Chapter-4 NotesDocument102 pagesAEN Chapter-4 Notesashwini yewaleNo ratings yet
- Batteries and EarthingDocument10 pagesBatteries and EarthingRobin ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Batteries Types ApplicationsDocument1 pageBatteries Types ApplicationsMariz Julian Pang-ao0% (1)
- Seminar ReportDocument11 pagesSeminar ReportAnkit GulumkarNo ratings yet
- Electric Vehicle 3rd ModuleDocument18 pagesElectric Vehicle 3rd Modulegirishvadde10No ratings yet
- BATTERY TECH GUIDE: PRIMARY VS SECONDARYDocument25 pagesBATTERY TECH GUIDE: PRIMARY VS SECONDARYVasudev GuptaNo ratings yet
- BatteryDocument8 pagesBatteryThithiksha JNo ratings yet
- EE0007 FA4 BatteryDocument2 pagesEE0007 FA4 BatteryLance CadiangNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Cells: BatteriesDocument4 pagesElectrochemical Cells: BatteriesMae TadaNo ratings yet
- Electric Vehicle 3rd ModuleDocument25 pagesElectric Vehicle 3rd ModuleSimi BaniNo ratings yet
- EV and HEV - Unit 2 FinalDocument63 pagesEV and HEV - Unit 2 FinalvenkateswarluvelisalNo ratings yet
- FEV Unit - 5Document13 pagesFEV Unit - 5Sai SiDNo ratings yet
- Optimizing BatteryDocument8 pagesOptimizing BatteryLGM NightNo ratings yet
- Automobile Electrical and Electronics NotesDocument72 pagesAutomobile Electrical and Electronics NotesManoj Shanmugam100% (2)
- Types of BatteriesDocument8 pagesTypes of BatteriesVaibhav AwareNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Electrics - Aircraft BatteriesDocument17 pagesAircraft Electrics - Aircraft BatteriesErica Zoe BantogNo ratings yet
- Warren 2Document1 pageWarren 2Leo Ejay Suriaga EjudoNo ratings yet
- Unit-III-Energy Storage DevicesDocument27 pagesUnit-III-Energy Storage DevicesAppu MadanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document4 pagesAssignment 3Mrkgandhi RaviNo ratings yet
- All Document Reader 1713030400295Document56 pagesAll Document Reader 1713030400295gadisad522No ratings yet
- Module 4Document31 pagesModule 4Pragati ShindeNo ratings yet
- BatteriesDocument14 pagesBatteriesBaskaran BaskaranNo ratings yet
- How Batteries Work: An Introduction to Battery Chemistry and ClassificationDocument30 pagesHow Batteries Work: An Introduction to Battery Chemistry and ClassificationUmesh ChandraNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2: ElectrochemistryDocument12 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2: ElectrochemistrySteinerNo ratings yet
- Low Volatge and BatteryDocument74 pagesLow Volatge and BatteryOladokun Sulaiman OlanrewajuNo ratings yet
- Paper Battery Full Seminar Report On WWW Way2project inDocument12 pagesPaper Battery Full Seminar Report On WWW Way2project inPhebe PeterNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: Batteries ExplainedDocument32 pagesElectrochemistry: Batteries ExplainedSHOBHIT GAUTAM 2K21/A12/72No ratings yet
- BatteryDocument50 pagesBatteryDenekew Getahun100% (1)
- Cell & BatteriesDocument16 pagesCell & BatteriesMahnoor AqeelNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii Cy19241Document25 pagesUnit Ii Cy19241Suresh Kumar A PNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Electrical Energy Storage Systems in Electric VehicleDocument7 pagesComparative Study of Electrical Energy Storage Systems in Electric VehicleBhogeshwar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument11 pagesSeminar Reporttushar20june71% (7)
- Che Unit 4 BatteriesDocument13 pagesChe Unit 4 BatteriesNEELESH ATOMNo ratings yet
- Batteries PDFDocument24 pagesBatteries PDFkaviyavikashini kaviyaNo ratings yet
- Flow Batteries: by Trung Nguyen and Robert F. SavinellDocument3 pagesFlow Batteries: by Trung Nguyen and Robert F. Savinell何家銘No ratings yet
- Paper Battery Full Seminar ReportDocument23 pagesPaper Battery Full Seminar ReportAshim K SNo ratings yet
- Engr. Jayde Paolo Castro Mirandilla Batteries: MIDTERM - ECE00 Basic ElectronicsDocument5 pagesEngr. Jayde Paolo Castro Mirandilla Batteries: MIDTERM - ECE00 Basic ElectronicsRomuel Villanueva AlmeydaNo ratings yet
- Battery Types and CharacteristicsDocument7 pagesBattery Types and CharacteristicsWai HinNo ratings yet
- Unit V: Topic 3-BatteriesDocument14 pagesUnit V: Topic 3-BatteriesBhageerathNo ratings yet
- Debashis Panda Regd No- 2101287489Document18 pagesDebashis Panda Regd No- 2101287489q8vie2eropNo ratings yet
- DC Electrics BatteriesDocument8 pagesDC Electrics BatteriesNick TsangNo ratings yet
- Batteries Guide: Types, Characteristics & ComparisonDocument14 pagesBatteries Guide: Types, Characteristics & ComparisonBhageerathNo ratings yet
- BATTERIESDocument14 pagesBATTERIESwagnerjames028No ratings yet
- Thesis On Lithium Ion BatteryDocument5 pagesThesis On Lithium Ion Batteryafjrtopab100% (2)
- Control and Integration of Renewable Energy Storage SystemsDocument21 pagesControl and Integration of Renewable Energy Storage SystemsSONU KUMARNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Cell Project FileDocument16 pagesElectrochemical Cell Project Filevabhay22435No ratings yet
- Emerging Automotive Battery TechDocument59 pagesEmerging Automotive Battery TechSuneet Khurana0% (1)
- Paper BatteryDocument16 pagesPaper BatterySakhamuri Ram'sNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Li-ion Batteries - BMSLec05_LIBDocument21 pagesLecture 6 - Li-ion Batteries - BMSLec05_LIBAnchal AnchalNo ratings yet
- Unit II EvhvDocument88 pagesUnit II EvhvRajesh BhaskarlaNo ratings yet
- Paper Battery Full Seminar Report On WWW Way2project inDocument19 pagesPaper Battery Full Seminar Report On WWW Way2project inSunil GondNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Activity 6 - Cell and Batteries WorksheetDocument1 pageUnit 5 - Activity 6 - Cell and Batteries WorksheetJared PalmerNo ratings yet
- Types of BatteriesDocument10 pagesTypes of BatteriesBakhshiNo ratings yet
- Lead Acid BatteryDocument7 pagesLead Acid BatteryMateti Madhu100% (1)
- Aircraft BatteriesDocument26 pagesAircraft BatteriesDaniel MkandawireNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument18 pagesChemistry ProjectMd RehanNo ratings yet
- Term PaperDocument3 pagesTerm PaperJonie MatienzoNo ratings yet
- Prysmian Click Fit AccessoriesDocument4 pagesPrysmian Click Fit AccessoriesselvamNo ratings yet
- Genset: Generating Set Powered byDocument2 pagesGenset: Generating Set Powered byManthan ShahNo ratings yet
- Is 2259 1963 PDFDocument23 pagesIs 2259 1963 PDFrohanmanimaniNo ratings yet
- 03F PowerSystem Stability DR MannanDocument27 pages03F PowerSystem Stability DR MannanNawshed AhmedNo ratings yet
- EEE201 Electrical Circuit Analysis AssignmentDocument12 pagesEEE201 Electrical Circuit Analysis AssignmentNarendra ShakamuriNo ratings yet
- GAIL UPS System Data SheetDocument7 pagesGAIL UPS System Data SheetPrakash SinhaNo ratings yet
- Class XII DP AssignmentDocument151 pagesClass XII DP AssignmentHumaira KhanamNo ratings yet
- Electrolyzer Modules A) Unipolar and B) Bipolar Cell ConfigurationsDocument8 pagesElectrolyzer Modules A) Unipolar and B) Bipolar Cell ConfigurationsAnuj ShahiNo ratings yet
- Ancillary Services NotesDocument31 pagesAncillary Services NotesRick JordanNo ratings yet
- 1420A TechdataDocument2 pages1420A TechdataSajith AliNo ratings yet
- ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND THE PERIODIC TABLEDocument20 pagesATOMIC STRUCTURE AND THE PERIODIC TABLEMrYameteNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet Templates Excel FormsDocument28 pagesData Sheet Templates Excel Formsbadryco04No ratings yet
- PRT RDM2Document42 pagesPRT RDM2jstclmethan100% (1)
- Epas Nc2: Electronic Products Assembly and Servicing Nc2Document22 pagesEpas Nc2: Electronic Products Assembly and Servicing Nc2Leunam SalpadNo ratings yet
- Build This Stun-GunDocument6 pagesBuild This Stun-GunagustinzmNo ratings yet
- Control Exercise Sheets 2021Document13 pagesControl Exercise Sheets 2021周暐凱No ratings yet
- PEMBAHASANDocument56 pagesPEMBAHASANAldisNo ratings yet
- Overview ZF Systems Procent Rev. 2.2Document1 pageOverview ZF Systems Procent Rev. 2.2Muhittin KNo ratings yet
- MK2200 User's ManualDocument49 pagesMK2200 User's Manualidha85100% (1)
- Television 1928Document58 pagesTelevision 1928Rick MendelezNo ratings yet
- J201 J202 MMBFJ201 MMBFJ202: N-Channel General Purpose AmplifierDocument14 pagesJ201 J202 MMBFJ201 MMBFJ202: N-Channel General Purpose AmplifierMisac AbdenagoNo ratings yet
- Al Mezan Services LAB-131 - 14 - 07 - 20201 - SEDocument9 pagesAl Mezan Services LAB-131 - 14 - 07 - 20201 - SEHassan Ahmed KhanNo ratings yet
- Access Full Complete Solution Manual Here: Chapter 1 SolutionsDocument8 pagesAccess Full Complete Solution Manual Here: Chapter 1 SolutionsAnanna TithiNo ratings yet
- Mini Hi-Fi System: Service ManualDocument85 pagesMini Hi-Fi System: Service ManualIvanilto Martins da Cruz100% (3)
- Electronics Minor Project Metro Train PrototypeDocument84 pagesElectronics Minor Project Metro Train PrototypeHemant93% (44)
- Kelompok 1: Deariza Gifari M. Adam A Eldi Novrizal M. Rizal Dwi Ilman Eva Nurfadhillah S Nur Hasyyati LDocument8 pagesKelompok 1: Deariza Gifari M. Adam A Eldi Novrizal M. Rizal Dwi Ilman Eva Nurfadhillah S Nur Hasyyati LEldi NovrizalNo ratings yet
- Trafoindo Catalogue Oil Immersed TransformersDocument2 pagesTrafoindo Catalogue Oil Immersed TransformersOcktafriandi HendraNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Fuzzy Logic Based Speed Control of Multi Level Inverter Fed PMBLDC DrivesDocument12 pagesSimulation of Fuzzy Logic Based Speed Control of Multi Level Inverter Fed PMBLDC Drivesdhanshri kolekarNo ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis I With MATLABDocument46 pagesCircuit Analysis I With MATLABsalemabu9No ratings yet
- Temperature SensorsDocument14 pagesTemperature SensorsManmeet RajputNo ratings yet