Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Media Information Literacy Reviewer
Uploaded by
Precia Alday0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views16 pagesMedia Information Literacy Reviewer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMedia Information Literacy Reviewer
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views16 pagesMedia Information Literacy Reviewer
Uploaded by
Precia AldayMedia Information Literacy Reviewer
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
Media Information Literacy Reviewer where you send and receive
messages (McLean, 2005)
MEDIA The physical objects used to
7. Context - the communication
communicate with, or mass
interaction involves the setting,
communication through physical
scene, and expectations of the
objects such as radio, television, films
individuals involved (McLean,
and more.
2005)
INFORMATION A broad term that can
cover data; knowledge derived from
study, experience, or institution; 8. Interference - anything that
signals, or symbols. blocks or changes the source’s
intended meaning of the
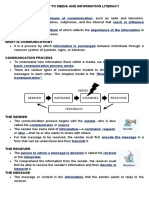
COMMUNICATION •It is the act of
message (McLean, 2005)
transferring information from one
place, person, or group to another
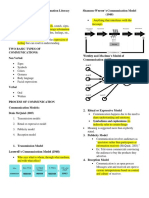
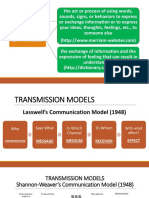
(SkillsYouNeed,2020). •It is the HAROLD LASSWELL’S
process of sending and receiving COMMUNICATION MODEL It shows a
messages through verbal or nonverbal one-way transmission of information
means, including speech, or oral and simply illustrates how
communication. communication starts from a sender
who transmits their message through a
Components of Communication
channel to an intended receiver,
1. Source - A person, group, or consequently with a corresponding
entity that forms, creates, effect.
sends, or forwards a message
or information.
2. Message - The stimulus or
meaning produced by the
source for the receiver or
audience (Mclean, 2005)
3. Channel - It is the tool or
manner in which the messages
will be carried through from the
source to the receiver.
4. Receives the message from the
source, analysing, and
interpreting the message in
ways both intended and SHANNON AND WEAVER’S
unintended by the source COMMUNICATION MODEL Much like
(McLean, 2005). in Lasswell, this model also indicates
5. Feedback - The message or how communication starts with the
information source who then sends a
response of the receiver which
message with the use of a transmitter
is sent back to the source.
(channel). The signals that are sent
6. Environment – The atmosphere,
and received can vary depending on
physical and psychological,
the method of communication.
However, the difference of the models
comes from the incorporation of the to many people through print or
“noise.” Noise refers to anything that electronic media.
may interfere – stop or alter – the
HOW COMMUNICATION IS
message being carried.
INFLUENCED BY MEDIA AND
INFORMATION
1. It makes the world a smaller
place. ✓Today, the world
seemed like a smaller place that
before, as through digital media,
a person can be connected to
anyone else in the word at any
given time.
2. It makes communication
convenient. ✓In the past,
communicating to someone
from far away meant sending
Forms of Communication telegrams and snail mails and
INTRAPERSONAL people need to wait months or
COMMUNICATION - It is a form of even years before their
communication with oneself using intended receivers obtain their
internal vocalization or reflective message
thinking (Communication in the Real 3. It shapes public opinion.
World, 2010). ✓Maxwell McCombs explained
that mass media shapes
INTERPERSONAL opinion through its wide reach,
COMMUNICATION - It is a form of not to mention the perceived
communication between two different credibility of the media, they can
people who may or may not have a sway the opinion of their
direct relationship with each other but audience according to the
are mutually and actively part of the message they convey.
communication process.
Literacy - Ability to identify,
GROUP COMMUNICATION - It is a understand, interpret, create,
type of communication between three communicate, and compute using
or more people interacting to achieve a printed and written materials
specific objective or certain goal. associated with varying context.
PUBLIC COMMUNICATION- This is a (UNESCO).
sender-focused form of communication Involves a wide range of learning,
in which one person is typically wherein individuals are able to develop
responsible for conveying information their knowledge and skills, achieve
to an audience. their goals, and participate fully in their
MASS COMMUNICATION - Public community and wider society.
communication becomes mass Media Literacy - The ability to access,
communication when it is transmitted analyze, evaluate, and create media in
a variety of forms. It aims to empower
citizens by providing them with the order to participate and engage in
competencies (knowledge and skills) personal, professional and societal
necessary to engage with traditional activities”.
media and new technologies.
MEDIA AND INFORMATION
MEDIA LITERATE - In essence, a LITERATE Being media and
media literate person can think information literate means being able
critically about what they see, hear, to know where and how to access
and read in books, newspapers, sources of information; to analyze the
magazines, television, radio, movies, meaning and importance of
music, advertising, video games, the information we come across; to
Internet, and new. emerging evaluate the value, truthfulness, and
technology. credibility of such information; to
create, produce, and share media
INFORMATION LITERACY The ability
products knowing fully well your
to recognize when information is
responsibility to your audience.
needed, and to locate, evaluate, and
effectively communicate information in Benefits of Media and Information
its various formats. Literacy
INFORMATION LITERATE An 1. It teaches you how to verify
information literate individual is able to: information and acknowledge
others’ perspectives.
• Access the needed information
2. It encourages audiences to
effectively and efficiently.
think critically.
• Evaluate information and its sources 3. It promotes responsible
critically. information sharing and
dissemination.
• Use information effectively to 4. It helps you identify and
accomplish a specific purpose. understand the media’s role in
TECHNOLOGY LITERATE - Being our culture.
tech literate means that you can use 5. It teaches you to think and
the correct technology tools with ease decide objectively, factually,
and know where to look for them. This and reasonably
includes knowing which sites are safe 6. It encourages you to actively
to view for underage viewers or participate in public affairs as a
knowing which settings to select on citizen.
social media platforms. 7. It teaches you to create your
own content responsibly.
MEDIA AND INFORMATION 8. It makes you better appreciate
LITERACY UNESCO defines Media media products.
and Information Literacy as “a set of
competencies that empowers citizens Responsible Use of Media and
to access, retrieve, understand, Information
evaluate and use, to create as well as INFORMATION DISORDER It refers
share information and media content in to the many ways our information
all formats, using various tools, in a environment is polluted – content are
critical, ethical and effective way, in fake, used out of context, or
weaponized to attack certain EFFECTS IF YOU USE MEDIA
individuals or groups of people. IRRESPONSIBLY
CATEGORIES OF INFORMATION a. Distraction and loss of productivity
DISORDER
b. Addiction
1. Misinformation – it refers to
c. Stress and mood - Flame war -
information that is false, but the person
FOMO (Fear of Missing Out)
sharing or disseminating it
unknowingly perceives it as something d. Social Isolation
true.
Flame War ▪ a series of angry, critical,
a. False connection - when headlines or disparaging comments exchanged
or visuals do not support the content by two or more people in an ongoing
online argument.
b. Misleading content - by cropping
photos or choosing quotes or statistics FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) ▪ The fear
selectively. of missing out (FOMO) is an emotional
response to the belief that other
2. Disinformation – it refers to content
people are living better, more
that contains false information with the
satisfying lives or that important
deliberate intention to mislead or
opportunities are being missed.
deceive the audience.
WAYS TO USE SOCIAL MEDIA
a. False context - when genuine
RESPONSIBLY
content is recirculated out of its original
context 1. Turn off notification while doing
something important
b. Imposter content - persons’ bylines
used alongside articles they did not 2. Limit your screen time
write, or organizations’ logos used in
videos or images they did not create. 3. Note the quality of your online
interactions
c. Manipulated context - when genuine
content is manipulated to deceive. 4. Go for more offline interaction
d. Fabricated content - fabricated 5. Always check the source, data and
“news sites” or fabricated visual. the author
3. Mal-information – it refers to 6. Be aware of what you post and
information that is based on reality but share online.
is used to inflict harm 7. Give credit where credit is due.
Examples: a. Leaks to the press of 8. Avoid sharing raw and unverified
private information for personal or information -Raw and unverified
corporate interest (e.g. revenge porn) information are those that has not yet
b. Using a picture (e.g. of a dead child, to be examined of confirmed.
with no context or false context) in an 9. Think about who can see what you
effort to ignite hatred of a particular have shared - Always assume that
ethnic group. anything that you see online can be
seen by other people – people who
may be influenced by your words or Cave paintings (also known as
opinions or people who may disagree. “parietal art”) are numerous
Moreover, always be aware of how paintings and engravings found
your message may be interpreted. on cave walls or ceilings around
35 000 BCE
10. Be open to learning and
Clay tablets are used a writing
constructive criticisms -Some people
medium especially for writing in
may share our view while some will
cuneiform. - one of the oldest
disagree. Thus, it is important to keep
forms of writing.
an open mind to contrasting opinions
and constructive suggestions. Papyrus is made form pith of
papyrus plant. It is used as
11. Respect other people’s privacy - writing surface to designate
Do not share information that friends, documents written on its sheets,
or family entrusted you to keep rolled up to scrolls
confidential or information that is Acta Diurna (130 BC) were daily
private in nature especially without Roman official notices, a sort of
their consent. daily gazette. They were carved
12. Always be respectful ✓Being on stone or metal and
respectful should be your default presented in message boards in
manner, whether talking to a friend or public places like the Forum of
dealing with someone professionally. Rome. They were also called
✓Being respectful includes accepting simply Acta
constructive criticism, politely Dibao in China (2nd Century)
disagreeing and never resorting to was a type of publication issued
bullying or personal attacks. by central and local
governments in imperial China.
13. Share expert knowledge ✓ The They have been called "palace
internet is a great platform for sharing reports" or "imperial bulletins".
good information. However, it can also Codex in the Mayan Region
be used to spread misinformation and (5th Century) the codices were
distortions used to set dates for rituals,
Plagiarism - is presenting someone often by linking them to
else’s work or ideas as your own, with astronomical events.
or without their consent, by Printing Press using wood
incorporating it into your work without blocks (220 AD) Woodblock
full acknowledgement. printing (or block printing) is a
technique for printing text,
DIFFERENT TOOLS USED IN images or patterns used widely
VARIOUS ERAS IN THE HISTORY throughout East Asia and
OF COMMUNICATION originating in China in antiquity
1. Pre-Industrial Age - Before as a method of printing on
1700 - People discovered fire, textiles and later paper.
developed paper from plants, 2.Industrial Age - 1700s – 1930s -
and forged weapons and tools People used the power of steam,
with stone, bronze, copper and developed machine tools,
iron.
established iron production, and later, he made the first ever
the manufacturing if various telephone call to his partner,
products (including books through Thomas Watson.
printing press) Motion Picture Photography
(1890) In 1890 Dickson
Industrial Age started with England
unveiled the Kinetograph, a
and other European Countries in
primitive motion picture camera.
the 18th Century. This period
In 1892 he announced the
started to shift from agricultural and
invention of the Kinestoscope, a
handicraft economy to one that is
machine that could project the
dominated by machines and
moving images onto a screen.
machine manufacturers.
In 1894, Edison initiated public
Communications were developed
film screenings in recently-
like telegraph, and telephone.
opened "Kinetograph Parlors.”
Printing press is typically used
3.Electronic Age - 1930s – 1980s -
for texts. It is a device that
The invention of the transistor
applies pressure to an inked
ushered in the electronic age.
surface resting upon a print
People learned to produce and use
medium (like paper or cloth).
transistor radio, electronic circuits,
Telegraph is used for long-
and the early computers.
distance communication by
transmitting electrical signals
over a wire laid between
stations.
Motion picture (also known as
film or movie) is series of still
photos on film, projected in
rapid succession on a screen by
means of light.
Newspaper The London
Gazette is one of the official
journals of record of the British 4. New Age or Information Age -
government, and the most The internet paved the way for
important among such official faster communication and the
journals in the United Kingdom creation of social network.
Typewriter (1800) It is a Personal computers, mobile
mechanical or devices and wearable
electromechanical machine for technology were invented on
writing characters like those this age
produced by printer's movable
Functions of Communications of Media
type.
Telephone (1876) On March 7, 1. Monitoring Function. This is to
1876, Alexander Graham Bell inform the citizens on what is
successfully received a patent happening around them.
for the telephone and secured 2. Information Function. This is to
the rights to the discovery. Days educate the audience on the
meaning and significance of the pictures, photos, images, and graphics
facts. used to channel communication using
3. Option Function. This is to the sense of sight.
provide a platform for public
TYPOGRAPHY • It refers to the art
political discourse. It is used to
and technique of arranging the visual
facilitate public opinion and
component of the written word. • It
expression of dissent.
features textual designs with optical
4. Watchdog Role of Journalism. It
illusions to improve readability and
denounces the wrongdoing of
help convey meaning.
the government and private
which leads to increasing of Types of Visual Media
accountability and
spearheading positive changes. Ideogram – these are graphical
5. Channel for Advocacy of symbols that represent ideas such as
Political Viewpoints. logos, signs, and symbols.
Types of media Statistical Visualization – refers to the
study and creation of data using visual
MEDIA • The physical objects used to representation such as charts and
communicate with, or mass graphs.
communication through physical
objects such as radio, television, films Picture – it is used widely by people to
and more. • Channels or ways we use express their ideas, opinions, and
to transmit or communicate messages. sentiments such as photography,
painting, and drawing
PRINT MEDIA • It refers to media
consisting of paper and ink, Graphic Design – this refer to art of
reproduced in a printing process that is combining text and pictures to
traditionally mechanical. • Printing communicate information.
started in Asia, in China by the end of Infographics, posters, and graphic ads
the 2nd century AD. • The first major are considered as graphic design.
role of printing was the reproduction of Video – if graphic design is the
books to spread literary works and combination of text and pictures, video
general information. is the combination of motion picture, or
EXAMPLES OF PRINT MEDIA • of motion and audio.
BOOKS • BUSINESS CARDS • BROADCAST MEDIA • It refers to
BROCHURES • COUPONS • ADS IN media that reaches target audiences
MAGAZINES • ADS IN using airwaves as the transmission
NEWSPAPERS • ADS ON medium such as radio and television.
BILLBOARD • NEWSLETTERS •
JOURNALS • COMICS • TEXTILES • BROADCASTING It is the
WALLPAPER • PRODUCT transmission of radio and television
PACKAGING programs that are intended for general
public reception.
KINDS PRINT MEDIA 1. Printed Text
Media - a simple and flexible format for More than a century after films were
conveying ideas, whether handwritten developed, audience are now amazed
or printed. 2. Printed Visual Media - with the action and creative
movements provided by films which • the co-existence of print media,
are highlighted in science fiction and broadcast media (radio and television),
action movies. Television, on the other the internet, mobile phones, as well as
hand, has also gone a long way others, allowing media content to flow
providing the latest news, both local across various platforms • the ability to
and international in real time while the transform different kinds of media into
news is happening. Radio is more digital code, accessible by a range of
popular in rural areas because there devices (ex. from the personal
are battery-operated radios that people computer to the mobile phone)
can be carried to the field to listen to creating a digital communication
news, music and radio dramas. environment.
KINDS OF BROADCAST MEDIA MEDIA CONVERGENCE • The
merging of different equipment and
a. Audio Media – uses audio or voice
tools for producing and distributing
recording as a medium in the delivery
news digitization and computer
of information to appeal to the auditory
networking. • It is the blending of
sense. b. Multimedia – concerned with
multiple media forms into one platform
computercontrolled integration of
for purposes of delivering a dynamic
different media types where every
experience.
information can be stored,
communicated, and handled digitally. SOURCES OF INFORMATION
NEW MEDIA • Also referred as PRIMARY: Unedited, firsthand access
“INTERNET”. • It is the term used to to words, images, or objects created
integrate the different technologies by persons directly involved in an
emerging on one digital platform to activity or event.
organize and distribute content.
SECONDARY: Commentary upon, or
INTERNET • It is a global system of analysis of, events, ideas, or primary
interconnected computer networks that sources.
use the standard Internet Protocol
TERTIARY: Tertiary sources offer a
Suite (TCP/IP) to serve billions of
summary of a topic, event or condition
users worldwide. • It is a network of
and include primary and secondary
networks consists of millions of private,
sources. Indexes that guide users to
public, academic, business and
specific locations within a book or
government networks of local to global
source are also considered tertiary.
scope that are linked by a broad array
of electronic and optical networking INDIGENOUS KNOWLEDGE
technologies.
According to Warren (1991), it is the
NEW MEDIA EXAMPLES ✓Websites knowledge that is unique to a given
✓Blogs ✓Vlogs ✓Social media culture or society. It may contrast with
platforms ✓Social networks ✓Text the international knowledge system
messaging ✓Wikis ✓Email ✓Online generated by universities, research
newspapers ✓Podcasts institutions and private firms. • IK is
owned, controlled and managed by
MEDIA CONVERGENCE • the co-
indigenous peoples in order for them
existence of traditional and new media
to develop and produce culturally
appropriate information in the standardized communication
languages understood by the protocols.
community by utilizing indigenous
• Unlike similar information found in
materials and resources, reflecting
newspapers or television
community needs and interests,
broadcasts, information available
visions and aspirations, and
on the Internet is not regulated for
independent from vested interest
quality or accuracy; therefore, it is
groups (Indigenous Media, Freedom of
particularly important for the
Expression and Right to Information:
individual Internet user to evaluate
ASEAN Scenario, 2014)
the resource of information
Ex Folktales, Folk Songs, Folk Dances
EVALUATING THE INFORMATION
Forms of Media FOUND IN THE INTERNET
. LIBRARY It is a place in which AUTHORSHIP •It is critical to relate
literary, musical, artistic, or reference the ideas you find at a site to a
materials (such as books, manuscripts, particular author, organization, or
recordings, or films) are kept for use business
but not for sale. • It was existed
PUBLISHING BODY •Anyone with an
because of the birth of the printing
Internet Service Provider (AT&T,
press. And expected to select and
UP.net, NMU, etc.) can put up a Web
provide content that area easy to
page. As a result, you need to have
access. • Its main role is to organize
some idea whether the group claiming
and provide you access information.
responsibility for the information on the
And labelled as “steward of good
Web site is legitimate.
information”.
ACCURACY AND VERIFIABILITY •A
Types of Library
source of information is known to be
1. School libraries - It serves scholarly when it provides references
students from Kindergarten to to the information presented. In this
Grade 12. way, the reader can confirm whether
2. Academic libraries - It serves the information is accurate or the
colleges and universities author's conclusions reasonable.
3. Public libraries - It serves cities
and towns of all types.
4. Special libraries – These are in CURRENCY • Some information is
specialized environments, such very time sensitive. For example, a
as hospitals, corporations, page talking about the top rate Web
museums, the military, private search engines in 1997 is going to be
business, and the government. horribly out of date in 2000. There
have been incredible changes in
INTERNET It is a global computer
search engine technology and new
network providing a variety of
developments appear almost monthly.
information and communication
However, a page discussing the Civil
facilities, consisting of
War is likely still relevant today even if
interconnected networks using
the page was created in 1996 and has
not been updated.’
APAC Value of information - Information is
said to be of value if it aids the user in
A Authorship : The source of the
making or improving decisions.
information
Authority of the source - Much of the
P Publishing body : Legitimacy of the
information we gather daily do not
information
come from a primary source but are
A Accuracy and Verifiability : Reliability passed on through secondary sources
and correctness of the information such as writers, reporters, and the like.
C Currency : The timeliness of the Timeliness - Reliability, accuracy, and
information value of information may vary based
on the time it was produced or
SKILLS IN DETERMINING THE acquired. While a piece of information
RELIABILITY OF INFORMATION may have been found accurate,
1. Check the Author reliable, and valuable during the time it
was produced, it may become.
2. Check the Date of Publication or of
update 3. Check for Citations MEDIA AND INFORMATION
LANGUAGES
4. Check the Domain or owner of the
site/page. .com .edu .mil .gov .org Languages It is a system of arbitrary,
local symbols that permit all people in
Skills in determining the accurate a given culture, or other people who
information. have learned the system of that culture
Look for facts Cross-reference with to communicate or interact.
other source for consistency (Finnocioro, cited in Jiang, 2010)
Determine the reason for writing and MEDIA LANGUAGES • It is describe
publishing the information Check for as the codes, conventions, formats,
advertising. Advertisers may use symbols and narrative structures that
related information to market their indicate the meaning of media
product messages to an audience. • It is what
RAVAT helps you understand the meaning
behind different media formats
THE KEY SKILLS TO BETTER GET because that is what the producer of
THE RIGHTFUL INFORMATION particular media output wants you to
Reliability of information - Information feel, understand, interpret or to learn
is said to be reliable if it can be verified from that particular media product.
and evaluated. GENRE ✓ It is a French word which
Accuracy of information - Accuracy means “Kind” or “Class”. The original
refers to the closeness of the report to Latin word is “genus” and mean class
the actual data. Measurement of of things that can be broken down into
accuracy varies, depending on the subcategories. ✓ A film’s genre
type of information being evaluated. category will be based on where most
of the content lands
NEWS ✓ These are stories that have
critical importance to community and
national life. News stories are also told with horror, action, and drama, but
following the basic structure of thrillers are about exciting situations
beginning, middle and end that have constant danger.
ENTERTAINMENT ✓It is derived from WAR/CONFLICT MOVIES
the French word “entretenir” which War/Conflict movies are about POVs,
means “to hold the attention, keep men in foxholes, tanks, and planes.
busy, or amused.
CODES ✓These are system of signs
ACTION MOVIES They are usually that when put together create
about a clear hero and a clear villain. meaning.
Action movie stakes are huge, like
Types of Codes
saving the world or the universe. ✓
They're often bombastic and move Technical Codes ✓ The way in which
quickly. equipment is used to tell the story
ADVENTURE MOVIES Adventure THE GRAMMAR OF THE CAMERA
movies are usually built around a
quest. ✓ Many adventures may be CAMERA SHOTS These are
period pieces, although more techniques to show the amount of
contemporary adventure stories are space in a scene.
coming back to the forefront. They can CAMERA SHOTS 1. Full Shot 2.
be swashbucklers or treasure hunts. Medium Close-up Shot 3. Extreme
COMEDY ✓ Comedy films usually are Long Shot 4. Long Shot 5. Medium
written with a few laughs a scene. The Shot 6. Close-up Shot 7. Reaction
stakes are usually much smaller or Shot 8. Point of View Shot
interpersonal. FULL SHOT ✓ It shows the entire
DRAMA ✓ Drama is regularly mashed object or character intended to place
up with other genres because most some relationship between characters
movies and tv rely on character-driven and environment.
stories to keep the audience involved. MEDIUM CLOSE-UP SHOT (over-the-
HORROR FILM Horror film focuses on shoulder shot) ✓ Shows a subject
adrenaline rides for the audience that down to his or her chest with a space
dial in the gore, scares and creative above to his or her head.
monsters. ✓ \ ✓ Horror is always re- EXTREME LONG SHOT ✓ it sets up
inventing old classics, like adding fast the context for a scene by showing
zombies, and CGI creatures large amount of landscape to establish
ROMANCE MOVIES ✓ Romance general setting.
movies are about people coming LONG SHOT ✓A view of situation or
together, falling apart, and all the setting from a distance
hurdles in between. Love is a universal
language. MEDIUM SHOT ✓ Shows a subject
down to his or her waist with a space
THRILLER MOVIES Thriller movies. above to his or her head.
What would you do when you were
over your head? This is usually linked
CLOSE UP ✓A full screen shot of a Mise en Scene ✓ It is a French term
subject face that means everything within the
frame’. In media terms it has become
REACTION SHOT ✓It is a short shot
to mean the description of all the
of a character’s response to an action.
objects within a frame of the media
POINT-OF-VIEW ✓ Also known as product and how they have been
POV shot, is an angle that shows what arranged.
a character is looking at. Typically
ACTING ✓ Actors portray characters
POV shots are placed in between a
in media products and contribute to
shot of a character looking at
character development, creating
something.
tension or advancing the narrative.
Camera angles It focuses on the
COLOUR ✓ Colour has highly cultural
viewers’ position to understand the
and strong connotations. When
relationship of the characters, objects
studying the use of colour in a media
and environment.
product there are different aspects to
BIRD’S EYE ANGLE It is usually used be looking at
for establishing shot, it is an angle that
Written Codes These are the formal
looks down on a scene.
written language used in a media
HIGH ANGLE It is used to product. It can be used to advance a
demonstrate to the viewers the narrative, communicate information
perspective of a character. By making about a character or issues and
the camera to look down on a themes.
character, the subject may look
vulnerable, small or weak.
EYE-LEVEL ANGLE It is the most
commonly used camera angle, it
makes the viewers comfortable with
the characters.
LOW ANGLE The camera is looking
up to the character, this makes the
character look more powerful and may
make the audience feel vulnerable or
small in the presence of that character.
Symbolic Codes It shows what is CONVENTION ✓These are the
beneath the surface of what we see. accepted ways of using media codes.
These are closely connected to the
SETTING ✓ When discussing setting, audience expectations of a media
you can describe the setting of the product
whole story or just a specific scene. A
setting can be as big as the outback or Types of Convention
space, or as small as a specific room. Form Convention These are the
Setting can even be a created certain ways we expect types of
atmosphere or frame of mind. media’s codes to be arranged. ✓ For
instance, an audience expects to have
a title of the film at the beginning, and
then credits at the end. Newspapers
will have a masthead, the most
important news on the front page and
sports news on the back page.
Story Convention These are common
narrative structures and
understandings that are common in
story telling media products.
Genre Convention ✓ It points to the PLAGIARISM An act or instance of
common use of tropes, characters, using or closely imitating the language
settings or themes in a particular type and thoughts of another author without
of medium. Genre conventions are authorization; the representation of
closely linked with audience that author's work as one's own, as by
expectations. not crediting the original author
LEGAL AND ETHICAL ISSUES IN TYPES OF PLAGIARISM
MEDIA AND INFORMATION Sources Not Cited
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY 1. The Ghost Writer -The writer turns
Intellectual property (IP) refers to in another’s work, word-for-word, as
creations of the mind, such as his or her own.
inventions; literary and artistic works
designs and symbols, names and 2. The Photocopy- The writer copies
images used in commerce. significant portions of text straight from
a single source, without alteration.
COPYRIGHT A legal device that gives
the creator of a literary, artistic, 3. The Potluck Paper- The writer
musical, or other creative work the copies from several different sources,
sole right to publish and sell that work. tweaking the sentences to make them
Copyright owners have the right to fit together while retaining most of the
control the reproduction of their work, original phrasing.
including the right to receive payment 4. The Poor Disguise- The writer has
for that reproduction. An author may altered the paper’s appearance slightly
grant or sell those rights to others, by changing key words and phrases.
including publishers or recording
companies. Violation of a copyright is 5. The Labor of Laziness - The writer
called infringement takes the time to paraphrase most of
the paper from other sources and
Copyright Infringement occurs when a make it all fit together.
copyrighted work is reproduced,
distributed, performed, publicly 6. The Self-Stealer- The writer
displayed, or made into a derivative “borrows” generously from his or her
work without the permission of the previous work.
copyright owner. Sources Not Cited (BUT STILL
PLAGIARIZED)
1. The Forgotten Footnote - The writer Netiquette Netiquette, or network
mentions an author’s name for a etiquette, is a set of socially
source, but neglects to include specific constructed rules and norms for
information on the location of the behaving and communicating
material referenced. responsibly in an online environment.
2. The Misinformer - The writer Rule 1: Remember the human -
provides inaccurate information remember that the receiver on the
regarding the sources, making it other side of your computer or phone
impossible to find them. is another human person capable of
understanding, feeling, and getting
3. The Too-Perfect Paraphrase- The
hurt. Putting yourself in others’ place
writer properly cites a source, but
can put everything in the right
neglects to put in quotation marks on
perspective.
text that has been copied word-for-
word, or close to it. Rule 2: Adhere to the same standards
of behavior online that you follow in
4. The Resourceful Citer- The writer
real life - Good netiquette is derived
properly cites all sources,
from the same standards set in real
paraphrasing and using quotations
life. While it can be argued that
appropriately. The catch? The paper
standards of behavior may be different
contains almost no original work!
in the virtual world, they certainly
5. The Perfect Crime- The writer should not be any lower.
properly quotes and cites sources in
Rule 3: Know where you are in
some places but goes on to
cyberspace -The Internet may be as
paraphrase other arguments from
vast as the earth’s oceans or the outer
those sources without citation.
space with parts least visited, not
FAIR USE Fair use means you can discovered, and some deemed even
use copyrighted materials without dangerous.
license only for certain purposes.
Rule 4: Respect other people's time
These include: ❖ Commentary ❖
and bandwidth - whenever you post
Criticism ❖ Reporting ❖ Research ❖
something online or send a message
Teaching
to someone, you’re taking up a few
Guidelines for Fair Use Guidelines for precious minutes from the already
Fair Use ❖A Majority of the content limited time of another. On the other
you create must be your own ❖Give hand, the word "bandwidth" is
credit to the copyright holder ❖Don’t sometimes used synonymously with
make money off of the copyrighted time, but it's really a different thing.
work
Rule 5: Make yourself look good
Responsible Digital Citizenship Digital online - In the real world, other
citizenship refers to having the people’s immediate judgment of you
appropriate knowledge and skills to would be based off of your physical
effectively use digital technologies to appearance, your demeanor, how you
communicate with others, participate in speak, how you carry yourself, or even
society and create and consume digital how you dress. The following tips in
content. mind: ❖ Always check for spelling and
grammar errors ❖ Verify the truth of developments due to a number of
what you are posting or sharing ❖ factors which include, but not limited
Know what you're talking about and to: race, age, education, income,
state it clearly ❖ Be pleasant and socioeconomic status, and
polite geographical location.
Rule 6: Share expert knowledge - The THE DIGITAL NATIVE AND THE
strength of the Internet is the extent of DIGITAL IMMIGRANTS
the information it offers and various
• The people born in the Internet and
sources these information come from.
digital technology age are who we call
Sharing your knowledge on something
as digital natives.
doesn’t count as one. So do your part
share what you know. • The term is often used synonymously
with ‘Millennial’, though not all digital
Rule 7: Help keep flame wars under
natives are millennials and not all
control - "Flaming is what people do
millennials are digital natives.
when they express a strongly held
opinion without holding back any • Digital natives are those that are
emotion." (Shea, 1994). immersed in digital technology growing
up making them more knowledgeable
Rule 8: Respect other people's
and comfortable in the digital age.
privacy - privacy is a human right.
Much like how you do not want your Digital immigrants, on the other hand,
phone opened just by anyone or your are those born before the widespread
messages read by someone without adoption of computers and the Internet
your permission, other people value and has had to adopt digital
their privacy as well. technology later in life. Due to the gap
in generations, not excluding other
Rule 9: Don't abuse your power - Just
factors, digital immigrants are
like in the real world, people in
considered to be less technically able
cyberspace have their own influence
than digital natives.
and power – some with power greater
than others. These people are the THE DIGITAL RICH AND THE
technology wizards, experts with years DIGITAL POOR
of experience, and system
administrators, among others. • A huge part of the digital divide,
especially in developing countries such
Rule 10: Be forgiving of other people's as the Philippines, is the differences in
mistakes - Not everyone has the same socioeconomic status of social groups.
amount of experience working in the
virtual world. And not everyone knows • The financial capacity of an
the. individual affects his ability to purchase
a gadget and a reliable Internet
DIGITAL DIVIDE • Digital Divide is an access.
inequality or disparity between
demographic groups in terms of • Learning materials and resources
access to, use of, or knowledge of ICT. may now be conveniently accessed
Different segments have varying levels online, technology has also paved way
of knowledge and access to digital for advancements in medicine and
healthcare, transportation is now made
more convenient and comfortable. place using electronic. This occurrence
While many are able to enjoy and can trigger traumatic experiences for
adapt to all these developments, sadly, the victims just like bullying in real life.
a lot more are struggling to keep up Cyberbullies post or send hateful and
mean messages as well images which
THE DIGITAL SKILLED AND THE
are deliberately meant to mock,
DIGITAL UNSKILLED
ridicule, embarrass, hurt, or attack a
• Lack of digital skills may stem from person.
an individual’s socioeconomic status.
As a conscientious person and a
A person belonging to a family falling
responsible media consumer and
below poverty line would most
producer, it is your unspoken duty to
probably have less to no access to
refrain from and denounce
digital devices and stable Internet
cyberbullying. Moreover, to further
connection. In effect, he will fall behind
avoid cyberbullying, you can promote
on updated information, up-to-date
proper netiquette to your peers, foster
learning resources, and even on job
mutual respect and courtesy by
openings. This limited access to
avoiding flame wars, and be vigilant
information would also limit his door of
against people’s intention to harm
opportunities to learn and improve his
other netizens.
skills.
INTERNET ADDICTION It is the
excessive or poorly controlled
preoccupations, urges, behaviors
regarding computer use and internet
access that lead to impairment or
distress
Internet addiction may be developed
due to several factors like stress,
anxiety, depression, other forms of
addiction, lack of social support, or
lack of parental guidance, or inactivity
CYBERBULLYING It is the use of
information technology to harm or
harass other people in deliberate,
repeated, and hostile manner.
Online violence, cyber bullying and
digital harassment affect over 70
percent of young people globally,
according to the United Nations
Children’s Fund (UNICEF), as it called
on internet users to “be kind online”
and prevent this form of violence.
Cyberbullying is a type of offensive
action toward another which takes
You might also like
- FCK g12 1Document51 pagesFCK g12 1Elizabeth BandaNo ratings yet
- MIL NotesDocument7 pagesMIL NotesEllah Iracielli TevesNo ratings yet
- Anything That Interferes With The Message.: Non VerbalDocument5 pagesAnything That Interferes With The Message.: Non VerbalCatherine Florence AustriaNo ratings yet
- MIL2Document7 pagesMIL2reychelleannsaturnino07No ratings yet
- 1st Quarter NotesDocument101 pages1st Quarter NotesVieyah Angela VicenteNo ratings yet
- Media Information and LiteracyDocument16 pagesMedia Information and LiteracyMary Grace T. BitasNo ratings yet
- Perpetual Succour Academy, Inc.: National RD., Poblacion Dos, Malabuyoc, CebuDocument7 pagesPerpetual Succour Academy, Inc.: National RD., Poblacion Dos, Malabuyoc, CebuMa. Joan FerrolinoNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy: Cambridge Dictionary - CommunicationDocument3 pagesMedia and Information Literacy: Cambridge Dictionary - CommunicationInol DuqueNo ratings yet
- MIL ReviewerDocument7 pagesMIL ReviewerJuliana Shane OrapNo ratings yet
- Reviewer-in-MIL 3rd QuarterDocument6 pagesReviewer-in-MIL 3rd QuarterBella PurisimaNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy: Quarter 1 Lesson 1Document49 pagesMedia and Information Literacy: Quarter 1 Lesson 1Jamil OrenciadaNo ratings yet
- Mil Handouts Module-1-4Document2 pagesMil Handouts Module-1-4Marrianne Grace MantujacNo ratings yet
- Anything That Interferes With The Message.: Non VerbalDocument5 pagesAnything That Interferes With The Message.: Non VerbalCatherine Florence AustriaNo ratings yet
- Notes MilDocument15 pagesNotes MilKristine AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Week 1 MILDocument40 pagesWeek 1 MILJohn Laverne Capalis BocadoNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Media and Information LiteracyDocument20 pagesIntroduction of Media and Information LiteracyJay JayNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Media and Information Literacy - SLAS 1Document11 pagesWeek 1 - Media and Information Literacy - SLAS 1do san namNo ratings yet
- Media and Information LiteracyDocument12 pagesMedia and Information LiteracyiNo ratings yet
- Mil ExamDocument35 pagesMil ExamJohn Erick OselaNo ratings yet
- Mil Notes in Quarter 1Document6 pagesMil Notes in Quarter 1InfiniteNo ratings yet
- Hobby PDFDocument13 pagesHobby PDFLorenzo CarreonNo ratings yet
- MIL - Quarter 3 - Module 1Document9 pagesMIL - Quarter 3 - Module 1Darlene Dacanay DavidNo ratings yet
- Media and Information LiteracyDocument18 pagesMedia and Information LiteracyShayne Janelle BandongNo ratings yet
- MIL 1st Quarter Lesson SummaryDocument5 pagesMIL 1st Quarter Lesson SummaryRalph Francis GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document4 pagesLesson 1Mark Russell MangubatNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Media and Information LiteracyDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Media and Information Literacykeynepeps201No ratings yet
- Mil Lesson 1Document14 pagesMil Lesson 1yorudump5176No ratings yet
- MIDEA INFORMATION LITERACY REVIEWER - 1masteryDocument13 pagesMIDEA INFORMATION LITERACY REVIEWER - 1masterySunghoon ParkNo ratings yet
- Mil L1 Intro To MilDocument2 pagesMil L1 Intro To MilreenaurgmzNo ratings yet
- MIL Notes (Midterms)Document33 pagesMIL Notes (Midterms)Jessa Sabrina AvilaNo ratings yet
- L1 Introduction To Media and Information Literacy MELC1Document28 pagesL1 Introduction To Media and Information Literacy MELC1Christine JacobNo ratings yet
- Media & Information Literacy First Grading Reviewer Introduction To Media & Information LiteracyDocument3 pagesMedia & Information Literacy First Grading Reviewer Introduction To Media & Information LiteracySid TuazonNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy: Self LearningDocument14 pagesMedia and Information Literacy: Self LearningPatrick B. CabrestanteNo ratings yet
- MED INFO Lesson 1 NotesDocument3 pagesMED INFO Lesson 1 NotesLOREEN BERNICE LACSONNo ratings yet
- Surigao Diocesan School System: Mt. Carmel School of Siargao, IncDocument4 pagesSurigao Diocesan School System: Mt. Carmel School of Siargao, IncEDMAR POLVOROZANo ratings yet
- MIL - Module 1Document5 pagesMIL - Module 1Imie Omamalin GuisehanNo ratings yet
- Mil ReviewerDocument6 pagesMil ReviewerKristine FernandezNo ratings yet
- Combine PDFDocument10 pagesCombine PDFrgnnbkdNo ratings yet
- Study Guide in MilDocument3 pagesStudy Guide in MilCj RomoNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy Week 2 FINALDocument9 pagesMedia and Information Literacy Week 2 FINALFritzie SulitanaNo ratings yet
- Lasswell's Communication ModelDocument3 pagesLasswell's Communication ModelRowenelle GeminezNo ratings yet
- Media and Information: Cultures, Communities, and TechnologiesDocument5 pagesMedia and Information: Cultures, Communities, and TechnologiesLlanell VictoriaNo ratings yet
- MIL WK 1Document16 pagesMIL WK 1Mebet MoralesNo ratings yet
- Media and Information LiteracyDocument4 pagesMedia and Information LiteracyHazel TarregaNo ratings yet
- PPT1 Introduction To Media and Information Literacy 1Document24 pagesPPT1 Introduction To Media and Information Literacy 1Heaven JaymeNo ratings yet
- Mil L2-6Document10 pagesMil L2-6Diana BendanilloNo ratings yet
- Q1 Module1 G11 12 MILDocument11 pagesQ1 Module1 G11 12 MILJensen TagudinNo ratings yet
- MIl ReviewerDocument4 pagesMIl Reviewerallen alabaNo ratings yet
- Globalization and Media Creating The GlobalizationDocument60 pagesGlobalization and Media Creating The GlobalizationFloreann BascoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 CommunicationDocument3 pagesLesson 1 CommunicationAngel MaguinsawanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Introduction To Media and Information LiteracyDocument9 pagesLesson 1: Introduction To Media and Information LiteracySteven Duane PradoNo ratings yet
- Yellow Green Pastel Blue Yellow Playful Scrapbook Pet Conspiracy Theory Presentation PartyDocument16 pagesYellow Green Pastel Blue Yellow Playful Scrapbook Pet Conspiracy Theory Presentation PartyJonah Jatte Muñez100% (1)
- Lesson1 and ActivitiesDocument9 pagesLesson1 and Activitiesyumeko JabamiNo ratings yet
- Purcom ReviewerDocument4 pagesPurcom ReviewerLumagui, Vanessa JoyNo ratings yet
- Mil Lesson 1Document3 pagesMil Lesson 1Mariel ObnascaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Mil PDFDocument5 pagesModule 2 - Mil PDFAzaleo Benedict TabucaoNo ratings yet
- Communication, Media, Information, and Technology LiteracyDocument12 pagesCommunication, Media, Information, and Technology LiteracyAgustin RonnNo ratings yet
- Media Literacy for Young Children: Teaching Beyond the Screen Time DebatesFrom EverandMedia Literacy for Young Children: Teaching Beyond the Screen Time DebatesNo ratings yet
- Summary of Supercommunicators by Charles Duhigg:How to Unlock the Secret Language of Connection: A Comprehensive SummaryFrom EverandSummary of Supercommunicators by Charles Duhigg:How to Unlock the Secret Language of Connection: A Comprehensive SummaryNo ratings yet
- 13 Taking Charge of Ones HealthDocument26 pages13 Taking Charge of Ones HealthPrecia AldayNo ratings yet
- Types of MediaDocument26 pagesTypes of MediaPrecia AldayNo ratings yet
- Unit Iiithe World of RegionsDocument9 pagesUnit Iiithe World of RegionsPrecia AldayNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Media: Media and Information LiteracyDocument33 pagesThe Evolution of Media: Media and Information LiteracyPrecia AldayNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document10 pagesLesson 3Precia AldayNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument20 pagesUntitledPrecia AldayNo ratings yet
- MELC6 Contrast Indigenous Media To The More Common Sources of Information Such As Library Internet Etc.Document40 pagesMELC6 Contrast Indigenous Media To The More Common Sources of Information Such As Library Internet Etc.Precia AldayNo ratings yet
- MELC8 Intellectual Property Copyright and Fair Use GuidelinesDocument26 pagesMELC8 Intellectual Property Copyright and Fair Use GuidelinesPrecia AldayNo ratings yet
- MELC7 Media Language Codes and ConventionsDocument61 pagesMELC7 Media Language Codes and ConventionsPrecia AldayNo ratings yet
- MELC9 Combatting Digital Divide Internet Addiction and CyberbullyingDocument18 pagesMELC9 Combatting Digital Divide Internet Addiction and CyberbullyingPrecia AldayNo ratings yet
- WordPress Theme - Magasin Uno - ManualDocument12 pagesWordPress Theme - Magasin Uno - ManualMG7STUDIONo ratings yet
- GROUP 4 Activity 1 and Reminders For EDASSL 2Document5 pagesGROUP 4 Activity 1 and Reminders For EDASSL 249 - Kaycee JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Graduate Studies Reference Form WithButtonsDocument2 pagesGraduate Studies Reference Form WithButtonsДилшод АбдуллахNo ratings yet
- MODULE 3: Gender Roles & StereotypesDocument15 pagesMODULE 3: Gender Roles & StereotypesTwisha SaxenaNo ratings yet
- CLB Can Do Statements S 01Document1 pageCLB Can Do Statements S 01hellkatNo ratings yet
- Freelance Sites To UseDocument4 pagesFreelance Sites To UseNieves Tampis100% (2)
- Balenciagagroupd 130125053752 Phpapp01Document24 pagesBalenciagagroupd 130125053752 Phpapp01Rahil CharaniaNo ratings yet
- Rosie Brennan CV OriginalDocument5 pagesRosie Brennan CV OriginalRosieBrennanNo ratings yet
- spd-590 Clinical Practice Evaluation 3Document12 pagesspd-590 Clinical Practice Evaluation 3api-501695666No ratings yet
- SEO ProposalDocument11 pagesSEO ProposalSubhash DharNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument7 pagesReviewerdaveandrewcramosNo ratings yet
- BCS1 Skripta 2020 - 21Document112 pagesBCS1 Skripta 2020 - 21Sanja TesicNo ratings yet
- 2 - Weekly JournalDocument8 pages2 - Weekly Journalapi-671822417No ratings yet
- Important Guidelines - Public Speaking CompetitionDocument3 pagesImportant Guidelines - Public Speaking CompetitionDipienshu BhatNo ratings yet
- Final Portfolio EssayDocument15 pagesFinal Portfolio Essayapi-290603336No ratings yet
- WestbyDocument3 pagesWestbyEllyn Grace100% (1)
- Solved MCQs On Computer NetworkingDocument10 pagesSolved MCQs On Computer NetworkinggurusodhiiNo ratings yet
- SM IKEA AssignmentDocument2 pagesSM IKEA AssignmentMuhammad Umair RajputNo ratings yet
- Ochoa Lit FinalDocument12 pagesOchoa Lit Finalapi-307736451No ratings yet
- Speaking Assessment Rubric - Based On FGD Scoring GuideDocument2 pagesSpeaking Assessment Rubric - Based On FGD Scoring GuideSahrul GusionNo ratings yet
- Recycle Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesRecycle Lesson Planapi-242240909No ratings yet
- Texture Painting RubricDocument1 pageTexture Painting Rubricapi-239099618No ratings yet
- IELTS Writing Band 9 Essays PDFDocument187 pagesIELTS Writing Band 9 Essays PDFEranda90% (31)
- 108202101654MBA Sem-IVDocument79 pages108202101654MBA Sem-IVAvantika BhardwajNo ratings yet
- The Digital World: Level 1 - Unit 2Document3 pagesThe Digital World: Level 1 - Unit 2Jahn Carlos Vazquez TeheranNo ratings yet
- Fandom Meets ActivismDocument1 pageFandom Meets ActivismMaria EstoriaNo ratings yet
- Cognate ReportDocument29 pagesCognate ReportTJ WAQUIM0% (1)
- Business Management - Creative Industries Management (Profile 410.X0)Document2 pagesBusiness Management - Creative Industries Management (Profile 410.X0)AMiNo ratings yet
- Script For PresentationDocument5 pagesScript For PresentationJohn Kenneth Reojano100% (2)
- Assignment On Women and Rural EnterpenurshipDocument49 pagesAssignment On Women and Rural EnterpenurshipManish PuriNo ratings yet