Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Skeletal System
Skeletal System
Uploaded by
Pessimus Kid0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
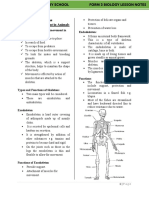
4 views2 pages1. Bone is composed of connective tissues and minerals that provide structure and support. It is constantly remodeled through the processes of bone formation and resorption.
2. Bones can be classified based on their shape as either long, short, flat, irregular or sesamoid. They contain red or yellow bone marrow and have an outer layer of compact bone and an inner layer of spongy bone.
3. The skull protects the brain and is formed from multiple flat and irregular bones that fuse together, including the frontal, occipital, temporal, parietal, sphenoid, ethmoid and maxilla bones. The facial bones form the structures of the face.
Original Description:
Original Title
SKELETAL SYSTEM
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. Bone is composed of connective tissues and minerals that provide structure and support. It is constantly remodeled through the processes of bone formation and resorption.
2. Bones can be classified based on their shape as either long, short, flat, irregular or sesamoid. They contain red or yellow bone marrow and have an outer layer of compact bone and an inner layer of spongy bone.
3. The skull protects the brain and is formed from multiple flat and irregular bones that fuse together, including the frontal, occipital, temporal, parietal, sphenoid, ethmoid and maxilla bones. The facial bones form the structures of the face.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesSkeletal System
Skeletal System
Uploaded by
Pessimus Kid1. Bone is composed of connective tissues and minerals that provide structure and support. It is constantly remodeled through the processes of bone formation and resorption.
2. Bones can be classified based on their shape as either long, short, flat, irregular or sesamoid. They contain red or yellow bone marrow and have an outer layer of compact bone and an inner layer of spongy bone.
3. The skull protects the brain and is formed from multiple flat and irregular bones that fuse together, including the frontal, occipital, temporal, parietal, sphenoid, ethmoid and maxilla bones. The facial bones form the structures of the face.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
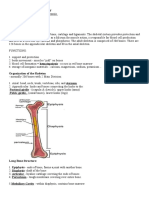
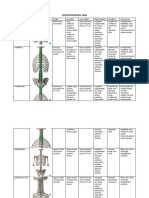
STRUCTURE AND SKELETAL TISSUES 31.
bone is constantly made and destroyed in
1. contains substances that are essential for an ongoing process
the make-up of our bones since the 32. one of the major factors affect bone
cartilages, tendons, ligaments, and even remodeling
our bones, are connective tissues. 33. stimulates osteoclasts whereas and
2. is a tough and rope-like protein giving our Calcitonin stimulates formation of
tendons, ligaments and cartilages great osteoblasts.
amount of strength like steel bars reinforced 34. stimulates cartilage and bone growth
in a concrete. 35. also influence sex-related differences in
3. the mineral in bone is in the form of calcium skeletal growth
phosphate crystals DIVISION OF SKELETAL SYSTEM
4. are large molecules consisting of 36. a hole in a bone is called a
polysaccharides attached to core proteins 37. tunnel-like passage through the bone, it is
5. are longer than they are wide and have called a
knobby ends where the articulations form 38. A depression in a bone is called a
6. a thin layer of hyaline cartilage called 39. A lump on a bone is called a
7. Dense connective tissues on the outside 40. and a projection from a bone is called
8. thinner inner lining called 41. _______ and ________ are sites of muscle
9. shaft or body attachment on the bone
10. head of each end of a long bone 42. The smooth, rounded end of a bone, where
11. marrow cavity or space that contains it forms a joint with another bone, is called a
yellow marrow The axial skeleton consists of
12. are equal in length and width, making them ______________
nearly cube-shaped. Appendicular skeleton consists
13. are thin and provide both protection and of__________
surfaces for muscle attachments. The
bones of the skull, sternum, and ribs are all
at bones
14. have complex shapes, such as those of the
face and vertebral column.
BONE HISTOLOGY
15. function in the formation of bone, as well as
in the repair and remodeling of bone.
16. contribute to bone repair and remodeling by
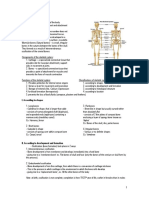
removing existing bone.
17. Bone is formed in thin sheets of
extracellular matrix called
18. with osteocytes located between the
lamellae within spaces called
19. Two types of bone tissue
20. is strong and dense, provides protection
and support, and resists the stresses
produced by weight and movement. is
found beneath the periosteum of all bones
and makes up the bulk of long bones
21. contain osteocytes, and smaller channels
called canaliculi
22. also known as cancellous bone
23. cancellous bone, contains irregular lattices
of thin bone columns called__________.
This tissue must be covered by compact
bone or cartilage because it could be
damaged easily if exposed.
24. _______spaces between the trabeculae of CRANIAL BONES
some bones are filled with red bone 43. forms the forehead, roofs of the eye
marrow. sockets, and front part of the cranial floor
25. Spongy bone is found mostly in 44. form the sides and roof of the cranium (2)
_________and irregular bones 45. form the lower side of the cranium and part
26. process of bone formation of the cranial floor
27. Bones form initially in the embryo by two The temporal bones have several features
processes.(2) 46. They form joints with the jawbone
28. bone forms directly from mesenchyme, (mandible) called the
occurs in the at bones of the skull, 47. is the canal that leads to the middle ear.
mandible, and clavicle 48. is a point of attachment for some of the
29. bone forms within and replaces cartilage. muscles involved in head movement
Intramembranous ossification is the simpler 49. The carotid artery passes through a
of these two processes. foramen called the
30. break down the inner surface of the 50. serves as a point of attachment for the
medullary cavity but at a slower rate than tongue and neck muscles
the bone forms on the outer surface. So, 51. The first cervical vertebra attaches to the
the medullary cavity grows in diameter as occipital bone at two processes called the
the bone thickens.
52. is in the middle of the cranial floor and is
where all the other cranial bones attach, VERTEBRAL COLUMN
like the keystone joining two arches to form 73. also called the spine, spinal column, or
a doorway. backbone) protects the spinal cord,
53. depression of the sphenoid bone called the supports the head and neck, permits
54. The optic nerve passes through movement, and provides attachment points
its________, and the mandibular nerve for the back muscles, ribs, and pelvis.
passes through its ___________ 74. vertebral column consists of 26 bones
55. The ____________forms the anterior part called
of the cranial floor, the medial part of the 75. is the thick, disc-shaped anterior portion
eye sockets, and superior portions of the that bears weight
nasal cavity. It has 3 to 18 __________and 76. extends posteriorly from the body.
mucus-lined _________ that warm and 77. is an opening through which the spinal cord
moisten inhaled air and trap foreign passes.
particles. The __________and _______ a 78. (1) projects from the laminae; it serves as
ridge on the superior portion of the ethmoid attachment point for muscles.
bone, serves as an attachment point for the 79. are lateral extensions that serve as
meninges. This is surrounded by the attachment points for muscles.
_________ through which the nerves 80. (2) attach to vertebra above.
associated with the receptors for smell pass 81. (7) are in the neck region. Each cervical
from the nose into the brain. vertebra has three openings (foramina)
56. The skull consists of______ and ________ 82. are posterior to the chest cavity and serve
that surrounds and protect the brain as attachments for the ribs.
FACIAL BONES 83. (5) form the lower back.
57. (2) form the bridge of the nose. 84. consists of 5 fused vertebrae and forms the
58. (2) form the upper jawbone and join with all posterior wall of the pelvis. Blood vessels
the other facial bones except the mandible and nerves pass through the openings
(lower jawbone) 85. sometimes referred to as the tailbone,
59. (2) form the posterior portion of the hard consists of 4 fused vertebrae.
palate, part of the lower eye sockets, and 86. A lateral curvature that causes the
part of the floor and the sides of the nasal spine to “lean” to one side more than
cavity. the other. This condition is seen more
60. are holes that allow passage of the mental
commonly in females than in males.
nerve
61. (2) form the cheek prominences and part of 87. —An exaggeration of the thoracic
the wall of the eye sockets. They form joints curve that forms a “humpback”
with the frontal, maxilla, sphenoid, and appearance
temporal bones. 88. exaggeration of the lumbar curve that
62. (2) are the smallest, thinnest bones on the causes a “sway back.”
medial eye socket. They house the tear THORACIC CAGE
ducts, which tunnel through to the nasal
89. articulates with the collarbone, or
cavity. This is why your nose runs when
you cry. clavicle, and the first rib.
63. (2) project into the nasal cavity to filter air 90. is made of cartilage that ossifies by
before it passes toward the trachea and age 40 No ribs attach to this pointed
lungs structure, which rescuers use to locate
64. joins with the maxillae and the palatine the proper hand position for
bones to form the floor of the nasal cavity. cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR).
FEATURES OF THE SKULL 91. The sternum attaches directly to the
65. is a special type of immovable joint that first through seventh pairs of ribs by a
joins most of the skull bones.
form of hyaline cartilage
4 major sutures in the skull:
66. unites the frontal bone and two parietal called_____________
bones 92. Rib pairs 1 through 7 are
67. attaches the two parietal bones. called_______
68. joins the parietal bones to the occipital 93. Rib pairs through 8-12 are called_____
bone. 94. Rib pairs 11 and 12 are referred to as
69. seal the parietal bones to the temporal __________
bones. 95. The sternum is made of three parts
70. are found in the sphenoid, frontal, ethmoid,
that fuse by age _________
and maxillary bones. They produce mucus,
lighten the weight of the skull, and serve as
echo chambers, which produce the unique
sounds of your voice
71. are mesenchyme-filled spaces between the
cranial bones of infants at birth. These soft
spots compress as the baby passes
through the birth canal
72. is located in the neck, between the
mandible and larynx. It is suspended from
the styloid process of each temporal bone
by ligaments and muscle.
You might also like
- Sprengel's ShoulderDocument21 pagesSprengel's ShoulderNahayo Xavier100% (1)
- Osteopathic Medicine RecallDocument186 pagesOsteopathic Medicine RecallDaniel Lopes100% (1)
- Skeletal System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument29 pagesSkeletal System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBD100% (1)
- Skeletal System TerminologyDocument15 pagesSkeletal System TerminologyNorhaifa Hadji EbrahimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - General Characteristics of The SpineDocument50 pagesChapter 2 - General Characteristics of The SpineveronicalovirgenNo ratings yet
- The Dental Distress Syndrome QuantifiedDocument37 pagesThe Dental Distress Syndrome QuantifiedDentalbay GrNo ratings yet
- Unit VIIIa Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesUnit VIIIa Lecture NotesSteve Sullivan100% (1)
- Veterinary OsteologyDocument279 pagesVeterinary OsteologyTatenda Mageja100% (2)
- Epidural AnalgesiaDocument16 pagesEpidural AnalgesiaspreeasNo ratings yet
- Skeletal 1Document8 pagesSkeletal 1Abegail Ashley PenoniaNo ratings yet
- Zoology Act 4Document3 pagesZoology Act 4Marrion PenieroNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument2 pagesSkeletal Systempsreelakshmi029No ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument3 pagesSkeletal SystemCristina AdolfoNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy Skeletal System FinalsssDocument16 pagesAnaPhy Skeletal System Finalsssalthea jade villadongaNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Skeletal System TopicDocument21 pagesFunctions of The Skeletal System TopicTUNGCALING ACNo ratings yet
- Lec Act Module 5Document17 pagesLec Act Module 5Hannah Vannerie AlanguiNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument121 pagesSkeletal SystemJang WonyoungNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology EditedDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology EditedAya BantuasNo ratings yet
- Muscloskeletal SystemDocument154 pagesMuscloskeletal SystemAbera AberaNo ratings yet
- Act08 The Skeletal System DiscussionDocument8 pagesAct08 The Skeletal System DiscussionSofia A.No ratings yet
- Skeleton & LocomotionDocument10 pagesSkeleton & Locomotionali mtNo ratings yet
- (Checked) Rodriguez Maria Andrea N Skeletal System Worksheet 5Document16 pages(Checked) Rodriguez Maria Andrea N Skeletal System Worksheet 5Mira AurumtinNo ratings yet
- 11 Axial Division of The Skeletal SystemDocument10 pages11 Axial Division of The Skeletal SystemMira Chariza Therese A. - BSN 1- CNo ratings yet
- Relationship To Other Organ SystemsDocument11 pagesRelationship To Other Organ SystemsVern NuquiNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy 4th Edition Saladin Solutions Manual DownloadDocument9 pagesHuman Anatomy 4th Edition Saladin Solutions Manual DownloadArturo Thomas100% (29)
- Presented By: Directed By:: Department of Tashreeh-UL-Badan (Anatomy)Document38 pagesPresented By: Directed By:: Department of Tashreeh-UL-Badan (Anatomy)QC quadcoreNo ratings yet
- 4 Main Groupsof TissuesDocument98 pages4 Main Groupsof TissuesKenvyne Quides-CalugayNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology 9Th Edition Marieb Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology 9Th Edition Marieb Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFAlexandraPerrymzyd100% (10)
- The Infrapatellar Fat Pad in The KneeDocument10 pagesThe Infrapatellar Fat Pad in The KneeDeogracias S. Espiritu IINo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System: 1. Hyaline CartilagesDocument9 pagesThe Skeletal System: 1. Hyaline CartilagesRaja Nurul JannatNo ratings yet
- Group2 - BSHM 1 BDocument43 pagesGroup2 - BSHM 1 BSAPILAN DENMARNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument27 pagesSkeletal SystemAlliyah SalindoNo ratings yet
- 3 Introduction To OsteologyDocument34 pages3 Introduction To OsteologyMajd HallakNo ratings yet
- Fascia and BonesDocument68 pagesFascia and Bonesheena solankiNo ratings yet
- Biology 01 BookDocument15 pagesBiology 01 BookJUNAID KHANNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System (Sem 1)Document231 pagesSkeletal System (Sem 1)joel david knda mjNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Information BookDocument15 pagesSkeletal System Information BookMartin SujaNo ratings yet
- Basis CraniiDocument11 pagesBasis Craniicharlesy TNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Cartilage and BoneDocument27 pages1.2 Cartilage and BonePema GaleyNo ratings yet
- SKELETAL SYSTEM ReviewerDocument7 pagesSKELETAL SYSTEM ReviewerKrize Colene dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Human Skeleton F3 NoradinDocument5 pagesHuman Skeleton F3 NoradinIbnu RaxaabNo ratings yet
- Biol 223 Exam 2: Gross Anatomy Group 1Document8 pagesBiol 223 Exam 2: Gross Anatomy Group 1Martina MicicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: The Skeletal System - Osteology: Reading: Moore, Dalley, & Agur ObjectivesDocument10 pagesChapter 2: The Skeletal System - Osteology: Reading: Moore, Dalley, & Agur ObjectivesVarsha SNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System IyahDocument55 pagesThe Skeletal System IyahAnna R. DionisioNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument17 pagesSkeletal SystemRachell AvecillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - BoneDocument17 pagesChapter 6 - Bonebussniesm05No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 MariebDocument6 pagesChapter 6 Mariebmissy23papNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 3 SkeletalDocument9 pagesLaboratory 3 SkeletalKyla InoferioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Content Review Questions 1-8Document3 pagesChapter 6 Content Review Questions 1-8Rhonique MorganNo ratings yet
- Axial SkeletonDocument38 pagesAxial SkeletonJoel EtomNo ratings yet
- 5the SkeletonDocument24 pages5the SkeletonIza ShaNo ratings yet
- Skull-Structure and FunctionsDocument33 pagesSkull-Structure and FunctionsMorris KariukiNo ratings yet
- Worksheet SkulllDocument6 pagesWorksheet SkulllJingle Capistrano TarucNo ratings yet
- Myocytes Cell Profile ReportDocument11 pagesMyocytes Cell Profile ReportAreesha FatimaNo ratings yet
- CHNCGDocument7 pagesCHNCGDANIEL LANCE NEVADONo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument80 pagesSkeletal SystemElaine Victoria ElizanNo ratings yet
- Summary of Muscosceletal System - Fuzna Dahlia M - I1J020010Document7 pagesSummary of Muscosceletal System - Fuzna Dahlia M - I1J020010Fuzna DahliaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Musculoskeletal System Chap 6 - 2401Document18 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Musculoskeletal System Chap 6 - 2401slyfoxkittyNo ratings yet
- Axial SkeletonDocument13 pagesAxial Skeletonfhkb7ymzbqNo ratings yet
- Classification of Bones: Chapter 5: The Skeletal SystemDocument12 pagesClassification of Bones: Chapter 5: The Skeletal SystemJaica Mangurali TumulakNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Introduction To Bones and The SkullDocument22 pagesUnit 4 Introduction To Bones and The SkullrynNo ratings yet
- DIT 104 LEC 1 - Classification & Types of BonesDocument27 pagesDIT 104 LEC 1 - Classification & Types of BonesRayan AndohNo ratings yet
- Advanced farriery knowledge: A study guide and AWCF theory course companionFrom EverandAdvanced farriery knowledge: A study guide and AWCF theory course companionNo ratings yet
- Tissues UnfinishedDocument5 pagesTissues UnfinishedPessimus KidNo ratings yet
- Cells QSDocument6 pagesCells QSPessimus KidNo ratings yet
- Foods To Avoid GoutDocument1 pageFoods To Avoid GoutPessimus KidNo ratings yet
- Legal ControlDocument3 pagesLegal ControlPessimus KidNo ratings yet
- LocomotionDocument13 pagesLocomotionPrakhar SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Snomed CT: Coping With Concept InactivationDocument38 pagesSnomed CT: Coping With Concept InactivationMeera FarmsNo ratings yet
- Neurologic AssessmentDocument2 pagesNeurologic AssessmentChaina MacaspacNo ratings yet
- Clay Modeling, Hu L/N Engineering and Aerodynamics in Passenger Car Body DesignDocument56 pagesClay Modeling, Hu L/N Engineering and Aerodynamics in Passenger Car Body Designveence spenglerNo ratings yet
- 2007 Agnolin & Martinelli OviraptoridDocument6 pages2007 Agnolin & Martinelli OviraptoridFederico AgnolinNo ratings yet
- Rehab BLDocument3 pagesRehab BLarissa razaliNo ratings yet
- Funda Sas3Document2 pagesFunda Sas3Jhan Veaver Lee Estrera MarquezNo ratings yet
- 3B Scientific Medical Education 2017 USDocument232 pages3B Scientific Medical Education 2017 USJuan Javier Apaza PillcoNo ratings yet
- Winspine 2.X For Windows: Operating InstructionsDocument29 pagesWinspine 2.X For Windows: Operating InstructionsLav LaviNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument14 pagesSkeletal SystemBea MiguelaNo ratings yet
- Q2-Activity in Science-Bones, Joint, MusclesDocument2 pagesQ2-Activity in Science-Bones, Joint, MusclesMaggie DreuNo ratings yet
- Spinal Injury and Spine Motion Restriction: Standard CompetencyDocument51 pagesSpinal Injury and Spine Motion Restriction: Standard CompetencyMichael DharshwinNo ratings yet
- CNS M1 Lecture Slides Compiled, DR OsaiDocument185 pagesCNS M1 Lecture Slides Compiled, DR OsaiMusaNo ratings yet
- 21 - Spondylolisthesis - D3Document31 pages21 - Spondylolisthesis - D3Mohamed Magdy El MeligieNo ratings yet
- Intrinsic Back Muscles - DeepDocument3 pagesIntrinsic Back Muscles - DeepmkklmlkNo ratings yet
- Basic Biomechanics Team Ira 9Th Edition Susan J Hall Full ChapterDocument51 pagesBasic Biomechanics Team Ira 9Th Edition Susan J Hall Full Chapterbenita.grimm191100% (5)
- Osteology-Vertebral Column Q&ADocument4 pagesOsteology-Vertebral Column Q&AsivaNo ratings yet
- Tuberculous Spondylodiscitis: Epidemiology, Clinical Features, Treatment, and OutcomeDocument15 pagesTuberculous Spondylodiscitis: Epidemiology, Clinical Features, Treatment, and OutcomeC-Bianca EmiliaNo ratings yet
- Ma. Celina C. Butalon, MD Department of Rehabilitation Medicine Philippine General HospitalDocument31 pagesMa. Celina C. Butalon, MD Department of Rehabilitation Medicine Philippine General HospitalcelinamdNo ratings yet
- The Female PelvisDocument6 pagesThe Female PelvisDrParth JoshiNo ratings yet
- Whiplash InjuryDocument25 pagesWhiplash InjuryMarco PeroliNo ratings yet
- 116 - Concept of Perception and CoordinationDocument3 pages116 - Concept of Perception and Coordinationalaisahmae02No ratings yet
- KyphosisDocument22 pagesKyphosisRaiganNo ratings yet
- DL TPSFDocument5 pagesDL TPSFPramod N KNo ratings yet
- Keynote Speakers: Evidence Based Practice (EBP) in Orthopaedic Physiotherapy (Module I)Document2 pagesKeynote Speakers: Evidence Based Practice (EBP) in Orthopaedic Physiotherapy (Module I)Ramya KishoreNo ratings yet
- CH 9 ArticulationsDocument40 pagesCH 9 ArticulationsRobin ToneyNo ratings yet