Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tenses - Present Perfect Continuous
Uploaded by
lamanandaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tenses - Present Perfect Continuous
Uploaded by
lamanandaCopyright:
Available Formats
Verb Tenses
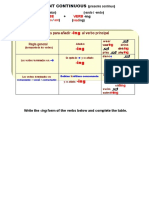
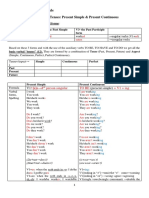
Present Perfect Continuous.
General Structure Have
(he estado jugando) Been + Verb ING
Has
(+) (-) (?)
I I
You you
have been playing haven't been playing Have been playing... ?
We we
They they
He he
She has been playing hasn't been playing Has she been playing... ?
It it
General Uses.
- Actions started in the past that still continue or have recently stopped:
We have been waiting here for three hours. (We are still waiting)
Tom has been painting the room. (That is why his clothes are so dirty)
* Comparison with the Present Perfect Simple:
- When talking about actions started in the past that still continue, both tenses are possible, but
the Present Perfect Continuous is more frequently used to emphasise duration.
They have lived in this house for twenty years.
They have been living in this house for twenty years.
- The Present Perfect Simple is more frequently used with instant actions, while the Present
Perfect Continuous is more frequently used with long actions, or repeated actions.
Oh, no! I have broken the glass! (Instant action)
She has been talking on the phone since she arrived from work. (Long action)
Mike has been sneezing all day. (Repeated action)
- The Present Perfect Simple is often used when talking about finished or complete actions,
while the Present Perfect Continuous gives the idea that the action is not completed yet.
Joe has been writing his new book all morning. (Probably, he hasn't finished yet)
Joe has written three chapters of his new book. (The chapters are finished now)
We are tired because we have repaired the car. (Completed action)
We are tired because we have been repairing the car. (Probably not completed)
You might also like
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideFrom EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Tenses - Present ContinuousDocument1 pageTenses - Present ContinuouslamanandaNo ratings yet
- Tenses - Present Perfect SimpleDocument1 pageTenses - Present Perfect SimplelamanandaNo ratings yet
- Grammar exercise: present perfect simple vs continuousDocument3 pagesGrammar exercise: present perfect simple vs continuousAndreeaNo ratings yet
- Gram MaireDocument19 pagesGram MaireSiham El aouitriNo ratings yet
- Present Simple, Continuous and Perfect TensesDocument14 pagesPresent Simple, Continuous and Perfect Tensesashraf4mNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Grammar Exercise Present PerfectDocument3 pagesIntermediate Grammar Exercise Present PerfectEsther León JorgeNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect SimpleDocument6 pagesPresent Perfect SimpleDiogo BarrosoNo ratings yet
- Passé ComposéDocument22 pagesPassé ComposézeeNo ratings yet
- Tenses - Past ContinuousDocument1 pageTenses - Past ContinuouslamanandaNo ratings yet
- Verb ChartDocument2 pagesVerb ChartEstrella MoraNo ratings yet
- Presente Perfecto ContinuoDocument4 pagesPresente Perfecto ContinuoPaula Soledad Villarreal ValdezNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Simple and Continuous - IntermediateDocument4 pagesPresent Perfect Simple and Continuous - IntermediateALEJANDRA2605No ratings yet
- Grammaire AnglaiseDocument48 pagesGrammaire AnglaiseMbemba Doumbouya100% (2)
- Present Perfect Tense MaterialDocument5 pagesPresent Perfect Tense MaterialJelya LenNo ratings yet
- Present PerfectDocument26 pagesPresent PerfectSusaku KururugiNo ratings yet
- Present Simple: Affirmative Negative InterrogativeDocument3 pagesPresent Simple: Affirmative Negative InterrogativeAlejandra MalettiNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Present Progressive/Continuous: Inglise Keele Ajavormid Ja Nende Kasutamine (9. Klassi Seisuga)Document4 pagesPresent Simple Present Progressive/Continuous: Inglise Keele Ajavormid Ja Nende Kasutamine (9. Klassi Seisuga)Reelika KomussarNo ratings yet
- VERB TENSES ExplanationsDocument8 pagesVERB TENSES ExplanationsMihaela GradinaruNo ratings yet
- Pres Cont Past SimpleDocument1 pagePres Cont Past SimpleAlejandra LopezNo ratings yet
- Excercices With Verb TobeDocument4 pagesExcercices With Verb TobeBárbaraRossiNo ratings yet
- Simple Past TenseDocument4 pagesSimple Past TenseShanti ApriliyaniNo ratings yet
- Activity 4 OkDocument1 pageActivity 4 OkVandian Rocha sorrosaNo ratings yet
- Present Continuous Tense: Aff.S+To Be+ V1-Ing Neg .S+To Be-Not+ V1-Ing Int. To Be-+s+ V1-Ing?Document3 pagesPresent Continuous Tense: Aff.S+To Be+ V1-Ing Neg .S+To Be-Not+ V1-Ing Int. To Be-+s+ V1-Ing?Clipea Crina StefaniaNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect ContinuousDocument4 pagesPresent Perfect ContinuousYareli GómezNo ratings yet
- English Grammar: The TensesDocument35 pagesEnglish Grammar: The TensesSzala LukeNo ratings yet
- PRESENT CONTINUOUS (PRESENTE CONTINUO) IN SPANISHDocument7 pagesPRESENT CONTINUOUS (PRESENTE CONTINUO) IN SPANISHRabell CruzzNo ratings yet
- GrammarDocument34 pagesGrammarMed BlhhNo ratings yet
- Tempos VerbaisDocument50 pagesTempos VerbaisJoao SilvaNo ratings yet
- Tenses (Summary 02)Document1 pageTenses (Summary 02)lamanandaNo ratings yet
- The Tense Chart ExplainedDocument2 pagesThe Tense Chart ExplainedJessi FernandezNo ratings yet
- Le Present SimpleDocument2 pagesLe Present SimpleClaircia KoualaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 TourismDocument18 pagesUnit 3 TourismElita IglesiasNo ratings yet
- English Verb TensesDocument28 pagesEnglish Verb TensesSoraya Yam100% (2)
- How Often Something Happens: S S Es Don't Do DoesDocument3 pagesHow Often Something Happens: S S Es Don't Do DoesAndrei BulgaruNo ratings yet
- English Tenses Table (Brief Presentation)Document5 pagesEnglish Tenses Table (Brief Presentation)Roberta AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Present Continuous Tense GuideDocument1 pagePresent Continuous Tense GuideGaraNo ratings yet
- Septimo Present ProgressiveDocument8 pagesSeptimo Present ProgressiveDiego CardenasNo ratings yet
- Tenses Positive Negative Introgative: I, You, We, They I, You, We, They I, You, We, TheyDocument2 pagesTenses Positive Negative Introgative: I, You, We, They I, You, We, They I, You, We, TheyRidwan baritoNo ratings yet
- PAST SIMPLE Vs PRESENT PERFECTDocument3 pagesPAST SIMPLE Vs PRESENT PERFECTMariaNo ratings yet
- Form Simple Present TenseDocument21 pagesForm Simple Present TenseLeo ZerpaNo ratings yet
- Present ContinuousDocument48 pagesPresent ContinuousPieroHuarachaGarciaNo ratings yet
- Tenses (Summary 01)Document1 pageTenses (Summary 01)lamanandaNo ratings yet
- Present-Continuous - English 2Document9 pagesPresent-Continuous - English 2Esteban MartínezNo ratings yet
- Handout 1Document3 pagesHandout 1edenamiriambutNo ratings yet
- Tableau ConjugaisonDocument2 pagesTableau Conjugaisonsimonroux24100No ratings yet
- Continuous Verb TensesDocument12 pagesContinuous Verb Tensesida rohmaningsihNo ratings yet
- Present Continuous TenseDocument3 pagesPresent Continuous TenseChiara Melissa Torres NeyraNo ratings yet
- A4english Tenses TableDocument2 pagesA4english Tenses TableWillipmeisterNo ratings yet
- Escuela Superior Politécnica de Chimborazo Facutlad de MecánicaDocument12 pagesEscuela Superior Politécnica de Chimborazo Facutlad de MecánicaÁngel PastoNo ratings yet
- Conjugación del verbo 'to work' en inglésDocument1 pageConjugación del verbo 'to work' en inglésrikan1821No ratings yet
- Diapositivas de Ingles, Tiempos VerbalesDocument116 pagesDiapositivas de Ingles, Tiempos VerbalesJeilys PajaroNo ratings yet
- Past Simple TenseDocument2 pagesPast Simple TenseBranko DjordjevicNo ratings yet
- Learn English Verb TensesDocument32 pagesLearn English Verb TensesANGIE LIZET RIVERA PRADONo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Simple (I Have Worked) : English Grammar TodayDocument26 pagesPresent Perfect Simple (I Have Worked) : English Grammar TodayEurico BrassoNo ratings yet
- WiderWorld2e 2 GrammarPresentation 2.2Document6 pagesWiderWorld2e 2 GrammarPresentation 2.2cooleugene64No ratings yet
- Review of English Present TensesDocument7 pagesReview of English Present TensesRamona DinuNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect and Simple Past TensesDocument17 pagesPresent Perfect and Simple Past TensesDragan StančevNo ratings yet
- English tenses guideDocument4 pagesEnglish tenses guideОлена КалинськаNo ratings yet
- Tenses - Future PerfectDocument1 pageTenses - Future PerfectlamanandaNo ratings yet
- Theory - Modal Verbs For Obligation & ProhibitionDocument2 pagesTheory - Modal Verbs For Obligation & ProhibitionlamanandaNo ratings yet
- Theory - Some - Any - A Lot ofDocument1 pageTheory - Some - Any - A Lot oflamanandaNo ratings yet
- Theory - QuantifiersDocument1 pageTheory - QuantifierslamanandaNo ratings yet
- Theory - Quantifiers (Theory)Document1 pageTheory - Quantifiers (Theory)lamanandaNo ratings yet
- Theory - Passive VoiceDocument4 pagesTheory - Passive VoicelamanandaNo ratings yet
- Phrasal VerbsDocument3 pagesPhrasal VerbslamanandaNo ratings yet
- Theory - Modal Verbs For Obligation & ProhibitionDocument2 pagesTheory - Modal Verbs For Obligation & ProhibitionlamanandaNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Continuous TenseDocument4 pagesPresent Perfect Continuous TenseNga ManNo ratings yet
- 13 1Document88 pages13 1Abdulaziz AlmutairiNo ratings yet
- U2 - L1 - How Can I Form Questions in EnglishDocument4 pagesU2 - L1 - How Can I Form Questions in EnglishLeo CentenoNo ratings yet
- Trends2 ANK SBCat 16615 PDF Educational Technology Grammatical TenseDocument1 pageTrends2 ANK SBCat 16615 PDF Educational Technology Grammatical TensepaualNo ratings yet
- Bai Tap Anh 9 Theo UnitDocument48 pagesBai Tap Anh 9 Theo UnitThoa Nguyen KimNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Present Perfect ContinuousDocument11 pagesPresent Perfect Present Perfect ContinuousFurryPriiiko100% (1)
- Yearly Scheme of Work - SJK - English - KSSR - Year 6: Week Listening and Speaking Reading Writing Language Arts GrammarDocument16 pagesYearly Scheme of Work - SJK - English - KSSR - Year 6: Week Listening and Speaking Reading Writing Language Arts GrammarSarath KumarNo ratings yet
- Past Perfect ProgressiveDocument4 pagesPast Perfect ProgressiveJessely RomoNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous Tenseaffirmative Sentences With GR Grammar Guides - 13572Document2 pagesPast Continuous Tenseaffirmative Sentences With GR Grammar Guides - 13572Laura VélezNo ratings yet
- What Is An Auxiliary Verb - Definition & ExamplesDocument13 pagesWhat Is An Auxiliary Verb - Definition & ExamplesHidayat RahmanNo ratings yet
- PTS Kelas Xi PeminatanDocument5 pagesPTS Kelas Xi PeminatanEnggelina TsunNo ratings yet
- Grammar Points For Each CEF LevelDocument2 pagesGrammar Points For Each CEF LevelBotella DeaguaNo ratings yet
- Active & Passive Voice GuideDocument5 pagesActive & Passive Voice Guidefathima sarahNo ratings yet
- PROFICIENCY 1 UNIT 4 (Sweet Rituals)Document61 pagesPROFICIENCY 1 UNIT 4 (Sweet Rituals)Pablo GomesNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH Scheme of Work FORM 5 2013Document12 pagesENGLISH Scheme of Work FORM 5 2013seechinNo ratings yet
- Gramar TensesDocument33 pagesGramar TensesSehrishNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan for Blended LearningDocument3 pagesLesson Plan for Blended LearningMubaraka FanuswalaNo ratings yet
- Past Perfect Tense: It's Used For A Past Action Which Happened Before Another or Before ADocument12 pagesPast Perfect Tense: It's Used For A Past Action Which Happened Before Another or Before ASelin AkalınNo ratings yet
- Worksheet N°24 - Unit 3 - Grammar SectionDocument3 pagesWorksheet N°24 - Unit 3 - Grammar SectionAldair VásquezNo ratings yet
- Exercise Your Past Tense With KeyDocument8 pagesExercise Your Past Tense With KeyAnaNițuNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument86 pagesUntitledBilal Ardi Yuli SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Makalah BHS InggrisDocument24 pagesMakalah BHS InggrisHasmawaty MansyurNo ratings yet
- PRESENT CONTINUOUS TENSEDocument7 pagesPRESENT CONTINUOUS TENSENebrass JmalNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument2 pagesConditional SentencesGibran LeonardyNo ratings yet
- Thinking of + Verb + - Ing To Talk About PlansDocument2 pagesThinking of + Verb + - Ing To Talk About PlansnursenaNo ratings yet
- Spreadsheet English Verb TensesDocument76 pagesSpreadsheet English Verb TensesRamonaNo ratings yet
- Ge9 LB IssuuDocument56 pagesGe9 LB IssuuJibran Soomro100% (1)
- How to Express Future Plans in the PastDocument4 pagesHow to Express Future Plans in the PastMiray DoğanNo ratings yet
- The Passive VoiceDocument4 pagesThe Passive VoiceDursunNo ratings yet
- Spis Treści:: Grammar Booklet Klasa 1 Lo - Success Pre-IntermediateDocument51 pagesSpis Treści:: Grammar Booklet Klasa 1 Lo - Success Pre-IntermediatemariushNo ratings yet