Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cartography Terms
Uploaded by
John Alester De Guzman0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views10 pagesThis document contains definitions of 137 cartography terms related to map projections, map features, map types, and other aspects of cartography. It defines common map projection types like Mercator, Lambert Conformal, and Azimuthal projections. It also defines common map elements, such as graticules, contours, spot heights, and grid systems. Finally, it provides definitions for different types of thematic maps including topographic, bathymetric, aeronautical, and statistical maps.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains definitions of 137 cartography terms related to map projections, map features, map types, and other aspects of cartography. It defines common map projection types like Mercator, Lambert Conformal, and Azimuthal projections. It also defines common map elements, such as graticules, contours, spot heights, and grid systems. Finally, it provides definitions for different types of thematic maps including topographic, bathymetric, aeronautical, and statistical maps.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views10 pagesCartography Terms
Uploaded by
John Alester De GuzmanThis document contains definitions of 137 cartography terms related to map projections, map features, map types, and other aspects of cartography. It defines common map projection types like Mercator, Lambert Conformal, and Azimuthal projections. It also defines common map elements, such as graticules, contours, spot heights, and grid systems. Finally, it provides definitions for different types of thematic maps including topographic, bathymetric, aeronautical, and statistical maps.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
Download the Android app!
Cartography Terms 137 terms by kaquisado
Scatter
Map Projection Any regular set of parallel and
meridians upon which a map can be
drawn
Equal-area Projection Projection where shape of any small
area remains unchanged
Transverse Projection Projection where turned right angles
to their usual orientation
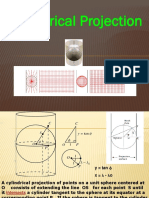
Cylindrical Projection Projection that is equi-rectangular and
one of the simplest, composed of
horizontal parallels and vertical
meridians. All loxodromes are straight
lines, used for nautical charts
Conical Projection Projections derived from projecting
parallel and meridians of a globe
upon a tangent or secant cone and
developing the cone into a plane.
Suitable for mapping geographical
features located in middle latitudes
Mercator Projection (Cylindrical One of most famous and widely used
Projection) projection, designed for sea
navigation. Great distortion beyond
70deg latitude. Used in mapping area
of predominantly EW. Least suitable
for general use in office. Straight lines
show true direction
Gall Projection (Cylindrical Projection) Projection derived from cylinder
cutting spheres at 45 deg N/S
parallels. Useful for showing
distribution of climatic, economic and
population data.
Miller Projection (Cylindrical Projection that resembles Mercator
Projection) but shows less exaggeration of area in
higher latitudes
Azimuthal Projection Projections where directions of all
lines radiating from center of map
have same directions as
corresponding lines on surface of
earth. Limitation is only one
hemisphere can be portrayed at a
time
Cassini Projection (Cylindrical Projection constructed by computing
Projection) lengths of arc along selected meridian
and plotting these as rectangular
coordinates in a plane
Lambert Conformal Projection Projection used for predominantly
(Conical Projection) EW, scale fixed by NS limitation
chosen
Polyconic Projection Projection used for predominantly NS,
all meridians curved except central
meridian. Error increase as you go
further from central meridian. Used
by LMB.
Aphylactic Projection Projection that is neither conformal
nor equal-area. Modified Equal-area
Gnomonic Projection Rays of projection originate from
center of earth and is tangent to the
equator. Used for navigation by
transpolar or trans-oceanic routes.
Orthographic Projection Rays of projection are parallel and
perpendicular to a plane tangent to a
plane
Stereographic Projection Rays of projection originate from a
point on the surface of the sphere
onto the plane
Altitude Tint (Layer Tint) Sequence of color, marking zones of
elevation between successive contour
lines
Graticules Network of lines of latitude
Fix Reference element such as line or
plane to which position of others are
related
Neatlines Inner border of a map
Tick Short line perpendicular to neatline
marking grid systems
Register Mark Pinpoint or crosses by which color
separation drawings are adjusted to
each other
Relative Relief Heights of hills and mountains over
adjacent valleys, basins or plains
Shadient Relief Plastic shading combined with
altitude tints
Contour Imaginary line on ground, all points of
which are at same elevation. Closed
backward contour lines indicate
depression
Hachures Short lines which run parallel to dip of
slope. Steeper the slope, heavier the
line
Shades Relative darkness of gray tone
Tone Relative darkness of gray
Halftone Shade between black and white
Tint Color gradiations on map
Moire Formation of regular light and dark
patches by interference of 2 halftone
screens
Grid Network of 2 sets of regularly spaced
straight lines normal to each other
Isogonic Lines with equal magnetic declination
Isopleths Lines drawn on maps connecting
points of equal value
Symbols Designs on maps used to represent
various features
Spot height Point whose elevation is noted on
map
Vanishing point Point in perspective where parallel
lines meet
Fiducial Mark Used to locate geometric center or
principal point of photo
Principal Point Point in the focal plane intersected by
optical axis of the lens
Focal length Distance between rear nodal point of
lens and focal plane
Short focal length Distance between rear nodal point of
lens and focal plane less than 305 mm
Long focal length Distance between rear nodal point of
lens and focal plane more than 305
mm
Maps Selective, symbolized and generalized
picture
Planimetric Map Map not showing relief. Shows
boundaries and subdivisions of tract
of land determined by surveying
Isoplets Small or medium scale map showing
nature of relief by semi-pictorial
symbols
Topographic Map General map showing all important
features, including relief
Thematic Map Map that shows the base map plus
economic information
Bedrock Map Shows geologic formation either
exposed or overlain by surface
deposits
Statistical Map Showing distribution of rainfall
acreage, represented by means of
dots, isopleths
Isopach Map Shows thickness of specific
stratigraphic interval by using isopach
thickness contours
Lithofacies Map Shows rock types in stratigraphic unit
Tectonic Map Display actual or projected surface
resulting from structural elements
such as fault planes
Hypsometric Map Map showing land or submarine
bottom relief in terms of height above
a datum at any contour, hachures and
shading
Chorographic Map Representing large regions, countries
or continents on a small scale
Bathymetric Map Topographic map of the sea
Chart Map for navigation in air or water
Gnomonic Chart Great circle chart
Aeronautical Chart Used for air navigation
Spread between end distance of Letters on map such as countries,
respective area mountains etc. are ______
Normal spacing of letterings in maps ______ less than width of normal
is letters
Gothic Lettering used in map representing
relief features
Orthomorphic Grid Grid system that is least complicated
British Grid Grid system used when area to be
mapped must be small, long and
narrow
Transverse Mercator Grid Grid system used when area is
predominantly NS. Portion of earth
between 2 selected parallels of
latitude to be horizontal slice of cone.
There is 90deg transposition of poles
to point at opposite position
Military Grid (UTM) Grid system where there is
quadrillage near equator
Brown Color used for relief of configuration
of ground surface
Green Color used for vegetation
Blue Color used for water features
Black Color used for man-made, political
subdivision, place, names, guidelines,
letterings and distances
Red Color used for longitude and latitude
Hydrography Science and art of representation of
water features on maps
Hypsography Science and art of determination
terrain relief with respect to datum
Topography Configuration or shape and
roughness of the ground
Uranography Science and art concerned with
describing and mapping the heavens.
Astronomy The branch of science that deals with
celestial objects, space, and the
physical universe as a whole.
Bathymetry Study of underwater depth of lake or
ocean floors. In other words, It is the
underwater equivalent to hypsometry
or topography.
Hypsometry The measurement of land elevation
relative to a datum
Photogrammetry Science and art of preparing maps
from photos
Orthodrome Shortest distance between points on
earth's surface which crosses
successive meridians
Loxodrome or Rhumb line Line of constant compass direction
along its length. It is spiral on a globe.
Analemma Shows the position which the sun
shine vertically at meridian when local
time is 12 noon
Vinylite Synthetic resin of great dimensional
stability, used in drawing maps
Gelatin Organic alloid, used in most
photographic emulsions
Geostenography Method of rapid notations of
geographic data
Globe gore Lune-shaped map to be fitted to a
globe
Guide copy Map which is sufficiently complete to
be given to engraver for printing
Isometric Diagram Drawing of 3D body related to 3 axes.
Dimension parallel to axes are true to
scale.
Gerardus Mercator Father of Dutch cartography,
foremost in development of modern
cartography
Charles Saxton Father of English cartography
Hipparchus Father of systematic astronomy as
well as mathematical mapping
Claudius Ptolamaeus Father of cartography
Captain William Nicholson Drawn nautical chart of Manila
unsurpassed in accuracy for 270yrs
Light Table A glass tapped table with lights
underneath the glass which is used
for copying
Offset Printing Method by the lithographic principle
in which a map is applied to kernelled
metal sheets with greasy ink
Series Maps Set of maps which are sections of
larger area, such as topo sheets
Mosaic Several air photos mounted together
to form a continuous picture of large
area
Map Compilation Several maps mounted to form a
continuous map
Proportional divider An x-shaped divider formed by joining
a pair of two-pointed arms which is
used for enlargement and reduction
Spline Devise used as tools in
projecting/plotting different curves
Pantograph Instrument for copying maps on
larger or smaller scale. Mostly are
made of roads forming a
parallelogram joined on the 4 corners
Photolithography Process consisting in making a
negative of map and contact printing
it on albumen-sensitized metal
printing plate
Photostat Design photographed directly on
sensitized paper
Pull-up Tracing of map, or part of it, on
transparent paper or plastic, done by
contact printing
Trachographic Relief Drawing Method using, curve hill shaped lines
to indicate relief on small maps
Stereoscopic Vision Method by which permits drawing
contour line by using two overlapping
air photos under stereoscopic
instrument
Scribing Engraving lines, symbol in a scribe
coating, for preparation of negative
for map production
Squeeze T-shaped tool to squeeze out
superfluous ink or any other liquid
from surface
3 Color Process Method of color reproduction using
filters and halftone screened
Planimeter Instrument used for measuring area
of map
Oblique Photography Mapping of tunnel can be done by
photogrammetric method with aid of
Philippine Insulae First map devoted exclusively to
Philippines
Ma-yi In long forgotten time, Philippines was
called by Chinese as
Carta y hydugraphica y Chorographica Best known ancient Philippine Map
de Las Islas Filipinas
Rutter Also known as nautical manual
Lens Most important part functions to
gather light rays for each point on
terrain
Normal Angle Lens Field of View less than 75
Wide Angle Lens Field of View from 75 - 100
Super Wide Lens Field of View more than 100
Single Lens Simplest type of lens, used for
mapping
Multi-Lens Has 2 or more lenses and expose 1 or
more film simultaneously
Strip Camera Used to obtain continuous photo of
strip of terrain
Camera Body Consists of one-piece casting which
houses the drive mechanism for
shutter assembly and magazine
Magazine Consists of light tight container which
holds the supply of exposed and
unexposed film
Lens Cone Assembly Contains the lens, filter, diaphragm,
nodal points and shutter
Shutter Controls the length of time that light
is permitted to pass through the lens
Diaphragm Functions is to control amount of light
striking the emulsion of film which is
positioned in focal plane
Filter Consists of pieces of colored glass
placed in front of camera lens to
prevent stray and undesirable lights
from entering camera
Viewfinder Enables continuous view of terrain
below aircraft
Camera Mount Devise which is used to attach camera
to aircraft
Intervalometer Device that automatically trip the
shutter of camera at specified time
Terrestrial Photogrammetry Taken with ground based cameras
from known positions
Aerial Photogrammetry Taken by a precision camera mounted
on an airplane
Metric Photogrammetry Refers to use of measurements made
on aerial photo to obtain quantitative
data about earth's surface
Interpretative Photogrammetry Used in recognizing and identifying
objects in photo, as well as judging
their significance
Composite Photograph Made by joining several photographs
taken at a single camera station
Extraterrestrial Photograph Emerged as result of space
exploration
Trimetrogon Photograph Has a photographic unit which
consists of 3 wide-angle-single-lens
camera
You might also like
- Geodetic Surveying CartographyDocument9 pagesGeodetic Surveying CartographyLozano HenryNo ratings yet
- Map ProjectionDocument28 pagesMap Projectionpranab ramanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Map ProjectionDocument40 pagesChapter 4 - Map Projectionሚልክያስ መናNo ratings yet
- Geodesy - TermsDocument22 pagesGeodesy - TermsJohn Alester De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- KL3103 03NauticalCharts Part2Document72 pagesKL3103 03NauticalCharts Part2Suciana100% (2)
- GIS - Lecture2 - Projection & CoordinatesDocument67 pagesGIS - Lecture2 - Projection & CoordinatesAsim RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Dersnot - 5262 - 1699425334 4Document48 pagesDersnot - 5262 - 1699425334 4Soner InanNo ratings yet
- Lec 4 - Map ProjectionsDocument64 pagesLec 4 - Map ProjectionsMurtaza MazharNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Coordinate Systems in SouthAfrica PDFDocument5 pagesAn Introduction To Coordinate Systems in SouthAfrica PDFMfanelo MbanjwaNo ratings yet
- Map Projections and Coordinate Systems: Jan-Van Sickle Khang-Tsung Chang Esri Using ArcmapDocument32 pagesMap Projections and Coordinate Systems: Jan-Van Sickle Khang-Tsung Chang Esri Using Arcmapsam13scribdNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of A GlobeDocument2 pagesCharacteristics of A GlobeAngel TsuiNo ratings yet
- Chart ProjectionDocument17 pagesChart ProjectionAmin Al QawasmehNo ratings yet
- 10.kuliah 9 CylinderProjection - PelajarDocument56 pages10.kuliah 9 CylinderProjection - PelajarILYA IZATIE100% (1)
- Map ProjectionsDocument28 pagesMap Projectionsmonika singh100% (1)
- Cylindrical ProjectionDocument7 pagesCylindrical ProjectionJuanapol ManaladNo ratings yet
- A New Notebook For Elementary SurveyDocument11 pagesA New Notebook For Elementary SurveyedwinmasaiNo ratings yet
- Cartography AssignmentDocument13 pagesCartography AssignmentAnitha MuruganNo ratings yet
- Cartography AssignmentDocument13 pagesCartography AssignmentAnitha MuruganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document14 pagesChapter 4Gamidi Suneetha Naidu100% (1)
- Projections Examples of Different Projections Coordinate Systems DatumsDocument53 pagesProjections Examples of Different Projections Coordinate Systems DatumsRajNo ratings yet
- Map ProjectionDocument9 pagesMap ProjectionchabarikadanzelNo ratings yet
- Surveying Na NagplateDocument6 pagesSurveying Na NagplateSalie OliciaNo ratings yet
- Map ProjectionDocument5 pagesMap ProjectionHazel BandayNo ratings yet
- Chart Projections PDFDocument2 pagesChart Projections PDFNikhil ReddyNo ratings yet
- Chart Projections PDFDocument2 pagesChart Projections PDFSanjay WaghmodeNo ratings yet
- 01 Co Ordinate SystemsDocument14 pages01 Co Ordinate SystemsVineetha VijayanNo ratings yet
- Azimuth ProjectionDocument32 pagesAzimuth Projectionsurvmichael16No ratings yet
- Chart Fundamentals: 300. Definitions 302. Selecting A ProjectionDocument28 pagesChart Fundamentals: 300. Definitions 302. Selecting A Projectionkitap kitapNo ratings yet
- What Are The Different Types of Map ProjectionsDocument4 pagesWhat Are The Different Types of Map ProjectionsSofia BoreroNo ratings yet
- Earth Shape and Earthwork Topographic Map Slope Form Slope Analysis GradingDocument18 pagesEarth Shape and Earthwork Topographic Map Slope Form Slope Analysis GradingNiroppama S SawantNo ratings yet
- Citsit Padl 1Document3 pagesCitsit Padl 1Rizky Agung NNo ratings yet
- Nautical Charts PDFDocument28 pagesNautical Charts PDFEng_2014100% (1)
- Mohamed Ashraf ProjectionDocument23 pagesMohamed Ashraf Projectionsanesur_emid20No ratings yet
- Prelim Week 3ADocument68 pagesPrelim Week 3AGESVIL DEJANONo ratings yet
- Map ProjectionsDocument20 pagesMap ProjectionsmikeNo ratings yet
- Chart ProjectionDocument3 pagesChart ProjectionHazel BandayNo ratings yet
- Map Projection 1Document9 pagesMap Projection 1Pankaj KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Map ProjectionsDocument2 pagesMap ProjectionsGodwillProsperSizibaNo ratings yet
- CE 559 - Lecture 3Document25 pagesCE 559 - Lecture 3county192No ratings yet
- Map ProjectionDocument45 pagesMap ProjectionKhenny25No ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document53 pagesPresentation 2Sherin KollakkodanNo ratings yet
- Coordinate SystemsDocument3 pagesCoordinate SystemsSantos DhexterNo ratings yet
- Zenithal Map ProjectionsDocument2 pagesZenithal Map ProjectionsS Afsana RahmanNo ratings yet
- Kaartpassen: 1. Chart FundamentalsDocument34 pagesKaartpassen: 1. Chart FundamentalsKaptanlar100% (2)
- 3 Properties of Map ProjectionsDocument15 pages3 Properties of Map ProjectionsOsama_Javed_7120No ratings yet
- Kuliah 3 - Coordinate System - Map ProjectionDocument33 pagesKuliah 3 - Coordinate System - Map ProjectionKevin aryaNo ratings yet
- 4.1 What Is A Map ProjectionDocument28 pages4.1 What Is A Map ProjectionAnonymous Gon7kIs100% (1)
- Chapter 2 - Geometric AspectsDocument37 pagesChapter 2 - Geometric AspectsAthirah IllainaNo ratings yet
- Carto Reviewer Les.4Document4 pagesCarto Reviewer Les.4Santos DhexterNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 4 Sistem Koordinat - Proyeksi PetaDocument40 pagesPertemuan 4 Sistem Koordinat - Proyeksi PetaKevin aryaNo ratings yet
- CartoDocument2 pagesCartoArnold FernandezNo ratings yet
- Projection System: Necessity of Map ProjectionDocument4 pagesProjection System: Necessity of Map ProjectionAsrul Syam'sNo ratings yet
- Stereographic Projection: Complex AnalysisDocument4 pagesStereographic Projection: Complex AnalysisEhsan UmerNo ratings yet
- 4 Map ProjectionsDocument38 pages4 Map ProjectionsAlex KuhudzaiNo ratings yet
- Map Proj EctionsDocument12 pagesMap Proj EctionsVarshithaNo ratings yet
- Aerial Photo and Mapping GlossaryDocument4 pagesAerial Photo and Mapping GlossaryErica OsinNo ratings yet
- Chart PojectionsDocument14 pagesChart PojectionsRay Anthony CajeloNo ratings yet
- Orthographic Projection: Exploring Orthographic Projection in Computer VisionFrom EverandOrthographic Projection: Exploring Orthographic Projection in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Isometric Projection: Exploring Spatial Perception in Computer VisionFrom EverandIsometric Projection: Exploring Spatial Perception in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Baltazar Dev - PlanDocument2 pagesBaltazar Dev - PlanJohn Alester De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Planning ModelsDocument51 pagesPlanning ModelsJohn Alester De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Inner ConstraintsDocument12 pagesInner ConstraintsJohn Alester De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- EMULSIONDocument4 pagesEMULSIONJohn Alester De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Topic 3bDocument15 pagesTopic 3bJohn Alester De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument2 pagesDecision MakingJohn Alester De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- TECHNOPRENEURSHIPDocument13 pagesTECHNOPRENEURSHIPJohn Alester De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Allama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad: (Secondary Teacher Education Department) WarningDocument2 pagesAllama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad: (Secondary Teacher Education Department) WarningAiNa KhanNo ratings yet
- Floline Size eDocument4 pagesFloline Size eNikesh ShahNo ratings yet
- 2017 - Behavioral Emergencies - Geriatric Psychiatric PatientDocument14 pages2017 - Behavioral Emergencies - Geriatric Psychiatric PatientAna María Arenas DávilaNo ratings yet
- My Personal Brand and Career GoalsDocument3 pagesMy Personal Brand and Career GoalsPhúc ĐàoNo ratings yet
- Markets and Commodity Figures: Total Market Turnover StatisticsDocument6 pagesMarkets and Commodity Figures: Total Market Turnover StatisticsTiso Blackstar GroupNo ratings yet
- Effectives of e Wallets NewDocument15 pagesEffectives of e Wallets NewRicardo SantosNo ratings yet
- The Magical Diaries of Ethel ArcherDocument7 pagesThe Magical Diaries of Ethel Archerleeghancock100% (1)
- 2016 Lesson 9Document34 pages2016 Lesson 9Junas Jr LaputNo ratings yet
- Reich 0001 PDFDocument87 pagesReich 0001 PDFYordys Domínguez RodríguezNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument6 pagesReportLâmViênNo ratings yet
- Errors Affecting The Trial BalanceDocument3 pagesErrors Affecting The Trial BalanceDarwin Lopez100% (1)
- STAS 111 - Information AgeDocument20 pagesSTAS 111 - Information AgeMayeee GayosoNo ratings yet
- The Case For A Concentrated Portfolio 6-30-16Document4 pagesThe Case For A Concentrated Portfolio 6-30-16Maria Gabriela PopaNo ratings yet
- Robot Structural Analysis 2017 Help - Push Over Analysis ParametersDocument3 pagesRobot Structural Analysis 2017 Help - Push Over Analysis ParametersJustin MusopoleNo ratings yet
- Arizona History and Social Science StandardsDocument57 pagesArizona History and Social Science StandardsKJZZ PhoenixNo ratings yet
- Thesis TopicsDocument9 pagesThesis TopicsInayath AliNo ratings yet
- Shyla Jennings Ebook FinalDocument17 pagesShyla Jennings Ebook FinalChye Yong HockNo ratings yet
- The Lion and The Boar Story EnglishDocument2 pagesThe Lion and The Boar Story EnglishKemal AmarullahNo ratings yet
- Sistem Informasi Pencatatan Data Pelanggan Pada Telkomsel Grapari Banda AcehDocument6 pagesSistem Informasi Pencatatan Data Pelanggan Pada Telkomsel Grapari Banda AcehJurnal JTIK (Jurnal Teknologi Informasi dan Komunikasi)No ratings yet
- October 2014 1413376166 06 PDFDocument3 pagesOctober 2014 1413376166 06 PDFDineshNo ratings yet
- CREW Whitaker Recusal Letter DOJ 11-8-2018Document9 pagesCREW Whitaker Recusal Letter DOJ 11-8-2018Beverly TranNo ratings yet
- Maulana Azad Library, Aligarh Muslim UniversityDocument38 pagesMaulana Azad Library, Aligarh Muslim Universitybijesh babuNo ratings yet
- RLB Procuring For Value 18 July PDFDocument56 pagesRLB Procuring For Value 18 July PDFDaniel LixandruNo ratings yet
- 10 Rules of Statcon by Atty Marcus NeelyDocument4 pages10 Rules of Statcon by Atty Marcus NeelyMorin OcoNo ratings yet
- Entrep Module 4 Q1 Week 4 1Document14 pagesEntrep Module 4 Q1 Week 4 1VirplerryNo ratings yet
- Rpms Template Master Teacher Design 30Document45 pagesRpms Template Master Teacher Design 30evan olanaNo ratings yet
- R Don Steele - How To Date Young Women For Men Over 35Document232 pagesR Don Steele - How To Date Young Women For Men Over 35gonzalo_barandiarán83% (6)
- Openstack Deployment Ops Guide PDFDocument197 pagesOpenstack Deployment Ops Guide PDFBinank PatelNo ratings yet
- LEASE CONTRACT Taytay Residentialhouse Kei Inagaki Nena TrusaDocument6 pagesLEASE CONTRACT Taytay Residentialhouse Kei Inagaki Nena TrusaJaime GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Global Strategy 3rd Edition Peng Solutions ManualDocument16 pagesGlobal Strategy 3rd Edition Peng Solutions ManualJenniferThompsonxergb100% (13)