Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Metal Vs Nonmetal
Uploaded by
ritchelle rueras0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageMetal vs Nonmetal notes
Original Title
Metal vs Nonmetal
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMetal vs Nonmetal notes
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageMetal Vs Nonmetal
Uploaded by
ritchelle ruerasMetal vs Nonmetal notes
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Metal vs Nonmetal
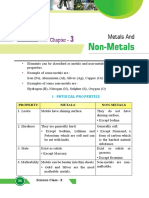
METALS vs NON-METAL in periodic table
There is a zig-zag or staircase line that divides the table.
Metals are on the left of the line, in blue.
Nonmetals are on the right of the line, in orange.
PROPERTIES OF METALS vs NON-METAL
METALS NON-METALS
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES Solid at room temperature Can be gas, solid, or liquid at room
- exception: Hg temperature
Good conductors of heat and electricity Come in all colors
Ductility and malleability No metallic luster
Shinning luster Poor conductors
High density Brittle
High melting points Odors or pungent
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES Lose Electrons Tend to gain electrons
(makes positive ion) (makes negative ion)
Corrode easily
Physical property of metal & non-metal
Corrosion of metal
Mechanism or steps Involved in corrosion
1. A metal in contact with a solution with corrode if there are chemical species in the solution which can be rediuced at a potential
more positive than the reduction
Corrosion – is the chemical attack on the metal by its environment
Chemical attack is a chemical reaction in which a metal is oxidized. The reaction is electrochemical in nature
Factors affect the rate of corrosion
Presence of corrosion agent
Example: SO2 and CO2 dissolve in water form acid solution (H2SO3) and increase rate of corrosion
Position in electrochemical series
Metals high in the electrochemical series, have large positive oxidation potentials corrode easily
Example: group 3B elements, lanthanides, alkali and alkaline earth
Type of film or coating formed on the surface of metal
Example: aluminum and magnesium actually reacts when expose to air but a thin closely packed film of oxide that forms on the
surface protects the underlying metal to prevent corrosion
WHAT IS A SEMICONDUCTOR?
A semiconductor is a material which has electrical conductivity between that of a conductor such as copper and an insulator such as
glass. The conductivity of a semiconductor increases with increasing temperature, behaviour opposite to that of a metal
You might also like
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Metallic and Nonmetallic PropertiesDocument24 pagesMetallic and Nonmetallic PropertiesEleanor Alma JuguetaNo ratings yet
- Metalsmetaloidsnon MetalsDocument26 pagesMetalsmetaloidsnon MetalsKorean dramaNo ratings yet
- Chemical PropertiesDocument1 pageChemical PropertiesjassgNo ratings yet
- Form 1 Science Chapter 6Document10 pagesForm 1 Science Chapter 6Koo SengleeNo ratings yet
- Chem PrintsDocument18 pagesChem Printsanayaa agarwalNo ratings yet
- Metals and NonmetalsDocument2 pagesMetals and NonmetalsAnnisa Ekaputri FebrianiNo ratings yet
- Metalic Elements and PropertiesDocument5 pagesMetalic Elements and PropertiesM.zuhair asifNo ratings yet
- M&NM-TABLE - Phy and Chem PropDocument3 pagesM&NM-TABLE - Phy and Chem PropanjanaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical CorrosioDocument29 pagesElectrochemical CorrosioKalyavalla SathyasaiNo ratings yet
- Combined Science (Chemistry) : METALS: Metal Properties UsesDocument2 pagesCombined Science (Chemistry) : METALS: Metal Properties UsesHn HMSNo ratings yet
- Properties of Metals Non-Metals MetalloidsDocument23 pagesProperties of Metals Non-Metals MetalloidsConnie Joy CalawagNo ratings yet
- Metals Non Metals Class 8 PDFDocument11 pagesMetals Non Metals Class 8 PDFTechnical AkshayNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Module 1 PDFDocument28 pagesLecture 1 Module 1 PDFPrathamesh KumbharNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Power Point Presentation: Concept: Metals and Non-MetalsDocument15 pagesChemistry Power Point Presentation: Concept: Metals and Non-MetalsBhavesh BhaveshNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non - MetalsDocument7 pagesMetals and Non - MetalsAshton PaulNo ratings yet
- Properties of MetalsDocument4 pagesProperties of MetalsYanika BarasNo ratings yet
- Properties of MetalsDocument4 pagesProperties of MetalsKevin Joe CuraNo ratings yet
- Me Non MeDocument25 pagesMe Non MeTulga EddieNo ratings yet
- 2 Metals and Non-MetalsDocument23 pages2 Metals and Non-MetalsArmaanNo ratings yet
- Year 8 Chemistry October PresentationDocument58 pagesYear 8 Chemistry October PresentationAshwini BNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Types of Metals: Taught By: Professor Khan Fremont High School: 8 Grade Chemistry 101Document8 pagesChapter 2: Types of Metals: Taught By: Professor Khan Fremont High School: 8 Grade Chemistry 101api-510492949No ratings yet
- PDF Document 5Document25 pagesPDF Document 5miriam harriottNo ratings yet
- Metals, Nonmetals, MetalloidsDocument17 pagesMetals, Nonmetals, Metalloidszendy llima malicdemNo ratings yet
- Metals Metalloids Non-MetalsDocument36 pagesMetals Metalloids Non-MetalsIsrael PopeNo ratings yet
- 01 Answers 10.1 Properties of Metals Vs Non-MetalsDocument3 pages01 Answers 10.1 Properties of Metals Vs Non-MetalsSky LimNo ratings yet
- Uydz Uw WV USKa N61 MM JC 4Document6 pagesUydz Uw WV USKa N61 MM JC 4varshatagade126No ratings yet
- Crop Production & ManagementDocument14 pagesCrop Production & ManagementAnkit PatelNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Properties of MetalsDocument12 pagesChemistry: Properties of Metalsakiv shettyNo ratings yet
- Libro MetalesDocument6 pagesLibro Metaleslicomar464No ratings yet
- X Chem Master Key Differences 23 - 24Document35 pagesX Chem Master Key Differences 23 - 24zilkag47No ratings yet
- Some Properties Between Metals and NonmetalsDocument2 pagesSome Properties Between Metals and Nonmetalsanon-632572No ratings yet
- Chemistry Endurance Race 5070Document29 pagesChemistry Endurance Race 507024avesh.kumarNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document32 pagesCH 3Prachi RaniNo ratings yet
- RedoxDocument39 pagesRedoxashleytham89No ratings yet
- CHE882Unit3 L15Document8 pagesCHE882Unit3 L15Ms Mayank YadavNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals - NotesDocument8 pagesMetals and Non Metals - NotesMohita RastogiNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals 1Document34 pagesMetals and Non Metals 1Alessandra myrnaNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non MetalsDocument15 pagesMetals and Non Metalskebepef613No ratings yet
- Metals and Non-Metals: Module - 6Document19 pagesMetals and Non-Metals: Module - 6Brandeice BarrettNo ratings yet
- Comparing Kinds of MatterDocument39 pagesComparing Kinds of MattereriNo ratings yet
- Aadhithyaa Practice Periodic Table TestDocument2 pagesAadhithyaa Practice Periodic Table TestVikramaadhithyaa JagannathanNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table (Chemical Bonding)Document8 pagesPeriodic Table (Chemical Bonding)Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Properties of MetalsDocument18 pagesProperties of MetalsMohan RaiNo ratings yet
- 6 The Periodic Table (Teacher)Document42 pages6 The Periodic Table (Teacher)otto wongNo ratings yet
- GCSE ChemistryDocument22 pagesGCSE ChemistryAmeerul HazeeqNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-MetalsDocument11 pagesMetals and Non-MetalsJoecor Campina Jr.No ratings yet
- The Periodic Table of ElementsDocument30 pagesThe Periodic Table of ElementsVillamor BaculiNo ratings yet
- Metals and Some Aspects of CorrosionDocument20 pagesMetals and Some Aspects of CorrosionVan CometaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 FullDocument69 pagesModule 1 FullR TharunishNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non MetalsDocument28 pagesMetals and Non MetalsALEENANo ratings yet
- Element ClassesDocument13 pagesElement ClassesHoàng Thị Thanh KiềuNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals Notes Class 10 2022-23Document37 pagesMetals and Non Metals Notes Class 10 2022-23ramkumarsingh12406100% (1)
- Alkali and Alkali Earth Metals - SRDocument20 pagesAlkali and Alkali Earth Metals - SRMuzahidul IslamNo ratings yet
- SaveDocument2 pagesSaveSteven TiczonNo ratings yet
- CHIR EndsemDocument516 pagesCHIR EndsemSoikat DasNo ratings yet
- Group Chemistry LEDocument152 pagesGroup Chemistry LERupokNo ratings yet
- Chem Notes 14Document20 pagesChem Notes 14JiajunNo ratings yet
- Ch5.1 Classification of Elements (Summary)Document2 pagesCh5.1 Classification of Elements (Summary)Tony 852No ratings yet
- MetalsDocument4 pagesMetalsJhade YapNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument2 pagesPeriodic Tableritchelle ruerasNo ratings yet
- Bunsen BurnerDocument1 pageBunsen Burnerritchelle ruerasNo ratings yet
- Basic Tools of ChemistryDocument2 pagesBasic Tools of Chemistryritchelle rueras100% (1)
- Common Lab TechniquesDocument2 pagesCommon Lab Techniquesritchelle ruerasNo ratings yet
- Bhushan Steel LTD - PresentationDocument34 pagesBhushan Steel LTD - PresentationHiren Shaw0% (1)
- Equipment Erection ProcedureDocument6 pagesEquipment Erection Procedureคุณพ่อน้อง บิ๊กบอส100% (1)
- Methodology For Design Process of A Snap-Fit JointDocument6 pagesMethodology For Design Process of A Snap-Fit JointGhenal RiveraNo ratings yet
- Construction Safety and Health Narrative MethodsDocument46 pagesConstruction Safety and Health Narrative MethodsEldreen Ann Jebulan Vargas100% (1)
- David Round Stainless Chain HoistDocument2 pagesDavid Round Stainless Chain HoistJuan Carlos RuizNo ratings yet
- WS1 5ciDocument2 pagesWS1 5ciramonmzaNo ratings yet
- GCSBSP-200 GCSBSP-150 GCSBSP-201: TURBO Steam Master Professional Iron Plancha Profesional Steam Master Con TURBODocument2 pagesGCSBSP-200 GCSBSP-150 GCSBSP-201: TURBO Steam Master Professional Iron Plancha Profesional Steam Master Con TURBOKickingEdgarAllenPoeNo ratings yet
- Ii Food PackagingDocument2 pagesIi Food PackagingLeila Bert Marie GamboaNo ratings yet
- Catalogue For C6236 PDFDocument2 pagesCatalogue For C6236 PDFSomasekhar Koushik AyalasomayajulaNo ratings yet
- Magnum Composite Plug Catalog 06-30-10Document21 pagesMagnum Composite Plug Catalog 06-30-10Emad JamshidiNo ratings yet
- E 9018 Sika Permac 2330Document4 pagesE 9018 Sika Permac 2330Mark InnesNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Entry No. 3: Minerals and Their UsesDocument4 pagesPortfolio Entry No. 3: Minerals and Their UsesReizel Joy Borja RasonaNo ratings yet
- An Evaluation of The Cross-Tension Test of Resistance Spot Welds in High-Strength Dual-Phase SteelsDocument8 pagesAn Evaluation of The Cross-Tension Test of Resistance Spot Welds in High-Strength Dual-Phase SteelsMuhammad Bahtiyar FirdausNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Report On Indian Metal Cutting Machine Tool Industry - 2019Document73 pagesComprehensive Report On Indian Metal Cutting Machine Tool Industry - 2019Dr-Prashanth GowdaNo ratings yet
- Ssnde14 Final LDocument72 pagesSsnde14 Final LmiamarchNo ratings yet
- Product Data: Hexply 916Document2 pagesProduct Data: Hexply 916McLemiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 21 PDFDocument14 pagesLecture 21 PDFMehmet Arvasi100% (1)
- PRS Lab Manual 2020 2 SP FinalDocument25 pagesPRS Lab Manual 2020 2 SP Finalstephan dsilvaNo ratings yet
- Installation - Typical 3.3m.precast Concrete Beam Design (EN1992)Document5 pagesInstallation - Typical 3.3m.precast Concrete Beam Design (EN1992)zms msswiNo ratings yet
- Linea L186SS Oven ManualDocument19 pagesLinea L186SS Oven Manualdmwx50% (2)
- Daikin VRV II R-22Document346 pagesDaikin VRV II R-22Danilo FIloteo73% (11)
- Prevention of Mould Growth in BuildingsDocument41 pagesPrevention of Mould Growth in BuildingsmaxgyzerNo ratings yet
- 1129011951BMCS4Document24 pages1129011951BMCS4DHEESHNA DILEEP 200545No ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Failure: How Do Materials Break?Document40 pagesChapter 8: Failure: How Do Materials Break?Leann FarleyNo ratings yet
- E155-00 Aluminum & Magnesium CastingsDocument4 pagesE155-00 Aluminum & Magnesium Castingschitti409No ratings yet
- PC-Bedienungsanleitung Heater enDocument33 pagesPC-Bedienungsanleitung Heater enZoran Tanja JarakovićNo ratings yet
- Precommissioning ChecklistDocument2 pagesPrecommissioning ChecklistPankaj PandeyNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine TrainingDocument52 pagesGas Turbine TrainingNoble_Truth90% (10)
- Polylite TDSDocument3 pagesPolylite TDSRAZA MEHDINo ratings yet
- BRCDocument114 pagesBRClzzhang10No ratings yet