Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BIOL Lab Notes-1
Uploaded by
Vibha ViswanathanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BIOL Lab Notes-1
Uploaded by
Vibha ViswanathanCopyright:
Available Formats
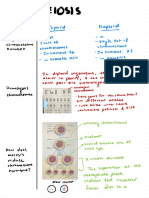
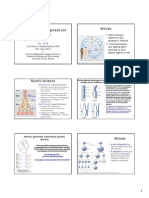
7: Mitosis
Week and Meiosis.
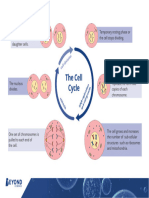
cell Largest Part of
cycle: the cell cycle:
Interphase:
·
two major stages ->
chromosomes are uncoiled.
and mitosis
1. 6, divided
interphase
z
Gap. No DNA synthesis. Not
2. Sesynthetic. Replication of DNA.
identical
·
mitosis: parental cell divides
↳ # of chromosomes stays the same,
however each chromosome is double stranded.
into a
daughter nuclei.
3.
G2-bape- mitosis -
Chromosome consists
of two sister chromatids, held
by centrometers.
These daughter cells are identical
to the parental cell.
components of chromosomes:
d
·
every chromosome is made of:
division: nuclear division (mitosis)
↳ ↳one linear, double stranded DNA molecule.
division: cytokinesis a mitosis.
eukaryotic cell
↳ It is condensed and compacted through the help of different proteins.
However, cytokinesis may not be linked in mitosis
↳ has centrometre the & sight of constriction
a
somewhere along chromosome length
↳in the centrometre, the protein kinetochore is assembled.
To of sell, the nucleus may be
identify stage observed.
·
the the
↳ be link chromosomes to spindle during mitosis.
ends of chromosomes -> telomeres
·
appearance of chromosomes in
can also help identifying stages of the cell.
#
toeffe
Mother cell.
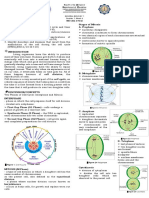
Prophase:
of
argue
to
eachdhonosour consenses - sphagnetilisers peace
Premetaphase:
The end of the prophase, the nuclear membrane dissappears
I t is scattered The spindle
among cytoplasm. is formed
Anaphase:
and the chromosomes move to the center of the cell
centrometres separates the duplicated genetic material.
Metaphase "
chromosomes are centered in the cell. Telophase:
In the
enzyme Kinetochore, each chromosome chromosomes begin to uncoil. New nucleus looks like
gets attached to separate spinale fibers. Cells
interphase nucleus. separate
You might also like
- 12 Lecture Presentation-1Document61 pages12 Lecture Presentation-1amin zargarNo ratings yet
- Cell Division, Mitosis, and MeiosisDocument15 pagesCell Division, Mitosis, and MeiosisanisnazihahNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Mind MapDocument1 pageMitosis Mind MapMaria alejandra Penagos CeballosNo ratings yet
- 7.3: Mitotic Phase - Mitosis and CytokinesisDocument4 pages7.3: Mitotic Phase - Mitosis and CytokinesisMartinoKhanzaniaNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Bio400Document32 pages5.1 Bio400m-5243143No ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document39 pagesGeneral Biology 2Reynail SumayaNo ratings yet
- The Cell: The Cytoplasm and Nucleus: Cytoplasmic Organelles MitochondriaDocument5 pagesThe Cell: The Cytoplasm and Nucleus: Cytoplasmic Organelles Mitochondriavinnie0905No ratings yet
- Cell Cycle PosterDocument1 pageCell Cycle PosterAlizaNo ratings yet
- Bio 9.2 NotebookDocument3 pagesBio 9.2 NotebookpiperlyncourtneylauNo ratings yet
- Modeling Mitosis ActivityDocument3 pagesModeling Mitosis ActivityJobanie AmadhayNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1Document65 pagesGeneral Biology 1Anand Wealth JavierNo ratings yet
- Infographic Mitosis 1Document1 pageInfographic Mitosis 1텅텅No ratings yet
- AhhaDocument4 pagesAhhaashley cagadasNo ratings yet
- 12 Lecture Presentation ShortDocument84 pages12 Lecture Presentation ShortnohaNo ratings yet
- MITOSISDocument3 pagesMITOSISDaphne Ezra F. OlegarioNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument9 pagesMeiosisRudzi UdziNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ergoren - Cell DivisionsDocument51 pagesDr. Ergoren - Cell DivisionsSaraNo ratings yet
- Chromosomes and Cell Cycle Mitosis Meiosis Mitosis and Meiosis Comparison Chromosome InheritanceDocument32 pagesChromosomes and Cell Cycle Mitosis Meiosis Mitosis and Meiosis Comparison Chromosome InheritanceAmandaSherman100% (2)
- Chapter 9Document5 pagesChapter 9blopsieNo ratings yet
- Mitosis WorksheetDocument3 pagesMitosis WorksheetHipster48No ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document6 pagesChapter 11blopsieNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument40 pagesCell CycleNaomi EllaNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Class NotesDocument1 pageScience 9 Class NotesTien NguyenNo ratings yet
- (BIOLOGY) Cell DivisionDocument12 pages(BIOLOGY) Cell DivisionHAJIRA RAMLANNo ratings yet
- Science 8 - Q4 - Week 2Document19 pagesScience 8 - Q4 - Week 2AlfielAquino100% (3)
- Study of MeiosisDocument6 pagesStudy of MeiosisKhushiNo ratings yet
- Sipilä - 30.1.2018 - Spermatogenesis - Oogenesis - FertilizationDocument7 pagesSipilä - 30.1.2018 - Spermatogenesis - Oogenesis - FertilizationBasma RagabNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument8 pagesCell Divisionzade zadeNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 CellGrowthReproductionReviewDocument6 pagesUnit 5 CellGrowthReproductionReviewShannon ErdmanNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument10 pagesCell DivisionGale SatsatinNo ratings yet
- Cell Division MitosisDocument7 pagesCell Division MitosisAmelie BalibagonNo ratings yet
- Presentation1 - Chapter 8Document40 pagesPresentation1 - Chapter 8Mohamed AminNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument22 pagesMeiosisvalerie.bonilla.1282No ratings yet
- Diploid Produce Homologous: Meiosis ReproductiveDocument6 pagesDiploid Produce Homologous: Meiosis ReproductiveKashvi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Biology Marathon A4 DocumentDocument12 pagesBiology Marathon A4 DocumentSamiksha ChettriNo ratings yet
- Week 6 MitosisDocument55 pagesWeek 6 MitosistahaberrkayNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle ReviewerDocument2 pagesThe Cell Cycle ReviewerNcle NaborNo ratings yet
- W3 - Cell Cycle and MitosisDocument38 pagesW3 - Cell Cycle and MitosisNisshokuNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle, Mitosis, MeiosisDocument34 pagesCell Cycle, Mitosis, Meiosisroylene mae samontinaNo ratings yet
- Week 9 and 10 WorksheetDocument4 pagesWeek 9 and 10 WorksheetHope NdwandweNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Cell DivisionDocument51 pagesChapter 6 Cell DivisionAA ProductionNo ratings yet
- Mitosis: J. Richard McintoshDocument16 pagesMitosis: J. Richard McintoshLizbeth EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Bio Chap 5 and 6Document19 pagesBio Chap 5 and 6mjNo ratings yet
- Mitosis: J. Richard McintoshDocument17 pagesMitosis: J. Richard McintoshAlejandro CastañedaNo ratings yet
- MEIOSISDocument2 pagesMEIOSISKate Lynne CamonayanNo ratings yet
- Mitosis/Meiosis: How Cells Reproduce: Exercise IDocument10 pagesMitosis/Meiosis: How Cells Reproduce: Exercise ITAHA GABRNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument80 pagesCell CycleBrandon Alforque EsmasNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle: BiologyDocument82 pagesThe Cell Cycle: BiologymiraolaguerNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument11 pagesCell Cycleashley cagadasNo ratings yet
- Meiosis in Onion Bud Cell...Document3 pagesMeiosis in Onion Bud Cell...abinashp295No ratings yet
- Deal Siklus SelDocument50 pagesDeal Siklus Selanisa rahmaNo ratings yet
- LSPU BSBIO - ZOO1 - SLM4 ExerciseDocument11 pagesLSPU BSBIO - ZOO1 - SLM4 ExerciseJohn ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument72 pagesCell Divisionnor ainiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 The Cell CycleDocument57 pagesChapter 12 The Cell CycleMargarette SimanjuntakNo ratings yet
- Training Module - The Basics of STR Typing - 210725Document16 pagesTraining Module - The Basics of STR Typing - 210725Hager El mahashhashNo ratings yet
- Mitosis MADocument53 pagesMitosis MAMarija PetrovicNo ratings yet
- Cas 3Document1 pageCas 3api-559521963No ratings yet
- Ch10 Standard TestDocument2 pagesCh10 Standard TestosamaNo ratings yet
- Phase Stage DescriptionDocument1 pagePhase Stage DescriptionshanNo ratings yet
- Genetic RecombinationDocument55 pagesGenetic RecombinationRiyaniMartyasariNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance PDFDocument19 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritance PDFBiju Mylachal94% (16)
- Chapter 1 - The Cell As A Unit of Health and DiseaseDocument14 pagesChapter 1 - The Cell As A Unit of Health and DiseaseMon Dominguez100% (2)
- PlasmidDocument26 pagesPlasmidDustin müllerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Genetic Analysis 11Th Edition Griffiths Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesIntroduction To Genetic Analysis 11Th Edition Griffiths Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFarthur.hendricks257100% (12)
- ENCODE Project Writes Eulogy For Junk DNADocument3 pagesENCODE Project Writes Eulogy For Junk DNAפאוזי ג'ומעהNo ratings yet
- Dna Cloning: by Karla Jane E. OrpianoDocument18 pagesDna Cloning: by Karla Jane E. OrpianoXian LeeNo ratings yet
- 2019 - Using Genetically Incorporated Unnatural AminoDocument30 pages2019 - Using Genetically Incorporated Unnatural AminodymscientificNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication and Repair.Document23 pagesDNA Replication and Repair.Muhammad sherNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument83 pagesMolecular Basis of InheritanceKeerthi Sagar100% (1)
- Module Ii-Genetics-G PDFDocument30 pagesModule Ii-Genetics-G PDFJennena Marie VeranoNo ratings yet
- Third Quarter Performance Task No. 2 Science 10Document2 pagesThird Quarter Performance Task No. 2 Science 10MIKE REMBRANT FERNANDEZ100% (2)
- Transcription and TranslationDocument58 pagesTranscription and Translationkevin_ramos007No ratings yet
- Biology Note For Grade 12 (Unit Three Molecular GeneticsDocument24 pagesBiology Note For Grade 12 (Unit Three Molecular GeneticsDaniel GtsadkanNo ratings yet
- DBT BET JRF 2008 Solved Question PaperDocument27 pagesDBT BET JRF 2008 Solved Question PaperDiksha GahlotNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 2 - Module 24: Genetic EngineeringDocument15 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 2 - Module 24: Genetic Engineeringmaria matsuokaNo ratings yet
- BIO 1 - Course Worksheet Week 5Document15 pagesBIO 1 - Course Worksheet Week 5Danielle Marie ImbestroNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-Viii Notes Prepared by Dr. Dhondiba Vishwanath Suryawanshi, GFGC KR Puram Bengaluru-36Document18 pagesChemistry-Viii Notes Prepared by Dr. Dhondiba Vishwanath Suryawanshi, GFGC KR Puram Bengaluru-36Dr. Dhondiba VishwanathNo ratings yet
- SR Neet Star Super Chaina (Biology GT) Q.P Ex - Dt. 18.03.2024Document11 pagesSR Neet Star Super Chaina (Biology GT) Q.P Ex - Dt. 18.03.2024divya202230014No ratings yet
- The Cell 6Document12 pagesThe Cell 6ZagorkaStambolicNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument5 pagesDNA ReplicationNikki SStarkNo ratings yet
- Dna Rna Protein Synthesis Homework 4 Translation AnswersDocument5 pagesDna Rna Protein Synthesis Homework 4 Translation Answersh4aa4bv8100% (1)
- TranslationDocument51 pagesTranslationAleena MustafaNo ratings yet
- Genome Organization and ControlDocument32 pagesGenome Organization and Controllmiguel92100% (1)
- 11.1.proteins Interacting With DNA Turn Prokaryotic Genes On or Off in Response To Environmental ChangesDocument16 pages11.1.proteins Interacting With DNA Turn Prokaryotic Genes On or Off in Response To Environmental Changeshanatabbal19No ratings yet
- 9 Dna Replication Scramble KeyDocument2 pages9 Dna Replication Scramble KeyTy Neal25% (4)
- Mutations Worksheet 2Document3 pagesMutations Worksheet 2Dazza DattoNo ratings yet
- Transcripción Alberts 2014 PDFDocument240 pagesTranscripción Alberts 2014 PDFLaliito LeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5: The Chemical Basis of HeredityDocument19 pagesLecture 5: The Chemical Basis of HeredityShigrid Ann DocilNo ratings yet
- Practical Report - BiotechnologyDocument23 pagesPractical Report - Biotechnologylightning proNo ratings yet