Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Q2 - Week 2 - Practical Research 2 - PART 1
Uploaded by
Sir JrOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Q2 - Week 2 - Practical Research 2 - PART 1
Uploaded by
Sir JrCopyright:
Available Formats
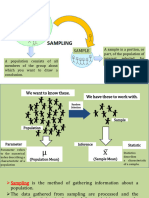
SAMPLING
Sampling
The process of using a
small number of items or
parts of larger population
to make a conclusions
about the whole population
Division of General Trias City 1
SAMPLING
Reasons for Sampling
● Necessity: Sometimes it’s ● Cost-effectiveness: There
simply not possible to study are fewer participant,
the whole population due to laboratory, equipment, and
its size or inaccessibility. researcher costs involved.
● Practicality: It’s easier and ● Manageability: Storing and
more efficient to collect data running statistical analyses
from a sample. on smaller datasets is easier
and reliable.
Division of General Trias City 2
SAMPLE SIZE DETERMINATION
Slovin’s Formula:
Margin of Error
Measures the maximum
amount by which the
sample results are expected
to differ from those of
actual population.
Division of General Trias City 3
SAMPLE SIZE DETERMINATION
Sample Size Determination
For example, suppose that a group
of 1,000 public school teachers
from the Division of General Trias
City needs to be surveyed to find out
their perception in limited face to
face classes. For this survey, a margin
of error of 0.05 is considered
sufficiently accurate.
Division of General Trias City 4
SAMPLE SIZE DETERMINATION
http://www.raosoft
.com/samplesize.h
tml
Division of General Trias City 5
SAMPLING TECHNIQUES
Division of General Trias City 6
SAMPLING TECHNIQUES
Probability Sampling Non-Probability Sampling
• involves random • involves non-random
selection, allowing you selection based on
to make strong statistical convenience or other
inferences about the criteria, allowing you to
whole group. easily collect data.
Division of General Trias City 7
Probability Sampling
Example 1 Example 2 Example 3
Simple Random Sampling
Population Set of all Set of all Set of all
Simple Random Sampling (SRS) is students faculty employees
applicable when the population is enrolled in members in a in a
homogeneous and that all of the STEM strand university company
units are given equal chances to be Obtain a 100 students 50 names of 50
selected as sample Simple from the list faculty employees
Random of all members by using
Sample students by corresponding draw lots
using to the random
calculator. numbers
generated by
computer.
Division of General Trias City 8
Probability Sampling
Stratified Random Sampling Example 1 Example 2
Used when the population is Population Set of all SHS Set of all Elementary
heterogeneous. The population is students in Cavite Students in GTC, Cavite
first divided into homogeneous
Group/ 23 Each of the 75
subgroups called strata and then a Cities/Municipalities Elementary Schools in
Strata
random sample of units will be in Cavite GTC
selected from each stratum. The
Obtain a 100 SHS students 1000 Students from all
selection can be done in two ways: Simple from each of the 75 schools will be
Proportional Allocation (PA) and Random municipalities selected depending on
Equal Allocation (EA). Sample (Equal Allocation) the population of the
school
(Proportional Allocation)
Sample 100 students x 23 A total of 1000 students
municipalities=2300 from 75 Elementary
SHS selected students Schools
Division of General Trias City 9
Probability Sampling
Systematic Sampling Say a student wants to select 100 random
selecting every kth in the complete sample of students from the list of 1000
list. K is called the sampling
students. The process starts by identifying
interval. The formula for K is given
by: 𝐾 = 𝑁/𝑛; where the value of k, in this case
N=population and n=sample. K=1000/100=10 as the sampling interval
and the number to start with will be
selected from 1 to 10 and then every 10th
in the list will be selected. If the student
randomly selected 5 as the random start,
then the samples would be 5, 15,
25,…until the student reached the 100
samples needed.
Division of General Trias City 10
Probability Sampling
Cluster Sampling Example 1 Example 2
If the population is too large, cluster sampling
Population Set of all SHS Set of all
is being used. Like the stratified sampling, the
teachers in faculty
population is divided into subgroups called
Dasmarinas members in a
clusters (usually along geographic boundaries) City, Cavite university
then selecting a simple random sample of
clusters for which all the units in the selected Obtain a 10 schools 5
clusters will be considered. Simple offering departments
Random Senior High
Sample School (SHS)
Sample All SHS All faculty
teachers in members of
the selected the selected
schools departments
Division of General Trias City 11
Probability Sampling
● In multistage sampling, you always go from
higher-level to lower-level clusters at each stage.
The clusters are often referred to as sampling
units.
Multi-Stage Sampling ● At the first stage, you divide up the population
into clusters and select some of them: these are
Combination of the different your primary sampling units (PSUs).
type of sampling techniques ● At the second stage, you divide up your PSUs
into further clusters, and select some of them
as your secondary sampling units (SSUs).
● You can end at the second stage, or continue
this process with as many stages as you need.
In the last stage, you’ll get to your final sample
of ultimate sampling units (USUs).
Division of General Trias City 12
Non-Probability Sampling
Convenience Sampling
type of non-probability
sampling where the samples
are selected from a population ● If a student is interested in the effect of
that is easy to reach. It is caffeine on the study habits of all SHS
students, the research requires to ask all
usually being utilized in poll the SHS students nationwide. A
surveys or pilot testing. convenience sample would be a large set
of SHS students in the institution where
the student is enrolled.
Division of General Trias City 13
Non-Probability Sampling
Purposive Sampling
the selection is based on the
purpose or objective of the
study and characteristics of
the population.
Division of General Trias City 14
Non-Probability Sampling
Quota Sampling
This should be done tailoring
the proportion to the
characteristics or traits of the
population. • A researcher is interested in
comparing the differences in career
goals between male and female
students of a university. Say 50 male
and 50 female students to represent
the two groups.
Division of General Trias City 15
Non-Probability Sampling
Snowball Sampling
This purposive sampling is
also known as the referral
sampling or networking. The
samples are selected by • A resident doctor is conducting a
research about a certain disease. The
recruiting acquaintances who doctor then identified one victim of the
meet the criteria of disease and from that one person, he
inclusion. was able to identify many respondents
by the referral of the first victim he
selected.
Division of General Trias City 16
You might also like
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument4 pagesReview of Related LiteratureSir Jr100% (1)
- Multiple Classification Analysis Using SpssDocument34 pagesMultiple Classification Analysis Using SpssBuana WidyoNo ratings yet
- Leigh Shawntel J. Nitro Bsmt-1A Biostatistics Activity n0.2Document3 pagesLeigh Shawntel J. Nitro Bsmt-1A Biostatistics Activity n0.2Lue Soles100% (3)
- Math11statprob FinalsDocument28 pagesMath11statprob FinalsNeil Trezley Sunico BalajadiaNo ratings yet
- Applied Econometrics ModuleDocument141 pagesApplied Econometrics ModuleAH Tadele100% (1)
- Week 4Document29 pagesWeek 4LUISA CARESSE FLAVIANO BRITANICONo ratings yet
- Sampling TechniquesDocument28 pagesSampling Techniquesbasiliomervin012007No ratings yet
- SamplingDocument21 pagesSamplingjassermeneses2k21No ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability Module 3 ModifiedDocument16 pagesStatistics and Probability Module 3 ModifiedUsman DitucalanNo ratings yet
- Probability Sampling Methods and Nonprobability Sampling MethdsDocument48 pagesProbability Sampling Methods and Nonprobability Sampling MethdsMarjorie Joyce BarituaNo ratings yet
- 4 - Probability Sampling - Pr2Document12 pages4 - Probability Sampling - Pr2Yerenika CalypseNo ratings yet
- 3Document55 pages3wabdushukurNo ratings yet
- AE 9 AY 2021-2022 Module 2 (Complete)Document32 pagesAE 9 AY 2021-2022 Module 2 (Complete)Mae Ann RaquinNo ratings yet
- WEEK 2. Sampling TechniquesDocument23 pagesWEEK 2. Sampling Techniquesandrell.alfafaraNo ratings yet
- Sampling Design: Basic Concepts and Procedure: Sampling Frame. Known. Random SamplesDocument18 pagesSampling Design: Basic Concepts and Procedure: Sampling Frame. Known. Random SamplesJohn Aaron MirabelNo ratings yet
- Dr. Mohd Amir Department of Management Uttaranchal UniversityDocument40 pagesDr. Mohd Amir Department of Management Uttaranchal UniversitySuhotra GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sampling and Sampling TechniquesDocument25 pagesSampling and Sampling TechniquesNinoNo ratings yet
- Ruhs College of Nursing Sciences, Jaipur: Assignment ON Sampling TechniquesDocument13 pagesRuhs College of Nursing Sciences, Jaipur: Assignment ON Sampling TechniquesDr-Sanjay SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document85 pagesLesson 3Timothy Louisse Allen LizardoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document19 pagesUnit 1sankar velisettyNo ratings yet
- Types of Random Sampling TechniquesDocument3 pagesTypes of Random Sampling Techniquesjrbautista80% (10)
- Name: Pangilinan, Maria Angela Q. Section: BSMT1-1D Biostatistics Activity n0.2Document3 pagesName: Pangilinan, Maria Angela Q. Section: BSMT1-1D Biostatistics Activity n0.2Mira Swan100% (1)
- Types of Random Sampling TechniquesDocument3 pagesTypes of Random Sampling TechniquesAna ClaveNo ratings yet
- Sampling TechniquesDocument35 pagesSampling Techniqueskeithfrancine83No ratings yet
- Sampling: Iiird Year ResidentDocument26 pagesSampling: Iiird Year ResidentdranshulitrivediNo ratings yet
- Sampling Sampling: Concepts-Types of Sampling - Probability Sampling - Simple Random SamplingDocument10 pagesSampling Sampling: Concepts-Types of Sampling - Probability Sampling - Simple Random SamplingUday GowdaNo ratings yet
- PR2 Learning Material Q2 Week 6 7Document16 pagesPR2 Learning Material Q2 Week 6 7John Michael CastilloNo ratings yet
- Probability SamplingDocument22 pagesProbability Samplingbasaallen566No ratings yet
- Random Sampling 5es LPDocument9 pagesRandom Sampling 5es LPHannah ToringNo ratings yet
- Local Media5026080788931008114Document25 pagesLocal Media5026080788931008114Norsaifah AbduljalalNo ratings yet
- Caema6 - Set eDocument16 pagesCaema6 - Set efa.shaberayasminNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 Elem Stat and ProbDocument5 pagesLESSON 3 Elem Stat and ProbMilanie lihaylihayNo ratings yet
- Probability Theory and Statistical Techniques (SMA-61105)Document36 pagesProbability Theory and Statistical Techniques (SMA-61105)Er Anindya GhoshNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability RANDOM SAMPLINGDocument8 pagesStatistics and Probability RANDOM SAMPLINGfaith marceloNo ratings yet
- SamplingDocument50 pagesSamplingGurusha RajNo ratings yet
- 37778Document30 pages37778Jose Benavente100% (1)
- Sampling Techniques: Dr. Shilpi GuptaDocument59 pagesSampling Techniques: Dr. Shilpi GuptaTashi WangmoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Sampling Methods/TheoryDocument34 pagesIntroduction To Sampling Methods/TheoryBea Dacillo BautistaNo ratings yet
- Sampling and Sampling TechniquesDocument23 pagesSampling and Sampling TechniquesJessie Jr Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Co4 - Sampling and Sampling Distributions (Mean)Document64 pagesCo4 - Sampling and Sampling Distributions (Mean)RFSNo ratings yet
- Sampling Design and TechniquesDocument39 pagesSampling Design and TechniquesSumit palNo ratings yet
- Notes No. 6 For 11 E SAMPLING AND SAMPLING DISTRIBUTIONDocument11 pagesNotes No. 6 For 11 E SAMPLING AND SAMPLING DISTRIBUTIONnikkigabanto.24No ratings yet
- Sampling KKKKDocument21 pagesSampling KKKKShimul HossainNo ratings yet
- Research in Education HandoutsDocument4 pagesResearch in Education HandoutsJessa Quiño EscarpeNo ratings yet
- J. K. Shah Classes Sampling Theory and Theory of EstimationDocument37 pagesJ. K. Shah Classes Sampling Theory and Theory of EstimationGautamNo ratings yet
- Sampling and Sampling TechniquesDocument3 pagesSampling and Sampling TechniquesTeomar RomaNo ratings yet
- Sampling TechniquesDocument54 pagesSampling TechniquesJagdish Raj BaralNo ratings yet
- MODULE in Stat Week 6Document10 pagesMODULE in Stat Week 6Joshua GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Eda Lecture NotesDocument7 pagesEda Lecture NotesVenven PertudoNo ratings yet
- Sampling Design: DR Rasidah Arshad Fep, UkmDocument55 pagesSampling Design: DR Rasidah Arshad Fep, UkmSyaril ShahNo ratings yet
- BS 1 4Document74 pagesBS 1 4archit sahayNo ratings yet
- Illustrate Random SamplingDocument22 pagesIllustrate Random SamplingJeemark Naceel AlojadoNo ratings yet
- Sampling ProceduresDocument10 pagesSampling ProceduresRonel BarcelonaNo ratings yet
- Sampling MethodDocument8 pagesSampling MethodKanchanNo ratings yet
- Sampling 1Document59 pagesSampling 1Anonymous mzuRnewGNo ratings yet
- Sampling TechniquesDocument8 pagesSampling TechniquesMARIA ABIGAIL PAMAHOYNo ratings yet
- Sampling ProceduresDocument53 pagesSampling Procedureschumenzoo100% (1)
- Sampling Procedure: Abdulrahman M. IsmaelDocument17 pagesSampling Procedure: Abdulrahman M. Ismaelalioden MarohomslicNo ratings yet
- Types Sampling MethodsDocument40 pagesTypes Sampling MethodsRAJESH67% (6)
- Systematic SamplingDocument7 pagesSystematic SamplingJacinta WanjiruNo ratings yet
- Sampling Fundamentals ModifiedDocument45 pagesSampling Fundamentals ModifiedArjun KhoslaNo ratings yet
- QL_Exploring the Phenomenology on the Strand Discrimination Among Humanities and Social Sciences StudentsDocument44 pagesQL_Exploring the Phenomenology on the Strand Discrimination Among Humanities and Social Sciences StudentsSir JrNo ratings yet
- Pio - PR2Document11 pagesPio - PR2Sir JrNo ratings yet
- Monsanto - PR2Document9 pagesMonsanto - PR2Sir Jr100% (1)
- CriterionDocument1 pageCriterionSir JrNo ratings yet
- Lebato-Pr2Document6 pagesLebato-Pr2Sir JrNo ratings yet
- Q2 - Week 5 - Practical Research 2Document21 pagesQ2 - Week 5 - Practical Research 2Sir JrNo ratings yet
- Q2 - Week 1 - Practical Research 2Document28 pagesQ2 - Week 1 - Practical Research 2Sir JrNo ratings yet
- L8paknjnp - SCC Learning Module 6 CS7 1ST SEM 2021 2022Document7 pagesL8paknjnp - SCC Learning Module 6 CS7 1ST SEM 2021 2022Sir JrNo ratings yet
- Q2 - Week 4 - Practical Research 2Document15 pagesQ2 - Week 4 - Practical Research 2Sir JrNo ratings yet
- Q2 - Week 3 - Practical Research 2 - PART 2Document22 pagesQ2 - Week 3 - Practical Research 2 - PART 2Sir JrNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Completion: John Reck L. NiepesDocument1 pageCertificate of Completion: John Reck L. NiepesSir JrNo ratings yet
- Training and Technical Support Provided To TeachersDocument2 pagesTraining and Technical Support Provided To TeachersSir JrNo ratings yet
- q1 - LMC - Filipino Sa Piling LarangDocument2 pagesq1 - LMC - Filipino Sa Piling LarangSir JrNo ratings yet
- New Cover 3Document34 pagesNew Cover 3Sir JrNo ratings yet
- q1 - LMC - Filipino Sa Piling LarangDocument2 pagesq1 - LMC - Filipino Sa Piling LarangSir JrNo ratings yet
- Teachers' Workload in Relation To Burnout and Work PerformanceDocument6 pagesTeachers' Workload in Relation To Burnout and Work PerformanceSir JrNo ratings yet
- Additional ActivityDocument3 pagesAdditional ActivitySir Jr100% (2)
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument4 pagesReview of Related LiteratureSir JrNo ratings yet
- SF2 Updated 30 Male 30 FemaleDocument15 pagesSF2 Updated 30 Male 30 FemaleSir JrNo ratings yet
- SF1 - 2020 - Grade 7 (Year I) - AKLEDocument6 pagesSF1 - 2020 - Grade 7 (Year I) - AKLESir JrNo ratings yet
- STATISTICS FINAL EXAM (MPM) Answer SheetDocument15 pagesSTATISTICS FINAL EXAM (MPM) Answer SheetyetmNo ratings yet
- Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches Dr. William M. BauerDocument17 pagesQuantitative and Qualitative Approaches Dr. William M. BauerDatumanong Abdul RachmanNo ratings yet
- Judgment Under Uncertainty: Heuristics and BiasesDocument9 pagesJudgment Under Uncertainty: Heuristics and BiasesArturo RsNo ratings yet
- SKRIPSI Koperasi PDFDocument122 pagesSKRIPSI Koperasi PDFRio Rahmat Hidayat Part IINo ratings yet
- Writing An Inspection ReportDocument17 pagesWriting An Inspection ReportYazan TamimiNo ratings yet
- Applying The Analytics Framework:: How To Get To Actionable Analytics InitiativesDocument2 pagesApplying The Analytics Framework:: How To Get To Actionable Analytics Initiativessilhare_sNo ratings yet
- 1 Evaluating ArgumentsDocument6 pages1 Evaluating ArgumentsxyrylsiaoNo ratings yet
- CONNAWAY (2010) Basic-research-Methods-For-Librarians PDFDocument384 pagesCONNAWAY (2010) Basic-research-Methods-For-Librarians PDFMarília CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- Nonparametric Methods: Analysis of Ranked Data: AnswerDocument20 pagesNonparametric Methods: Analysis of Ranked Data: AnswerShekhar MishraNo ratings yet
- Selecting Methods of Data Collection: Kumar: Research MethodologyDocument20 pagesSelecting Methods of Data Collection: Kumar: Research MethodologyMohamed Hassan Mohamed KulmiyeNo ratings yet
- Chpter 3 6 1 2Document8 pagesChpter 3 6 1 2Katherine AliceNo ratings yet
- Integrating Lean Construction With BIM and Sustainability: A Comparative Study of Challenges, Enablers, Techniques, and Bene FitsDocument16 pagesIntegrating Lean Construction With BIM and Sustainability: A Comparative Study of Challenges, Enablers, Techniques, and Bene FitsYulius Chaesario KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Project Presentation TemplateDocument17 pagesProject Presentation TemplateAsoba AyambaNo ratings yet
- Class 1Document46 pagesClass 1nanaNo ratings yet
- Crumple and ShootDocument24 pagesCrumple and ShootDianne MasapolNo ratings yet
- MA ThesisGuide - 2022 2024 PDFDocument31 pagesMA ThesisGuide - 2022 2024 PDFОлимбек АзимбековNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1Document5 pagesCase Study 1Nisha Lauren VishvanathNo ratings yet
- Sample Thesis Title For Information SystemDocument7 pagesSample Thesis Title For Information Systemmkdswzgig100% (2)
- Applied Research Tools For BusinessDocument6 pagesApplied Research Tools For BusinessGilbert AbelaNo ratings yet
- Sumber Data SIKDocument34 pagesSumber Data SIKandy azizNo ratings yet
- Mattick Et Al-2018-The Clinical TeacherDocument6 pagesMattick Et Al-2018-The Clinical TeacherhydeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Hypothesis TestingDocument23 pagesLecture 4 - Hypothesis TestingAyodele OgundipeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document30 pagesLecture 1Jansher Khan DawarNo ratings yet
- Research: Marlon C. Dela Cruz, RPM, M.ADocument51 pagesResearch: Marlon C. Dela Cruz, RPM, M.AJay Vee LaxamanaNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Course Rationale Required ReadingsDocument6 pagesIntroduction and Course Rationale Required Readingsjamilqazii719No ratings yet
- Systematic ReviewDocument60 pagesSystematic ReviewSarahGustiaWoromboniNo ratings yet
- Perbedaan Persepsi Akuntan Publik, Akuntan Pendidik, Dan Mahasiswa Akuntansi Terhadap Kode Etik Ikatan Akuntan IndonesiaDocument16 pagesPerbedaan Persepsi Akuntan Publik, Akuntan Pendidik, Dan Mahasiswa Akuntansi Terhadap Kode Etik Ikatan Akuntan IndonesiaNur AzlinaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Introduction To Qualitative ResearchDocument43 pagesLecture 1 Introduction To Qualitative ResearchpetomNo ratings yet