Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aircraft Batteries
Uploaded by
irene pafraCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Aircraft Batteries
Uploaded by
irene pafraCopyright:
Available Formats
AIRCRAFT ELECTRICAL
SYSTEMS
Electrical Power (ATA 24)
BATTERIES
A battery is an energy storage device that relies on electrochemical reactions to deliver energy.
PRIMARY CELL BATTERIES
The dry cell is the most common type of primary-cell battery and is
similar in its characteristics to that of an electrolytic cell
When the battery is in a discharge condition an electrochemical
reaction takes place resulting in one of the rnetals being consumed.
Because of this consumption, the charging process is not reversible.
SECONDARY CELL BATTERIES
A secondary cell is any kind of electrolytic cell in which
the electrochemical reaction that releases energy is
reversible. The lead-acid car battery is a secondary-cell
battery as are some aircraft batteries.
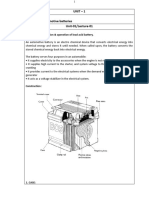
A typical lead-acid battery
consists of six lead-acid cells
in a case. Each cell produces
2 volts, so the whole battery
produces a total of 12 volts.
DRY CHARGED (FLOODED) LEAD ACID BATTERIES
The electrolyte is added to the battery when it is placed in service, and battery life begins when the electrolyte is
added. An aircraft storage battery consists of 6 or 12leadacid cells connected in series. The open circuit voltage of the 6
cell battery is approximately 12 volts, and the open circuit voltage of the 12-cell battery is approximately 24 volts.
AIRCRAFT ELECTRICAL
SYSTEMS
Electrical Power (ATA 24)
VALVE-REGULATED (SEALED) LEAD-ACID BATTERIES (VRLA)
VRLA batteries contain all electrolyte absorbed in glass-mat separators with no free
electrolyte and are sometimes referred to as sealed batteries. When VRLA batteries are
on charge, oxygen combines chemically with the lead at the negative plates in the
presence of HzS04 to form lead sulfate and water.
These types of battery are used in general aviation and turbine powered aircraft and are
sometimes authorized replacements for NiCd batteries.
NICKEL CADMIUM (NICD) BATTERIES
A NiCd battery consists of a metallic box, usually stainless steel, plastic-coated steel, painted steel, or
titanium containing a number of individual cells. The battery has a ventilation system to allow the
escape of the gases produced during an overcharge condition and provide cooling during normal
operation. NiCd cells installed in an aircraft battery are typical. of the vented cell type. The cells are
rechargeable and deliver a voltage of 1.2 volts during discharge.
Aircraft that are outfitted with NiCd batteries typically have a fault protection system that monitors
the condition of the battery. The battery charger is the unit that monitors the battery and the following conditions are monitored:
1. Overheat condition
2. Low temperature condition (below -40 oF)
NiCd batteries have a ventilation
3. Cell imbalance system to control the temperature of the battery.
4. Open circuit A combination of high battery temperature (in excess
of 160 oF) and overcharging can lead to a condition
5. Shorted circuit
called thermal runaway.
If the battery charger finds a fault, it turns off and sends a fault signal to the Electrical Load Management System (ELMS).
LITHIUM ION BATTERIES
The most recent type of battery to be certified in aircraft is the lithium ion battery. These batteries have greater capacity and weigh less
than NiCd or lead acid types. They have no memory as NiCd batteries have and discharge less than half as slowly when not being used.
Lithium ion aircraft batteries require built-in safety devices to prevent overheating and thermal runaway.
They are constructed with a wide variety of material choices that result in compromise between capacity, longevity, environmental
endurance and operating range, current loading, specific energy, size and weight, etc. Additional current monitoring and other safety
and alerting devices are included to warn flight crew of battery status and malfunction.
You might also like
- Aircraft BatteriesDocument26 pagesAircraft BatteriesDaniel MkandawireNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Electrics - Aircraft BatteriesDocument17 pagesAircraft Electrics - Aircraft BatteriesErica Zoe BantogNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - BatteryDocument16 pagesChapter 2 - BatteryTrương Hoài PhongNo ratings yet
- Battery - Basics For TechnicansDocument33 pagesBattery - Basics For TechnicansAbdelaziz RagabNo ratings yet
- Module 11.6 - Electrical Power (ATA 24)Document24 pagesModule 11.6 - Electrical Power (ATA 24)Kuldeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Automotive Batteries: University of Technical Education Ho Chi Minh CityDocument14 pagesAutomotive Batteries: University of Technical Education Ho Chi Minh CityThao HuynhNo ratings yet
- Topics Covered in Introduction To Batteries The Voltaic Cell Common Types of Primary Cells Lead-Acid Wet Cell Additional Types of Secondary CellsDocument32 pagesTopics Covered in Introduction To Batteries The Voltaic Cell Common Types of Primary Cells Lead-Acid Wet Cell Additional Types of Secondary CellsArvind VNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Batteries: Secondary (Where They Can Be Recharged) - It Can Be Dangerous To AttemptDocument17 pagesAircraft Batteries: Secondary (Where They Can Be Recharged) - It Can Be Dangerous To AttemptSheetalNo ratings yet
- Che Unit 4 BatteriesDocument13 pagesChe Unit 4 BatteriesNEELESH ATOMNo ratings yet
- Battery ResumeDocument30 pagesBattery ResumeEduardo ValleNo ratings yet
- Batteries and EarthingDocument10 pagesBatteries and EarthingRobin ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Categories and Types of Batteries 22Document6 pagesCategories and Types of Batteries 22abdul ali munderNo ratings yet
- BATTERIESDocument14 pagesBATTERIESwagnerjames028No ratings yet
- Battery Introduction PDFDocument17 pagesBattery Introduction PDFlavanyaNo ratings yet
- Test, Charge and Replace Batteries and Jump-Start VehiclesDocument11 pagesTest, Charge and Replace Batteries and Jump-Start Vehiclesajay100% (1)
- Assignment 3Document4 pagesAssignment 3Mrkgandhi RaviNo ratings yet
- Nickel Cad BatteriesDocument34 pagesNickel Cad BatteriesRaghavendra_PNo ratings yet
- EV and HEV - Unit 2 FinalDocument63 pagesEV and HEV - Unit 2 FinalvenkateswarluvelisalNo ratings yet
- BatteryDocument42 pagesBatterySubhuNo ratings yet
- Engr. Jayde Paolo Castro Mirandilla Batteries: MIDTERM - ECE00 Basic ElectronicsDocument5 pagesEngr. Jayde Paolo Castro Mirandilla Batteries: MIDTERM - ECE00 Basic ElectronicsRomuel Villanueva AlmeydaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - BatteriesDocument33 pagesChapter 1 - BatteriesAinan SyabilNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Cells: BatteriesDocument4 pagesElectrochemical Cells: BatteriesMae TadaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Moodle Lecture 1Document9 pagesUNIT 1 Moodle Lecture 1aryanNo ratings yet
- Types of Batteries PDFDocument1 pageTypes of Batteries PDFMariz Julian Pang-ao0% (1)
- Battery Charger of A Aircraft BatteryDocument34 pagesBattery Charger of A Aircraft BatterysrisaitejaswiniNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument11 pagesSeminar ReportAnkit GulumkarNo ratings yet
- Battery ManagementDocument53 pagesBattery ManagementSovan Ghosh100% (1)
- Basic Electricity 03Document31 pagesBasic Electricity 03Tanvir AhmedNo ratings yet
- BatteriesDocument123 pagesBatteriesSajid BabuNo ratings yet
- Paper Battery Full Seminar Report On WWW Way2project inDocument12 pagesPaper Battery Full Seminar Report On WWW Way2project inPhebe PeterNo ratings yet
- Cell & BatteriesDocument16 pagesCell & BatteriesMahnoor AqeelNo ratings yet
- Chapter No. 4 - Automobile Electronics and Electrical SystemsDocument125 pagesChapter No. 4 - Automobile Electronics and Electrical Systemsashwini yewaleNo ratings yet
- AEN Chapter-4 NotesDocument102 pagesAEN Chapter-4 Notesashwini yewaleNo ratings yet
- CELLS AND BATTERIES AllDocument18 pagesCELLS AND BATTERIES AllVictor mulotaNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2015-16 CP3624 26-Aug-2015 RM01 Module-6Document26 pagesFALLSEM2015-16 CP3624 26-Aug-2015 RM01 Module-6Playa 5No ratings yet
- Ch09 1 PDFDocument50 pagesCh09 1 PDFSabri BouloumaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry CHY1701Document80 pagesEngineering Chemistry CHY1701Xavier HunterNo ratings yet
- A Learning Report On Batteries and CellsDocument7 pagesA Learning Report On Batteries and Cellsajmat140No ratings yet
- ZZZ Battter yDocument12 pagesZZZ Battter yPokemon GoNo ratings yet
- Electrical Hobbies RayerDocument82 pagesElectrical Hobbies RayerK “Thermionicist” GNo ratings yet
- UNIT-2 Battery TechnologyDocument25 pagesUNIT-2 Battery TechnologyVasudev GuptaNo ratings yet
- Types of Batteries: Presented By:-Yash Aggarwal Yash Grewal Wasim Rouf ChoudhuryDocument15 pagesTypes of Batteries: Presented By:-Yash Aggarwal Yash Grewal Wasim Rouf ChoudhuryYash GrewalNo ratings yet
- Definition Types of Batteries Primary Batteries Secondary BatteriesDocument32 pagesDefinition Types of Batteries Primary Batteries Secondary BatteriesBhupesh Chandra GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document30 pagesChapter 3Umesh ChandraNo ratings yet
- BatteryDocument50 pagesBatteryDenekew Getahun100% (1)
- Test & Maintain BatteriesDocument11 pagesTest & Maintain BatteriesRamlugon Larveen SharmaNo ratings yet
- BatteriesDocument8 pagesBatteriesKarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Lead Acid Battery Terminology Glossary: Technical BulletinDocument21 pagesLead Acid Battery Terminology Glossary: Technical Bulletinmaituan100% (1)
- Battery TechnologyDocument59 pagesBattery TechnologySuneet Khurana0% (1)
- BATTERYDocument4 pagesBATTERYAHMER AYUBNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Avionics: Learning ObjectivesDocument24 pagesAircraft Avionics: Learning ObjectivesJesus MarianoNo ratings yet
- How To Charge Li-Ion Battery CorrectlyDocument9 pagesHow To Charge Li-Ion Battery CorrectlyGaryNo ratings yet
- 3.220 Notes (Opt.) - Electrochemical CellsDocument16 pages3.220 Notes (Opt.) - Electrochemical CellsAngel MariaNo ratings yet
- AVT 1104 MidtermDocument14 pagesAVT 1104 MidtermSup remoNo ratings yet
- Modul Electrical System SMS III - 2020Document82 pagesModul Electrical System SMS III - 2020Dzakwan LikoNo ratings yet
- Lead Acid Battery: Department of Electrical & Electronics EngineeringDocument13 pagesLead Acid Battery: Department of Electrical & Electronics EngineeringnagarjunaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Automotive Batteries ConstructionDocument62 pagesChapter 1 - Automotive Batteries ConstructionMsaiful MiyoshiNo ratings yet
- Lead Acid Battery: Department of Electrical & Electronics EngineeringDocument13 pagesLead Acid Battery: Department of Electrical & Electronics EngineeringHoneylyn IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Canadair CL-415 - Wikipedia PDFDocument1 pageCanadair CL-415 - Wikipedia PDFirene pafraNo ratings yet
- HW 2Document1 pageHW 2irene pafraNo ratings yet
- Final Project EquirmentsDocument2 pagesFinal Project Equirmentsirene pafraNo ratings yet
- Final Project AV2 RequirementsDocument6 pagesFinal Project AV2 Requirementsirene pafraNo ratings yet
- Outcome 1 - 2Document2 pagesOutcome 1 - 2irene pafraNo ratings yet
- Final Project Equirments 2Document6 pagesFinal Project Equirments 2irene pafraNo ratings yet
- HW5Document13 pagesHW5irene pafraNo ratings yet
- HW5Document13 pagesHW5irene pafraNo ratings yet
- Outcome 1Document3 pagesOutcome 1irene pafraNo ratings yet
- Outcome 1 - 2Document2 pagesOutcome 1 - 2irene pafraNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Lighting SystemsDocument2 pagesAircraft Lighting Systemsirene pafraNo ratings yet
- Processes 10 00859Document22 pagesProcesses 10 00859irene pafraNo ratings yet
- EASADocument3 pagesEASAirene pafraNo ratings yet
- AutopilotDocument2 pagesAutopilotirene pafraNo ratings yet
- Outcome 2Document4 pagesOutcome 2irene pafraNo ratings yet
- M13.1.c-Rotary WingDocument13 pagesM13.1.c-Rotary Wingirene pafraNo ratings yet
- Emergency Power DistrbutionDocument1 pageEmergency Power Distrbutionirene pafraNo ratings yet
- Outcome 1Document3 pagesOutcome 1irene pafraNo ratings yet
- Outcome 3Document1 pageOutcome 3irene pafraNo ratings yet
- Fracking Products 120111Document2 pagesFracking Products 120111irene pafraNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in Gas Hydrate-Based CO2 CaptureDocument13 pagesRecent Advances in Gas Hydrate-Based CO2 Captureirene pafraNo ratings yet
- M13-Flight ControlsDocument47 pagesM13-Flight Controlsirene pafraNo ratings yet
- Electrical - Module 3 - Part 66 - DAY 24Document32 pagesElectrical - Module 3 - Part 66 - DAY 24irene pafraNo ratings yet
- Module 13Document2 pagesModule 13irene pafraNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 - Pressure DistributionDocument1 pageExercise 1 - Pressure Distributionirene pafraNo ratings yet
- Solved Exercises in Nodal AnalysisDocument4 pagesSolved Exercises in Nodal Analysisirene pafra100% (1)
- Short Project On MBAlDocument19 pagesShort Project On MBAlirene pafraNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Economics and LawDocument2 pagesPetroleum Economics and Lawirene pafraNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Petroleum Economics and LawDocument7 pagesAssignment On Petroleum Economics and Lawirene pafraNo ratings yet
- Carregador de Bateria KRAFTPAKETDocument2 pagesCarregador de Bateria KRAFTPAKETMarco NicoNo ratings yet
- FischerDocument1 pageFischerJericho Morales0% (1)
- EPEVER Tracer-An Series Charging Calculator Lithium-Ion BatteriesDocument4 pagesEPEVER Tracer-An Series Charging Calculator Lithium-Ion BatteriesBeau DownsNo ratings yet
- Imax B6AC-v2 Battery Charger Manual PDFDocument28 pagesImax B6AC-v2 Battery Charger Manual PDFstummel6636No ratings yet
- Bateria Long de 36 Ah. U1 36NEDocument2 pagesBateria Long de 36 Ah. U1 36NElucholecasaNo ratings yet
- CB60 0Document1 pageCB60 0Enrique JuradoNo ratings yet
- Competitor Comparison Table - v2Document2 pagesCompetitor Comparison Table - v2Cherry EstradaNo ratings yet
- Fujikura Battery - PacksDocument2 pagesFujikura Battery - PacksTM TECH JSCNo ratings yet
- Coslight 100Document1 pageCoslight 100Intong22No ratings yet
- Miboxer C2-3000Document2 pagesMiboxer C2-3000makosrepasNo ratings yet
- LDC6 400 L16Document2 pagesLDC6 400 L16npNo ratings yet
- SJACDCSWALLOWEQDocument12 pagesSJACDCSWALLOWEQArmandNo ratings yet
- 6.0ah LiFePO4 Cell SpecificationDocument10 pages6.0ah LiFePO4 Cell SpecificationГригорійNo ratings yet
- Comparison-Plante Tubular Vrla NicdDocument4 pagesComparison-Plante Tubular Vrla Nicdgopal100% (1)
- Growatt Hope 3.3L C1 Lithium BatteryDocument2 pagesGrowatt Hope 3.3L C1 Lithium BatteryKing KoyeNo ratings yet
- Exide Xpress BatteryDocument1 pageExide Xpress BatteryPisupati_1234No ratings yet
- APPLICATION Battery ManagementDocument1 pageAPPLICATION Battery ManagementAfsar ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Flipkart Labels 16 Jan 2020 08 06Document26 pagesFlipkart Labels 16 Jan 2020 08 06Dharani KumarNo ratings yet
- Datablad Benton bx2pdf PDFDocument4 pagesDatablad Benton bx2pdf PDFirfan_1982No ratings yet
- Lionic enDocument9 pagesLionic enSzymon WronowskiNo ratings yet
- EverExceed Spiral AGM BatteriesDocument7 pagesEverExceed Spiral AGM BatteriesAish MohammedNo ratings yet
- Electric Vehicle BatteryDocument30 pagesElectric Vehicle BatteryUpendraJavaNo ratings yet
- Solar Sagm 12 205: Data SheetDocument2 pagesSolar Sagm 12 205: Data Sheetsofia hernandezNo ratings yet
- Radio Shack - Battery Charger - Cat 23-422Document2 pagesRadio Shack - Battery Charger - Cat 23-422Henry MaiNo ratings yet
- En 50604 1Document2 pagesEn 50604 1kishore msnNo ratings yet
- GP 2700mah SeriesDocument8 pagesGP 2700mah SeriesRadio PartsNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet BATT4 Battery For Flame Detector Test Lamps T-229/4P and T-169/1Document1 pageData Sheet BATT4 Battery For Flame Detector Test Lamps T-229/4P and T-169/1Saro RootNo ratings yet
- Types of BatteriesDocument4 pagesTypes of BatteriesShane Marshel San PedroNo ratings yet
- Catalogo de Pilas BulltronicDocument110 pagesCatalogo de Pilas Bulltroniccristobal_tl2277No ratings yet
- Batt MGMT 3q00Document16 pagesBatt MGMT 3q00DhanukaNo ratings yet