Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ACTIVITY Ex-1 To 4-1
Uploaded by
GajiniOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ACTIVITY Ex-1 To 4-1
Uploaded by
GajiniCopyright:
Available Formats
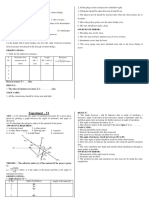
Experiment- I Experiment- II
AIM – To identify a diode, a LED, a transistor, an IC (Integrated AIM – To observe refraction and lateral deviation of a beam of light
Circuit), a resistor and a capacitor from a mixed collection of such items. incident obliquely on a glass slab.
YOU NEED YOU NEED
1. A mixed collection of LED 2. A diode 1. Glass slab 2. Drawing board
3. A transistor 4. An IC 3. A sheet of white paper 4. Drawing pins
5. A resistor 6. A capacitor 5. Office pins 6. Protractor
THEORY THEORY
Diode, LED, Resistor, Capacitor are two terminal devices, while a When a ray of light incident on a parallel faced glass slab, it emerges
transistor has three terminals and an IC is a multiterminal device (Which from it in a same direction as the incident ray. It only suffers a lateral
has minimum of eight terminals). Generally an IC has flat back. displacement which is proportional to the thickness of the slab. (Fig. 2)
From the mixture of diode, LED, transistor, IC, resistor, capacitor one
can easily indentify the transistor being a three terminal device and an IC
being multiterminal, i.e., at least eight terminal device simply by looking
at the various components.
Remaining two terminal devices, i.e., diode, LED, capacitor and resistor
one can utilize the characteristics of the components.
Capacitor – It does not conduct when connected with D.C. circuit.
Resistor – It gives the constant current when connected with D.C. circuit.
Diode – It conducts when forward biased and it does not conduct when it
is reverse biased. It does not emit light while conducting.
A LED – It conducts when forward biased and does not conduct when
reverse biased. It emits light while conducting.
OBSERVATIONS
S. No. No. of terminals (legs) Component
1. More then three legs IC (integrated circuit)
2. Three legs Transistor
3. Two legs Resistor, Capacitor, Diode or LED
S. No. Possibility of current flow Component
1. Current flows in one direction and emits no light Diode
2. Current flows in one direction and emits light LED
3. Current flows in both direction and it is steady Resistor OBSERVATIONS
4. Initially high current but decays to zero Capacitor The ray of light emerging from a glass slab is parallel to the incident ray
and it is laterally displaced.
Experiment- III THEORY
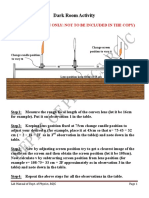
AIM – To study the nature and size of the image formed by a concave The position, nature and the relative size of the image of an object
mirror, on a screen by using a candle and screen (for different distances formed by a concave mirror depends upon position of the object with
of the candle from the mirror) respect to the pole of the mirror. It is shown by the ray diagrams in Fig.
YOU NEED 7.
1. A concave mirror with holder OBSERVATIONS
2. An optical bench with three uprights Table for the position and nature, size of the image formed by concave
3. Meter scale 4. Candle mirror
5. A cardboard screen 6. A matchbox S. Position of Nature of Image
No.
Object (Candle) Image (Screen)
1. At infinity At F Real, inverted, highly diminished
2. Beyond C Between F and C Real, inverted, diminished
3. At C At C Real, inverted, same size
4. Between F and C Beyond C Real, inverted, magnified
5. At F At infinity Real, inverted, magnified but blurred
6. Between F and Behind the Virtual (cannot be taken on
P mirror screen), erect, highly magnified.
CONCLUSION
The change in position, nature and size of the image is according to the
theoretical predictions.
Experiment- IV THEORY
AIM – To study the nature and size of the image formed by a convex The size of the image of an object formed by a convex lens depends
lens, on a screen by using a candle and screen (for different distances of upon the position of the object w.r.t. the convex lens. Various images
the candle from the lens). formed for the different positions of the object are shown in Fig. 8.
YOU NEED OBSERVATIONS
1. A convex lens with lens holder Rough focal length of the convex lens = F = …. Cm
2. An optical bench with three uprights Positions of 2F = …… cm
3. A cardboard screen 4. A candle 5. A matchbox Table for the position, nature, size of the image formed by convex lens
S. Position Position of candle Position of
No of lens flame relative to the the image Nature of Image
. (cm) lens (cm) (cm)
Real, inverted, highly
1. At infinity At F
diminished
Between F Real, inverted,
2. Beyond 2F
and 2F diminished
3. At 2F At 2F Real, inverted, same size
4. Between F and 2F Beyond 2F Real, inverted, magnified
Real, inverted, magnified
5. At F At infinity
but blurred
Virtual (cannot be taken
Same side
6. Between F and O on screen), erect, highly
of the object
magnified.
CONCLUSION
The change in position, nature and size of the image is according to
theoretical predictions.
You might also like
- Light Reflection and Refraction NotesDocument34 pagesLight Reflection and Refraction NotesMurli100% (3)
- Sony Playstation 3 Cecha00 Cecha01 Sm-Ps3-0013e-02Document45 pagesSony Playstation 3 Cecha00 Cecha01 Sm-Ps3-0013e-02naoyakatsu100% (2)
- Kenwood KDC-316S Service ManualDocument18 pagesKenwood KDC-316S Service ManualMarckos FrancoNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 (B) Aim: TheoryDocument3 pagesActivity 3 (B) Aim: TheoryMeghan KumarNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection and RefractionDocument20 pagesLight Reflection and RefractionShaurya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Physics NotesDocument23 pagesGrade 12 Physics NotesAlphonso TulayNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Light FullDocument11 pagesCH 3 Light Fullriwivoj527No ratings yet
- Reflection and MirrorsDocument51 pagesReflection and MirrorsLieh Arvey MabilingNo ratings yet
- Buenasher Learning Academy Inc.: Km.39 Cityland Ave., Pulong Buhangin, Sta. Maria, BulacanDocument9 pagesBuenasher Learning Academy Inc.: Km.39 Cityland Ave., Pulong Buhangin, Sta. Maria, BulacanEl CruzNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Q2 - W5Document13 pagesScience 10 - Q2 - W5rawisadaniNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Reflection of LightDocument16 pages5.1 Reflection of LightJunaidah Mohamad RamliNo ratings yet
- Light: Mass Training For Grade 10 Science Teachers On The K To 12 Enhanced Basic Education ProgramDocument99 pagesLight: Mass Training For Grade 10 Science Teachers On The K To 12 Enhanced Basic Education ProgramLucy Jhamaicka Maruquin IliNo ratings yet
- 05 LIGHT Physics Form 4Document11 pages05 LIGHT Physics Form 4Nikki NinjaNo ratings yet
- Light PuntlandDocument131 pagesLight PuntlandSaid Mohamed Mahad100% (1)
- Light WavesDocument72 pagesLight WavesJeffrey MaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Phyiscs LensesDocument10 pagesIGCSE Phyiscs LensesneelNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Optics NotesDocument5 pagesScience 10 - Optics NotesRina Marie Besin CartesianoNo ratings yet
- Expt-8 XIIDocument7 pagesExpt-8 XIISHIBAM MANDALNo ratings yet
- Ncjescoa 10Document61 pagesNcjescoa 10ODDENSIGN 2007No ratings yet
- Wave and Optics DLPDocument8 pagesWave and Optics DLPlopezchinshin28No ratings yet
- Q2 - Grade10 - Week5 - Bautista, Ferdinand SDocument2 pagesQ2 - Grade10 - Week5 - Bautista, Ferdinand SRhian PanaganeNo ratings yet
- 2020 S5 CHP 6 LightDocument39 pages2020 S5 CHP 6 LightFaith VooNo ratings yet
- Class Note 10 LightDocument31 pagesClass Note 10 LightDiptimayee JenaNo ratings yet
- M.E.S Indian School, Doha - Qatar Notes 2024 - 2025Document10 pagesM.E.S Indian School, Doha - Qatar Notes 2024 - 2025Rafiya95z MynirNo ratings yet
- SG Session6 Phys GaviolaDocument15 pagesSG Session6 Phys GaviolaLaurel S. MedinaNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical Experiment Class 12 (2022 Term 2)Document24 pagesPhysics Practical Experiment Class 12 (2022 Term 2)Arghyadeep DasNo ratings yet
- Refraction 10TH Class Physics Important Questions SSC Abyasa Deepika.Document8 pagesRefraction 10TH Class Physics Important Questions SSC Abyasa Deepika.prakashNo ratings yet
- AnalysisDocument3 pagesAnalysisLAXMI NUNIANo ratings yet
- 10 Cbse Physics CH - 1 & 2 Revision MaterialDocument33 pages10 Cbse Physics CH - 1 & 2 Revision Material12-Criswin v geo-8ANo ratings yet
- Learning Plan in Science 10: Unit Topic: Content Standard: Learning CompetenciesDocument13 pagesLearning Plan in Science 10: Unit Topic: Content Standard: Learning Competenciesakoaysijoy100% (1)
- SG - Session2 Opticsphys - RealingoDocument15 pagesSG - Session2 Opticsphys - RealingoJudarlyn Madria100% (1)
- ZabateJaymarieC QuizNo4 Waves&OpticsLecDocument8 pagesZabateJaymarieC QuizNo4 Waves&OpticsLecJaymarie ZabateNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction of LightDocument44 pagesReflection and Refraction of LightArman Akram100% (1)
- 77 Topper 21 101 2 4 62 Light Reflection and Refraction Up201807101458 1531214913 5575 PDFDocument10 pages77 Topper 21 101 2 4 62 Light Reflection and Refraction Up201807101458 1531214913 5575 PDFsudhaNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument15 pagesPhysicsakshatbhargava2021No ratings yet
- Class 7 Chapter 12 LightDocument12 pagesClass 7 Chapter 12 Lightsiddharthsg37No ratings yet
- Year of The YouthDocument13 pagesYear of The YouthJustin A VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Optics Mirrors and LensesDocument43 pagesOptics Mirrors and LensesKwenzie FortalezaNo ratings yet
- Activity Ta: Using of Candle Adt AkDocument5 pagesActivity Ta: Using of Candle Adt AkRakeshNo ratings yet
- Subject: PHYSICS: Topic: Convex LensDocument29 pagesSubject: PHYSICS: Topic: Convex LensEdu 4 UNo ratings yet
- Light PresentationDocument91 pagesLight PresentationRohan SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter VII OpticHTAMDocument67 pagesChapter VII OpticHTAMIhza Fikry Aryaditama ArroziNo ratings yet
- DLL Sept 20 Reflection in PLane MirrorDocument4 pagesDLL Sept 20 Reflection in PLane MirrorHelen Grace Llemos Cabalag100% (1)
- Light: by Neil BronksDocument95 pagesLight: by Neil BronksAlessia BostiogNo ratings yet
- Activity Spherical MirrorsDocument1 pageActivity Spherical MirrorsAizel AlmonteNo ratings yet
- The Nature and Properties of Light PDFDocument19 pagesThe Nature and Properties of Light PDFB VIDATTE VILLANIEVANo ratings yet
- CBSE Class X Science CH 10 Light - Reflection and Refraction Part 1Document18 pagesCBSE Class X Science CH 10 Light - Reflection and Refraction Part 1Saumil S. SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sci10 Module 2 (Q2-Week 6-8)Document12 pagesSci10 Module 2 (Q2-Week 6-8)Chris John SantosNo ratings yet
- RRB NTPC - Physics - LightDocument5 pagesRRB NTPC - Physics - LightAkella LokeshNo ratings yet
- S10FE-11g-50 MELC: Predict The Qualitative Characteristics, Orientation, Type ConceptsDocument4 pagesS10FE-11g-50 MELC: Predict The Qualitative Characteristics, Orientation, Type ConceptsMikaela MosqueraNo ratings yet
- 09.ray Optics-FDocument92 pages09.ray Optics-Fsiddharth sharmaNo ratings yet
- Light - Reflection and Refraction 03 - Class Notes - (Udaan 2024)Document16 pagesLight - Reflection and Refraction 03 - Class Notes - (Udaan 2024)Anant GhatiyaNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Optics: Curved MirrorDocument61 pagesGeometrical Optics: Curved MirrorMr. XNo ratings yet
- Chapter 34B - Reflection and Mirrors II (Analytical)Document28 pagesChapter 34B - Reflection and Mirrors II (Analytical)Heindrich Lloyd Mendoza BasiNo ratings yet
- LightDocument18 pagesLightAyush BarnwalNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12th Physics Volume 2 Guide English Medium 215874 PDFDocument26 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Physics Volume 2 Guide English Medium 215874 PDFvasanthagokilam rajendranNo ratings yet
- NCERT Science Lab Manual X Expt 47Document5 pagesNCERT Science Lab Manual X Expt 47Samarth AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Properties of LightDocument10 pagesProperties of LightKesanam SpNo ratings yet
- Activity 4 7 Mirrors Lenses Motors and GeneratorsDocument10 pagesActivity 4 7 Mirrors Lenses Motors and GeneratorsMarley Chelsea LevantinoNo ratings yet
- The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding of The Images Formed by The Different Types of Mirrors and LensesDocument78 pagesThe Learners Demonstrate An Understanding of The Images Formed by The Different Types of Mirrors and LensesWarren Dela CernaNo ratings yet
- Act - 1 To 4Document3 pagesAct - 1 To 4GajiniNo ratings yet
- Ex - 5 To 8Document4 pagesEx - 5 To 8GajiniNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Class 11 Biology Chapter 21 Neural Control and Coordination - 0Document35 pagesNcert Solutions Class 11 Biology Chapter 21 Neural Control and Coordination - 0GajiniNo ratings yet
- 6 Who Works MoreDocument12 pages6 Who Works MoreGajiniNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease - 0Document12 pagesNcert Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease - 0GajiniNo ratings yet
- 7 Revealing Secrets of SilicatesDocument6 pages7 Revealing Secrets of SilicatesGajiniNo ratings yet
- 2 Really An Ideal Gases!Document14 pages2 Really An Ideal Gases!GajiniNo ratings yet
- 6 What Is Common in LPG and CNGDocument13 pages6 What Is Common in LPG and CNGGajiniNo ratings yet
- 5 Does An Ideal Gas Really ExistDocument16 pages5 Does An Ideal Gas Really ExistGajiniNo ratings yet
- 10 Aaa21305caDocument25 pages10 Aaa21305cakędzierzawyNo ratings yet
- (1902-22V1906) VX Catalogue PDFDocument51 pages(1902-22V1906) VX Catalogue PDFMinhcong PhanNo ratings yet
- Phmkp... Cylindrical Aluminum Estaprop /estadry Power Factor Correction Capacitors Low VoltageDocument8 pagesPhmkp... Cylindrical Aluminum Estaprop /estadry Power Factor Correction Capacitors Low VoltagesebastianNo ratings yet
- DBX 266xl SCHDocument9 pagesDBX 266xl SCHFazar AhmadNo ratings yet
- D05 Directional Control Valves EngineeringDocument11 pagesD05 Directional Control Valves EngineeringVentas Control HidráulicoNo ratings yet
- Automatic Car Parking SystemDocument3 pagesAutomatic Car Parking SystemHarsha100% (2)
- W 48 × H 48 MM Power ON Delay Analog Timers: ATE8 SeriesDocument3 pagesW 48 × H 48 MM Power ON Delay Analog Timers: ATE8 Seriesyanier martinezNo ratings yet
- 1.1 QE-COC Application Form No.1.1+ (Solar) - Vernov2023Document2 pages1.1 QE-COC Application Form No.1.1+ (Solar) - Vernov2023noias49No ratings yet
- Trapatt and Baritt DiodeDocument4 pagesTrapatt and Baritt DiodevenkatNo ratings yet
- HC AP ODU Installation Quick Reference GuideDocument10 pagesHC AP ODU Installation Quick Reference Guidevsaa12No ratings yet
- CAN Interface For FMS: Important!Document10 pagesCAN Interface For FMS: Important!abo mhdeNo ratings yet
- Electric Field and CapacitorsDocument18 pagesElectric Field and CapacitorsTharushiNethmiNo ratings yet
- HISAC Ultima - Test Report: HeaderDocument2 pagesHISAC Ultima - Test Report: HeaderAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- E3TA One Touch Setting Photoelectric Sensor With Teachin FunctionDocument2 pagesE3TA One Touch Setting Photoelectric Sensor With Teachin Functionzheng zhengNo ratings yet
- DTC B1182/19 Short in D Squib (2Nd Step) Circuit (To Ground)Document4 pagesDTC B1182/19 Short in D Squib (2Nd Step) Circuit (To Ground)Phang KumwingNo ratings yet
- NAD 402 Service ManualDocument20 pagesNAD 402 Service ManualalweekesNo ratings yet
- RX Frequency Inverter: Customised To Your MachineDocument18 pagesRX Frequency Inverter: Customised To Your MachineardinNo ratings yet
- 30.72 KWP SLDDocument1 page30.72 KWP SLDDaniel Gnanaselvam100% (1)
- Semikron SKD30 12A1 DatasheetDocument3 pagesSemikron SKD30 12A1 DatasheetseamanzNo ratings yet
- Lab Report #4Document6 pagesLab Report #4Aisha NurymgaliNo ratings yet
- Moseley PCL6000 ManualDocument278 pagesMoseley PCL6000 ManualJuan PerezNo ratings yet
- LAB-Models 2100 and 2100S Manual-ABDocument16 pagesLAB-Models 2100 and 2100S Manual-ABkevin diazNo ratings yet
- CCM1620CSL Spec PDFDocument11 pagesCCM1620CSL Spec PDFJuan RenteriaNo ratings yet
- Ekm64 1 IngDocument54 pagesEkm64 1 IngTaoualit SaidNo ratings yet
- ARIA SOHO Installation ManualDocument66 pagesARIA SOHO Installation ManualxelavNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Compressor: Model 104G7550 115V/60Hz 1Document6 pagesTechnical Data Compressor: Model 104G7550 115V/60Hz 1Camilo CarreñoNo ratings yet
- Star Delta Star TransformationsDocument6 pagesStar Delta Star TransformationsHassan MahgoubNo ratings yet