Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Quiz1 Solution
Uploaded by
Arya dbdbOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Quiz1 Solution
Uploaded by
Arya dbdbCopyright:
Available Formats
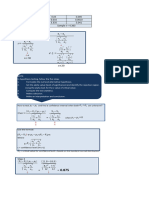
Question number 1
Remove["Global`*"]
l = 750;
t= 6;
do = 250;
di = 250 - 12;
W = 45 000;
p = 3.5;
r = 125;
T = W r;
M = W l;
π
Ib = do 4 - di 4
64
π
Jt = do 4 - di 4
32
10 901 676 π
21 803 352 π
Polar moment of Inertia
π
Jt = do 4 - di 4
32
21 803 352 π
Second Area moment of Inertia
π
Ib = do 4 - di 4
64
��� ��� N[10 901 676 π]
���� �� 3.42486 × 107
Two most critical points are A and B, Let the axis be zz and hoop be θθ
At A there will be bending stress and axial stress due to pressure
������� �� ������� ����������� ������� �������
2 Quiz1_sol.nb
Mr
σzzb =
Ib
pr
σzzp =
2t
pr
σθθ =
t
Tr
τzθ =
Jt
351 562 500
908 473 π
36.4583
72.9167
29 296 875
908 473 π
351 562 500
N
908 473 π
123.18
29 296 875
N
908 473 π
10.265
σzz = σzzb + σzzp
159.638
σzz + σθθ σzz - σθθ 2
σ1 = + + τzθ2
2 2
σzz + σθθ σzz - σθθ 2
σ2 = - + τzθ2
2 2
σ3 = 0
160.837
71.7182
1
σvmA = σ1 - σ22 + σ2 - σ32 + σ3 - σ12
2
139.56
Clear["Global`*"]
At B,
������� �� ������� ����������� ������� �������
Quiz1_sol.nb 3
σzzb = 0
pr
σzzp =
2t
pr
σθθ =
t
Tr
τzθ =
Jt
0
36.4583
72.9167
29 296 875
908 473 π
σzz = σzzb + σzzp
σzz + σθθ σzz - σθθ 2
σ1 = + + τzθ2
2 2
σzz + σθθ σzz - σθθ 2
σ2 = - + τzθ2
2 2
σ3 = 0
75.6081
33.7669
1
σvmB = σ1 - σ22 + σ2 - σ32 + σ3 - σ12
2
65.602907971277`
At C in the bottom,
������� �� ������� ����������� ������� �������
4 Quiz1_sol.nb
Mr
σzzb = -
Ib
pr
σzzp =
2t
pr
σθθ =
t
Tr
τzθ =
Jt
351 562 500
-
908 473 π
36.4583
72.9167
29 296 875
908 473 π
351 562 500
N-
908 473 π
- 123.18
σzz = σzzb + σzzp
- 86.7218
σzz + σθθ σzz - σθθ 2
σ1 = + + τzθ2
2 2
σzz + σθθ σzz - σθθ 2
σ2 = - + τzθ2
2 2
σ3 = 0
73.574
- 87.3791
1
σvmB = σ1 - σ22 + σ2 - σ32 + σ3 - σ12
2
139.56
Most critical location is A The vonMises is 139.56 and the Tresca gives 160 MPa
If the hydrostatic tests 1.5 p and load is 1.25 W
������� �� ������� ����������� ������� �������
Quiz1_sol.nb 5
l = 750;
t= 6;
do = 250;
di = 250 - 12;
W = 45 000;
p = 1.5 × 3.5;
r = 125;
T = 1.25 W r;
M = 1.25 W l;
π
Ib = do 4 - di 4
64
π
Jt = do 4 - di 4
32
10 901 676 π
21 803 352 π
Mr
σzzb =
Ib
pr
σzzp =
2t
pr
σθθ =
t
Tr
τzθ =
Jt
153.975
54.6875
109.375
12.8313
σzz = σzzb + σzzp
208.663
σzz + σθθ σzz - σθθ 2
σ1 = + + τzθ2
2 2
σzz + σθθ σzz - σθθ 2
σ2 = - + τzθ2
2 2
σ3 = 0
210.294
107.744
������� �� ������� ����������� ������� �������
6 Quiz1_sol.nb
1
σvmA = σ1 - σ22 + σ2 - σ32 + σ3 - σ12
2
182.139
The factor of safety is 182.13 139.56 = 1.30
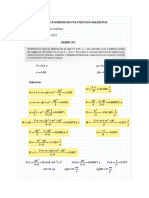
Question number 2 solution
��������� Remove["Global`*"]
Note that if the plate is immersed in cryogenic for a short period. The skin layer will experience
sudden contraction whereas the core is still at the room temperature. This will result in zero strains
in x and y axes and the free surface results in zero stress along z axis. If you physically think the skin
wants to contract but the contraction is not allowed by the core, hence it will be under tension. It
can be seen by following equations:
σx ν σy ν
��������� Solve - σy + α ΔT ⩵ 0 && - σx + α ΔT ⩵ 0, {σx , σy }
E1 E1 E1 E1
E1 α ΔT E1 α ΔT
��������� σx → , σy →
-1 + ν -1 + ν
��������� E1 = 200 × 10 ^ 9
ν = 0.3
ΔT = - 120
α = 12 × 10 ^ - 5
��������� 200 000 000 000
��������� 0.3
��������� - 120
3
���������
25 000
E1 α ΔT
��������� σx =
-1 + ν
��������� 4.11429 × 109
������� �� ������� ����������� ������� �������
3
You might also like
- Dokumen - Tips Homework 3 Solution Department of Statistics Ovitekstat526 Spring11filespdfshw3 SolpdfstatDocument12 pagesDokumen - Tips Homework 3 Solution Department of Statistics Ovitekstat526 Spring11filespdfshw3 Solpdfstatbourday RachidNo ratings yet
- Jackson SolutionDocument219 pagesJackson Solutionsimiwd100% (8)
- BB831 Xa03xen E1 PDFDocument62 pagesBB831 Xa03xen E1 PDFDaniel RamirezNo ratings yet
- N q N h N h N γ n w C ϕ γ h γ γ n) ) ( (+ w) ) γ' γ γ n) ) abordarea1 gruparea1 γ γ γ γ γ γ γ γ γ γ γ' γ' γ γ'Document4 pagesN q N h N h N γ n w C ϕ γ h γ γ n) ) ( (+ w) ) γ' γ γ n) ) abordarea1 gruparea1 γ γ γ γ γ γ γ γ γ γ γ' γ' γ γ'IonNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Engineering Mechanics Statics Si Edition 4Th Edition by Pytel Kiusalaas Isbn 1305577434 9781305577435 Full Chapter PDFDocument17 pagesSolution Manual For Engineering Mechanics Statics Si Edition 4Th Edition by Pytel Kiusalaas Isbn 1305577434 9781305577435 Full Chapter PDFruby.kinkel639100% (12)
- Quiz1 Solution-6Document1 pageQuiz1 Solution-6Pranith KumarNo ratings yet
- Basic Calculus: Week 5 ActivitiesDocument8 pagesBasic Calculus: Week 5 ActivitiesREAP lNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Engineering Mechanics Statics Si Edition 4th EditionDocument24 pagesSolution Manual For Engineering Mechanics Statics Si Edition 4th EditionAaronPhillipsnqjo100% (41)
- Rezolvare 1Document3 pagesRezolvare 1Bogdan ArmeancaNo ratings yet
- Oy Oy OyDocument4 pagesOy Oy OyCarlos S. VásquezNo ratings yet
- 7 StressDocument1 page7 StressR S PappuNo ratings yet
- Some Personalities of NumberDocument6 pagesSome Personalities of NumberPablo MoyaNo ratings yet
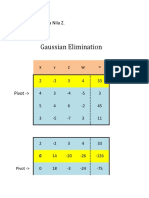
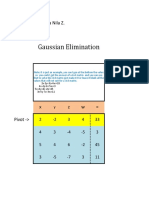
- Gaussian Elimination: Palacio, Maria Nila ZDocument22 pagesGaussian Elimination: Palacio, Maria Nila ZMariaNilaZaragozaPalacioNo ratings yet
- Para Ti BebeDocument5 pagesPara Ti BebeSebastián Tovar BravoNo ratings yet
- 5.CMT - Stalp de ColtDocument8 pages5.CMT - Stalp de ColtDavidescu DanielNo ratings yet
- 5.CMT - Stalp de ColtDocument8 pages5.CMT - Stalp de ColtDavidescu DanielNo ratings yet
- Reshenie Trigonometricheskih Uravnenij - 2Document1 pageReshenie Trigonometricheskih Uravnenij - 2nadykouzNo ratings yet
- 4.Cmt - Stalp de MijlocDocument8 pages4.Cmt - Stalp de MijlocDavidescu DanielNo ratings yet
- Palacio, Maria Nila Gauss JordanDocument23 pagesPalacio, Maria Nila Gauss Jordanmia palacioNo ratings yet
- Serie de Potencias 6Document2 pagesSerie de Potencias 6Eduardo Daniel Flores CarpioNo ratings yet
- Problem 1Document17 pagesProblem 1Roqaia AlwanNo ratings yet
- Full Download Engineering Mechanics Statics Si Edition 4th Edition Pytel Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesFull Download Engineering Mechanics Statics Si Edition 4th Edition Pytel Solutions ManualriflingbeholdenvxuynvNo ratings yet
- Known Families of Integer Solutions of X 3+y 3+z 3 NDocument6 pagesKnown Families of Integer Solutions of X 3+y 3+z 3 NAnónimo PorsiacasoNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Assignment SolutionDocument12 pagesWeek 5 Assignment SolutionRohit DuttaNo ratings yet
- Formulario - Mec - SolDocument1 pageFormulario - Mec - SolAline Costa LopesNo ratings yet
- Kef Laio 7 Dianusmatikoð Q Roi Kai Grammik Sust Mata: 7.1 Grammik Anexarthsða Dianusm TWNDocument11 pagesKef Laio 7 Dianusmatikoð Q Roi Kai Grammik Sust Mata: 7.1 Grammik Anexarthsða Dianusm TWNMihalis NikolaouNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Statics Si Edition 4th Edition Pytel Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesEngineering Mechanics Statics Si Edition 4th Edition Pytel Solutions Manualjoelcurrydvmpiqrdxenyg100% (21)
- Crypto HW2Document4 pagesCrypto HW2呂尚豪No ratings yet
- Operatii in Criptografia Aplicata 1.exponetierea Modulara: LUCRARE PRACTICA: Exponentierea ModularăDocument7 pagesOperatii in Criptografia Aplicata 1.exponetierea Modulara: LUCRARE PRACTICA: Exponentierea ModularăMMRT MMRT1No ratings yet
- HW1 16p8-1xpaibvDocument4 pagesHW1 16p8-1xpaibvIvanNo ratings yet
- Calculos Practica 10Document3 pagesCalculos Practica 10Yanin RamírezNo ratings yet
- 6.cit - Stalp de MijlocDocument8 pages6.cit - Stalp de MijlocDavidescu DanielNo ratings yet
- 12JPCM01 Answer KeyDocument13 pages12JPCM01 Answer Keyaachathyaa0032No ratings yet
- ESO202, Assignment-5, Solution: September 12, 2018Document3 pagesESO202, Assignment-5, Solution: September 12, 2018Neha KumariNo ratings yet
- Stress TransformationDocument22 pagesStress TransformationTran Manh HuyNo ratings yet
- Jee Mains August 27 2021 Shift2Document45 pagesJee Mains August 27 2021 Shift2Atharva Sheersh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Full Download Fundamentals of Business Math Canadian 3rd Edition Jerome Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download Fundamentals of Business Math Canadian 3rd Edition Jerome Solutions Manualtartanepigramc0io7100% (41)
- Pi PersonalitiesDocument6 pagesPi PersonalitiesAndres GranadosNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Engineering Mechanics Statics Si Edition 4th Edition Pytel Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Engineering Mechanics Statics Si Edition 4th Edition Pytel Solutions Manual PDFreredos.middingewbt100% (10)
- Chapter7 PDFDocument34 pagesChapter7 PDFWillian DiazNo ratings yet
- Сопромат 8-без опоры - 2-4стрDocument3 pagesСопромат 8-без опоры - 2-4стрАлександрNo ratings yet
- MA111 Short Test 1 With SolutionsDocument8 pagesMA111 Short Test 1 With SolutionsPete PhilipsNo ratings yet
- TryDocument3 pagesTryghanemlyna05No ratings yet
- Metodo de Newmark FINALDocument6 pagesMetodo de Newmark FINALedison JimenezNo ratings yet
- 12073-0130670227 Ismsec7 PDFDocument19 pages12073-0130670227 Ismsec7 PDFAngel HilasacaNo ratings yet
- Sifat Monga Maths Test CH 1Document6 pagesSifat Monga Maths Test CH 1SifatNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument9 pagesFinalRaquel MañacapNo ratings yet
- Simplification TMDocument13 pagesSimplification TMAnonymous 1nwZ5xiTDNo ratings yet
- MTH 218 Homework 31 Solutions: X Yz, Sin (Xyz), Xyz Y-AxisDocument6 pagesMTH 218 Homework 31 Solutions: X Yz, Sin (Xyz), Xyz Y-AxisLoh Jun XianNo ratings yet
- 293 PDFDocument2 pages293 PDFarief_7No ratings yet
- QUIZ9 SolDocument2 pagesQUIZ9 Sol高詠毛No ratings yet
- Strength Factor: Mohr-Coulomb Failure CriterionDocument4 pagesStrength Factor: Mohr-Coulomb Failure CriterionLuisRodrigoPerezPintoNo ratings yet
- Ejercios Teoris 2Document5 pagesEjercios Teoris 2Cristopher QuilleNo ratings yet
- 11TH Full SolDocument7 pages11TH Full SolshankarNo ratings yet
- Iit Paper II SolutionsDocument7 pagesIit Paper II SolutionsRajeshKP65No ratings yet
- Sec 3 - TrigonometryDocument9 pagesSec 3 - TrigonometryJian TiongNo ratings yet
- Analysis of StressDocument15 pagesAnalysis of Stressrizky tri amaliaNo ratings yet
- Parcijalni Ispit IM1 S RješenjimaDocument4 pagesParcijalni Ispit IM1 S RješenjimaherminaNo ratings yet
- A. Data Pretes Kelas Eksperimen: F Fxi Fxi F - )Document7 pagesA. Data Pretes Kelas Eksperimen: F Fxi Fxi F - )Dea ApriliaNo ratings yet
- Numerical - Jacobi and Gauss-Seidel LinearDocument3 pagesNumerical - Jacobi and Gauss-Seidel LinearBonifacio SautNo ratings yet
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Class14 Annotated Module04 Problems PDFDocument14 pagesClass14 Annotated Module04 Problems PDFArya dbdbNo ratings yet
- Mechanics 2Document14 pagesMechanics 2Arya dbdbNo ratings yet
- Bolt PDFDocument41 pagesBolt PDFArya dbdbNo ratings yet
- Encoders PDFDocument30 pagesEncoders PDFArya dbdbNo ratings yet
- Bearings1 PDFDocument21 pagesBearings1 PDFArya dbdbNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Sniper ReportDocument8 pagesHydraulics Sniper ReportKhumo Ezekiel MoraNo ratings yet
- Uem Ai & ML SyllabusDocument103 pagesUem Ai & ML SyllabusAvradip DasNo ratings yet
- Numericals Related To Spherical MirrorDocument2 pagesNumericals Related To Spherical MirrorThe Special ThingNo ratings yet
- Measurement of SolidsDocument7 pagesMeasurement of SolidsWasim AkramNo ratings yet
- Apr 2024 Preboard 1 HgeDocument3 pagesApr 2024 Preboard 1 HgeChrisjohn Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer 6th Edition-901-1000-51-100Document50 pagesFundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer 6th Edition-901-1000-51-100abibas olaNo ratings yet
- SadfasdfasdfdasdfdasDocument15 pagesSadfasdfasdfdasdfdasRoni AmaralNo ratings yet
- Books Doubtnut Question BankDocument260 pagesBooks Doubtnut Question Bankrohan sinhaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 29 Nov DPP 1Document1 pageThermodynamics 29 Nov DPP 1Aditya SallyNo ratings yet
- Tear Strength of Conventional Vulcanized Rubber and Thermoplastic ElastomersDocument9 pagesTear Strength of Conventional Vulcanized Rubber and Thermoplastic ElastomersSebastian DiazNo ratings yet
- Geometry Final 2020Document30 pagesGeometry Final 2020Sergio Cuautle JuarezNo ratings yet
- Winscosin DOT Complete ExampleDocument166 pagesWinscosin DOT Complete ExampletarekhocineNo ratings yet
- StudentGradeHistory 21MAE0053Document2 pagesStudentGradeHistory 21MAE0053Piyush BidwaiNo ratings yet
- 1588244806UPHTE-601 Unit3.7 JU - Hysteresis CurveDocument2 pages1588244806UPHTE-601 Unit3.7 JU - Hysteresis CurveMihir RanaNo ratings yet
- Exercises Component Method 2Document57 pagesExercises Component Method 2Vanderleia CalazansNo ratings yet
- Narayana - 15!06!2022 - Outgoing SR - Jee Main Model Gtm-10 - QuesDocument22 pagesNarayana - 15!06!2022 - Outgoing SR - Jee Main Model Gtm-10 - QuesShreyas VedantiNo ratings yet
- Rawl Bolts and CapacityDocument2 pagesRawl Bolts and Capacitykevinisonline0% (1)
- Unit-1 M.tech (Vector Space) Dec. 2017Document22 pagesUnit-1 M.tech (Vector Space) Dec. 2017Naveen DubeyNo ratings yet
- Materials Science: Abhijit Chatterjee Jayesh BellareDocument19 pagesMaterials Science: Abhijit Chatterjee Jayesh BellareAbhishekNo ratings yet
- Gradient Intercept FormDocument3 pagesGradient Intercept FormsaadNo ratings yet
- 2799 Astm D - 2011Document7 pages2799 Astm D - 2011M0197 BatenkhNo ratings yet
- Module Two Science Journal Joelle MatarDocument6 pagesModule Two Science Journal Joelle MatarJoelle MatarNo ratings yet
- Development of Eco-Efficient and Cost-Effective Reinforced Self-Consolidation Concretes With Hybrid Industrial - Recycled Steel FibersDocument13 pagesDevelopment of Eco-Efficient and Cost-Effective Reinforced Self-Consolidation Concretes With Hybrid Industrial - Recycled Steel FibersDiego SukNo ratings yet
- core-worksheets-1-12Document12 pagescore-worksheets-1-12munna kumar vermaNo ratings yet
- gt2011 45614Document10 pagesgt2011 45614DeckrunNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchangers: The Effectiveness - NTU MethodDocument15 pagesHeat Exchangers: The Effectiveness - NTU MethodVenkitaraj K PNo ratings yet
- Pipette CalibrationDocument9 pagesPipette CalibrationMaame Efua NeizerNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ayman Abd El-Hamid - Performance Based Design of StructuresDocument58 pagesDr. Ayman Abd El-Hamid - Performance Based Design of Structuresعبدالرحمن النجدي100% (1)
- ViiiDocument32 pagesViiiShaurya ShubhamNo ratings yet