Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Math0303 Completing The Square
Uploaded by
Anna NdunaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Math0303 Completing The Square
Uploaded by
Anna NdunaCopyright:
Available Formats
Math 0303
Solving Quadratic Equations
by Completing The Square
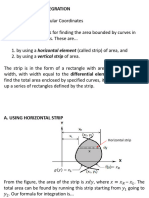
Using the square root property it is possible to solve any quadratic equation written in the form
( x + b )2 = c . The key to setting these problems into the correct form is to recognize that
(x + b)2 is a perfect square trinomial. To turn the equation given into one that can be solved using
the square root property, the following must be done:
Given : ax2 + bx + c = 0
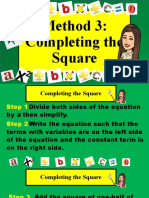
1.) If a ≠ 1 divide both sides by a.
2.) Rewrite the equation so that both terms containing variables are on one side of the
equation and the constant is on the other.
3.) Take half of the coefficient of x and square it.
4.) Add the square to both sides.
5.) One side should now be a perfect square trinomial.
Write it as the square of a binomial.
6.) Use the square root property to complete the solution.
Example 1. Solve 2a2 – 4a – 5 = 0 by completing the square.
Solution
Step 1: Divide the equation by a
5
a 2 − 2a −
=0
2
Step 2: Move the constant term to the right side of the equation
5
a 2 − 2a =
2
Step 3: Take half of the coefficient for x and square it
⎛ 1 ⎞ ⎛ −2 ⎞
⎜ ⎟ ⎜ ⎟ = −1
⎝ 2 ⎠⎝ 1 ⎠
( −1) =1
2
Step 4: Add the square to both sides of the equation
5
a 2 − 2a + 1 = +1
2
Student Learning Assistance Center - San Antonio College 1
Math 0303
Example 1 (Continued):
Step 5: Factor the perfect square trinomial
7
( a − 1) =
2
Step 6: Take the square root of both sides
7⎛ 2 ⎞
(a − 1) 2
=± ⎜ ⎟=±
14
2 ⎜⎝ 2 ⎟⎠ 2
14
( a − 1) = ±
2
14
a = 1±
2
2 14 2 14
a= + or a= −
2 2 2 2
2 + 14 2 − 14
a= or a=
2 2
Example 2. Solve 9a2 – 24a = -13 by completing the square.
Solution
Step 1: Divide the equation by a
24 13
a2 − a=−
9 9
Step 2: Move the constant term to the right side of the equation
8 13
a2 − a = −
3 9
Student Learning Assistance Center - San Antonio College 2
Math 0303
Example 2 (Continued):
Step 3: Take half of the coefficient for x and square it
⎛ 1 ⎞ ⎛ −8 ⎞ 8 4
⎜ ⎟⎜ ⎟ = − = −
⎝ 2 ⎠⎝ 3 ⎠ 6 3
⎛ −4 ⎞ 16
2
⎜ ⎟ =
⎝ 3 ⎠ 9
Step 4: Add the square to both sides of the equation
8 16 13 16
a2 − a + = − +
3 9 9 9
8 16 3
a2 − a + =
3 9 9
8 16 1
a2 − a + =
3 9 3
Step 5: Factor the perfect square trinomial
2
⎛ 4⎞ 1
⎜a − ⎟ =
⎝ 3⎠ 3
Step 6: Take the square root of both sides
1⎛ 3⎞
2
⎛ 4⎞ 3
⎜a − ⎟ = ± ⎜⎜ ⎟⎟ = ±
⎝ 3⎠ 3⎝ 3⎠ 3
4 3
a− =±
3 3
4 3
a= ±
3 3
4+ 3 4− 3
a= or a=
3 3
Student Learning Assistance Center - San Antonio College 3
Math 0303
Example 3. Solve 9x2 – 30x + 29 by completing the square.
Solution
Step 1: Divide the equation by a
30 29
x2 − x+ =0
9 9
Step 2: Move the constant term to the right side of the equation
10 29
x2 − x=−
3 9
Step 3: Take half of the coefficient for x and square it
⎛ 1 ⎞ ⎛ 10 ⎞ 10 5
⎜ ⎟⎜ − ⎟ = − = −
⎝ 2 ⎠⎝ 3 ⎠ 6 3
2
⎛ 5⎞ 25
⎜− ⎟ =
⎝ 3⎠ 9
Step 4: Add the square to both sides of the equation
10 25 25 29
x2 − x+ = −
3 9 9 9
10 25 4
x2 − x+ =−
3 9 9
Step 5: Factor the perfect square trinomial
2
⎛ 5⎞ 4
⎜x− ⎟ =−
⎝ 3⎠ 9
Student Learning Assistance Center - San Antonio College 4
Math 0303
Example 3 (Continued):
Step 6: Take the square root of both sides
−4
2
⎛ 5⎞
⎜x− ⎟ =±
⎝ 3⎠ 9
5 2i
x− =±
3 3
5 2i
x= ±
3 3
5 + 2i 5 − 2i
x= or x=
3 3
Student Learning Assistance Center - San Antonio College 5
You might also like
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan Grade 9Document4 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson Plan Grade 9Anonymous g2aTkG81% (21)
- BBMP1103 Mathemaics For Management AssignmentDocument12 pagesBBMP1103 Mathemaics For Management AssignmentANGEL DEBORAH JOHN studentNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet Algebra 2 TrigDocument4 pagesFormula Sheet Algebra 2 TrigfrancescoabcNo ratings yet
- Toshiba E-Studio 306SE Trouble Error Codes List 12pageDocument11 pagesToshiba E-Studio 306SE Trouble Error Codes List 12pagenafees50% (2)
- Application of Integrals To Plane AreasDocument30 pagesApplication of Integrals To Plane AreasMildred Cardenas BañezNo ratings yet
- Matrices - Part 2 of 2Document26 pagesMatrices - Part 2 of 2Jae-Moy KeymistNo ratings yet
- 3NML4Document29 pages3NML4abdulrazaq bibinuNo ratings yet
- 3 Math1 Linear, Quadratic, and System of EquationsDocument6 pages3 Math1 Linear, Quadratic, and System of EquationsdimlaowenNo ratings yet
- Learning Module: Malasiqui Catholic School, IncDocument11 pagesLearning Module: Malasiqui Catholic School, IncAnazthazia AshannaNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2: Polynomial and Rational FunctionsDocument53 pagesAlgebra 2: Polynomial and Rational FunctionsDianne -chanNo ratings yet
- MATH 9 Q1 Supplemental MaterialDocument47 pagesMATH 9 Q1 Supplemental MaterialJuliaclaire DarantinaoNo ratings yet
- Math0303 Equations of A LineDocument4 pagesMath0303 Equations of A LineJaeNo ratings yet
- Misrimal Navajee Munoth Jain Engineering College, Chennai - 97Document24 pagesMisrimal Navajee Munoth Jain Engineering College, Chennai - 97daredemon92No ratings yet
- 1Document2 pages1Quicksilver 1975No ratings yet
- Completing The Square (A 1)Document6 pagesCompleting The Square (A 1)Alexander BautistaNo ratings yet
- Exponential GraphDocument19 pagesExponential GraphPaula FanaNo ratings yet
- G11-GenMath FinalsExamDocument24 pagesG11-GenMath FinalsExambrgy.agdaoproper2023No ratings yet
- JEE Mains 2019 Shift 1 Maths (10 Jan)Document7 pagesJEE Mains 2019 Shift 1 Maths (10 Jan)neomatrix70No ratings yet
- Quarter 1 Week 6Document38 pagesQuarter 1 Week 6Eliza Antolin CortadoNo ratings yet
- D 16) 1 (1 ) 4) 1 - (Arsinh: January 2006 6675 Pure Mathematics P5/FP2 Mark SchemeDocument6 pagesD 16) 1 (1 ) 4) 1 - (Arsinh: January 2006 6675 Pure Mathematics P5/FP2 Mark SchemeykkamNo ratings yet
- Completing The SquareDocument5 pagesCompleting The SquareZoraiz KhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ParabolaDocument5 pagesIntroduction To ParabolaMelvin EstoleroNo ratings yet
- Diff Calculus SECTION 5Document19 pagesDiff Calculus SECTION 5ParthasarathiNo ratings yet
- SPM Add Maths Formula List Form4Document16 pagesSPM Add Maths Formula List Form4Alvin HonNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Precalculus Concepts Through Functions A Right Triangle Approach To Trigonometry 3rd Edition Sullivan 032193105X 9780321931054Document25 pagesSolution Manual For Precalculus Concepts Through Functions A Right Triangle Approach To Trigonometry 3rd Edition Sullivan 032193105X 9780321931054stephanieriversfmpxnojzcr100% (21)
- Solving Quadratic EquationsDocument2 pagesSolving Quadratic Equationsas7tbiNo ratings yet
- Precalculus Week3 Day1Document24 pagesPrecalculus Week3 Day1dwayneNo ratings yet
- Completing The Square and Quadratic FormulaDocument15 pagesCompleting The Square and Quadratic FormulaDame YooheeNo ratings yet
- AI AA SL Core Diagnostic Test Ch. 1 3-5 Suggested SolutionsDocument26 pagesAI AA SL Core Diagnostic Test Ch. 1 3-5 Suggested SolutionsAlexandr BostanNo ratings yet
- Basic Calculus - Q2 - Week 1 - 4Document65 pagesBasic Calculus - Q2 - Week 1 - 4Venice Gwyn ChavezNo ratings yet
- Equation of Quadratic FunctionsDocument5 pagesEquation of Quadratic FunctionsJerson YhuwelNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 4 Solving Quadratic Equation by Quadratic FormulaDocument9 pagesLesson 2 4 Solving Quadratic Equation by Quadratic FormulaflyleafNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationsDocument11 pagesQuadratic EquationsMary Ann NazarNo ratings yet
- PIT For DEDocument14 pagesPIT For DEReymark Fernandez GingoneNo ratings yet
- Xii Maths M.S.Document13 pagesXii Maths M.S.Poonam TripathiNo ratings yet
- L2 - Simultaneous Equation SolutionDocument10 pagesL2 - Simultaneous Equation Solutionama kumarNo ratings yet
- Notre Dame of Jaro, Inc.: Motivation/DrillDocument5 pagesNotre Dame of Jaro, Inc.: Motivation/DrillVia Terrado CañedaNo ratings yet
- Math Rep SolutionsDocument6 pagesMath Rep SolutionsSkola paperNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Notes Gr.11Document59 pagesMathematics Notes Gr.11iyermagsNo ratings yet
- Q1 Reviewer Grade 9 '23 - '24Document39 pagesQ1 Reviewer Grade 9 '23 - '24zandercompletoNo ratings yet
- Equations and Inequalities of ModulusDocument27 pagesEquations and Inequalities of ModulusLisaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics ReviewerDocument10 pagesMathematics Reviewerian naNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Quadratic EquationDocument9 pagesLesson 1 Quadratic EquationErwin Garalde100% (1)
- Basic AlgebraDocument50 pagesBasic AlgebraFranc Ventura100% (1)
- MATHINTIIIU16Solving NumbersDocument13 pagesMATHINTIIIU16Solving NumbersMostafa AhmedNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Formula ProjectDocument6 pagesQuadratic Formula ProjectCameron TomNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationDocument6 pagesQuadratic EquationDanielNo ratings yet
- FINAL PROJECT (Basic Calculus)Document10 pagesFINAL PROJECT (Basic Calculus)Abigail CostalesNo ratings yet
- Module in Mathematics 9: Department of Education-National Capital Region Schools Division of Pasay CityDocument5 pagesModule in Mathematics 9: Department of Education-National Capital Region Schools Division of Pasay CityShein SheilaNo ratings yet
- BASA Performance-Task-Problems-Involving-Tangent-Line-to-a-CurveDocument4 pagesBASA Performance-Task-Problems-Involving-Tangent-Line-to-a-CurveMartinito, Crisleo John II E.No ratings yet
- Transformation of A Straight Line: MathematicsDocument10 pagesTransformation of A Straight Line: MathematicsWilma Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Solving Quadratic EquationsDocument2 pagesSolving Quadratic Equationsmclaughlin_pNo ratings yet
- Solving Quadratic Equation Using Quadratic FormulaDocument12 pagesSolving Quadratic Equation Using Quadratic FormulaJelliane grace RagoNo ratings yet
- c4 Jan 2009 MsDocument25 pagesc4 Jan 2009 MsMk D. AssassinoNo ratings yet
- V1663930820koswaal CBSE Class-9 Mathematics - Self Assessment Paper-3Document6 pagesV1663930820koswaal CBSE Class-9 Mathematics - Self Assessment Paper-3Ryan TakkarNo ratings yet
- Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing The Square: ObjectivesDocument6 pagesSolving Quadratic Equations by Completing The Square: ObjectivesBaems AmborNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Math 24th Feb Shift 2Document9 pagesJEE Main Math 24th Feb Shift 2Abhinav KumarNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Accounts Scheme Form 3-1Document15 pagesAccounts Scheme Form 3-1Anna NdunaNo ratings yet
- Housing of PigsDocument17 pagesHousing of PigsAnna NdunaNo ratings yet
- Pig Production Using Concentrates - by Joel MuzamhindoDocument2 pagesPig Production Using Concentrates - by Joel MuzamhindoAnna NdunaNo ratings yet
- A5 Pig Management GuidlinesDocument4 pagesA5 Pig Management GuidlinesAnna NdunaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Prepositions Test With Answers Online Exercise Quiz 3 - Learnenglishteam - ComDocument4 pages3 - Prepositions Test With Answers Online Exercise Quiz 3 - Learnenglishteam - ComAnna NdunaNo ratings yet
- Multi Parking System Fional Project ReportDocument54 pagesMulti Parking System Fional Project ReportVinay MuleyNo ratings yet
- German Cars-Mercedes-S-Class-W222Document10 pagesGerman Cars-Mercedes-S-Class-W222DorusNo ratings yet
- Ia Masonry 17Document8 pagesIa Masonry 17Alliah Jane DelfinNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Ophthalmology: An International Journal of Clinical and Investigative OphthalmologyDocument3 pagesVeterinary Ophthalmology: An International Journal of Clinical and Investigative OphthalmologyBlanca A SerranoNo ratings yet
- 12 Pipes and CisternDocument40 pages12 Pipes and Cisternhemanth kumarNo ratings yet
- The Correlation of Central Corneal Thickness (CCT) To Degree of Myopia and Compare It With EmmetropesDocument4 pagesThe Correlation of Central Corneal Thickness (CCT) To Degree of Myopia and Compare It With EmmetropesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Vizzini Et Al 2024 - 240131 - 201545Document82 pagesVizzini Et Al 2024 - 240131 - 201545aedsp2No ratings yet
- PSLVDocument14 pagesPSLVVinod SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Digit Private Car PolicyDocument15 pagesDigit Private Car PolicyLegal NoticeNo ratings yet
- Additol-Xw-330 en LetterDocument2 pagesAdditol-Xw-330 en Letternicolas chNo ratings yet
- Appendix DatabankDocument4 pagesAppendix DatabankMiriam Torres TorresNo ratings yet
- Whitepaper Case Study Bell CanadaDocument12 pagesWhitepaper Case Study Bell CanadageehbeeNo ratings yet
- Micro-Surfacing Construction Inspection GuidelinesDocument12 pagesMicro-Surfacing Construction Inspection Guidelinesvinay rodeNo ratings yet
- 2015-2-JOHOR-SMKdatoAMARmuar - MATHS QADocument10 pages2015-2-JOHOR-SMKdatoAMARmuar - MATHS QAXue Yi LamNo ratings yet
- P-Block Elements (Group 15-18) : Hints and SolutionsDocument4 pagesP-Block Elements (Group 15-18) : Hints and SolutionsGagan GoyalNo ratings yet
- 09 - Carbon Dioxide - G71143R04Document5 pages09 - Carbon Dioxide - G71143R04chem.rajavithiNo ratings yet
- PROFIBUS Tester 5 (BC-700-PB) : Mobile Diagnosis of Bus Physics, Communication and CablingDocument3 pagesPROFIBUS Tester 5 (BC-700-PB) : Mobile Diagnosis of Bus Physics, Communication and Cablingchristian villagranNo ratings yet
- Nemo Outdoor Brochure Oct 2014Document2 pagesNemo Outdoor Brochure Oct 2014treejumboNo ratings yet
- Thermo-Mechanical and Morphological Characterization of Needle Punched Non-Woven Banana Fiber Reinforced Polymer CompositesDocument13 pagesThermo-Mechanical and Morphological Characterization of Needle Punched Non-Woven Banana Fiber Reinforced Polymer CompositesRajeshwaranNo ratings yet
- SonarWiz OptionDocument45 pagesSonarWiz Optionmiko sjNo ratings yet
- Social Life of Small Urban Spaces by William H Whyte - Book ReviewDocument7 pagesSocial Life of Small Urban Spaces by William H Whyte - Book ReviewSherly IreneNo ratings yet
- Point Schedule BAS - LAVENUE - r2Document10 pagesPoint Schedule BAS - LAVENUE - r2Quantum SalesNo ratings yet
- Tube Filling Machines: TFS 80-1 TFS 80-2Document8 pagesTube Filling Machines: TFS 80-1 TFS 80-2mhafizanNo ratings yet
- CSR of Infosys, P& G and ItcDocument18 pagesCSR of Infosys, P& G and ItcnageshalwaysNo ratings yet
- Oxy IQ OxigenoDocument70 pagesOxy IQ OxigenoDavidNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Determination of Total Hardness As PPM Calcium CarbonateDocument26 pagesExperiment 4 Determination of Total Hardness As PPM Calcium CarbonateJordanNo ratings yet
- KORLOYDocument22 pagesKORLOYJuan Jose Ruiz FreyreNo ratings yet
- Lab 19: Properties of Buffer Solutions: Driving QuestionDocument12 pagesLab 19: Properties of Buffer Solutions: Driving QuestionyuvaraajaNo ratings yet
- Culata 3406E C15Document19 pagesCulata 3406E C15carlos moralesNo ratings yet