Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electricity
Electricity
Uploaded by
hehe hahaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electricity
Electricity
Uploaded by
hehe hahaCopyright:
Available Formats
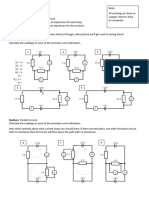
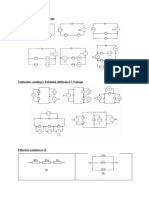
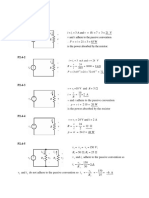
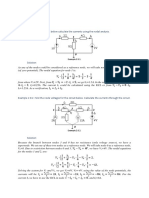
Resistors connected in series Find V2 and V5
Method 1 (finding current first) Current is the same throughout the
ℰ=3V
Reff =2+5 =7Ω whole circuit as the circuit is in series,
V 3 therefore, a current of 0.429 A passes
I= = = 0.429 A
Reff 7 through the 2 Ω resistor, the 5 Ω
V = IR = 0.429 × 2 = 0.857 V resistor and even the battery.
2Ω 5Ω
I Method 2 (using proportions) V2 + V5 =3
P.d. across the 2 Ω resistor = I×2 +I×5 =3
V2 V5 2 2
× 3 = 0.857 V V2 is of the total p.d.
2+7 2+5
5
V5 is of the total p.d.
2+5
Resistors connected in parallel Find I2, I5 and I
ℰ=3V Method 1 (using V = IR directly) Method 2 (finding I first using Reff)
V 3 −1
I2 = 2 = = 1.5 A 1 1 10
R 2 Reff = + = Ω
V 3 5 2 7
I5 I5 = 5 = = 0.6 A 10
R 5 I =3÷ = 2.1 A
I = I2 + I5 = 2.1 A 7
5Ω I 5
Recognise that V2 = V5 = 3 V I2 = × 2.1 = 1.5 A
2+5
(not drawn in diagram) I5 = 2.1 – 1.6 = 0.5 A
I
2Ω
I2
Find I1, I2 and I Find Vx
Method 1 (you can try Method 2) • V3 = I1R = 0.875 × 3 = 2.625 V
ℰ=7V V + V5 7 • V4 = I2R = 1.17 × 4 = 4.67 V
I1 = 3 = =0.875 A
R 3+5 • Suppose A has a potential of 7 V.
V + V2 7
I1 I2 = 4 = =1.17 A • Since Points A, B and C are “the
R 4+2
D I = I2 + I5 = 2.04 A same wire”, they all are at 7 V.
B
3Ω 5Ω Recognise that • D’s potential is 2.63 V lower than B’s.
Vx V3 + V5 = V4 + V2 = 7 V • E’s potential is 4.67 V lower than C’s.
• Potential at D = 7 – 2.63 = 4.37 V
A I 4Ω 2Ω • Potential at E = 7– 2.67 = 2.33 V
C I E
2 • Vx = 4.37 – 2.33 = 2.04 V
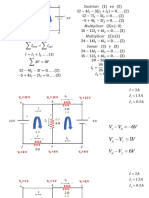
n resistors of the same Find the effective resistance of these resistors
resistance connected −1
1 1
in parallel 8Ω 3Ω 8Ω 3Ω = +
8+3 4
2Ω = 2.93 Ω
4Ω 4Ω
1 1 −1
7Ω = + 5Ω
7 7
−1 5Ω
7Ω 2 6Ω 1 1 1 −1
= = + +
7 6Ω 5 6 7
7 = 1.96 Ω
= Ω 7Ω
2 7Ω
9Ω
1 1 1 −1
= + + 2Ω 2.93 Ω
7 7 7
7Ω 2Ω 2.93 Ω
−1
3
= 1.96 Ω
7Ω 7
1.96 Ω −1
7 1 1
= Ω = +
7Ω 3 9Ω 2+2.93 1.96
= 1.40 Ω
If there are n of such
resistors, 1.40 Ω −1
1 1
n −1 7 Reff = +
1.40 9
= 1.21 Ω
Reff = = Ω
7 n
9Ω
You might also like
- Plessey LinearIntegratedCircuitHandbook TextDocument209 pagesPlessey LinearIntegratedCircuitHandbook TextAnonymous QakmLc3kTI100% (1)
- Elecs Compilation 1Document42 pagesElecs Compilation 1Raine LopezNo ratings yet
- PDM User ManualDocument60 pagesPDM User Manualjlee_296737100% (1)
- Advanced Electric Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionFrom EverandAdvanced Electric Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Microelectronic Circuits 3rd Edition by RashidDocument28 pagesSolution Manual For Microelectronic Circuits 3rd Edition by Rashida84803472733% (3)
- 7012 DeltaV Training NotesDocument197 pages7012 DeltaV Training Notesfransiskus matondang100% (3)
- SAP Programming LanguageDocument76 pagesSAP Programming Languagejabbar1959No ratings yet
- 80-Yb952-3 D Wlan Conformance Testing and Compliant Power Configuration For 802.11a B N Ac Chipsets, Information To Share With Test LabDocument47 pages80-Yb952-3 D Wlan Conformance Testing and Compliant Power Configuration For 802.11a B N Ac Chipsets, Information To Share With Test Lab趙致鈞100% (1)
- Azure App ServicesDocument8 pagesAzure App ServicesAditya SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Experiment #4: Ohm's Law Problem Set: Show Calculations and UnitsDocument4 pagesExperiment #4: Ohm's Law Problem Set: Show Calculations and UnitsMari KuljanishviliNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Exercise 3 SolDocument4 pagesCurrent Electricity Exercise 3 SolAyush AroraNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2022-23 EEE1024 ETH VL2022230107633 Reference Material I 07-10-2022 Module 1 L3 Node Voltage Analysis Mesh Current AnalysisDocument11 pagesFALLSEM2022-23 EEE1024 ETH VL2022230107633 Reference Material I 07-10-2022 Module 1 L3 Node Voltage Analysis Mesh Current AnalysisKaushik VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- 10V and V - 2V.: Unit I - IIDocument4 pages10V and V - 2V.: Unit I - IINarendra SNo ratings yet
- 돌프 회로이론 9판 솔루션2장Document23 pages돌프 회로이론 9판 솔루션2장k2003040No ratings yet
- ch02 (ch02 PDFDocument11 pagesch02 (ch02 PDFAyadNo ratings yet
- Lecture-05 Simple Circuit ReductionsDocument8 pagesLecture-05 Simple Circuit Reductionsnonton youtubeNo ratings yet
- UHD EET1411 - Direct Current Circuit - Final-Homework Fall 2020 Name of Student - Problem 1 (15pts)Document6 pagesUHD EET1411 - Direct Current Circuit - Final-Homework Fall 2020 Name of Student - Problem 1 (15pts)Angela AliNo ratings yet
- EENG 223 Final Exam S08-09 SolnDocument7 pagesEENG 223 Final Exam S08-09 Solnkwakwa4No ratings yet
- Problems: Section 2-2 Engineering and Linear Models P2.2-1Document15 pagesProblems: Section 2-2 Engineering and Linear Models P2.2-1Oscar OmarNo ratings yet
- EE204 Lecture Notes Lecture 05Document12 pagesEE204 Lecture Notes Lecture 05Quantum SaudiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document20 pagesChapter 2badrilaminNo ratings yet
- Practice 7: Voltage and Current DividerDocument11 pagesPractice 7: Voltage and Current DividerAndres RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Ohm'S Law and Power I. ObjectivesDocument7 pagesOhm'S Law and Power I. ObjectivesMark GalerioNo ratings yet
- Physics 1161: Lecture 10Document20 pagesPhysics 1161: Lecture 10sumitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document61 pagesChapter 2CHEAH HUI TING STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Be - Electronics and Telecommunication - Semester 4 - 2018 - May - Linear Integrated Circuits CbcgsDocument24 pagesBe - Electronics and Telecommunication - Semester 4 - 2018 - May - Linear Integrated Circuits CbcgsRatnakar YadavNo ratings yet
- EEE1001 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering: Node Voltage Analysis, Mesh Current AnalysisDocument11 pagesEEE1001 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering: Node Voltage Analysis, Mesh Current AnalysisISHAAAAAAAAAAANNo ratings yet
- Ass 2022Document4 pagesAss 2022gogajauharNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit Fundamentals: Sinan BalçiDocument19 pagesElectric Circuit Fundamentals: Sinan BalçikjjsbdfjkjhafNo ratings yet
- Node and Supernode Final 2Document10 pagesNode and Supernode Final 2Ellen Kay CacatianNo ratings yet
- Bab 5 - Circuit AnalysisDocument4 pagesBab 5 - Circuit AnalysisLuqman HakimNo ratings yet
- Electric - 03 Task Performance 1 ARG DAIZ G301Document4 pagesElectric - 03 Task Performance 1 ARG DAIZ G301Regie PascuaNo ratings yet
- AnswersDocument1 pageAnswersCristhiancho100No ratings yet
- Mesh Node AnalysisDocument35 pagesMesh Node AnalysisjashmithajanuNo ratings yet
- Principle of EE1: Lesson 2Document64 pagesPrinciple of EE1: Lesson 2Nguyễn Hoàng LânNo ratings yet
- EE2001 Tutorial 8 QuestionsDocument3 pagesEE2001 Tutorial 8 QuestionsPeiXuan HoNo ratings yet
- Question #1:: Homework #1Document2 pagesQuestion #1:: Homework #1DavidRubeomNo ratings yet
- Prob3 7s PDFDocument1 pageProb3 7s PDFclaireNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Homework SolutionDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Homework SolutionPao JJNo ratings yet
- Basic Laws - Voltage and Current DivisionDocument12 pagesBasic Laws - Voltage and Current DivisionSTACEYLEEN CYENTHIA LADIUN BK22110177No ratings yet
- Chapter 27 - Practice 1Document2 pagesChapter 27 - Practice 1Mohd KassabNo ratings yet
- Electrodinámica - II Teoría y PrácticaDocument3 pagesElectrodinámica - II Teoría y PrácticaJAIME ROANo ratings yet
- Kirchhoffs Law WorksheetDocument2 pagesKirchhoffs Law Worksheetkm6jzq7tt6No ratings yet
- Ammeter Reading CurrentDocument4 pagesAmmeter Reading CurrentNoorNo ratings yet
- Nodal and MeshDocument57 pagesNodal and MeshDharamNo ratings yet
- 03TaskPerformance1 PECHONDocument4 pages03TaskPerformance1 PECHONAbug Jaime Jr.No ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Ohm Law TutorialDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 - Ohm Law TutorialNur FazilaNo ratings yet
- Prob3 21sDocument2 pagesProb3 21sFelipe TordecillaNo ratings yet
- CH2 Sec 4Document3 pagesCH2 Sec 4김성준No ratings yet
- EEE Exams: Emman Joshua B. Busto June 8, 2017Document5 pagesEEE Exams: Emman Joshua B. Busto June 8, 2017reneSantosIVNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Solving Circuit DiagramsDocument2 pagesWorksheet - Solving Circuit DiagramsdiclNo ratings yet
- Chap3 HW2 SolutionDocument6 pagesChap3 HW2 SolutionAbdi ZerihunNo ratings yet
- DC CircuitsDocument37 pagesDC CircuitsRouxNo ratings yet
- 60286-Chapter 02 PDFDocument50 pages60286-Chapter 02 PDFYvesNo ratings yet
- To Learn Analysis of DC Series-Parallel Circuit. To Verify Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) - To Verify Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL)Document5 pagesTo Learn Analysis of DC Series-Parallel Circuit. To Verify Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) - To Verify Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL)taynaNo ratings yet
- Adapun Analisis Data Pada Pengukuran Multimeter Analog Dan DigitalDocument4 pagesAdapun Analisis Data Pada Pengukuran Multimeter Analog Dan Digitaltuti suoriyantiNo ratings yet
- P=Vi I= P V I= I=0.06 A V =Ri R= V I R= R=2083.33ΩDocument2 pagesP=Vi I= P V I= I=0.06 A V =Ri R= V I R= R=2083.33ΩKevin A. ChavarriaNo ratings yet
- Taller 7Document2 pagesTaller 7Kevin A. ChavarriaNo ratings yet
- Resistors in Series-Parallel CircuitDocument3 pagesResistors in Series-Parallel CircuitMarianneIvon AndayaNo ratings yet
- Circuitos RCDocument20 pagesCircuitos RCSergio MontejoNo ratings yet
- SP DC Nodal - AnalysisDocument2 pagesSP DC Nodal - Analysisflory vicarNo ratings yet
- Calculus II (MATH 1062) Test #2 Practice ProblemsDocument4 pagesCalculus II (MATH 1062) Test #2 Practice ProblemsasdfasdfasdfNo ratings yet
- Description of Diodes.Document25 pagesDescription of Diodes.Ard Tangonumb ArvindNo ratings yet
- INC 111 Basic Circuit AnalysisDocument32 pagesINC 111 Basic Circuit AnalysisAugustine JR RobertNo ratings yet
- KVL, KCL, Nodal Analysis 111261003Document4 pagesKVL, KCL, Nodal Analysis 111261003r0.082.be11No ratings yet
- Configuring and Extending ApplicationsDocument192 pagesConfiguring and Extending Applicationsanirudhabhuyar1No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - ExercisesDocument5 pagesChapter 2 - ExercisesHiếu Phạm Jr.No ratings yet
- Fact - Sheet - ESAA150ACTA0101 - en - Rev01 (5017272800)Document5 pagesFact - Sheet - ESAA150ACTA0101 - en - Rev01 (5017272800)PhạmNo ratings yet
- Huawei PCN DBS3900 (AC) APM30H&TMC11H&IBBS200D&T - Ver.B To Ver.DDocument13 pagesHuawei PCN DBS3900 (AC) APM30H&TMC11H&IBBS200D&T - Ver.B To Ver.DNataša Mihić BoskovićNo ratings yet
- User Manual: Firmware v1.06Document6 pagesUser Manual: Firmware v1.06Josè GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Geforce GTX 1050 2GB DDR5 GF1050GTX2GEPB: Pure Performance, Ultimate ExperienceDocument1 pageGeforce GTX 1050 2GB DDR5 GF1050GTX2GEPB: Pure Performance, Ultimate ExperienceHerkul BoyNo ratings yet
- CCNA Exploration: Accessing The WAN Demo Practical Exam Topology DiagramDocument16 pagesCCNA Exploration: Accessing The WAN Demo Practical Exam Topology Diagramlachmannmarcel100% (3)
- Transistor Counts: 1 Billion TransistorsDocument15 pagesTransistor Counts: 1 Billion TransistorsNeeraj KalraNo ratings yet
- Campus Mobile Implementation GuideDocument30 pagesCampus Mobile Implementation GuidePakDefenderDefenderNo ratings yet
- CSC612M Problem Set #7 - 1st Term SY 2016-2017Document5 pagesCSC612M Problem Set #7 - 1st Term SY 2016-2017Chester Paul H. IbarrientosNo ratings yet
- I 1691Document32 pagesI 1691Juan Carlos Montes CastillaNo ratings yet
- Oracle 6 Admin GuideDocument386 pagesOracle 6 Admin GuideIla IlanNo ratings yet
- OPS243 Product Brief - 004 DDocument2 pagesOPS243 Product Brief - 004 DChristophe GreffeNo ratings yet
- 02 - Components of The System Unit PDFDocument59 pages02 - Components of The System Unit PDFJohn Michael ÜyNo ratings yet
- Lic Project Report Vinod GroupDocument12 pagesLic Project Report Vinod GroupPavase SumitNo ratings yet
- Etm Chapter 3 4 5Document304 pagesEtm Chapter 3 4 5prathamesh GawadeNo ratings yet
- CB-780 Cleaver Brooks 1Document2 pagesCB-780 Cleaver Brooks 1alfredomitzihNo ratings yet
- Requirements Modeling: Flow, Behavior, Patterns, and WebappsDocument46 pagesRequirements Modeling: Flow, Behavior, Patterns, and WebappsAnonymous 9XShfF100% (1)
- Number: C9510-418 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 Min File Version: 1Document39 pagesNumber: C9510-418 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 Min File Version: 1Ahmed KhaledNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Question BankDocument7 pagesMicroprocessor Question Bankjpradeek0% (1)
- iTWO costX Standalone Database Backup and RecoveryDocument28 pagesiTWO costX Standalone Database Backup and RecoveryMikeNo ratings yet
- Dell1950 I DatasheetDocument2 pagesDell1950 I DatasheetJasen YoungNo ratings yet
- Electronic Design Chapter 1 PDFDocument136 pagesElectronic Design Chapter 1 PDFAisyah CANo ratings yet
- A Git Cheat Sheet (Git Command Reference) - A Git Cheat Sheet and Command ReferenceDocument14 pagesA Git Cheat Sheet (Git Command Reference) - A Git Cheat Sheet and Command ReferenceMohd AzahariNo ratings yet