Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Galela - DVM2DX - Exercise 11.
Uploaded by
Shengrace Gavino0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesThe document summarizes the male and female reproductive systems. It provides diagrams and descriptions of the microscopic structures of both systems. For the female system it includes a table listing the main structures (ovary, oviduct, uterus, cervix, vagina, mammary glands) and their microscopic features such as epithelial cell types and layers. The objectives are to identify the anatomical structures of both systems and differentiate their components.
Original Description:
Original Title
GALELA.DVM2DX- EXERCISE 11.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the male and female reproductive systems. It provides diagrams and descriptions of the microscopic structures of both systems. For the female system it includes a table listing the main structures (ovary, oviduct, uterus, cervix, vagina, mammary glands) and their microscopic features such as epithelial cell types and layers. The objectives are to identify the anatomical structures of both systems and differentiate their components.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesGalela - DVM2DX - Exercise 11.
Uploaded by
Shengrace GavinoThe document summarizes the male and female reproductive systems. It provides diagrams and descriptions of the microscopic structures of both systems. For the female system it includes a table listing the main structures (ovary, oviduct, uterus, cervix, vagina, mammary glands) and their microscopic features such as epithelial cell types and layers. The objectives are to identify the anatomical structures of both systems and differentiate their components.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
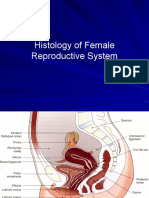
THE MALE AND FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
Laboratory Offline Activity 11
Name: CLAROS,
ALLEAH MARIE
RICCI A. GALELA
JANE O. Date: 5/8/2022
Section: VM2B
Specific objectives are the following:
At the end of the laboratory lesson, the student must have:
1. Identified the microscopic anatomical structures of the male and female
reproductive system.
2. Differentiated the structural components of the reproductive tissues from each
other.
Activity Proper
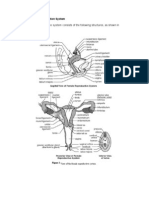
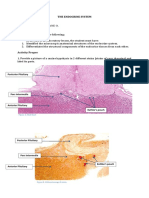
1. Provide a picture (gross) of a male avian reproductive system and label its parts.
Figure 1. Reproductive tract of a male chicken
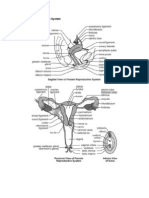
2. List on a table the microscopic structures and features of a female reproductive system
(The epithelium of the different parts and structures, the cells found, you may give
functions or descriptions, etc).
Microscopic structures & Description
features of female
reproductive system
OVARY Lined with Simple cuboidal epithelium.
Capsule Covers the outer surface.
Cortex Outer region that is the site of oocyte development.
Ovarian Follicles oocytes surrounded by one or more layers of cells
Medulla Inner region of fibroelastic connective tissue with many large, tortuous
blood vessels, lymph vessels and nerve fibers. Does not contain ovarian
follicles.
OVIDUCT Are fibromuscular tubes.
Mucosa Lined with Simple Columnar Ciliated.
Muscularis consists of an inner circular or spiral layer and an outer longitudinal layer
whose peristaltic contractions help propel the ovum or fertilized zygote to
the uterus
Serosa Composed of a simple cuboidal epithelium (or mesothelium) supported by
a thin layer of connective tissue.
UTERUS The uterus is the muscular organ that nourishes and supports the growing
embryo.
Endometrium Simple Columnar Epithelium - ciliated columnar and non-ciliated secretory
cells
Myometrium composed of three indistinct layers of smooth muscle
Perimetrium Covered by an outer serous layer or visceral peritoneum that is continuous
with the broad ligament.
CERVIX The lower end of the uterus that opens into the vagina.
Endocervix Forms the wall of the cervical canal. The epithelium of the endocervix is
composed of simple columnar cells.
Ectocervix Part of the cervix that protrudes in the vagina endocervi. Lined with
Stratified Squamous Non-Keratinized Epithelium - continuous with the
lining of the vagina.
Transformation Zone Abrupt junction between the mucus secreting columnar epithelium of the
endocervix and the squamous epithelium of the ectocervix.
VAGINA A fibromuscular tube that connects the cervix of the uterus to the
vestibule of the external genitalia. Line with Stratified Squamous Non-
Keratinized Epithelium
MAMMARY GLANDS Compound, tubulo-alveolar glands whose structure changes depending on
the reproductive status of females.
Lactiferous Duct Opens into the nipple. It is lined by a double layer of cuboidal or columnar
cells surrounded by a sheath of connective tissue with myoid cells.
Alveoli Simple Epithelium - cuboidal or columnar secretory cells that synthesis
and secrete milk
3. Write your references.
Microscopic anatomy Laboratory material, female reproductive histology.pdf
Image by Dr. Jacquie Jacob, University of Kentucky.
You might also like
- Male & Female Reproductive SystemDocument9 pagesMale & Female Reproductive Systemعبدالرحمن عدي عبدالفتاحNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument60 pagesFemale Reproductive Systemjeenath justin dossNo ratings yet
- Histology 2018 1Document38 pagesHistology 2018 1Marvin Ndashimye100% (1)
- Crissman Epithelial ObjectivesDocument6 pagesCrissman Epithelial Objectiveskkonci01No ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument5 pagesEpithelial TissueSofia LiNo ratings yet
- The Female Reproduction SystemDocument10 pagesThe Female Reproduction Systemrafaelvillacorta100% (1)
- The Ovaries - Structure - Ligaments - Vascular Supply - FunctionDocument3 pagesThe Ovaries - Structure - Ligaments - Vascular Supply - FunctionTameshwarNo ratings yet
- Lab SupplementDocument5 pagesLab SupplementcaterappleyeNo ratings yet
- Histo Module 12 Female Repro 2Document6 pagesHisto Module 12 Female Repro 2kristian markus delos santosNo ratings yet
- Microscopic Study of Epithelial Tissue and Connective TissueDocument16 pagesMicroscopic Study of Epithelial Tissue and Connective TissueSinger Rahul Sharma100% (1)
- Histology AssignmentDocument4 pagesHistology AssignmentNico LokoNo ratings yet
- Biology of UterusDocument23 pagesBiology of UterusSrividyaNo ratings yet
- Histology of Female Genital System For Reproductive ModuleDocument35 pagesHistology of Female Genital System For Reproductive ModuleTeklemuz KahsayNo ratings yet
- 3rd Lecture On The Histology of Female Reproductive System by Dr. RoomiDocument19 pages3rd Lecture On The Histology of Female Reproductive System by Dr. RoomiMudassar RoomiNo ratings yet
- The Female Reproduction SystemDocument9 pagesThe Female Reproduction Systemjhoanamariequilates182369No ratings yet
- TissuesDocument91 pagesTissuesSon Ezekiel Gabriel I. BenitezNo ratings yet
- Tissues (Anatomy 1)Document83 pagesTissues (Anatomy 1)nanakwame5769No ratings yet
- Epithelium: Prepared By: Michael John R. Aguilar, RMTDocument124 pagesEpithelium: Prepared By: Michael John R. Aguilar, RMTFrankenstein MelancholyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyLouie Kem Anthony BabaranNo ratings yet
- Lab. NO. 4: System: ReproductiveDocument10 pagesLab. NO. 4: System: ReproductiveKarrar BassimNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System Histology II Lecture NotesDocument4 pagesFemale Reproductive System Histology II Lecture NotesSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- Anatomi ServiksDocument12 pagesAnatomi ServiksIda Ayu ApsariNo ratings yet
- Tissue Level of OrganizationDocument49 pagesTissue Level of Organizationainabayhon7No ratings yet
- Basic TissueDocument60 pagesBasic TissueSantoshini RaviNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 Anaphy+tissuesDocument12 pagesChapter4 Anaphy+tissuesCASSANDRA BARQUILLANo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Cervix, Squamocolumnar Junction, Metaplastic Change and Transformation ZoneDocument24 pagesAnatomy of The Cervix, Squamocolumnar Junction, Metaplastic Change and Transformation ZoneAlfonsus Zeus SNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument44 pagesAnimal TissuesMary Sutingco100% (1)
- English Task 2Document3 pagesEnglish Task 2Tiara ArmiliaNo ratings yet
- Simple EpitheliumDocument64 pagesSimple EpitheliumRajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Xamidea Human ReproductionDocument42 pagesXamidea Human Reproductionkeren spamzNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument42 pagesReproductive SystemAileen Grace Delima100% (1)
- Epithelium: Dr. Kalpajyoti BhattacharjeeDocument125 pagesEpithelium: Dr. Kalpajyoti Bhattacharjeelochi gmNo ratings yet
- The Female Reproductive System: Dr. Emanuel Muro HkmuDocument41 pagesThe Female Reproductive System: Dr. Emanuel Muro HkmuMustafa DadahNo ratings yet
- Histology of The Epithelium TissueDocument9 pagesHistology of The Epithelium TissueKelvin HillsNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument20 pagesTissueJagruti MaratheNo ratings yet
- HistocologyDocument10 pagesHistocologyKelvin HillsNo ratings yet
- Histology of Female Reproductive System: Dr. Rajesh Ranjan Assistant Professor Deptt. of Veterinary Anatomy C.V.SC., RewaDocument26 pagesHistology of Female Reproductive System: Dr. Rajesh Ranjan Assistant Professor Deptt. of Veterinary Anatomy C.V.SC., RewaDiahNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue PDFDocument20 pagesEpithelial Tissue PDFshafa cahyani100% (1)
- Q3 Science Reproductive System 1Document21 pagesQ3 Science Reproductive System 1Andrea Kaiser BallartaNo ratings yet
- Epithelium: (Edit) Classification (Structural)Document4 pagesEpithelium: (Edit) Classification (Structural)Mirriam Joy CortezNo ratings yet
- ANA 222 Female Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesANA 222 Female Reproductive SystemprincessmakklisNo ratings yet
- Jaringan EpitelDocument20 pagesJaringan EpitelKitsune TakaNo ratings yet
- A Case Study About Cervical PolypsDocument8 pagesA Case Study About Cervical PolypsJisel-Apple BulanNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument8 pagesTissuesBibek SahNo ratings yet
- Epithel Connective TissuesDocument47 pagesEpithel Connective TissuesAnonymous nErkwtXnuS100% (1)
- Tissue ReviewerDocument10 pagesTissue ReviewerDaniela Nicole Manibog Valentino100% (1)
- Human Reproduction - II Puc - Regular NotesDocument23 pagesHuman Reproduction - II Puc - Regular NotesVasudevNo ratings yet
- Animaltissues 180604115637Document40 pagesAnimaltissues 180604115637proud.student2023No ratings yet
- Female RSystemDocument71 pagesFemale RSystemicliftonguytonNo ratings yet
- 3 Tissue of Human Body NotesDocument11 pages3 Tissue of Human Body Notesghanshyam agnihotryNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument15 pagesFemale Reproductive Systemada.codreanuNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue Lecture 1Document52 pagesEpithelial Tissue Lecture 1Saphira PramuditaNo ratings yet
- Gen Zoo Animal TissuesDocument84 pagesGen Zoo Animal TissuesDale Gil JuliaNo ratings yet
- Structural OrganismsDocument58 pagesStructural Organismssivarigil1918No ratings yet
- Body TissuesDocument10 pagesBody TissuesNaanmatha PuspanathanNo ratings yet
- Combine PDFDocument23 pagesCombine PDFsigninNo ratings yet
- EEU2020 Adfinex HDocument23 pagesEEU2020 Adfinex HZainab Jamal SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Organa Genitalia Feminina: Oleh Dr. Hendra SutardhioDocument90 pagesOrgana Genitalia Feminina: Oleh Dr. Hendra SutardhioMirah WilayadiNo ratings yet
- Female ReproductiveDocument34 pagesFemale ReproductiveAbdallah A. Abu Mattar100% (2)
- Dost FicDocument16 pagesDost FicShengrace GavinoNo ratings yet
- Activity 4 Paper ChromatographyDocument7 pagesActivity 4 Paper ChromatographyShengrace Gavino100% (1)
- Claros-The Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesClaros-The Endocrine SystemShengrace GavinoNo ratings yet
- RPMS Portfolio 2020 2021Document29 pagesRPMS Portfolio 2020 2021Shengrace GavinoNo ratings yet
- Fields of Anatomy Dog Breeds Converted MergedDocument44 pagesFields of Anatomy Dog Breeds Converted MergedShengrace GavinoNo ratings yet
- RPMS FinalDocument29 pagesRPMS FinalShengrace GavinoNo ratings yet
- Action Plan 2021 2022Document8 pagesAction Plan 2021 2022Shengrace GavinoNo ratings yet
- Da BiotechDocument241 pagesDa BiotechShengrace GavinoNo ratings yet
- TF Monitoring 2021Document194 pagesTF Monitoring 2021Shengrace GavinoNo ratings yet
- Tissue Revitalizing 2018Document463 pagesTissue Revitalizing 2018Shengrace GavinoNo ratings yet
- Exercise IxDocument27 pagesExercise IxShengrace GavinoNo ratings yet
- SampleDocument41 pagesSampleShengrace GavinoNo ratings yet
- COT1 DATAgatheringDocument54 pagesCOT1 DATAgatheringShengrace GavinoNo ratings yet
- Feb. 16 28 AWA Dept HEADS FLoatingDocument2 pagesFeb. 16 28 AWA Dept HEADS FLoatingShengrace GavinoNo ratings yet
- Art AnalysisDocument3 pagesArt AnalysisShengrace GavinoNo ratings yet
- Development of The ForebrainDocument11 pagesDevelopment of The ForebrainShengrace GavinoNo ratings yet
- CB Past Form 3aDocument6 pagesCB Past Form 3aShengrace GavinoNo ratings yet
- Abello MP3Document11 pagesAbello MP3Shengrace GavinoNo ratings yet
- Development of The Brain Hindbrain CupinDocument6 pagesDevelopment of The Brain Hindbrain CupinShengrace GavinoNo ratings yet
- AcadArena Alliance Application Form (New Org)Document3 pagesAcadArena Alliance Application Form (New Org)Shengrace GavinoNo ratings yet
- COT1 Polygon CLAROSDocument42 pagesCOT1 Polygon CLAROSShengrace GavinoNo ratings yet
- 2021 RPRH Annual ReportDocument108 pages2021 RPRH Annual ReportVNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Pengajaran Tahunan Form 1 Science DLP 2021Document19 pagesRancangan Pengajaran Tahunan Form 1 Science DLP 2021SITI SHAHARZAD BINTI WAHAB MoeNo ratings yet
- Leifer: Maternity Nursing, 10th Edition: Chapter 3: Fetal Development Test Bank Multiple ChoiceDocument11 pagesLeifer: Maternity Nursing, 10th Edition: Chapter 3: Fetal Development Test Bank Multiple ChoiceJennifer RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Summative Test in SCIENCE V Name: - Date: - Grade and Section: - ScoreDocument1 pageSummative Test in SCIENCE V Name: - Date: - Grade and Section: - ScoreMhafolz Arong BardosNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 1Document6 pagesJurnal 1Sri FitriaNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Hormonal Contraception On The Voice Rodney SataloffDocument8 pagesThe Effects of Hormonal Contraception On The Voice Rodney SataloffIvory PlatypusNo ratings yet
- Nancy CampbellDocument281 pagesNancy CampbellItzcoatl Torres AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- WLP Science q2 w3 Nov 28 Dec 2Document6 pagesWLP Science q2 w3 Nov 28 Dec 2Maria Aurea BorjaNo ratings yet
- Case-Scenario No. 2 Ectopic-PregnancyDocument2 pagesCase-Scenario No. 2 Ectopic-PregnancyJoegie ArioNo ratings yet
- Examen OralDocument5 pagesExamen OralFernando Lipa TiconaNo ratings yet
- Data AnalysisDocument1 pageData AnalysisRicardoNo ratings yet
- Langman's Medical Embryology - CoverDocument11 pagesLangman's Medical Embryology - CoverAriesta Wijaya PutraNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing 5 BulletsDocument4 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing 5 BulletsQueen ElizabethNo ratings yet
- Clinical Anatomy of UterusDocument12 pagesClinical Anatomy of UterusAsha dsouzaNo ratings yet
- Updated Thin Endometrium and ReceptivityDocument33 pagesUpdated Thin Endometrium and ReceptivityHappybaby inc100% (2)
- Lesson 2: The Sexual Self: It Was Pressumed That The Dominant Role Is The Male. The MaleDocument13 pagesLesson 2: The Sexual Self: It Was Pressumed That The Dominant Role Is The Male. The MaleJhon dave SurbanoNo ratings yet
- Diffun Campus: "Molding Minds, Shaping Future"Document41 pagesDiffun Campus: "Molding Minds, Shaping Future"Mary Joy BernasolNo ratings yet
- Embryology TerminologiesDocument2 pagesEmbryology TerminologiesSomaya QuaziNo ratings yet
- Era University / Era'S College of Nursing: Case Presentations On Uterine ProlapseDocument24 pagesEra University / Era'S College of Nursing: Case Presentations On Uterine Prolapsearchana verma89% (9)
- Ectopic Pregnancy: Aldilyn J. Sarajan, MD, MPH 2 Year Ob-Gyn Resident ZCMCDocument61 pagesEctopic Pregnancy: Aldilyn J. Sarajan, MD, MPH 2 Year Ob-Gyn Resident ZCMCDee SarajanNo ratings yet
- Log FrameDocument6 pagesLog FrameYenThiLeNo ratings yet
- Hons Presentation Monogenea 2022Document31 pagesHons Presentation Monogenea 2022nigeldkdcNo ratings yet
- Placental AbruptionDocument34 pagesPlacental Abruptionrosekatekate929No ratings yet
- The Male Reproductive System: Module in Science 5Document21 pagesThe Male Reproductive System: Module in Science 5June Winver JoaquinNo ratings yet
- 10 Penyakit Terbanyak Bedah (Ok) : NO Diagnosa TindakanDocument6 pages10 Penyakit Terbanyak Bedah (Ok) : NO Diagnosa TindakanPUTRINo ratings yet
- Labor Induced AugmentedDocument9 pagesLabor Induced Augmentednursereview83% (6)
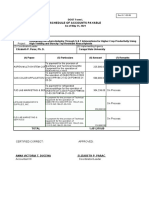
- Office of The Punong BarangayDocument2 pagesOffice of The Punong BarangaymichelleNo ratings yet
- Biology SS3 1ST Term E-NotesDocument55 pagesBiology SS3 1ST Term E-NotesINIOLUWA AKEJU100% (1)
- NCP-DR Final PDFDocument9 pagesNCP-DR Final PDFPaula AbadNo ratings yet
- Biological Terms Paper 1 - 230906 - 110335Document10 pagesBiological Terms Paper 1 - 230906 - 110335Silindile PreciousNo ratings yet