Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topic 2.8 Worksheet324
Uploaded by
haniaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic 2.8 Worksheet324
Uploaded by
haniaCopyright:
Available Formats
2.
8 Cell Respiration
ATP Production
Define cell respiration
cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from organic compounds to produce ATP.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..........
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..........
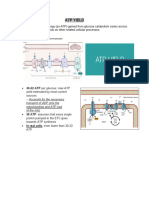
Describe how ATP acts as the energy currency for the cell
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..........
The advantage of ATP as an energy supply is that the energy is immediately available.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..........
Compare anaerobic and aerobic respiration
Anaerobic Aerobic
Required Conditions no oxygen needs oxygen
2 ATP per glucose
Energy Yield up to 38 ATP per glucose
carbon dioxide and water
lactate OR ethanol and carbon dioxide
Products
Location cell's cytoplasm cell's mitochondria
Outline the purpose (and products) of fermentation
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..........
fermentation is a kind of anaerobic respiration. extraction of energy from carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen.
products of fermentation are lactic acid and ethanolic fermentations.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..........
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..........
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..........
Describe the use of respirometry in measuring respiration rates
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..........
Respirometers can be used to perform various experiments:
the respiration rate of different organisms could be compared;
the effect of temperature on respiration rate could be investigated;
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..........
respiration rates could be compared in active and inactive organisms.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..........
You might also like
- MCAT Review Biology Notes (Full 1)Document30 pagesMCAT Review Biology Notes (Full 1)Chris_Barber09100% (2)
- Learners Activity Sheet in General Biology 1: "Cellular Respiration"Document2 pagesLearners Activity Sheet in General Biology 1: "Cellular Respiration"Cristine TingzonNo ratings yet
- 4 RespirationDocument80 pages4 RespirationNURUL TAQINAH BINTI ISMAIL BMNo ratings yet
- Cell Respiration Cornell Notes TeacherDocument5 pagesCell Respiration Cornell Notes TeacherErik Artur100% (1)
- 3.1.1.6 - Energy Systems: Learning ObjectivesDocument79 pages3.1.1.6 - Energy Systems: Learning Objectiveszedy gullesNo ratings yet
- Cell RespirationDocument27 pagesCell RespirationJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- Transpor Elektron Dan Fosforilasi Oksidatif Part 2Document12 pagesTranspor Elektron Dan Fosforilasi Oksidatif Part 2AMALIA 11No ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Fermentation 1Document29 pagesCellular Respiration Fermentation 1Lorraine LibioNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria & Cellular RespirationDocument36 pagesMitochondria & Cellular RespirationNuRien HaziQah ZaMri100% (1)
- BIO20 Cell Resp Teacher Notes 2020Document39 pagesBIO20 Cell Resp Teacher Notes 2020Shariq KhanNo ratings yet
- Cellularrespiration2012 130110052718 Phpapp02Document59 pagesCellularrespiration2012 130110052718 Phpapp02Kimberly Anne PagdangananNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration STUDY GUIDEDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration STUDY GUIDEJee MascardoNo ratings yet
- LGIS. Kreb CycleDocument25 pagesLGIS. Kreb Cyclehasaanmushtaq98765No ratings yet
- Learning Activity#4Document4 pagesLearning Activity#4Angela ErandioNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument15 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular RespirationAngel FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Obligate Aerobes & Most Facultative Anaerobes Most Aerotolerant Anaerobes Obligate AnaerobesDocument1 pageObligate Aerobes & Most Facultative Anaerobes Most Aerotolerant Anaerobes Obligate AnaerobesWafiNo ratings yet
- BIOL223-Lab 6Document35 pagesBIOL223-Lab 6chicken friesNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Cellular RespirationDocument32 pagesWeek 7 Cellular RespirationJiverlyn PatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Cellular RespirationDocument36 pagesChapter 9: Cellular RespirationMary GarciaNo ratings yet
- Metabolisme KatabolismeDocument3 pagesMetabolisme KatabolismeGiska AliyaNo ratings yet
- Cell RespirationDocument19 pagesCell RespirationPauline FrascaNo ratings yet
- Grade 11: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialDocument19 pagesGrade 11: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialJake LacanlaleNo ratings yet
- GB 1 NotesDocument10 pagesGB 1 Notesrenlie jane pedronanNo ratings yet
- Efficiency of Atp ProductionDocument3 pagesEfficiency of Atp ProductionOdessa FileNo ratings yet
- Ho10 Tca & EtsDocument26 pagesHo10 Tca & EtstresnowahyudienNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Anaerobic RespirationDocument29 pagesAerobic Anaerobic RespirationAnonymous e0TdsoxUNo ratings yet
- Bio Reviewer 2Document2 pagesBio Reviewer 2Prince Lawrence Garcia100% (1)
- Concept of Aerobic CapacityDocument32 pagesConcept of Aerobic CapacityRania KhelilNo ratings yet
- Energy GenerationDocument4 pagesEnergy GenerationDeena ChadiNo ratings yet
- 8 3Document22 pages8 3lianneNo ratings yet
- Respiration: Friday, January 12, 2018Document21 pagesRespiration: Friday, January 12, 2018fatima al neyadiNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: Trisha Vinch D. NavarceDocument34 pagesCellular Respiration: Trisha Vinch D. NavarceTrisha NavarceNo ratings yet
- PS and CRDocument34 pagesPS and CRErika MatiasNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument100 pagesRespirationColin RiddellNo ratings yet
- Cellular+Respiration+ +reactionsDocument28 pagesCellular+Respiration+ +reactionsAnonno DipNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration DefinitionDocument9 pagesCellular Respiration Definitionmaria genioNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis & Respiration 2Document15 pagesGlycolysis & Respiration 2kayannaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration 2Document4 pagesCellular Respiration 2Naledi Noxolo BhenguNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Study GuideDocument30 pagesCellular Respiration Study Guideroselyn acpacNo ratings yet
- Cell RespirationDocument10 pagesCell RespirationChristine SangilNo ratings yet
- Week 8 - GenBio1 CELL RESPIRATION 1st Term SY 2021-2022Document3 pagesWeek 8 - GenBio1 CELL RESPIRATION 1st Term SY 2021-2022JAN PAULINE BABINANo ratings yet
- Ch. 7 Pre Reading QuestionsDocument8 pagesCh. 7 Pre Reading QuestionsDJ ISAACS25% (4)
- Chapter 7 BIO 1510Document25 pagesChapter 7 BIO 1510Chachi CNo ratings yet
- Respiration in PlantsDocument29 pagesRespiration in PlantsJahanzeb SafdarNo ratings yet
- Energy Relationships in Metabolic Processes and EnzymesDocument16 pagesEnergy Relationships in Metabolic Processes and EnzymesMighty Warrior GSRNo ratings yet
- Chapt6 LectureDocument34 pagesChapt6 LectureSoumil AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Metabolism 1 BGJE 2017Document30 pagesMetabolism 1 BGJE 2017Gîrneţ AlinaNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic Energy SystemsDocument44 pagesAnaerobic Energy SystemsBaxton Paul GarzaNo ratings yet
- g11 Cell Respiration 2Document23 pagesg11 Cell Respiration 2AH 78No ratings yet
- PHMP Topic 2Document8 pagesPHMP Topic 2yhcaesthetic proNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 - Lecture 3Document24 pagesTopic 4 - Lecture 3bibi.hansmuddyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document19 pagesChapter 7skywalkerNo ratings yet
- Cell RespirationDocument29 pagesCell RespirationJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- (Cellular Respiration) : Organisms Capture and Store Free Energy For Use in Biological ProcessesDocument41 pages(Cellular Respiration) : Organisms Capture and Store Free Energy For Use in Biological Processesapi-373344212No ratings yet
- Lecture 4, Ch. 9Document30 pagesLecture 4, Ch. 9S. SpencerNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument18 pagesCellular Respirationapi-355214789No ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: Food ATPDocument43 pagesCellular Respiration: Food ATPAmolkumar W DiwanNo ratings yet
- Variable Speed Pumping: A Guide to Successful ApplicationsFrom EverandVariable Speed Pumping: A Guide to Successful ApplicationsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- GLYCOLYSISDocument6 pagesGLYCOLYSISHAZEL SANDRONo ratings yet
- SHS Biology 1 LPDocument4 pagesSHS Biology 1 LPEmerick QuevedoNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics of Edentulous StateDocument15 pagesBiomechanics of Edentulous StateNadeemNo ratings yet
- 4life Transfer Factor: Which Product Is Right For Me?Document1 page4life Transfer Factor: Which Product Is Right For Me?jhimsyNo ratings yet
- 1) Varaz Chaniago 2) Vicka Zahara Firdaus 3) Vina Nur Sholikhah 4) Zidan Abdul GaniDocument22 pages1) Varaz Chaniago 2) Vicka Zahara Firdaus 3) Vina Nur Sholikhah 4) Zidan Abdul GaniFikri RamaNo ratings yet
- Male Genital Organs in The Red Fox (Vulpes Vulpes) Macroanatomic and Three-Dimentional Reconstruction AspectDocument10 pagesMale Genital Organs in The Red Fox (Vulpes Vulpes) Macroanatomic and Three-Dimentional Reconstruction AspectAva DávidNo ratings yet
- SNS2023 BookletDocument44 pagesSNS2023 BookletAryan FeryNo ratings yet
- CHM4116 Nitrogen Metab ReviewerDocument22 pagesCHM4116 Nitrogen Metab ReviewerBEA FRANCINE DELOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Topic 2.8 SL Respiration QuestionsDocument9 pagesTopic 2.8 SL Respiration QuestionsIzabella Rea100% (1)
- Musculoskeletal System Lecture NotesDocument169 pagesMusculoskeletal System Lecture Noteszygote0711578796% (28)
- Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs) and Other Adducts in Aging-Related Diseases and Alcohol-Mediated Tissue InjuryDocument21 pagesAdvanced Glycation End Products (AGEs) and Other Adducts in Aging-Related Diseases and Alcohol-Mediated Tissue Injurysorin.morosan64No ratings yet
- 5.1 Estudio Farmacognostico de P.oleraceaDocument5 pages5.1 Estudio Farmacognostico de P.oleraceaNatalia OlmosNo ratings yet
- Messengers From The MicrobiotaDocument3 pagesMessengers From The MicrobiotaDra. Ianna CarmoNo ratings yet
- Full Answer Scheme Bioscore f4Document99 pagesFull Answer Scheme Bioscore f4EMAN NUR DANIEL BIN MOHD ZULKIFLY100% (1)
- Zampedri EtalDocument15 pagesZampedri EtalAronyMartinezNo ratings yet
- Hema Lec Week 16 Leukocyte Disorders Part 2Document4 pagesHema Lec Week 16 Leukocyte Disorders Part 2Max RuideraNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis: Homoios - "The Same" Stasis - "Standing" Homeostasis - "Standing or Staying The Same"Document6 pagesHomeostasis: Homoios - "The Same" Stasis - "Standing" Homeostasis - "Standing or Staying The Same"Jayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- Placentation in MammalsDocument261 pagesPlacentation in Mammalsjabeenjaveria98No ratings yet
- Effect of Environmental Factors On Fish Growth: Sonia BajajDocument5 pagesEffect of Environmental Factors On Fish Growth: Sonia BajajMoaz FiazNo ratings yet
- M2F Cardiovascular SystemDocument8 pagesM2F Cardiovascular SystemMeteor 858No ratings yet
- Mcqs On Hemoglobin and Myoglobin: Answer BDocument25 pagesMcqs On Hemoglobin and Myoglobin: Answer BYasif Abbas100% (1)
- 0 BooksDocument20 pages0 Bookslaraib zahidNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption - Practice SheetDocument4 pagesDigestion and Absorption - Practice Sheetsubhash devpalNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Worksheet 6.1Document5 pagesDigestive System Worksheet 6.1alice mamaNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Exercise: The HipDocument39 pagesTherapeutic Exercise: The HipMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- IBD (Crohn's and Ulcerative Colitis) TransDocument7 pagesIBD (Crohn's and Ulcerative Colitis) TranstristineNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Biomolecules and CellsDocument9 pagesUnit 2 Biomolecules and CellskathNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Pharmacology of Neuropeptides - Oxytocin (PDFDrive)Document586 pagesBehavioral Pharmacology of Neuropeptides - Oxytocin (PDFDrive)Emine Mamuti100% (1)
- Lec 16 Normal Radiographic AnatomyDocument56 pagesLec 16 Normal Radiographic Anatomyعباس اركان صيوان عطوانNo ratings yet
- The Pathophysiology of Sepsis - 2021 Update - Part 2, Organ Dysfunction and AssessmentDocument13 pagesThe Pathophysiology of Sepsis - 2021 Update - Part 2, Organ Dysfunction and AssessmentValerie ZimmermannNo ratings yet