Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Impedance Relays
Uploaded by
MrOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Impedance Relays
Uploaded by
MrCopyright:
Available Formats
ImpedanceRelays
Protective Relays Examples - Impedance Relays Hydro Circuit Protection
Overcurrent Relays Directional OC Relays Voltage Relays Differential Relays Pilot Protection
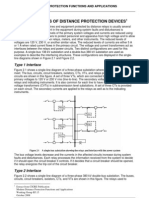
IMPEDANCE RELAYS NEMA number 21
Impedance relays are used whenever overcurrent relays do not provide adequate protection. They
function even if the short circuit current is relatively low. The speed of operation is independent of
current magnitude.
Impedance relays monitor the impedance between the relay location and the fault. If the impedance falls
within the relay setting, the relay will operate. The basic construction for impedance relays on which the
principle of operation is easily explained is the balanced beam.
Figure: Principle of Impedance Relay
The relay consists of a balanced beam. At each end of the balanced beam is a coil that exerts a force on
the beam at that end. One coil is connected to a current from a current transformer, the other coil is
connected to a potential transformer. The voltage coil functions as a restraining coil, the current coil
functions as an operating coil. Under normal conditions, the contact of the relay is kept open. During a
fault, the voltage drops, and the current rises. The torque due to the current coil overpowers the torque
due to the voltage coil, and the relay closes its contact.
The torque caused by the current through the current coil is
where Ki is a constant of proportionality that depends on the relay construction
The torque caused by the voltage coil is
where Kv is a constant of proportionality that depends on the relay construction
file:///D|/Engineering%20Stuff%2015-june-2008/Electrica...%20Guides/Protection%20and%20relays/ImpedanceRelays.htm (1 of 9)7/5/2008 9:29:35 AM
ImpedanceRelays
When the torques are balanced,
The ratio of voltage and current is the impedance the relay detects at the point of its connection.
To close its contacts,
The contacts will close anytime the impedance the relay sees is less than a preset value given by
This can be represented on an impedance graph X vs R
Figure: Operating Diagram of an Impedance Relay
This type of impedance relay is not directional. It will detect a fault in any direction. If it is used, it is used
together with a directional relay that eliminates half of its characteristic.
file:///D|/Engineering%20Stuff%2015-june-2008/Electrica...%20Guides/Protection%20and%20relays/ImpedanceRelays.htm (2 of 9)7/5/2008 9:29:35 AM
ImpedanceRelays
Figure: Operating Diagram of an Impedance Relay with a Directional Unit
OFFSET IMPEDANCE RELAY
Offset impedance relay is also known under names ADMITTANCE RELAY or MHO RELAY
Phasor Diagram
file:///D|/Engineering%20Stuff%2015-june-2008/Electrica...%20Guides/Protection%20and%20relays/ImpedanceRelays.htm (3 of 9)7/5/2008 9:29:35 AM
ImpedanceRelays
The torque of the watt element is
where Kw is a constant of proportionality that depends on the relay
construction
The torque caused by the voltage coil is
where Kv is a constant of proportionality that depends on the relay construction
Relay operates if
The phase angle θ depends on impedance Zs . Zs can be chosen so that θ = 0. Also, both voltage coils are
connected to the same voltage V. ( )
It follows that
Similarly as for the impedance relay, this impedance can be represented by an X vs R graph. This time
the circle is offset from the center.
file:///D|/Engineering%20Stuff%2015-june-2008/Electrica...%20Guides/Protection%20and%20relays/ImpedanceRelays.htm (4 of 9)7/5/2008 9:29:35 AM
ImpedanceRelays
Figure: Operating Diagram for an Offset Impedance Relay with Characteristic Angle equal to 0
If impedance Zs is chosen so that θ ≠ 0, the circle shifts:
Figure: Operating Diagram for an Offset Impedance Relay with Characteristic Angle Different from 0
For impedance relays detecting short circuits on transmission lines, impedance Zs is chosen so that θ is
the same as the impedance angle of the line. This relay will detect a fault in only one direction.
RESISTANCE AND REACTANCE RELAYS
file:///D|/Engineering%20Stuff%2015-june-2008/Electrica...%20Guides/Protection%20and%20relays/ImpedanceRelays.htm (5 of 9)7/5/2008 9:29:35 AM
ImpedanceRelays
The torque of the watt element is
where Kw is a constant of proportionality that depends on the relay construction
The torque caused by the current coil is
where Ki is a constant of proportionality that depends on the relay construction
Relay operates if
The phase angle θ depends on impedance Zs . Zs can be chosen so that θ = 0. Also, both current coils are
connected to the same current I.
It follows that
The operating characteristic of this relay is a straight line
file:///D|/Engineering%20Stuff%2015-june-2008/Electrica...%20Guides/Protection%20and%20relays/ImpedanceRelays.htm (6 of 9)7/5/2008 9:29:35 AM
ImpedanceRelays
Figure: Operating Diagram for a Resistance Relay
Figure: Operating Diagram for a Reactance Relay
All distance relays are connected to the power system through instrument transformers. The relay
monitors the impedance in secondary ohms. Secondary ohms are related to the primary ohms by the
equation
where CTR is the current transformer ratio
PTR is the potential transformer ratio
file:///D|/Engineering%20Stuff%2015-june-2008/Electrica...%20Guides/Protection%20and%20relays/ImpedanceRelays.htm (7 of 9)7/5/2008 9:29:35 AM
ImpedanceRelays
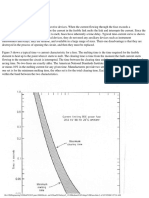
Zones of Protection
In general, distance protection includes three steps of protection, with each step reaching a fixed preset
distance and operating in a preset time.
Zone 1 reaches 80 - 90% of the protected line. The tripping is instantaneous.
Zone 2 extends beyond the protected line up to about 50% of the adjacent line. The tripping has a time
delay, usually set to a value between 0.3 s to 0.5 s.
Zone 3 covers the protected line, the adjacent line, and up to 25% of the line next to the adjacent line.
Tripping is delayed between 0.6 s to 1.0 s.
file:///D|/Engineering%20Stuff%2015-june-2008/Electrica...%20Guides/Protection%20and%20relays/ImpedanceRelays.htm (8 of 9)7/5/2008 9:29:35 AM
ImpedanceRelays
Protective Relays Hydro Circuit Protection
Overcurrent Relays Directional OC Relays Voltage Relays Differential Relays Pilot Protection
file:///D|/Engineering%20Stuff%2015-june-2008/Electrica...%20Guides/Protection%20and%20relays/ImpedanceRelays.htm (9 of 9)7/5/2008 9:29:35 AM
You might also like
- Diésel San Pedro-PACCAR MX-13. Manual PDFDocument378 pagesDiésel San Pedro-PACCAR MX-13. Manual PDFOriel100% (8)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Power System Protection - Part 08Document16 pagesPower System Protection - Part 08Rahul MandalNo ratings yet
- Protection CTsDocument5 pagesProtection CTscsontosbaluNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Basic Principles of Distance ProtectionDocument21 pagesBasic Principles of Distance Protectionsabill arasyid0% (1)
- CBCTDocument14 pagesCBCTYPV TECHNICAL SERVICES100% (1)
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- 04 TransformerDocument28 pages04 TransformerTheysingh RajaNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)Document45 pagesBipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)RizalNo ratings yet
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsFrom EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Principles of Differential RelayingDocument115 pagesPrinciples of Differential RelayingelitesankarNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Overcurrent ProtectionDocument9 pagesThe Importance of Overcurrent ProtectionR Is100% (1)
- Paralleling Cts For Line Differential ProtectionDocument15 pagesParalleling Cts For Line Differential ProtectionYeissonSanabria100% (1)
- The Application of High Impedance RelaysDocument24 pagesThe Application of High Impedance RelaysAhmad ShawkyNo ratings yet
- ProtectionDocument144 pagesProtectionSatyanarayana Raju100% (5)
- ABB Transformers Protection CourseDocument56 pagesABB Transformers Protection CourseWalid SonjiNo ratings yet
- The Fundamentals of Protection Relay Co-Ordination and Timecurrent Grading PrinciplesDocument9 pagesThe Fundamentals of Protection Relay Co-Ordination and Timecurrent Grading Principlesfredhalder99No ratings yet
- Protection System Design For SubstationDocument35 pagesProtection System Design For SubstationTimon Tim100% (1)
- Relaying Short LinesDocument16 pagesRelaying Short LinesrogeriojuruaiaNo ratings yet
- Toshiba E7242x Tube RXDocument10 pagesToshiba E7242x Tube RXcamv_847601No ratings yet
- Dosing Unit Modifications FinalDocument11 pagesDosing Unit Modifications FinalMrNo ratings yet
- OC EF RLY SET Chap9-122-151Document30 pagesOC EF RLY SET Chap9-122-151Falulus SalamNo ratings yet
- Different Types of RelaysDocument34 pagesDifferent Types of RelayssupriyarakshitNo ratings yet
- Basler Electric Electriccalcs - r2Document17 pagesBasler Electric Electriccalcs - r2MrNo ratings yet
- Distance ProtectionDocument23 pagesDistance Protectionhadrien100% (2)
- Auxiliary Units For 7SR23 Catalogue Sheet PDFDocument12 pagesAuxiliary Units For 7SR23 Catalogue Sheet PDFSteven RodriquezNo ratings yet
- Types of Switching Surges Found in MV Motors Fed Via Cables and Switched by Vacuum Circuit BreakersDocument19 pagesTypes of Switching Surges Found in MV Motors Fed Via Cables and Switched by Vacuum Circuit BreakersRatoka LekhemaNo ratings yet
- Lecture-02: Samiya Zafar Assistant Professor, EED NEDUET M.Engg Fall Semester 2017Document66 pagesLecture-02: Samiya Zafar Assistant Professor, EED NEDUET M.Engg Fall Semester 2017Jalees100% (1)
- Code Part Name Description Detail Specification: PXR-321B/401B/501B/322B/502BDocument3 pagesCode Part Name Description Detail Specification: PXR-321B/401B/501B/322B/502Beng5mostafa5humaid100% (1)
- RelaysDocument7 pagesRelaysRajeev RawatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-2-3Document170 pagesChapter 1-2-3Nitish Nageshwara RaoNo ratings yet
- The Restricted Earth Fault Relay Operation: Impact of Current Transformer Knee Point VoltagesDocument5 pagesThe Restricted Earth Fault Relay Operation: Impact of Current Transformer Knee Point VoltagesPradeep_VashistNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mcag14 & Mfac r6136b High Imp Rlys, 0Document12 pagesMcag14 & Mfac r6136b High Imp Rlys, 0smcraftNo ratings yet
- BEF Calculation - Part 2 PDFDocument8 pagesBEF Calculation - Part 2 PDFLin HengNo ratings yet
- Impedance RelaysDocument7 pagesImpedance RelaysDiseño y Gestión de ProyectosNo ratings yet
- About Impedance RelayDocument8 pagesAbout Impedance RelayVikas GuptaNo ratings yet
- Specification of CTS:: Saturated Values of Rated Burden AreDocument25 pagesSpecification of CTS:: Saturated Values of Rated Burden ArePranendu MaitiNo ratings yet
- HiZ Auxiliary Units Catalogue SheetDocument12 pagesHiZ Auxiliary Units Catalogue SheetSteven RodriquezNo ratings yet
- Necessity of A Protection SystemDocument29 pagesNecessity of A Protection Systemarmanmanyata010299No ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document62 pagesChapter 7alhajriaxNo ratings yet
- SGP 8Document9 pagesSGP 8Soumajit PoddarNo ratings yet
- Chap11 20 170 191Document22 pagesChap11 20 170 191Bin SotheaNo ratings yet
- Vector Groups: Winding ConnectionsDocument12 pagesVector Groups: Winding ConnectionskhaifhalathNo ratings yet
- Power System Lab Exp 3Document3 pagesPower System Lab Exp 3Riya PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- The Application of Relay Coil Suppression With DC RelaysDocument3 pagesThe Application of Relay Coil Suppression With DC RelaysJesus Deneb Juarez GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.1Document12 pagesAssignment No.1NomanNo ratings yet
- Ee8602 PSG Notes - New - Unit2Document30 pagesEe8602 PSG Notes - New - Unit2Vairaperumal KNo ratings yet
- Applications & Characteristics of Differential Relays, ANSI 87Document3 pagesApplications & Characteristics of Differential Relays, ANSI 87maungsoekhinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document10 pagesChapter 3nassim.1979No ratings yet
- Relayoperationprinciples 141126065914 Conversion Gate01Document43 pagesRelayoperationprinciples 141126065914 Conversion Gate01kenlavie2No ratings yet
- Transient Suppression Devices and PrinciplesDocument8 pagesTransient Suppression Devices and Principleskunalbhavsar1No ratings yet
- Web - Itu.edu - TR Yumakk Downloads Lab Notes Distance Protection v1Document6 pagesWeb - Itu.edu - TR Yumakk Downloads Lab Notes Distance Protection v1sunitharajababuNo ratings yet
- IRXm Product GuideDocument8 pagesIRXm Product Guidedeepak2628No ratings yet
- Ref FerDocument5 pagesRef Feranon_387538941No ratings yet
- Earth Fault Protection R1Document27 pagesEarth Fault Protection R1Chirobocia GabriellaaNo ratings yet
- Earth Fault Protection PDFDocument27 pagesEarth Fault Protection PDFSuresh Chandra PadhyNo ratings yet
- 005 PDFDocument22 pages005 PDFbansalrNo ratings yet
- Lec5 Transformer ProtectionDocument48 pagesLec5 Transformer ProtectionEVTNo ratings yet
- Influence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesFrom EverandInfluence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesNo ratings yet
- Equipment Damage Curves ConductorsDocument4 pagesEquipment Damage Curves ConductorsMrNo ratings yet
- Overcurrent Coordination Setting Guidelines MotorsDocument7 pagesOvercurrent Coordination Setting Guidelines MotorsMrNo ratings yet
- Specification For 460 Volt MCCDocument4 pagesSpecification For 460 Volt MCCMrNo ratings yet
- New Cover Document 2 Api Separator MCCDocument2 pagesNew Cover Document 2 Api Separator MCCMrNo ratings yet
- Corporation Tax Act 2016 (75.02)Document65 pagesCorporation Tax Act 2016 (75.02)MrNo ratings yet
- 06060-01-RC-CTC-0070 - SignedDocument2 pages06060-01-RC-CTC-0070 - SignedMrNo ratings yet
- Cover Letter - EEDocument1 pageCover Letter - EEMrNo ratings yet
- ITB - Electrical Works For No. 2 API Separator Rev ADocument84 pagesITB - Electrical Works For No. 2 API Separator Rev AMrNo ratings yet
- Cover Document For LV CablesDocument2 pagesCover Document For LV CablesMrNo ratings yet
- ITB - CCR Naptha Transfer PumpsDocument36 pagesITB - CCR Naptha Transfer PumpsMrNo ratings yet
- MJCVDocument5 pagesMJCVMrNo ratings yet
- ITB - Electrical Works For WWTF Chemical Dosing Unit Rev A (Wit Sig)Document86 pagesITB - Electrical Works For WWTF Chemical Dosing Unit Rev A (Wit Sig)MrNo ratings yet
- IEEEPESApr14 - Grounding Configurations and Detection!Document66 pagesIEEEPESApr14 - Grounding Configurations and Detection!MrNo ratings yet
- Grounding - 3 PhaseDocument4 pagesGrounding - 3 PhaseMrNo ratings yet
- ELP-IP1881 CameraDocument4 pagesELP-IP1881 CameraMrNo ratings yet
- Neutral Earthing in LV SystemsDocument1 pageNeutral Earthing in LV SystemsMrNo ratings yet
- DC Molded Case BreakersDocument6 pagesDC Molded Case BreakersMrNo ratings yet
- Focus On The Fundamentals of Shielded MV Power CableDocument3 pagesFocus On The Fundamentals of Shielded MV Power CableMrNo ratings yet
- I-Gard Consultant Specification GuideDocument16 pagesI-Gard Consultant Specification GuideMrNo ratings yet
- Resistance Grounded SystemsDocument2 pagesResistance Grounded SystemsMrNo ratings yet
- Installation of Single Conductor CableDocument4 pagesInstallation of Single Conductor CableMrNo ratings yet
- Circuit Breaker RatingsDocument2 pagesCircuit Breaker RatingsMrNo ratings yet
- Differential RelaysDocument9 pagesDifferential RelaysMrNo ratings yet
- 2 - 1 Medium Voltage FusesDocument8 pages2 - 1 Medium Voltage FusesMrNo ratings yet
- 2 - 2 Circuit Breaker DesignDocument3 pages2 - 2 Circuit Breaker DesignMrNo ratings yet
- 1 - 3 Transient ComponentsDocument1 page1 - 3 Transient ComponentsMrNo ratings yet
- Basler Electric 87T - Great InfoDocument3 pagesBasler Electric 87T - Great InfoMrNo ratings yet
- 2 - 4 Protective RelaysDocument3 pages2 - 4 Protective RelaysMrNo ratings yet
- PWMDocument1 pagePWMSharungomesNo ratings yet
- BMS Keystrokes - Old Vs NewDocument16 pagesBMS Keystrokes - Old Vs NewDave91No ratings yet
- Cable Fault Location Measuring Methods - HV TechnologiesDocument21 pagesCable Fault Location Measuring Methods - HV Technologieskokonut1128No ratings yet
- VanTran Submersible Brochure-EDocument4 pagesVanTran Submersible Brochure-ERigeNo ratings yet
- World Charger 36 Volt Fully Automatic Dual Mode Battery ChargerDocument7 pagesWorld Charger 36 Volt Fully Automatic Dual Mode Battery ChargerAntanas Grusas0% (1)
- An17821a PDFDocument9 pagesAn17821a PDFhectorsevillaNo ratings yet
- Aeq Bravo: User'S Manual ED. 12/07Document25 pagesAeq Bravo: User'S Manual ED. 12/07raan4No ratings yet
- DS - 20210206 - SG110CX Datasheet (Including Premium) - V1.1.1 - ENDocument2 pagesDS - 20210206 - SG110CX Datasheet (Including Premium) - V1.1.1 - ENMichelle BridgerNo ratings yet
- ROLL - UP.100: ManualDocument11 pagesROLL - UP.100: ManualRoberto VelascoNo ratings yet
- Epifani American Tweed User ManualDocument8 pagesEpifani American Tweed User ManualMateus MendesNo ratings yet
- Tiny Package, High Performance, Constant Current Switching Regulator For White LEDDocument15 pagesTiny Package, High Performance, Constant Current Switching Regulator For White LEDFahed AlmaktariNo ratings yet
- A3 Series All PDFDocument320 pagesA3 Series All PDFHà Chính100% (1)
- 43ff-TGard Part Number Book - DigitalDocument21 pages43ff-TGard Part Number Book - DigitalAlan David Rojo HernandezNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet Level Alarm Switches S85 PDFDocument2 pagesData Sheet Level Alarm Switches S85 PDFfaraidun100% (1)
- Distance Protection SchemesDocument10 pagesDistance Protection SchemesdebasishNo ratings yet
- Current Sense Switch 1-3ADocument1 pageCurrent Sense Switch 1-3AHuy TuongNo ratings yet
- EV Class NotesDocument30 pagesEV Class NotesVinod BabaleshwarNo ratings yet
- DD353481Document2 pagesDD353481Hayden LovettNo ratings yet
- Sepam Series 10 REL59819Document3 pagesSepam Series 10 REL59819catalinmarusNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual ECE 1Document15 pagesLab Manual ECE 1Macky Malupangue100% (1)
- Thermocouples Mineral InsulatedDocument10 pagesThermocouples Mineral InsulatedEliasNo ratings yet
- Rotary Limit Switch GF4CDocument16 pagesRotary Limit Switch GF4CIvan PimentelNo ratings yet
- E82EV - 8200 Vector 0.25-90kW - v3-0 - ENDocument548 pagesE82EV - 8200 Vector 0.25-90kW - v3-0 - ENMr.K ch100% (1)
- MGE UPS Systems EPS 6000 User Manual PDFDocument84 pagesMGE UPS Systems EPS 6000 User Manual PDFlyax1365No ratings yet
- Motor Protection Circuit BreakersDocument410 pagesMotor Protection Circuit BreakersHernan PatarroyoNo ratings yet