Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Name: M.Jawad Roll No: 2021-Bsc-03 Class: 4 Semester Department: Electrical Engineering & Technology Subject: Power Transmission
Name: M.Jawad Roll No: 2021-Bsc-03 Class: 4 Semester Department: Electrical Engineering & Technology Subject: Power Transmission
Uploaded by
ZAIN UL ABIDENOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: M.Jawad Roll No: 2021-Bsc-03 Class: 4 Semester Department: Electrical Engineering & Technology Subject: Power Transmission
Name: M.Jawad Roll No: 2021-Bsc-03 Class: 4 Semester Department: Electrical Engineering & Technology Subject: Power Transmission
Uploaded by
ZAIN UL ABIDENCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: M.
Jawad
Roll No: 2021-BSc-03
Class: 4th Semester Department:
Electrical Engineering & Technology Subject: Power Transmission
Practical No.4
Title:
Observe the voltage regulation at receiving end of a 3 phase transmission line as function of
inductive load (with line capacitance).
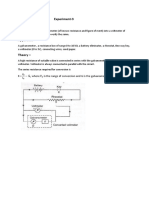
Equipment used :
3- phase power supply (DL103TI).
3- phase transmission line (DL790TT).
Inductive load (DL1017L.
Connecting leads.
Digital multimeter.
Theory
Inductive Loads:
Inductive loads provide power to electric motors. Examples are moving parts Fans, vacuum
cleaners, dishwashers, washing machines, compressors in refrigerators and air conditioners,
and other household items and gadgets. In contrast to resistive loads, purely inductive loads
have maximum, minimum, and zero points out of phase because the current follows a
sinusoidal pattern and peaks after the voltage sine wave.
Voltage regulation:
When a transformer is loaded, with a constant supply voltage, the terminal voltage changes due
to voltage drop in the internal parameters of the transformer i.e., primary and secondary
resistances and inductive reactance’s. The voltage drop at the terminals also depends upon the
load and its power factor. The change in terminal voltage from no-load to full-load at constant
supply voltage with respect to no-load voltage is known as voltage regulation of the transformer.
|v R ( NL)|−|v R ( FL |)
%VR = ×100
|v R (FL )|
Procedure
First we take three take 3phase from 3phase power supply
We connect this 3phase on 3phase transmission line DL709TT
After this we take three phase from transmission line DL709TT then we connect this
3phase to inductive load DL1017L
And after this we set Vin=100v and we get voltage on receiving end with no load =100v
And after this we connect L1on load and the output voltage decreasing
And step by step we increase the load and note the output voltage
And the same procedure we do with resistive and capacitive loads
inductive load
Sr.
With line
no
capacitance
1 VR(N.L) 55
2 VL1 46
3 VL2 43
4 VL3 39
5 VL4 33
6 VL5 30
|v R ( NL)|−|v L( FL |)
%VR= ×100
|v L ( FL )|
55−30
%VR= ×100
30
%VR=83%
Conclusion:
In this experiment we learn how to use ac power supply.
We learned how to use phase sequence indicator.
Using phase sequence indicator we learned how to check phase sequence is correct or
not.
You might also like
- Activity5 Group1Document24 pagesActivity5 Group1NicoNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line ManualDocument10 pagesTransmission Line ManualYADAVAMITKUMAR007No ratings yet
- Metode Perbaikan Tanah - Kuliah IIDocument25 pagesMetode Perbaikan Tanah - Kuliah IIVirginia gabyella saraunNo ratings yet
- Practical No. 5Document4 pagesPractical No. 5ZAIN UL ABIDENNo ratings yet
- Name: M.Jawad Roll No: 2021-Bsc-03 Class: 4 Semester Department: Electrical Engineering & Technology Subject: Power TransmissionDocument3 pagesName: M.Jawad Roll No: 2021-Bsc-03 Class: 4 Semester Department: Electrical Engineering & Technology Subject: Power TransmissionZAIN UL ABIDENNo ratings yet
- Practical No. 2Document3 pagesPractical No. 2ZAIN UL ABIDENNo ratings yet
- Practical No. 7Document4 pagesPractical No. 7ZAIN UL ABIDENNo ratings yet
- EEE Lab ManualDocument26 pagesEEE Lab ManualPrabin RoyNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ManualDocument23 pagesLaboratory ManualAnmol AhsaasNo ratings yet
- Half Wave and Full Wave RectifiersDocument5 pagesHalf Wave and Full Wave RectifiersRajesh PylaNo ratings yet
- Week 7-Transformers Voltage Regulation and Per Unit calculations-ELEC2300Document30 pagesWeek 7-Transformers Voltage Regulation and Per Unit calculations-ELEC2300Look AxxNo ratings yet
- 01M Equivalent CircuitDocument43 pages01M Equivalent Circuitবিবেক রত্নNo ratings yet
- P Practical 8Document5 pagesP Practical 8Doraemon हिंदीNo ratings yet
- Overhead Line and Substation InsulationDocument11 pagesOverhead Line and Substation InsulationRamesh BabuNo ratings yet
- قراوندددددددددددددDocument6 pagesقراوندددددددددددددarwa zeglamNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 PDFDocument19 pagesLec 1 PDFJoshua Roberto GrutaNo ratings yet
- Exp6 1Document12 pagesExp6 1Joel CatapangNo ratings yet
- Exp6 1Document12 pagesExp6 1Joel CatapangNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual: Hirasugar Institute of Technology, NidasoshiDocument67 pagesLaboratory Manual: Hirasugar Institute of Technology, NidasoshipriyaNo ratings yet
- Ch5 Power System Slide08Document47 pagesCh5 Power System Slide08hafiz azman100% (5)
- Basic Electrical Engineering Lab ManualDocument44 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Lab Manualdinuarslan86% (7)
- 2021MT10892 - Akshat Madhan - ELP Lab Report - Exp 4Document7 pages2021MT10892 - Akshat Madhan - ELP Lab Report - Exp 4Akshat MadhanNo ratings yet
- Electronics Study Material For MSCDocument23 pagesElectronics Study Material For MSCiswaleha100% (1)
- C2 Exp4.1Document13 pagesC2 Exp4.1NicoNo ratings yet
- 27U LCR Circuit W OscilloscopeDocument9 pages27U LCR Circuit W OscilloscopeValeria MendozaNo ratings yet
- PT Lab 02Document8 pagesPT Lab 02Arslan Bin ShabeerNo ratings yet
- Vector Group Measurement PDFDocument7 pagesVector Group Measurement PDFEdward Baleke SsekulimaNo ratings yet
- Bridges, 3-Ammeter, 3-VoltmeterDocument10 pagesBridges, 3-Ammeter, 3-Voltmeterమారుతీ రామ్. ధరణీప్రగడ.వెం.సుNo ratings yet
- 17eel37 Eml Lab ManualDocument64 pages17eel37 Eml Lab ManualpriyaNo ratings yet
- Lab 05Document9 pagesLab 0549 - 103 - Umair HossainNo ratings yet
- Inductive Reactance (In RL Circuits) : FALL2020: CNET219Document6 pagesInductive Reactance (In RL Circuits) : FALL2020: CNET219liam butlerNo ratings yet
- VSWR LabDocument5 pagesVSWR LabKrishna Prasad PheluNo ratings yet
- E207 - Communication Systems: Worksheet For Lesson 07: Standing WavesDocument8 pagesE207 - Communication Systems: Worksheet For Lesson 07: Standing Waves张瑜征No ratings yet
- Voltage+Regulation (20 Files Merged)Document20 pagesVoltage+Regulation (20 Files Merged)muhammadtahahussian474No ratings yet
- A Arte Da Eletronica 3oedicao (1) (0101-0150)Document50 pagesA Arte Da Eletronica 3oedicao (1) (0101-0150)Baba GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Power Angle CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesPower Angle Characteristicsmadhan_22No ratings yet
- CoaxDocument6 pagesCoaxDarian KaradjovNo ratings yet
- L2-Single Phase Part 1-Sem1-2016-17-Ver2 PDFDocument42 pagesL2-Single Phase Part 1-Sem1-2016-17-Ver2 PDFVievie Le BluewberrietrufflesNo ratings yet
- Pee Lab ManualDocument77 pagesPee Lab ManualRajendraTuraka100% (1)
- Overhead Line and Substation InsulationDocument11 pagesOverhead Line and Substation InsulationAnkat Rao RaoNo ratings yet
- Overhead Line Insulators: Example 4.1Document11 pagesOverhead Line Insulators: Example 4.1e TalalNo ratings yet
- Lab#3b: Setting Up A Power Supply Using A Zener Diode As Voltage RegulatorDocument5 pagesLab#3b: Setting Up A Power Supply Using A Zener Diode As Voltage RegulatorDaisy FlowerNo ratings yet
- Sinusoidal Steady State Circuit Analysis Topic 3Document14 pagesSinusoidal Steady State Circuit Analysis Topic 3dsweetalker100% (1)
- Me 005Document25 pagesMe 005Pratheesh S KumarNo ratings yet
- Long Transmission Line Under No & Light Load With Ferranti EffectDocument6 pagesLong Transmission Line Under No & Light Load With Ferranti EffectviksoniNo ratings yet
- LAB Presentation: Ing Ongkut's Nstitute of Echnology AdkrabangDocument28 pagesLAB Presentation: Ing Ongkut's Nstitute of Echnology Adkrabangญาณันธร เชิดชูไทยNo ratings yet
- Ac Single PhaseDocument35 pagesAc Single PhaseBerihun EngdaNo ratings yet
- Ho-1.1 Fault Analysis 2Document17 pagesHo-1.1 Fault Analysis 2japhet ontongNo ratings yet
- Expt 4Document24 pagesExpt 4Ariston EtormaNo ratings yet
- BEE Module 7Document31 pagesBEE Module 7zairus punzalanNo ratings yet
- Experiment-3 Aim-: Where Is The Range of Conversion and G Is The Galvanometer ResistanceDocument3 pagesExperiment-3 Aim-: Where Is The Range of Conversion and G Is The Galvanometer ResistanceCHIRAG GUPTANo ratings yet
- Phasor Concept: M V M VDocument11 pagesPhasor Concept: M V M VKim Andre MacaraegNo ratings yet
- 8_JEE_Physics_Alternating%20Current_RL,%20RC,%20LC%20CircuitsDocument5 pages8_JEE_Physics_Alternating%20Current_RL,%20RC,%20LC%20Circuitszorou984No ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Lab ManualsDocument31 pagesBasic Electronics Lab ManualsMirza Umar Farooq BaigNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics 15-LabsDocument63 pagesPower Electronics 15-LabsKrishna v.mNo ratings yet
- Experiment No-4Document6 pagesExperiment No-4devanshurajpoot1No ratings yet
- Lab Assignment 1Document13 pagesLab Assignment 1humayun azizNo ratings yet
- Alternating CurrentDocument24 pagesAlternating CurrentAnand KNo ratings yet
- 5 ELD255 Lab 5a - Bridge Rectifier Nov-23-18Document3 pages5 ELD255 Lab 5a - Bridge Rectifier Nov-23-18killtime921No ratings yet
- CAD Exp2Document8 pagesCAD Exp2ahad mushtaqNo ratings yet
- SS ISO 10993-1-2018 - PreviewDocument14 pagesSS ISO 10993-1-2018 - PreviewmarkNo ratings yet
- Psychological Foundation of CurriculumDocument15 pagesPsychological Foundation of CurriculumJhonalyn LubatonNo ratings yet
- 2021-AIPCP2331-030036 - Textbook With Augmented Reality Technology - Improve Crtitical Thinking Skill in Elasticity ConceptDocument6 pages2021-AIPCP2331-030036 - Textbook With Augmented Reality Technology - Improve Crtitical Thinking Skill in Elasticity ConceptPengajar FAUZI BAKRI, S.Pd, M.SiNo ratings yet
- Bueno-El-Animal-Divino - Bueno, El Animal Divino PDFDocument741 pagesBueno-El-Animal-Divino - Bueno, El Animal Divino PDFTory PrietoNo ratings yet
- Textile Printing Assignment - 1Document1 pageTextile Printing Assignment - 1Muhammad Imad YasirNo ratings yet
- Battery Safety-Instruction A5E02873837Document4 pagesBattery Safety-Instruction A5E02873837Francisco García de SoriaNo ratings yet
- Mock Exam Schedule January 2023Document2 pagesMock Exam Schedule January 2023Maryam ShehataNo ratings yet
- 365 FUNRAU QuestionsDocument8 pages365 FUNRAU QuestionsjsbachNo ratings yet
- Wind Energy Assessment-R1Document80 pagesWind Energy Assessment-R1Nitish GunessNo ratings yet
- Monitoring The Insulator Condition by On-Line Voltage Distribution MeasurementDocument3 pagesMonitoring The Insulator Condition by On-Line Voltage Distribution MeasurementmunirNo ratings yet
- Presentation Secrets Alexei KapterevDocument38 pagesPresentation Secrets Alexei KapterevJose Maria De VianaNo ratings yet
- P1 Chapter 3Document1 pageP1 Chapter 3Rehan ShahNo ratings yet
- CLIMATEREASONSDocument3 pagesCLIMATEREASONSBBBBNo ratings yet
- Manual - XL3t - MiningDocument27 pagesManual - XL3t - MiningHector Manuel GalvisNo ratings yet
- Test 1 (PM)Document5 pagesTest 1 (PM)Nabil NizamNo ratings yet
- 資料探勘應用於醫藥物流中心消耗預測Document70 pages資料探勘應用於醫藥物流中心消耗預測Harper ChengNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Paln in Photosynthesis Gen. Biology 1Document6 pagesDetailed Lesson Paln in Photosynthesis Gen. Biology 1Queng ElediaNo ratings yet
- Reinforcement CouplersDocument24 pagesReinforcement CouplersvishalgoreNo ratings yet
- Exploring Your True Self A2Document4 pagesExploring Your True Self A2Dasha AgavelovaNo ratings yet
- Flood Modelling Using Hec-Ras and Geo Informatics Technology in Lower Reaches of Shetrunji River, Gujarat, IndiaDocument11 pagesFlood Modelling Using Hec-Ras and Geo Informatics Technology in Lower Reaches of Shetrunji River, Gujarat, IndiaJhanielle AraNo ratings yet
- A Design of The Searcher Circuit: Sensing Channel Type: ProjectedDocument2 pagesA Design of The Searcher Circuit: Sensing Channel Type: ProjectedHu GyNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Concrete Box Girder Bridges Using Csi Bridge 2014Document50 pagesAnalysis of Concrete Box Girder Bridges Using Csi Bridge 2014oday albuthbahakNo ratings yet
- NIOS ENVIRONMENT - PDF 16Document2 pagesNIOS ENVIRONMENT - PDF 16Hema Mani Kiran PathuriNo ratings yet
- SLL Code For Lighting 2012Document3 pagesSLL Code For Lighting 2012joxyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 OBDocument29 pagesChapter 4 OBashenafi chekolNo ratings yet
- ?Jf&RERSPE6096: Carlberq, Continental Ofl CoDocument7 pages?Jf&RERSPE6096: Carlberq, Continental Ofl CoShamsiNo ratings yet
- Capstone Proposal Final Like Medj FinalDocument22 pagesCapstone Proposal Final Like Medj FinalCABABAN, SHAIRA A. STEM2No ratings yet
- Tree Structure - Syntax - OdtDocument5 pagesTree Structure - Syntax - OdtphuongthaospkNo ratings yet
- What is Citizenship Training ProgramDocument10 pagesWhat is Citizenship Training ProgramSkul TV ShowNo ratings yet