Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science 6.4
Uploaded by
Nestlee ArnaizOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Science 6.4
Uploaded by
Nestlee ArnaizCopyright:
Available Formats
School: Grade Level: 6
Teacher: Learning Area: SCIENCE
Date: Quarter: THIRD
I. OBJECTIVES:
A. Content Standards: The learners demonstrate understanding of gravity and friction affect movement of
objects
B. Performance Standards: The learners should be able to produce an advertisement demonstrate road safety.
C. Learning Competencies / Objectives: Infer how friction and gravity affects movements of different objects. S6FE-IIIa-c-1
1. Investigate why an object moving along a surface slows down and eventually
stops. (S6FE-IIIa-c-1.1)
2. Describe and define friction. (S6FE-IIIa-c-1.2)
II. CONTENT Frictional Force
III. LEARNING RESOURCES
A. References
1. Teacher’s Guide pages MELC IN SCIENCE page 509
2. Learner’s Materials pages ADM Module pages 1-9
DO_Q3_Science6_Module 1
3. Textbook pages
4. Additional Materials from Learning
B. Other Learning Resources Resources/Portal https://vcguro.valenzuela.gov.ph/Dashboard/SchoolTeacher/
IV. PROCEDURES
A. Reviewing previous lesson or presenting the The teacher recalls the activity during the other day.
new lesson
What is friction example?
Walking – When we walk on the ground or the floor, it is the frictional force that is
responsible for holding our feet to the ground. On slippery surfaces or ice, the friction
present is less, which is why we tend to slip on these surfaces.
What are effects of friction?
Effects of Friction
It produces heat, that helps in heating parts of any object or to warm ourselves. It also
causes loss in power. It produces noise during any kind of operation. It's because of
friction that we're able to walk, run, play, etc.
10 examples of friction in our daily life
Driving of a a vehicle on a surface.
Applying brakes to stop a moving vehicle.
Skating.
Walking on the road.
Writing on notebook/ blackboard.
Flying of aeroplanes.
Drilling a nail into wall.
Sliding on a garden slide.
B. Establishing a purpose for the lesson The teacher will show the signage or road sign “Slippery when wet”. The teacher asks
why there is a need to be careful if the floor or road is wet.
Frictional force is the force generated by two surfaces that contact and slide against
each other. A few factors affecting the frictional force: These forces are mainly
affected by the surface texture and the amount of force impelling them together.
What are the 4 types of frictional force?
Friction is the force that opposes the motion of a solid object over another. There are
mainly four types of friction: static friction, sliding friction, rolling friction, and fluid
friction.
C. Presenting examples/instances of the new The teacher will introduce the activity.
lesson
The pupils will do the activity.
The pupils recall the setting standards in doing the science activity.
What is frictional force and example?
a) The frictional force is defined as the force that is generated between the surfaces
that slide against each other. b) The frictional force is said to be a contact force
because frictional force occurs when two surfaces come in touch with each other.
Example of frictional force is walking on the road.
D. Discussing new concepts and practicing new Answer guided questions from the activity.
skills #1
What are 3 frictional forces?
Friction is the force that opposes motion between any surfaces that are in contact.
There are four types of friction: static, sliding, rolling, and fluid friction. Static,
sliding, and rolling friction occur between solid surfaces.
E. Discussing new concepts and practicing new How do you explain frictional force?
skills #2
Frictional force is the force generated by two surfaces that contact and slide against
each other. A few factors affecting the frictional force: These forces are mainly
affected by the surface texture and the amount of force impelling them together.
F. Developing Mastery (Leads to Formative Video can be shown and discussed.
Assessment 3)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PNDRIicw4E0
G. Finding practical applications of concepts and Describe what will happen to a vehicle that is running fast in highway if there is no
skills in daily living friction.
How about if roads are too rough?
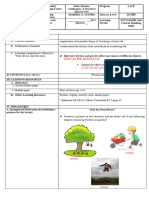
H. Making generalization and abstractions Through the use of Venn Diagram, let the pupils describe the effects of friction on the
about the lesson objects motion. (How friction affects motion?)
I. Evaluating Learning A. Read the questions carefully. Choose the letter of the best answer and
write it on your answer sheet.
1. Where is gravitational force directed as you stand on the floor?
A. upward C. backward
B. forward D. downward
2. Which of the following shows the presence of friction?
A. cars continuously roll down hills
B. things fall off on smooth surfaces
C. people stay in place as they move
D. cars stop when the driver steps on the brakes
3. What is the direction of the frictional force that acts on an object
moving to the left?
A. upward C. to the right
B. downward D. to the left
4. Which of the following statements is not true about friction?
A. it acts upward opposing the pull of gravity
B. it prevents things from sliding off surfaces
C. it keeps things that are in contact with each other
D. it holds objects that are separated by the great distance
5. A delivery man uses a wooden ramp when he delivers thus, packages do
not slide off easily making his work take longer. What would be the
best way to make the packages slide easily?
A. make his wooden ramp wider
B. use water on his wooden ramp
C. use a sandpaper to polish and smoothen his ramp
D. make his wooden ramp narrower
B. Identify what kind of force is acting on the object described in each
situation.
1. A fruit falling from a tree.
2. A ball rolling on the floor.
3. A jeepney moving on a sloping road.
4. A meteor falling through the Earth’s atmosphere.
5. Raindrops falling from the sky.
J. Additional activities for application or Group the class into 4. Let them make their own advertisement about the road safety.
remediation Remind them that their advertisement should be related to the concept of the effects
of friction on the motion of an objects.
V. REMARKS Re-teaching Transfer of lesson to the following day
Lack of Time
No class Achieved
VI.REFLECTION
A. No. of learners who earned 80% in the
evaluation:
B. No. of learners who require additional
activities for remediation who scored below 80%
C. Did the remedial lessons work? No. of
learners who have caught up with the lesson
D. No. of learners who continue to require
remediation
E. Which of my teaching strategies worked
well? Why did these works?
F. What difficulties did I encounter which my
principal or supervisor can help me solve?
G. What innovation or localized materials did I
use/discover which I wish to share with other
teachers?
You might also like
- Friction and the Laws of Motion - Physics Made Simple - 4th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandFriction and the Laws of Motion - Physics Made Simple - 4th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- WLP - Science Q3 Week1Document13 pagesWLP - Science Q3 Week1Maestro Sonny TVNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 6Document12 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 6Zhel Madz100% (3)
- Demo Teaching LP With 5 Ex27sDocument11 pagesDemo Teaching LP With 5 Ex27sehllamaeescobarNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Science6Document4 pagesLesson Plan Science6Hazel Mhee CastorNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Lesson 1 Monday FrictionDocument4 pagesWeek 1 Lesson 1 Monday Frictionkezia sacloloNo ratings yet
- DEMO Teaching LP With 5 E'sDocument12 pagesDEMO Teaching LP With 5 E'sTin Tin93% (14)
- Science6 TypesofFrictionDocument17 pagesScience6 TypesofFrictionJalen TayagNo ratings yet
- Science 6 Quarter 3 Week 1 Day 1Document4 pagesScience 6 Quarter 3 Week 1 Day 1ANA MAQUINANANo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Grade Iv ScienceDocument8 pagesLesson Plan Grade Iv ScienceJessebel RecillaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Cot1 (Final)Document10 pagesLesson Plan Cot1 (Final)chelion.lasagaNo ratings yet
- PLP Science-6 Q3 WK3Document4 pagesPLP Science-6 Q3 WK3Vallente Mae FlorenceNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Lesson 2 Wednesday FrictionDocument4 pagesWeek 1 Lesson 2 Wednesday Frictionkezia sacloloNo ratings yet
- Sle G6Q3W2 L1Document10 pagesSle G6Q3W2 L1ALDRIN REYNOSONo ratings yet
- Science 6 DLL OlibaDocument4 pagesScience 6 DLL OlibaclaudineNo ratings yet
- Science 6 Quarter 3 Module 1 Week 1 Friction Let's UnderstandDocument4 pagesScience 6 Quarter 3 Module 1 Week 1 Friction Let's UnderstandALLYSSA MAE PELONIANo ratings yet
- DLP SCIENCE Q3 W1 DAY 3 Kinetic FrictionDocument3 pagesDLP SCIENCE Q3 W1 DAY 3 Kinetic FrictionROSEBEL GAMABNo ratings yet
- DLP SCIENCE Q3 W1 DAY 1 FrictionDocument4 pagesDLP SCIENCE Q3 W1 DAY 1 FrictionROSEBEL GAMABNo ratings yet
- Phases of MatterDocument11 pagesPhases of MatterGeclaire Juan Diaz AgbisitNo ratings yet
- Sle G6Q3W1 L2Document8 pagesSle G6Q3W1 L2ALDRIN REYNOSONo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - FrictionDocument4 pagesLesson Plan - FrictionpritiNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesA Detailed Lesson Planhyacinth.kuizonNo ratings yet
- DLL Science W-1, Q3Document5 pagesDLL Science W-1, Q3Rodel AgcaoiliNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Science Grade 6: Questions To AskDocument5 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Science Grade 6: Questions To AskJoy Agustin100% (6)
- Final LeaP Sci6 Q3 W1-2Document7 pagesFinal LeaP Sci6 Q3 W1-2NIEVES FIGUEROANo ratings yet
- LS2 DLL (Friction and Gravity)Document6 pagesLS2 DLL (Friction and Gravity)Ronalyn Maldan100% (2)
- DLL Science W-1, Q3Document4 pagesDLL Science W-1, Q3JOSIE CRIS PARCAREYNo ratings yet
- Friction Semi Detailed Lesson Plan-G6Document5 pagesFriction Semi Detailed Lesson Plan-G6Patrick kenneth GacayanNo ratings yet
- Binangonan Sub-Office: Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Iv-A Calabarzon Division of RizalDocument7 pagesBinangonan Sub-Office: Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Iv-A Calabarzon Division of RizalArenas Jen100% (1)
- Report of Micro-Project.Document19 pagesReport of Micro-Project.Aniket GoliNo ratings yet
- Science Q3 W1Document17 pagesScience Q3 W1John Rich CaidicNo ratings yet
- LeaP Science G6 Weeks1 2 Q3Document4 pagesLeaP Science G6 Weeks1 2 Q3Irene BaquiranNo ratings yet
- Catch Up Friday - ScienceDocument3 pagesCatch Up Friday - ScienceGRACE MACADATNo ratings yet
- Gravitation and Frictional ForcesDocument33 pagesGravitation and Frictional ForcesNette Cervantes100% (3)
- DLP DemoDocument4 pagesDLP DemoMarizka BasañezNo ratings yet
- ForcesDocument144 pagesForcesVasanthaNo ratings yet
- How Friction Affect Movement of Objects SemiDocument5 pagesHow Friction Affect Movement of Objects SemiPatrick kenneth GacayanNo ratings yet
- Sle G6Q3W1 L4Document11 pagesSle G6Q3W1 L4ALDRIN REYNOSONo ratings yet
- Week 23 - Day 1 - FrictionDocument18 pagesWeek 23 - Day 1 - FrictionMichael Joshua Aprueldo ValeroNo ratings yet
- Mayang Detailed Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesMayang Detailed Lesson PlanLeafy SamaNo ratings yet
- Science 3rd QTR WEEK3 Day 1 2 FEb.11Document7 pagesScience 3rd QTR WEEK3 Day 1 2 FEb.11Shielanie EsclandaNo ratings yet
- LeaP Science G6 Weeks1 2 Q3Document4 pagesLeaP Science G6 Weeks1 2 Q3Mylene VergaraNo ratings yet
- Feb. 5,2024Document4 pagesFeb. 5,2024Irene BaquiranNo ratings yet
- 16 Module 16 q1 General Physics 1Document27 pages16 Module 16 q1 General Physics 1Ali Juvy De LeonNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Lesson 1 Monday GravityDocument5 pagesWeek 2 Lesson 1 Monday Gravitykezia sacloloNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q3 - W4Document6 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q3 - W4Allyza Fae DavidNo ratings yet
- 8 Notes ForceDocument4 pages8 Notes ForceUmair umairNo ratings yet
- LESSON EXEMPLAR Science QRT3WK2 Friction 1Document8 pagesLESSON EXEMPLAR Science QRT3WK2 Friction 1JIMMY NARCISENo ratings yet
- Gravity and Friction-LpDocument7 pagesGravity and Friction-LpErika AguilarNo ratings yet
- DLP TEMPLATE SCIENCE W-2 - Day 1Document3 pagesDLP TEMPLATE SCIENCE W-2 - Day 1REYIA LUMONTADNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3, Week 1 - FEBRUARY 13-17, 2023 EnglishDocument29 pagesQuarter 3, Week 1 - FEBRUARY 13-17, 2023 EnglishMARK GIL SALVINONo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Plan For Online Distance Learning-Q 3 Week 1Document8 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plan For Online Distance Learning-Q 3 Week 1ROVELYNE DE LUNANo ratings yet
- Week 2 Day 3 - EDITEDDocument14 pagesWeek 2 Day 3 - EDITEDsharon.vallecerNo ratings yet
- Third Quarter Lesson Plan in Science VI ContentDocument3 pagesThird Quarter Lesson Plan in Science VI ContentCatherine Renante100% (25)
- Class 8 - Science - CH - 5 - Friction - NotesDocument5 pagesClass 8 - Science - CH - 5 - Friction - Notes8eanjanimaitreyNo ratings yet
- CHP 9 - Notes (Express)Document20 pagesCHP 9 - Notes (Express)senthilkumarharishragavNo ratings yet
- Force Lesson Plan 7Document6 pagesForce Lesson Plan 7STEPHEN MILANNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in 1st QuarterDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in 1st QuarterArzjohn Niel BritanicoNo ratings yet
- week3-LS2 DLL (Friction and Gravity)Document6 pagesweek3-LS2 DLL (Friction and Gravity)Sherrisoy laishNo ratings yet
- DLP Science 4 Q1 W8.Document10 pagesDLP Science 4 Q1 W8.Nestlee ArnaizNo ratings yet
- DLP Science 4 Q1 W8.Document10 pagesDLP Science 4 Q1 W8.Nestlee ArnaizNo ratings yet
- Science 6.5Document6 pagesScience 6.5Nestlee ArnaizNo ratings yet
- Science 6.3Document4 pagesScience 6.3Nestlee ArnaizNo ratings yet
- Science 6.5Document6 pagesScience 6.5Nestlee ArnaizNo ratings yet
- Science 6.1Document6 pagesScience 6.1Nestlee ArnaizNo ratings yet
- Industrial Flow Measurement: Basics and PracticeDocument0 pagesIndustrial Flow Measurement: Basics and PracticeBijoy AyyagariNo ratings yet
- Durethan B30S 000000: PA 6, Non-Reinforced, Injection Molding ISO Shortname: ISO 1874-PA 6, GR, 14-030Document3 pagesDurethan B30S 000000: PA 6, Non-Reinforced, Injection Molding ISO Shortname: ISO 1874-PA 6, GR, 14-030zoranNo ratings yet
- Shreyas Pawale ResumeDocument1 pageShreyas Pawale ResumeRahulRajGoldyNo ratings yet
- Predetermined Time System: TI 2111 Work System Design and ErgonomicsDocument20 pagesPredetermined Time System: TI 2111 Work System Design and Ergonomicskevin21790No ratings yet
- Origin and Nature of Radiation (English)Document23 pagesOrigin and Nature of Radiation (English)laloooppNo ratings yet
- Multiphoton PolymerizationDocument9 pagesMultiphoton PolymerizationMircavid HeydəroğluNo ratings yet
- Ce6304 - Pec Surveying I - 5 Unit NotesDocument62 pagesCe6304 - Pec Surveying I - 5 Unit Notesဒုကၡ သစၥာNo ratings yet
- Inconel 600 Alloy 600 Uns n06600 Din 2.4816Document3 pagesInconel 600 Alloy 600 Uns n06600 Din 2.4816SamkitNo ratings yet
- 5 6154457525488977613Document5 pages5 6154457525488977613ankith sNo ratings yet
- Engguide PDFDocument92 pagesEngguide PDFBIJOYNo ratings yet
- Calculating Eigenvalues of Many-Body Systems From Partition FunctionsDocument25 pagesCalculating Eigenvalues of Many-Body Systems From Partition FunctionsAmina IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Unlocking The Secrets of Gann PDFDocument11 pagesUnlocking The Secrets of Gann PDFfsolomon100% (1)
- ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesThermodynamicsliezyl_15No ratings yet
- Enhanced Degradation of Persistent Pharmaceuticals Found in Wastewater Treatment Ef Uents Using Tio2 Nanobelt PhotocatalystsDocument14 pagesEnhanced Degradation of Persistent Pharmaceuticals Found in Wastewater Treatment Ef Uents Using Tio2 Nanobelt PhotocatalystsSourav SutradharNo ratings yet
- DE38#######KS###: Data Sheet and Instruction Manual DE38 Digital Differential Pressure Transmitter / SwitchDocument12 pagesDE38#######KS###: Data Sheet and Instruction Manual DE38 Digital Differential Pressure Transmitter / SwitchAmirouche BenlakehalNo ratings yet
- Com Flor 60 BrochureDocument28 pagesCom Flor 60 BrochureMilena JanicijevicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - Essential Mathematical Methods Unit 1&2Document49 pagesChapter 17 - Essential Mathematical Methods Unit 1&2Kelley0% (1)
- Self Evaluation Test-Sets and RelationsDocument3 pagesSelf Evaluation Test-Sets and RelationsShamim RahmatNo ratings yet
- Leaflet Poly Met 3394 en LowDocument2 pagesLeaflet Poly Met 3394 en LowCamiloNo ratings yet
- Slip FormationDocument28 pagesSlip Formationpawan_aggarwal_22100% (2)
- Guide To Better Geotextile Specifying US FABRICSDocument19 pagesGuide To Better Geotextile Specifying US FABRICSOladunni AfolabiNo ratings yet
- Downloaded From Uva-Dare, The Institutional Repository of The University of Amsterdam (Uva)Document12 pagesDownloaded From Uva-Dare, The Institutional Repository of The University of Amsterdam (Uva)Iqioo RedefiniNo ratings yet
- ASAP 2020: Accelerated Surface Area and Porosimetry SystemDocument462 pagesASAP 2020: Accelerated Surface Area and Porosimetry SystemMargiani FortesNo ratings yet
- What Is Solvatochromism?: Alberto Marini, Aurora Mun Oz-Losa, Alessandro Biancardi, and Benedetta MennucciDocument8 pagesWhat Is Solvatochromism?: Alberto Marini, Aurora Mun Oz-Losa, Alessandro Biancardi, and Benedetta MennucciJadaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document20 pagesChapter 4Nasyitah RusliNo ratings yet
- Water DistillerDocument13 pagesWater DistillerjordanrmaNo ratings yet
- Shaft Model With Mathlook EquationsDocument112 pagesShaft Model With Mathlook EquationsMoisés MachadoNo ratings yet
- CNC Router CalculationsDocument4 pagesCNC Router Calculationsmorteza nourooziNo ratings yet
- GE Lighting Systems HM-1000 Asymmetrical High Mast Series Spec Sheet 12-74Document2 pagesGE Lighting Systems HM-1000 Asymmetrical High Mast Series Spec Sheet 12-74Alan Masters100% (1)
- F Wedge+Pseudo 18 07 2021 TestDocument2 pagesF Wedge+Pseudo 18 07 2021 TestAryanNo ratings yet