Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Para - Amoeba
Uploaded by
KaoriMarieSembrano0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
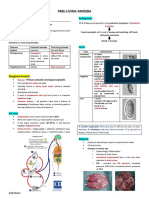
8 views2 pages1. Amoeba are single-celled protozoan parasites that inhabit the intestines of humans and other vertebrates.
2. There are pathogenic and non-pathogenic species of amoeba. Entamoeba histolytica is a pathogenic species that can cause intestinal infection or spread to other organs and cause amoebic liver abscess.
3. The life cycle of E. histolytica involves an infective cyst stage that is ingested and an active trophozoite stage that feeds and multiplies in the intestines before encysting again.
Original Description:
Amoeba review.. MLT
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. Amoeba are single-celled protozoan parasites that inhabit the intestines of humans and other vertebrates.
2. There are pathogenic and non-pathogenic species of amoeba. Entamoeba histolytica is a pathogenic species that can cause intestinal infection or spread to other organs and cause amoebic liver abscess.
3. The life cycle of E. histolytica involves an infective cyst stage that is ingested and an active trophozoite stage that feeds and multiplies in the intestines before encysting again.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesPara - Amoeba
Uploaded by
KaoriMarieSembrano1. Amoeba are single-celled protozoan parasites that inhabit the intestines of humans and other vertebrates.
2. There are pathogenic and non-pathogenic species of amoeba. Entamoeba histolytica is a pathogenic species that can cause intestinal infection or spread to other organs and cause amoebic liver abscess.
3. The life cycle of E. histolytica involves an infective cyst stage that is ingested and an active trophozoite stage that feeds and multiplies in the intestines before encysting again.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
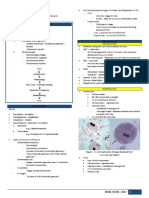
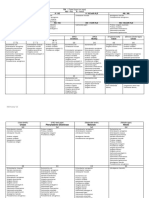
AMOEBA Inhibit large intestine of vertebrate hosts except gingivalis (man’s 1.
Diarrheic/dysenteric/liquid feces - TROPH
Pseudopodial locomotion: mouth) & bovis (cow mouth) - Non-fecal mat: blood & mucus (pick out)
- Rootlike, finger-like or tongue like Exclusive lumen dwellers exc. E. histo (invade tissue) & E. - w/in 30 mins. after voiding (if not, troph disintegrates)
- Locomotor organelle (ameboid) invadens (invade tissue – reptiles) - do at 3-4 day intervals, not daily
- Procurement of food (pseudopodial encirclement) Holozoic a. E. coli - Wet mounts – NSS (I2 inhibits movement)
(ingest organic matter) LC: (5 stages) - Preservative:
Subkingdom: Protozoa 1. Mature cyst Ingested – infective stage 1) MIF (Merthiolate iodine formaldehyde)
Phylum: Sarcomastigophora 2. Stomach (gastric juices on cystic wall) 2) PVA (Polyvinyl alcohol)
Subphylum: Sarcodina 3. Small intestine (Excystation) 3) Schaudinn’s fixative
Family: Endamoebidae 4. Enclosed Metacyst (w/o wall, 8-nuclei) escapes Cyst W #2) & 3) – for permanent staining
Strictly parasitic in GIT (alimentary canal) 5. Metacyst – cytop. division - Permanent mounts – IH or Trichome stain
Small; binary fission 6. Metacystic trophozoites 2. Solid or formed feces – CYST (carriers/chronic patient)
Lack contractile vacuoles 7. Large intestine (cecum) – maturation to troph (feeding st) - Should include a portion of any fleck of mucus
Most undergo encystation 8. Mature troph multiply by binary fission adherent to feces or blood
Genus: 9. Encystation start – unfavorable condition in cecum - Wet mounts – NSS or I2
10. Undigested food extruded - If only few cysts conc. by ZnSO4 centrifugal
Achromatic
11. Precyst – spherical flotation method cyst on surface troph killed
Karyosome Chromatin thread
12. Precyst secrete tough wall Encystation complete b. Saline-purged specimens (for TROPH)
(connect K-NM)
13. Uninucleate cyst - Provide mat for (+) diagnosis if routine fecal exam has
Entamoeba
14. Nuclear division been rewarding
Numerous
Small, center of N Present 15. Binucleate cyst (Young cyst) - Na2SO4 (Glauber salts) or phosphosoda preferred
granules line NM
16. Quadrinucleate cyst - After purgation discard earlier fecal evacuations
17. Octanucleate cyst (Mature cyst) pipette sedimented el. of mucus & tissue cells from 2 nd &
Endolimax
18. Passed out w/ feces 3rd bowel movement onto slide coverslip examine
Thin layer, periph,
Large, blot-like Present b. E. histolytica c. Sigmoidoscopy material
inconspicuous
LC: (5 stages) - Scrapings from suspected sites of amoebic ulceration by
1. Mature cyst ingested gentle pressure from long handled curette or loop
Iodamoeba Large (1/2 Nuc. 1 layer of
Radiating 2. Stomach - 1/3 of scrapings are from sigmoidorectal area
Diameter) Periendosomal
achromatic 3. Excystation – duodenum - Look for typical lesions
Rich in chroma granules, no
fibrils 4. Enclosed metacyst (4 nuclei) escapes its cystic wall - NSS suspension immediately – for motile TROPH
(endosome) periph. chroma
5. Metacyst – cytoplasmic division 4 metacystic troph - Punch biopsy – fix, section & stain 1st before examining
Parasitic amoeba (accdg to pathogenicity & habitat): d. Culture – last resort
(Amoebulae)
A. Nonpathogenic - Study metabolism, pathogenicity & production of
6. Cecum (colonize & feed) maturation to troph
a. Mouth (gingivalis easy to transfer) antigens for serodiagnosis
7. Mature troph – binary fission
b. Intestinal (coli, nana, buetschlii, dispar, hartmanni) - Inoculum – troph / cyst from feces or mat from c
8. Start of encystation – unfavorable envi
B. Pathogenic - Medium: dibasic medium of Boeck & Drbohlav (egg slant
9. Undigested food extruded out
a. Intestinal (histolytica) base w/ isotonic overlay = Locke egg serum)
10. Troph rounds up Precyst
2 main stages: - Diamond’s medium TYI-S-33 reveal E. histo if
11. Precyst secretes cystic wall
Trophozoite Cyst 12. Uninucleate cyst (has glycogen mass & chroma. bodies) microscopic exam has failed
- Chromatoidal bars – 13. 2 nuclear divisions binucleate quadrinucleate (mature) B. Hepatic Amoebiasis
- Bacteria & food
crystallized ribonucleoproteins 14. Mature cyst a. Presence of Intestinal amoebiasis
particles, ingestion
in cytop. protein source - 2 significant sizes for strains: b. Clinical manifestations, inc. WBC, liver function tests
(feeding stage)
Only - Glycogen vacuole– a) Large race – ave. diameter: > 10µ, generally virulent (BSP, ALP)
- RBC
carb source b) Small race - < 10µ (cyst: 5-9µ; troph: 12-15µ) c. Aspiration of abscess – punch/needle biopsy
- Motility (living
- Both are lost in Commensal, non-pathogenic, “E. hartmanni” - Troph recovered in 1/3 of cases
state)
mature cyst 15. Passed out w/ feces - Content of abscess (choco colored, “anchovy sauce”)
- Irregular – - Smooth & rounded Divided into 2: mix of sloughed liver tissue & blood or degenerated
cytop. extension walls 1. Non-invasive – E. dispar liver cells, RBC, leukocytes (sometimes)
Most
undergo fixation - Multinuclear (old); - Nonpathogenic in man d. X-ray: exhibit damage extent
- Uninuclear young = 1 - In experimental animals: produce intestinal lesions e. Seroimmunologic test:
A. Entamoeba - Difficult to distinguish from E. histo (done by culture & 1. Complement fixation
3 grps accdg to no. of nuclei in mature cyst: biochemical methods) 2. FAT of Goldman
1. 1 – E. polecki (pigs, monkey, man) 2. Invasive (?) 3. Indirect hemagglutination (IHA) – more sensitive
2. 4 – E. histo Strains of E.histo – differing in pathogenicity – distinguished Contamination thru:
3. 8 – E. coli from nonpathogenic by isozyme analysis 1. Polluted H2O supply – cyst viable in damp soil (8 days), cool
Gingivalis – no encysted form Diagnosis: (12 days), H2O (9-30 days), H2O at -4°C (3 months)
Natural parasites of GIT of vertebrates & invertebrate hosts except A. Intestinal Amoebiasis 2. Unclean handling of infected indivs (formites, hands, clothes)
E. moshkovskii (sewage H2O & plants) a. Stool exam by direct smears & stained mounts 3. Droppings of flies & other insects
- Cysts unchanged in intestine of flies & cockroach
- Viable in their feces & vomitus for 48 hrs.
- Filth flies (Musca domestica) & cockroaches – mechanical FREE-LIVING AMOEBA
vectors of cysts (sticky, bristly appendages carry cyst from Order: Schizopyrenida
fresh stool; their habit of vomiting & defecating when Fam: Valkamphidae
feeding MoT) Genus:
4. Human excreta in veggie gardens A. Naegleria
5. Carelessness in personal hygiene in children’s asylums, a. N. fowleri = N. aerobia
mental hospitals, prisons & other congested areas - Cause of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM)
Transmission – sexually transmitted disease (oral – anal route) - From lakes, swimming pools (dive - troph nasal passages
- Human carrier (cyst passers) – sources; show no symptoms olfactory nerves cribriform plate cranium)
Pathogenicity - Uninucleate cyst
1. Intestinal amoebiasis – localized in colon (colonize & feed) - 2 forms:
- multiply in crypts 1. Flagellate
- attachment mediated by amoebal galactose or N-acetyl-d- 2 long flagella at one end
galactosamine adherence lectins Elongated
- when ingesting starch granules (rice) Form pseudopods
- utilize mucous secretions as food 2. Ameboid
- Metabolize anaerobically w/ enteric bacteria Single blunt lobopodium
- Once they invade tissue – cause lysis B. Acanthamoeba
- Don’t depend on bacteria – obtain their nourishment thru a. Several species (i.e. culbertsoni)
absorption of dissolved tissue juices - Can’t tolerate hot H2O as A
- Encystation – not in tissue or outside intestinal lumen - Cause chronic infection of skin or CNS in:
specimen taken outside lumen will contain troph only 1. Immunocompromised hosts
- Affect other organs (liver, brain, lungs, spleen 2. Agents of keratits (corneal inflammation) w/ contact lenses
& meningoencephalitis
E. coli E. histo
c. Nuclear divisions 3 2 E.
Infective stage Mature cyst Young cyst
Metacystic troph 8 4
hartmanni – LC, morpho & appearance identical to E. histo
except size (like E. nana)
Troph: - don’t ingest RBC
- motility less vigorous than histo
- Nuc: like coli in char. of its chromatin & karyosome
Cyst: - glycogen mass
- chromatoidal bodies (short w/ tapered ends; rice-grain
shaped or thin, bar-like)
d. E. dispar
B. Endolimax
a. E. nana - Same stage & LC as E.coli
C. Iodamoeba
a. I. buetschlii
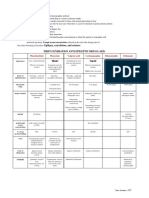
Amoebic Dysentery Bacillary Dysentery
Gross Appearance Gelatinous mixture of Mucopurulent mass
blood, mucus & feces streaked w/ blood
Amt Copious Small
Odor Offensive (fishy) Inoffensive
Color Dark red Bright red
Reaction Acidic Alkaline
Microscopic
Ghost cells
None 95% degenerated
(WBC remnants)
Macrophages Rare Present
Never clumped,
RBC Clumped
discrete
Charcot-Leyden
crystals (in stools Present Absent
w/ parasitic infxn)
Bacteria Numerous Nil to none
Pus cells Scanty numerous
You might also like
- Parasite Summary Table FinalDocument3 pagesParasite Summary Table FinalTamarah Yassin100% (1)
- Permaculture - Plants Suitable For Ground Cover (P) - Plants For A FutureDocument2 pagesPermaculture - Plants Suitable For Ground Cover (P) - Plants For A Futurecontadino_impazzitoNo ratings yet
- CHEM2112 General Chemistry 1 First Quarter Exam 50 PDFDocument13 pagesCHEM2112 General Chemistry 1 First Quarter Exam 50 PDFviehazeNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom Mind MapDocument4 pagesAnimal Kingdom Mind MapVedanti Naik100% (2)
- Distance Relay BasicsDocument58 pagesDistance Relay Basicsaalamz93_854917254100% (1)
- 2 Parasitology Parasitic AmoebasDocument8 pages2 Parasitology Parasitic AmoebasknkjnNo ratings yet
- TrematodesDocument20 pagesTrematodesmiguel gaquitNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Tests in MicrobiologyDocument7 pagesBiochemical Tests in MicrobiologyKaoriMarieSembrano100% (1)
- 974-0753 Onan RDJC RDJF Diesel Engine Service Manual (09-1984)Document64 pages974-0753 Onan RDJC RDJF Diesel Engine Service Manual (09-1984)Leo BurnsNo ratings yet
- Parasitic Amoebas by Dr. C. J. Castro PDFDocument4 pagesParasitic Amoebas by Dr. C. J. Castro PDFMiguel CuevasNo ratings yet
- PROTOZOA (Sarcodina) : ProtozoologyDocument7 pagesPROTOZOA (Sarcodina) : ProtozoologyReyven Niña DyNo ratings yet
- ACVPM Toxicology ReviewDocument21 pagesACVPM Toxicology ReviewShamely CruzNo ratings yet
- Stresses in Large Horizontal Cylindrical Pressure Vessels On Two Saddle Supports - Zick (1951) OriginalDocument11 pagesStresses in Large Horizontal Cylindrical Pressure Vessels On Two Saddle Supports - Zick (1951) OriginalBryan Pérez PérezNo ratings yet
- Basic Labour Rate ListDocument6 pagesBasic Labour Rate ListmaheshNo ratings yet
- Parasitology On AmoebaDocument2 pagesParasitology On AmoebaKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Protista (Subdivision Protozoa) : Bütschlii), or Pathogenic (E. Histolytica)Document6 pagesProtista (Subdivision Protozoa) : Bütschlii), or Pathogenic (E. Histolytica)Primo GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Amoeba: Ms. Helga SyDocument7 pagesAmoeba: Ms. Helga Syanti romantic txtNo ratings yet
- Ameba and E.histolyticaDocument18 pagesAmeba and E.histolyticapenonia.abegailashleyNo ratings yet
- PARASITOLOGY (Quizlet)Document9 pagesPARASITOLOGY (Quizlet)Allyssa AniNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Hemoflagellates and Ciliates (Limpin)Document4 pages1.3 Hemoflagellates and Ciliates (Limpin)arvinkennethdelacruzNo ratings yet
- Tabular Parasitology MICROPARADocument19 pagesTabular Parasitology MICROPARAJerlyn FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Histology Lab Practicals - AY 2021-2022Document15 pagesHistology Lab Practicals - AY 2021-2022H TNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyWeng WengNo ratings yet
- Amoeba PrefinalsDocument5 pagesAmoeba PrefinalsKervy Jay AgraviadorNo ratings yet
- TrematodesDocument2 pagesTrematodesIan Josef R. VibarNo ratings yet
- Amoeba paraDocument9 pagesAmoeba paraHANNA CASANDRA GARCIANo ratings yet
- Micro ParasitesDocument4 pagesMicro ParasitesKrisha Marie BadilloNo ratings yet
- 2 Approaches: 1. Clinical Diagnosis 2. Laboratory Diagnosis 2 Phases: 1. MacroscopicDocument4 pages2 Approaches: 1. Clinical Diagnosis 2. Laboratory Diagnosis 2 Phases: 1. Macroscopiccayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Review On FlagellatesDocument2 pagesParasitology Review On FlagellatesKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Free Living AmoebaDocument5 pagesFree Living AmoebaEiveren Mae SutillezaNo ratings yet
- Amoeba Part 2 NotesDocument8 pagesAmoeba Part 2 Notesjefftuazon01No ratings yet
- Histo - Fresh Tissue Examination and Intro To Histological TechniquesDocument4 pagesHisto - Fresh Tissue Examination and Intro To Histological TechniquesBSMT Kharylle divine FuentibellaNo ratings yet
- Parasites by Apple TanDocument16 pagesParasites by Apple TanOlivia LimNo ratings yet
- Free-Living Amoeba: General CharacteristicsDocument3 pagesFree-Living Amoeba: General CharacteristicsIrvin SamaniegoNo ratings yet
- Dientamoeba Fragilis: Intestinal FlagellatesDocument4 pagesDientamoeba Fragilis: Intestinal FlagellatesRitz CelsoNo ratings yet
- Significance of Commensal Amebae in StoolDocument12 pagesSignificance of Commensal Amebae in StoolNicolle PanchoNo ratings yet
- (PARA) 1.5 - Blood and Tissue FlagellatesDocument6 pages(PARA) 1.5 - Blood and Tissue FlagellatesGuia De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Balantidum Coli: EBON, SISON - 2017Document5 pagesBalantidum Coli: EBON, SISON - 2017Abcd ReyesNo ratings yet
- EPITHELIUMDocument2 pagesEPITHELIUMALEXIS MOIRAH CALIGAGANNo ratings yet
- 5 WormsDocument5 pages5 Wormsreaj.jumsaliNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Intestinal FlagellatesDocument7 pages4.3 Intestinal FlagellatesJudith Dianne Ignacio100% (1)
- F1 Bio MSDocument3 pagesF1 Bio MSVernonNo ratings yet
- Unicellular Mostly Flagellated/ciliated Hetero/AutotrophsDocument9 pagesUnicellular Mostly Flagellated/ciliated Hetero/AutotrophsKobee BacolodNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Table 1Document5 pagesParasitology Table 1William BufNo ratings yet
- PARASITIC AMOEBAS (Lab)Document5 pagesPARASITIC AMOEBAS (Lab)Xie LianNo ratings yet
- AMOEBADocument11 pagesAMOEBAMicaella RemilloNo ratings yet
- Nonpathogenic Amoebae - FlagellatesDocument20 pagesNonpathogenic Amoebae - FlagellatesHend AtijaniNo ratings yet
- 6.2 2021para ReviewlocalwactsDocument35 pages6.2 2021para ReviewlocalwactsHeyzel joy FabianNo ratings yet
- 2nd Exam ReviewerDocument11 pages2nd Exam Reviewerdmt01081991No ratings yet
- Malaika Ifx DZ SummaryDocument17 pagesMalaika Ifx DZ SummaryZhi Ning CNo ratings yet
- Cestodes (Tapeworm) : Diphyllobotium Latum - 20 Yrs Life SpanDocument4 pagesCestodes (Tapeworm) : Diphyllobotium Latum - 20 Yrs Life SpanMicael Andrei MendozaNo ratings yet
- Clinical+Parasitology-Module+10 2Document12 pagesClinical+Parasitology-Module+10 2Geresh MagsinoNo ratings yet
- OkieDocument3 pagesOkieFebeval CastilloNo ratings yet
- Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Complex & NtmsDocument4 pagesMycobacterium Tuberculosis Complex & NtmsCindy Mae Flores UtlegNo ratings yet
- Cysts of The Jaw and Soft Tissues: A-Odontogenic Keratocyst. B - Dentigerous CystDocument15 pagesCysts of The Jaw and Soft Tissues: A-Odontogenic Keratocyst. B - Dentigerous CystruchikaNo ratings yet
- Para - Amoeba TabulatedDocument1 pagePara - Amoeba TabulatedKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Bot 3 2 Lec Exam Reviewer: I. Euglenophyta Chlorophyceae Ulvophyceae Charophyceae Iii. BryophytesDocument4 pagesBot 3 2 Lec Exam Reviewer: I. Euglenophyta Chlorophyceae Ulvophyceae Charophyceae Iii. BryophytesXearis SangalangNo ratings yet
- Zoology - Animal Tissues - Lecture NotesDocument8 pagesZoology - Animal Tissues - Lecture NotesKARYLLE JUNE PONTERASNo ratings yet
- Ch1 XI Animal Kingdom Zlgy Minhad Hsslive PDFDocument9 pagesCh1 XI Animal Kingdom Zlgy Minhad Hsslive PDFBrilliant Cloudprint100% (1)
- Tabulated Review On AmoebaDocument1 pageTabulated Review On AmoebaKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Two Main Excretory Ducts CA Cells and Intercalated Duct CellsDocument3 pagesTwo Main Excretory Ducts CA Cells and Intercalated Duct CellsNoel JoaquinNo ratings yet
- 2 - TrematodesDocument3 pages2 - TrematodesAliyah Julianne PayumoNo ratings yet
- Direct Fecal SmearDocument2 pagesDirect Fecal SmearVera June RañesesNo ratings yet
- LT 2 ReviewerDocument17 pagesLT 2 ReviewerJAY ROBIN WEENo ratings yet
- ParasitologyDocument8 pagesParasitologyNonki VargasNo ratings yet
- Zoology LT 3Document6 pagesZoology LT 3Jonathan CuezonNo ratings yet
- DRUGS2Document1 pageDRUGS2KaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Para - Amoeba TabulatedDocument1 pagePara - Amoeba TabulatedKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Intro ParasitologyDocument4 pagesIntro ParasitologyKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Tabulated Review On AmoebaDocument1 pageTabulated Review On AmoebaKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Review On FlagellatesDocument2 pagesParasitology Review On FlagellatesKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Table Review of ParasitesDocument6 pagesTable Review of ParasitesKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- TrophozoitesDocument4 pagesTrophozoitesKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Micro Lab EnterobacteriaceaeDocument5 pagesMicro Lab EnterobacteriaceaeKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Anti-Epileptic DrugsDocument2 pagesAnti-Epileptic DrugsKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Psychoactive and AntibioticsDocument2 pagesPsychoactive and AntibioticsKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- CSCI101 - Lab08 - Functions Zewail CityDocument4 pagesCSCI101 - Lab08 - Functions Zewail CityMahmoud Ahmed 202201238No ratings yet
- SVE Event GuideDocument22 pagesSVE Event GuideMadalina MarinacheNo ratings yet
- Unit Operation QBDocument7 pagesUnit Operation QBsmg26thmayNo ratings yet
- s1160 Jorvet Infusion PumpDocument4 pagess1160 Jorvet Infusion PumpGhulam HyderNo ratings yet
- JVC KD-G331Document179 pagesJVC KD-G331Saša DumanovićNo ratings yet
- Measure Guide Air Cond DiagnosticsDocument70 pagesMeasure Guide Air Cond Diagnosticsayad60No ratings yet
- Equipment: MR 51 / MR 51V42 - Handy Power MR 56 / MR 56V42 - Strong PowerDocument4 pagesEquipment: MR 51 / MR 51V42 - Handy Power MR 56 / MR 56V42 - Strong PowerIsmailBelguithNo ratings yet
- 01 TMCR Heat Balance DiagramDocument1 page01 TMCR Heat Balance DiagramPrescila PalacioNo ratings yet
- Bubble Slabs Burned at 800 °C With Different Periods: IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and EngineeringDocument10 pagesBubble Slabs Burned at 800 °C With Different Periods: IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineeringshilpa jacobNo ratings yet
- Língua Inglesa: Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesLíngua Inglesa: Reported SpeechPatrick AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Response-2000 - Stalp 30x30Document1 pageResponse-2000 - Stalp 30x30tikianNo ratings yet
- WBMDocument90 pagesWBMMiguel RegisNo ratings yet
- Customer Service Skills For Success 6th Edition Lucas Test Bank 1Document36 pagesCustomer Service Skills For Success 6th Edition Lucas Test Bank 1yolandarichardsqiyrfwmazc100% (23)
- 2b. TESDA-OP-CO-01-F14 TOOLSDocument2 pages2b. TESDA-OP-CO-01-F14 TOOLSRommel SelgaNo ratings yet
- TransportationDocument4 pagesTransportationShrinidhi Priyankaa 1912985630No ratings yet
- Embryo AssignmentDocument2 pagesEmbryo AssignmentA.j. MasagcaNo ratings yet
- Questions On Function and I T FDocument19 pagesQuestions On Function and I T FNilansh RajputNo ratings yet
- Idioms & PhrasesDocument4 pagesIdioms & PhrasesHimadri Prosad RoyNo ratings yet
- CekocideDocument1 pageCekocideKaren Claire HorcaNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Uses and Applications of Inorganic Chemistry. An OverviewDocument4 pagesBiomedical Uses and Applications of Inorganic Chemistry. An OverviewHiram CruzNo ratings yet
- View Result - CUMS Comprehensive University Management System - M.K.Bhavnagar University Powered by AuroMeera A College Management System ProviderDocument1 pageView Result - CUMS Comprehensive University Management System - M.K.Bhavnagar University Powered by AuroMeera A College Management System ProviderKiaanNo ratings yet
- QuizBowl QuestionsDocument84 pagesQuizBowl QuestionsJowel MercadoNo ratings yet
- Spesifikasi Vista 120 S Patient Monitor - StandardDocument2 pagesSpesifikasi Vista 120 S Patient Monitor - StandardHadi AtmojoNo ratings yet
- Keeling 1960 PDFDocument4 pagesKeeling 1960 PDFErick AmâncioNo ratings yet