Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Series and Parallel Circuits
Uploaded by
Ayush Patel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views3 pagesThe document summarizes the key differences between series and parallel circuits. It provides examples to illustrate how to calculate total voltage, equivalent resistance, current, voltage drops, and current through individual components in each type of circuit. For a series circuit, the total voltage is the sum of the individual voltage drops and the current is the same through all components. For a parallel circuit, the total voltage is equal across all branches and the current divides across the parallel paths according to resistance. Combination circuits can also be analyzed using these series and parallel circuit rules.
Original Description:
Original Title
Series and Parallel Circuits (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the key differences between series and parallel circuits. It provides examples to illustrate how to calculate total voltage, equivalent resistance, current, voltage drops, and current through individual components in each type of circuit. For a series circuit, the total voltage is the sum of the individual voltage drops and the current is the same through all components. For a parallel circuit, the total voltage is equal across all branches and the current divides across the parallel paths according to resistance. Combination circuits can also be analyzed using these series and parallel circuit rules.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views3 pagesSeries and Parallel Circuits
Uploaded by
Ayush PatelThe document summarizes the key differences between series and parallel circuits. It provides examples to illustrate how to calculate total voltage, equivalent resistance, current, voltage drops, and current through individual components in each type of circuit. For a series circuit, the total voltage is the sum of the individual voltage drops and the current is the same through all components. For a parallel circuit, the total voltage is equal across all branches and the current divides across the parallel paths according to resistance. Combination circuits can also be analyzed using these series and parallel circuit rules.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Series and Parallel Circuits
Series Circuit Rules Parallel Circuit Rules
A “Series Circuit” follows a single loop or path A “Parallel Circuit” follows a multi loop or path
Voltage Gain = Sum of V1 +V2+V3 Voltage Gain = VT = V1 = V2 = V3
Current = IT = I1 = I2 = I3 Current = IT = I1+I2+I3
Equations Equations
Total Resistance = RT = R1+R2+R3 Total Resistance = 1/RT= 1/R1+1/R2+1/R3
Voltage = Ohm’s Law V= I x R Voltage = Ohm’s Law V= I x R
Let’s do an Example for the following Series Circuit:
1. What is the total voltage gain in the circuit?
VT = 12V
2. What is the Equivalent Resistance of the circuit?
RT = R1+R2+R3
RT = 10Ω+20Ω+30Ω
RT = 60Ω
3. What is the total current through the circuit?
V=IxR
IT = VT /RT
IT= 12V/60Ω
IT = 0.2A
4. What is the current through each Resistor?
IT = I1 = I2 = I3 Note: there is no place to add or remove current
Therefore:
I1 = 0.2A
I2 = 0.2A
I3 = 0.2A
5. What is the Voltage drop?
V1 = I1 x R1 VT = V1+V2+V3
V1 = 0.2A x 10Ω = 2V VT = 2V+4V+6V
V2 = 0.2A x 20Ω = 4V VT = 12V
V3 = 0.2A x 30Ω = 6V
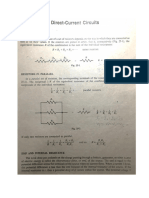
Let’s do an Example for the following Parallel Circuit:
6. What is the total voltage gain in the circuit?
VT = 20V
7. What is the Equivalent Resistance of the circuit? 20V
1/RT = 1/R1+1/R2+1/R3
7Ω 15Ω 12Ω
1/RT = 1/7Ω+1/15Ω+1/12Ω
1/RT = 0.293
RT = 1/ 0.293Ω
RT = 3.41Ω
8. What is the total current through the circuit?
V = I x R = you need to divide each side by R
IT = VT /RT
IT= 20V/3.41Ω
IT = 5.87A
9. What is the Voltage drop?
VT = V1 = V2 = V3
V1 = 20V
V2 = 20V
V3 = 20V
10. What is the current through each Resistor?
IT = I1 + I2 + I3
I1 = V1/R1 I2 = V2/R2 I3 = V3/R3
I1 = 20V/7Ω I2 = 20v/15Ω I3 = 20v/12Ω
I1 = 2.86A I2 = 1.34A I3 = 1.67A
IT = 2.86A + 1.34A + 1.67A
IT = 5.87A
Combination Circuit Example:
8Ω
12Ω
24V
1. What is the total voltage gain in the circuit?
VT = 24V
2. What is the Equivalent Resistance of the circuit?
1/R1, R2 = 1/R1 +1/ R2
1/R1, R2 = 1/12Ω + 1/5Ω
1/R1, R2 = 1/0.283
R1, R2 = 3.53Ω
RT = 3.53Ω + 8Ω
RT = 11.53Ω
3. What is the total current through the circuit?
V=IxR
IT = VT /RT
IT= 24V/11.53Ω
IT = 2.08A
4. What is the current through each Resistor?
I3 = IT = 2.08A
I1 = V1/R1 I2 = V2/R2
I1 = 7.36V/12Ω I2 = 7.36/5Ω
I1 = 0.61A I2 = 1.47A
I1 + I2 = 0.61A + 1.47A = 2.08A
5. What is the Voltage drop? NOTE THIS QUESTION NEEDS TO BE DONE PRIOR TO Q#4
V3 = I3xR3 V1, 2 = VT –V3
V3 = 2.08A x 8Ω V1, 2 = 24V – 16.64V
V3 = 16.64V V1, 2 = 7.36V
V1, 2 = I1, 2 x R1, 2
V1, 2 = 2.08A x 3.53Ω
V1, 2 = 7.34V
You might also like
- Resistive Circuit PracticeDocument11 pagesResistive Circuit PracticeBrandon BarndtNo ratings yet
- Experiment #3 Final - Report - CODocument8 pagesExperiment #3 Final - Report - COEisen Jaylord100% (1)
- Simple Circuits and Kirchoffs LawsDocument24 pagesSimple Circuits and Kirchoffs LawsJoseMiguelDomingo100% (1)
- RESISTANCEDocument50 pagesRESISTANCECdqdpNo ratings yet
- 12-MGDP-T-1033-0 (Spec For PAGA System) PDFDocument31 pages12-MGDP-T-1033-0 (Spec For PAGA System) PDFheikel100% (2)
- David Jiles (Author) - Introduction To Magnetism and Magnetic Materials-CRC Press (2015)Document616 pagesDavid Jiles (Author) - Introduction To Magnetism and Magnetic Materials-CRC Press (2015)Krishna kusmi100% (1)
- By: Mr. Augosto M. DirectoDocument34 pagesBy: Mr. Augosto M. DirectoJames RojasNo ratings yet
- Power Cable Testing and Diagnostics OverviewDocument22 pagesPower Cable Testing and Diagnostics OverviewanuragpugaliaNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument32 pagesOhm's LawPortia A. EgkenNo ratings yet
- Calculating Equivalent Resistance, Total Current and TotalDocument39 pagesCalculating Equivalent Resistance, Total Current and TotalNeil Aldrin Olvina100% (1)
- Series and Parallel CircuitsDocument27 pagesSeries and Parallel CircuitsClarence Virata100% (1)
- Report Elec Lab 3Document7 pagesReport Elec Lab 3HARITH IZHAMNo ratings yet
- Series and Parallel CircuitDocument7 pagesSeries and Parallel Circuitcaparosmaneth0No ratings yet
- Circuit DiagramDocument44 pagesCircuit DiagramMariah Jeanne De VeraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 (Equivalent Resistance)Document113 pagesChapter 02 (Equivalent Resistance)Mahra AlaliNo ratings yet
- By: Mr. Augosto M. DirectoDocument34 pagesBy: Mr. Augosto M. DirectoArt DollosaNo ratings yet
- Circuit TheoryDocument17 pagesCircuit TheoryMuhammad Anaz'sNo ratings yet
- Series Circuits Ohms LawDocument13 pagesSeries Circuits Ohms Lawidk- accNo ratings yet
- By: Mr. Augosto M. DirectoDocument34 pagesBy: Mr. Augosto M. DirectoPaul Senen DiduloNo ratings yet
- Two Types of CircuitDocument36 pagesTwo Types of CircuitRowell A. SalvatierraNo ratings yet
- Genphy2 SA2 BuquirAngel S12-05 Attempt#1Document17 pagesGenphy2 SA2 BuquirAngel S12-05 Attempt#1ANGEL BUQUIRNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Series CircuitDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Series CircuitAston ShawNo ratings yet
- Resistors in Series and Parallel101Document10 pagesResistors in Series and Parallel101Menzel GabuatNo ratings yet
- Direct-Current Circuits: Resistor ResistanceDocument5 pagesDirect-Current Circuits: Resistor ResistanceAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- Series and Parallel CircuitDocument30 pagesSeries and Parallel CircuitAmirul Syazwan100% (1)
- Electrical Circuits (Parallel) TopicDocument3 pagesElectrical Circuits (Parallel) TopicPerol YuuzouNo ratings yet
- MOD1 - Part 1-BEEEDocument22 pagesMOD1 - Part 1-BEEEBALRAM SRININo ratings yet
- Series and Parallel Circuits Experiment No. 3: Group #: - 1Document12 pagesSeries and Parallel Circuits Experiment No. 3: Group #: - 1Jomar RosalesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document8 pagesLecture 8Rohan WorkNo ratings yet
- Circuits Q1W7Document4 pagesCircuits Q1W7quackity obamaNo ratings yet
- IE 255 Equivalent ResistanceDocument12 pagesIE 255 Equivalent ResistanceDavid Pogi MenesesNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law and Kirchhoff's LawsDocument22 pagesOhm's Law and Kirchhoff's LawsTiarra MojelNo ratings yet
- Series and Parallel ConnectionDocument17 pagesSeries and Parallel ConnectionVitaliana VillaverdeNo ratings yet
- Basic DC Circuit - TKLDocument17 pagesBasic DC Circuit - TKLFaris RiyadiNo ratings yet
- Direct Current Circuits (Part 1) : General Physics 2 (Genphy280)Document25 pagesDirect Current Circuits (Part 1) : General Physics 2 (Genphy280)Mary Gold GaudiaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Series and Parallel CircuitsDocument18 pagesLesson 8 Series and Parallel Circuits23 ZACH Benjamin Isaac IV LabayenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 28A - Direct Current CircuitsDocument39 pagesChapter 28A - Direct Current CircuitsRAJESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Electric CircuitDocument39 pagesElectric CircuitRannie Ayaay Jr.No ratings yet
- Series and ParallelDocument6 pagesSeries and ParalleledessaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Week 2 Series CircuitDocument11 pages2nd Quarter Week 2 Series CircuitjNo ratings yet
- Lesson 14Document11 pagesLesson 14o.g.t.martinezjhudieljohnNo ratings yet
- DC Circuits 1Document39 pagesDC Circuits 1Julios Charl Panuncialman TagupaNo ratings yet
- BRP Bee Module 1Document15 pagesBRP Bee Module 1priyaNo ratings yet
- Department of Physics, de La Salle University 2401 Taft Avenue, Manila, Philippines 1004Document8 pagesDepartment of Physics, de La Salle University 2401 Taft Avenue, Manila, Philippines 1004student10100No ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 - AC - QNDocument7 pagesTutorial 2 - AC - QNdavisvun8No ratings yet
- ELE 3305 Power Supply DesignDocument23 pagesELE 3305 Power Supply DesignMuhammad SalisNo ratings yet
- WEEK 7 Module - CircuitsDocument6 pagesWEEK 7 Module - CircuitsSatsuki MomoiNo ratings yet
- Parallelcircuit 130428172536 Phpapp02Document17 pagesParallelcircuit 130428172536 Phpapp02api-269906432No ratings yet
- Terminal VoltageDocument8 pagesTerminal VoltageJun PerezNo ratings yet
- ch18 - Lecture 1 S06Document7 pagesch18 - Lecture 1 S06NurulWardhani11No ratings yet
- BEE Module 2 Series and Parallel NetworksDocument36 pagesBEE Module 2 Series and Parallel NetworksHawin ChitNo ratings yet
- Schmitt Trigger, Multivibrator Circuits Lab ReportDocument11 pagesSchmitt Trigger, Multivibrator Circuits Lab ReportPriya S0% (1)
- Solve The Following in Each Circuit:: T 1 2 3 T T T T T 2 T 2Document2 pagesSolve The Following in Each Circuit:: T 1 2 3 T T T T T 2 T 2Crystal Joy EduriaNo ratings yet
- Prelab Louise Tang Shi Yuan CE210002 Ts. Wan Nur Hafsha Binti Wan KhairuddinDocument11 pagesPrelab Louise Tang Shi Yuan CE210002 Ts. Wan Nur Hafsha Binti Wan KhairuddindharwinNo ratings yet
- DC CircuitsDocument34 pagesDC CircuitsPeach BubbleNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Work No. 2: Series Circuits and Parallel CircuitsDocument11 pagesLaboratory Work No. 2: Series Circuits and Parallel CircuitsARJAYCHRISTOPHER MORALESNo ratings yet
- Series Parallel L Study GuideDocument2 pagesSeries Parallel L Study GuideCris JacksonNo ratings yet
- Series and Parallel NetworksDocument6 pagesSeries and Parallel NetworksNorest SitchaNo ratings yet
- V = IR = (2A) (8Ω) =16V: - Chapter 17 & 18 - Practice ProblemsDocument3 pagesV = IR = (2A) (8Ω) =16V: - Chapter 17 & 18 - Practice ProblemsNeda SpasojevićNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- 2021 Sept 10 SATEC Parent Letter School OpeningDocument2 pages2021 Sept 10 SATEC Parent Letter School OpeningAyush PatelNo ratings yet
- Invention Project ItemsDocument4 pagesInvention Project ItemsAyush PatelNo ratings yet
- Historical Thinking Concept #4 - Cause and ConsequenceDocument2 pagesHistorical Thinking Concept #4 - Cause and ConsequenceAyush PatelNo ratings yet
- Prepared by Rufus StewartDocument7 pagesPrepared by Rufus StewartAyush PatelNo ratings yet
- How The Three Phase System Voltages Are Derived With Respect To ABC and CBA SequenceDocument13 pagesHow The Three Phase System Voltages Are Derived With Respect To ABC and CBA SequenceRyan CortesNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical Engineering, PCE, Nagpur: Thanks For Filling OutDocument5 pagesDepartment of Electrical Engineering, PCE, Nagpur: Thanks For Filling OutJAYANT BORDENo ratings yet
- HV9910BDB7 HV9910B PFC 40W LED Driver Demoboard: Specifications General DescriptionDocument5 pagesHV9910BDB7 HV9910B PFC 40W LED Driver Demoboard: Specifications General DescriptionNT372No ratings yet
- EHB465E Lecture 4 - Electromagnetic OpticsDocument12 pagesEHB465E Lecture 4 - Electromagnetic OpticsfrknNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Shielded MV Power CableDocument3 pagesFundamentals of Shielded MV Power CableLedred1No ratings yet
- As Run Sheet PQR 051 PDF FreeDocument14 pagesAs Run Sheet PQR 051 PDF Freeel_sharkawy2011No ratings yet
- Pengujian Generator Dan Operasi GeneratorDocument4 pagesPengujian Generator Dan Operasi Generatoravika anjaniNo ratings yet
- Aa9j PDFDocument67 pagesAa9j PDFNazar ChizhNo ratings yet
- PFC Small SignalDocument14 pagesPFC Small SignalMeral MeralNo ratings yet
- Yr1030 en (Draft)Document10 pagesYr1030 en (Draft)Cường Mchw100% (1)
- Ec6304-Electronic Circuits - I Iii Semester Ece Two Marks Questions and Answers EC6304 - Electronic Circuits - IDocument33 pagesEc6304-Electronic Circuits - I Iii Semester Ece Two Marks Questions and Answers EC6304 - Electronic Circuits - IgayathriNo ratings yet
- Toshiba Rd-xv48dtkb SMDocument124 pagesToshiba Rd-xv48dtkb SMmarshall tmNo ratings yet
- ATX Forward 1 PC PowerDocument36 pagesATX Forward 1 PC PowerAntonio Jose Rodriguez AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- What Is Back EMF in A DC Motor - Circuit GlobeDocument13 pagesWhat Is Back EMF in A DC Motor - Circuit GlobeRuwaim KmmNo ratings yet
- DSW PRK95 B02e enDocument2 pagesDSW PRK95 B02e enArthur Rueda CastilloNo ratings yet
- Model 201 Pressure Transducer: Very Low Differential Gauge PressureDocument2 pagesModel 201 Pressure Transducer: Very Low Differential Gauge PressurewjawichNo ratings yet
- SIEMENS Rev24rf Instruction ManualDocument2 pagesSIEMENS Rev24rf Instruction ManualHumberto AcostaNo ratings yet
- ET7014-Application of MEMS TechnologyDocument11 pagesET7014-Application of MEMS TechnologymaryNo ratings yet
- MPL15SXDocument5 pagesMPL15SXDragos ComanNo ratings yet
- EGCP-3 Engine Generator Control Package: Operation ManualDocument230 pagesEGCP-3 Engine Generator Control Package: Operation Manualcyrus6_998128No ratings yet
- SAGC 3rd Published Version December 2021Document222 pagesSAGC 3rd Published Version December 2021Hamza BousbiaNo ratings yet
- Control Components SiemensDocument9 pagesControl Components SiemensCris DucusinNo ratings yet
- DevicesDocument116 pagesDevicesresearch4maniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Electric Charges and FieldsDocument26 pagesChapter 1 - Electric Charges and FieldsRavi Inder Singh SandhuNo ratings yet
- Ame 3L Experiment 5 To Perform Speed Control of DC Motor by Using Ward-Leonard Method of Speed Control AIMDocument12 pagesAme 3L Experiment 5 To Perform Speed Control of DC Motor by Using Ward-Leonard Method of Speed Control AIMCeline Kate BentayaoNo ratings yet
- bss84 TaitronDocument8 pagesbss84 TaitronGlam BarberiaNo ratings yet
- Radar Transmitters and 2Document8 pagesRadar Transmitters and 2mas3565560No ratings yet