Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ejercicios 3.2 Con Soluciones - Documentos de Google
Uploaded by
Juan Carlos SALAS MESA0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesEjercicios 3.2 Con Soluciones - Documentos de Google
Uploaded by
Juan Carlos SALAS MESACopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
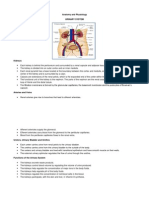
1. Say the main characteristics of arteries.
Have a circular cross section, thick elastic walls and transport
blood from the heart to the organs. They branch off into thinner
vessels called arterioles.
2. Say the main characteristics of veins.
Have an oval cross section and thin less elastic wall than
arteries. They transport blood from the organs to the heart. They
have valves to prevent the reverse blood flow. They are formed
by the joining together of venules.
3. Name the functions of the blood.
- Transport substances.
- Defend the body.
- Regulate the body temperature.
4. Name the functions of the:
- Erythrocytes: transport oxygen and carbon dioxide.
- Leucocytes: defend the body against infections and
tumor cells.
- Platelets: are involved in blood clotting
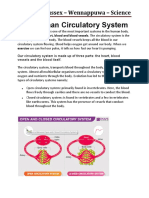
5. Write the path of a red blood cell from the right ventricle to the
right ventricle passing through the pancreas.
Right ventricle- semilunar valve- pulmonary artery- arterioles- lung
capillaries- venules-pulmonary veins- left atrium- mitral valve- left
ventricle- semilunar valve- aorta artery- pancreatic artery-arterioles-
pancreatic capillaries- venules- pancreatic vein- inferior vena cava -
right atrium- tricuspid valve
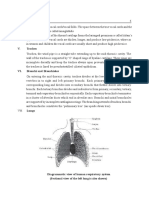
6. Name the function of the pulmonary circuit.
Its function is to transport blood to the lungs to oxygenate it and
to expell the carbon dioxide.
7. Name the function of the systemic circuit.
Its function is to transport
nutrients and oxygen to the cells and to remove carbon dioxide
and waste products from them in order to be expelled.
8. Name the function of the lymphatic system.
- Remove the excess of interstitial fluid.
- Transport fats.
- Defend the organism by producing white blood cells.
9. Name the liquids of the internal environment.
interstitial fluid, lymph, blood.
10. Explain the function of the valves in the circulatory system.
The function is to prevent the reverse blood flow.
11. Name the stages of the urine formation indicating the place of
the nephron where they take place.
- Filtration: in the glomerulus.
- Reabsorption: in the renal tubule.
- Secretion: in the last part of the renal tubule.
12. Name all the excretory organs.
liver, sweat glands, lungs, kidneys.
13. Name the stages of the cardiac cycle indicating what
happens in each one of them.
- Atrial systole: the atria contract and force the blood towards
the ventricles through the open tricuspid and mitral valve.
- Ventricular systole: the ventricles contract, mitral and
tricuspid valve close and the blood passes towards the
semilunar valves into the pulmonary and aorta artery.
- Diastole: atria and ventricles are relaxed, semilunar valves
are closed and blood enters into the heart from the veins.
14. Define systole, diastole and cardiac cycle.
Systole: the contraction movement of the heart.
Diastole: dilatation movements of the heart.
Cardiac cycle: the sequence of contraction and dilatation
movements of the heart.
You might also like
- Circulatory System: A Tutorial Study GuideFrom EverandCirculatory System: A Tutorial Study GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- CIRCULATORY SYSTEM - CopyDocument13 pagesCIRCULATORY SYSTEM - Copy2015.562fatimazaherakhanumNo ratings yet
- Test ReviewDocument7 pagesTest ReviewOliver NamyaloNo ratings yet
- Review and Comprehension (Blood Vessel)Document4 pagesReview and Comprehension (Blood Vessel)9pjh6pzxmsNo ratings yet
- Human Circulatory SystemDocument9 pagesHuman Circulatory SystemEvansNo ratings yet
- AcknowledgementDocument9 pagesAcknowledgementJovin AshickNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Transport in HumansDocument11 pages5.2 Transport in Humans박찬우No ratings yet
- Chapter 42 Reading GuideDocument5 pagesChapter 42 Reading GuideCaleb SchantzNo ratings yet
- 8th CIRCULATORY SYSTEMDocument6 pages8th CIRCULATORY SYSTEMammarahn0No ratings yet
- Lab 9 - Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesLab 9 - Circulatory SystemClobelle Marie SiachuaNo ratings yet
- Transport in Animals-Topic 9Document14 pagesTransport in Animals-Topic 9sukiiNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Cardio XIIDocument15 pagesAnaphy Cardio XIIRue Cheng MaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument7 pagesCirculatory SystemWisdom DzombeNo ratings yet
- DomingoDocument3 pagesDomingoMikaellah DomingoNo ratings yet
- Types of Circulatory SystemsDocument8 pagesTypes of Circulatory SystemsJanis Micaela EsmasNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyCherry Oña AntoninoNo ratings yet
- Heart and CirculationDocument12 pagesHeart and CirculationEizelle Zabyne VerzosaNo ratings yet
- Ventricle and Atria), Have Different Blood VesselsDocument5 pagesVentricle and Atria), Have Different Blood VesselsAnastasia MartynenkoNo ratings yet
- BookDocument8 pagesBookmohamed aweys abuukarNo ratings yet
- 2 CardioDocument26 pages2 Cardiorashmi_harryNo ratings yet
- Normal AnatomyDocument4 pagesNormal AnatomyDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- KS3 Science Year 9 The Circulatory System-2Document15 pagesKS3 Science Year 9 The Circulatory System-2f72ktyd78nNo ratings yet
- W.G. Igcse Transport in HumansDocument20 pagesW.G. Igcse Transport in Humansbloodshooter1996No ratings yet
- 6th Lecture Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pages6th Lecture Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDwnya S HasanNo ratings yet
- The Human Circulatory System: Grade 9 - Sussex - Wennappuwa - ScienceDocument23 pagesThe Human Circulatory System: Grade 9 - Sussex - Wennappuwa - ScienceSwarnapaliliyanageNo ratings yet
- The Heart: Anatomy, Chambers, Circulation & ValvesDocument14 pagesThe Heart: Anatomy, Chambers, Circulation & ValvesGary Bowen100% (1)
- Chp 05 (Blood and Circulation) DrRiyadAhmed PC 3Document69 pagesChp 05 (Blood and Circulation) DrRiyadAhmed PC 3Kamrun NaherNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory and Excretory SystemsDocument9 pagesThe Circulatory and Excretory SystemsMeneses Oriano SaraNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Q&A.Document77 pagesCirculatory System Q&A.Alyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3: Chapter 2 Blood Circulation and TransportDocument39 pagesScience Form 3: Chapter 2 Blood Circulation and TransportNadzirah RedzuanNo ratings yet
- Review Transport System TaylorDocument5 pagesReview Transport System TaylorPaola MontenegroNo ratings yet
- +1 Bio Zoo em Vol 2Document38 pages+1 Bio Zoo em Vol 2Ameena BegumNo ratings yet
- Presidium Indirapuram Students Handout-3 Grade X (Biology) Chapter: Life Processes Topic: TransportationDocument8 pagesPresidium Indirapuram Students Handout-3 Grade X (Biology) Chapter: Life Processes Topic: TransportationSaniya nebNo ratings yet
- CirculationDocument9 pagesCirculationakkaranniNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 ScienceDocument17 pagesLesson 1 SciencePrincess Jane TulinNo ratings yet
- Campbell Chapter 42 NotesDocument17 pagesCampbell Chapter 42 NotesRyan LiuNo ratings yet
- Transportation 1 PDFDocument9 pagesTransportation 1 PDFNakshatra PaliwalNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 pagesCirculatory System: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaBruce WayneNo ratings yet
- Note On F3 SC C2 TransportationDocument4 pagesNote On F3 SC C2 Transportationgan tong hock a.k.a ganosNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument10 pagesCardiovascular SystemDhea BugnaNo ratings yet
- Three Circulatory Systems Working TogetherDocument4 pagesThree Circulatory Systems Working TogetherSteven OwenNo ratings yet
- 10th BIOLOGY PRACTICALS (1-19)Document31 pages10th BIOLOGY PRACTICALS (1-19)vidisha bhansaliNo ratings yet
- PALMA, LYCA D. - CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM (Heart and Blood Vessels)Document6 pagesPALMA, LYCA D. - CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM (Heart and Blood Vessels)G-Palma, Lyca D.No ratings yet
- Blood Circulation and TransportDocument23 pagesBlood Circulation and TransportcikzafirahNo ratings yet
- The Composition and Functions of BloodDocument5 pagesThe Composition and Functions of BloodMariam AbesadzeNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Iii. Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 pagesCardiovascular System: Iii. Anatomy and PhysiologyYam Bite-Size FabelloNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 NotesDocument18 pagesTopic 1 NotesKesithan AnandarashNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesRespiratory SystemMaria FelizeNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Reviewer First QRTDocument4 pagesScience 9 Reviewer First QRTAshleyNo ratings yet
- Alwadi International School Grade 9 Biology 9. Transport in Animals NotesDocument62 pagesAlwadi International School Grade 9 Biology 9. Transport in Animals NotesMohammed HelmyNo ratings yet
- Study Guide 24 - Urinary SystemDocument19 pagesStudy Guide 24 - Urinary SystemcharlesNo ratings yet
- Circulation Notes I To VIDocument8 pagesCirculation Notes I To VIStacey KwiatkowskiNo ratings yet
- Heart Chambers, Valves & Blood FlowDocument3 pagesHeart Chambers, Valves & Blood FlowArshad M HabibNo ratings yet
- Circulatory Long ActivityDocument5 pagesCirculatory Long Activity26jmuzychenkoNo ratings yet
- Candon City, Ilocos Sur Grade 9 Reviewer School Year 2021 - 2022Document7 pagesCandon City, Ilocos Sur Grade 9 Reviewer School Year 2021 - 2022Aleah TungbabanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12, BioDocument26 pagesChapter 12, BioRylee LNo ratings yet
- Transport in MammalDocument45 pagesTransport in MammalShanzay SaqibNo ratings yet
- V. Trachea: Zoology-IIDocument22 pagesV. Trachea: Zoology-IIVenkatesh JoguNo ratings yet
- 0610 m15 QP 12Document16 pages0610 m15 QP 12zzzNo ratings yet
- Pig Heart DissectionDocument4 pagesPig Heart DissectionHarvey DabonNo ratings yet
- Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump GuideDocument27 pagesIntra-Aortic Balloon Pump GuideJadie Barringer IIINo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic ManuelDocument115 pagesHemodynamic ManuelMayuresh Chaudhari100% (2)
- Abnormal heart sounds explainedDocument3 pagesAbnormal heart sounds explainedmuhammad azizulhakimNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE - X Golden Sample Paper - 2021-22Document72 pagesSCIENCE - X Golden Sample Paper - 2021-22krish patelNo ratings yet
- Basic Cardiac Electrophysiology ExplainedDocument53 pagesBasic Cardiac Electrophysiology ExplainedFikriYTNo ratings yet
- Molecules To and From The Different Parts of The Body. S9LT-la-b-26Document7 pagesMolecules To and From The Different Parts of The Body. S9LT-la-b-26Lara ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- Embryology Practice Questions With Answers: Click To FlipDocument31 pagesEmbryology Practice Questions With Answers: Click To FlipTofik MohammedNo ratings yet
- Localization On ECG: Myocardial Ischemia / Injury / InfarctionDocument56 pagesLocalization On ECG: Myocardial Ischemia / Injury / InfarctionduratulfahliaNo ratings yet
- s.3 Biology Transport in Plants and Animals NotesDocument40 pagess.3 Biology Transport in Plants and Animals Notesgeofreyvybz95No ratings yet
- BS IN ACCOUNTANCY (PHYSICAL EDUCATION) Assignments and QuizzesDocument23 pagesBS IN ACCOUNTANCY (PHYSICAL EDUCATION) Assignments and QuizzesRegine VegaNo ratings yet
- Human Circulatory System - CBSE Class 10Document2 pagesHuman Circulatory System - CBSE Class 10Gurukul24x767% (3)
- Optimising Colour Flow Doppler ImagingDocument1 pageOptimising Colour Flow Doppler ImagingMihaela IonescuNo ratings yet
- Cycle 1 Lab 2 Cardiomecanogramxzv XDocument27 pagesCycle 1 Lab 2 Cardiomecanogramxzv XanaNo ratings yet
- Online Session 19Document2 pagesOnline Session 19addy 05No ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument20 pagesCirculatory SystemsuryanshNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Coverings, Walls of HeartDocument8 pagesAnatomy, Coverings, Walls of HeartDeniebev'z OrillosNo ratings yet
- NSO Class 8 Solved Sample PaperDocument8 pagesNSO Class 8 Solved Sample Papergopi_dey8649100% (1)
- Chapter 12 VocabDocument2 pagesChapter 12 VocabwdsfNo ratings yet
- First Responder NotesDocument8 pagesFirst Responder Notesjoe_a_salvatoreNo ratings yet
- Cardiology Mcq's Part - 1Document31 pagesCardiology Mcq's Part - 1aymenNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology On ArrhythmiaDocument34 pagesPathophysiology On ArrhythmiaYhr Yh100% (1)
- Permanent Pacemaker Implantation Technique Part IIDocument10 pagesPermanent Pacemaker Implantation Technique Part IIRaul OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Preeclampsia FinalDocument112 pagesPreeclampsia FinalEarl John DayanghirangNo ratings yet
- Atrioventricular Block (Heart Block) : Causes of Atrio-Ventricular BlockDocument5 pagesAtrioventricular Block (Heart Block) : Causes of Atrio-Ventricular BlockLiza MPNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular System: Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical CollegeDocument125 pagesThe Cardiovascular System: Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical Collegedomo domoNo ratings yet
- Science-6 - PT - Q-2Document7 pagesScience-6 - PT - Q-2Erwin AcebucheNo ratings yet
- Body Fluids and Circulation NotesDocument8 pagesBody Fluids and Circulation Notessatyam6449No ratings yet
- TOEFL EXERCISE FOR SKILL 1: Carbon Tetrachloride Banned in Home ProductsDocument5 pagesTOEFL EXERCISE FOR SKILL 1: Carbon Tetrachloride Banned in Home ProductsKhomsiatul MunawarohNo ratings yet
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (14)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (402)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementFrom EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (40)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsFrom EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (34)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (33)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingFrom EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)