Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ee 17
Ee 17
Uploaded by
GOT7 for 70 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesThe document discusses ascites, which is a complication caused by an increase in hydrostatic pressure or decrease in colloid osmotic pressure due to underlying conditions like cirrhosis, congestive heart failure, or partial obstruction of the common bile duct. It notes that ascites itself is not an illness, but rather a consequence of an established underlying disease. The pathophysiology section then lists specific causes of increased hydrostatic pressure or decreased colloid osmotic pressure that can lead to ascites.
Original Description:
Original Title
ee17
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses ascites, which is a complication caused by an increase in hydrostatic pressure or decrease in colloid osmotic pressure due to underlying conditions like cirrhosis, congestive heart failure, or partial obstruction of the common bile duct. It notes that ascites itself is not an illness, but rather a consequence of an established underlying disease. The pathophysiology section then lists specific causes of increased hydrostatic pressure or decreased colloid osmotic pressure that can lead to ascites.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesEe 17
Ee 17
Uploaded by
GOT7 for 7The document discusses ascites, which is a complication caused by an increase in hydrostatic pressure or decrease in colloid osmotic pressure due to underlying conditions like cirrhosis, congestive heart failure, or partial obstruction of the common bile duct. It notes that ascites itself is not an illness, but rather a consequence of an established underlying disease. The pathophysiology section then lists specific causes of increased hydrostatic pressure or decreased colloid osmotic pressure that can lead to ascites.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
may cause extravasation of fluids
Sodium retention
Peritoneal inflammation
In most cases, ascites appears as part of a well-recognized illness, such as:
Cirrhosis
Congestive heart failure
Nephrosis
Disseminated carcinomatosis
Note: Ascites in itself is not an illness but a complication of an established illness. The
physician should determine that the development of ascites is a consequence of the
basic underlying disease and not due to the presence of a separate or related disease
process (Harrison’s).
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Increased hydrostatic pressure
Cirrhosis
Hepatic vein occlusion (Budd-Chiari syndrome)
IVC obstruction
Constrictive pericarditis
Congestive heart failure
Decreased colloid osmotic pressure
in patients with
Partial obstruction of the common bile duct
Cirrhosis or primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), where scarring prevents intrahepatic
ducts from dilating
If you look at the imaging, there shouldn’t have space between the liver and the right
kidney
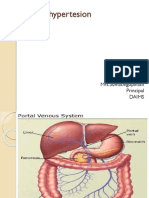
Most common: portal hypertension
Better than ultrasonography
Assessing head of pancreas
Indentifying choledocholithiasis in distal common bile duct
When ducts are not dilated
ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography)
“Gold Standard” for identifying choledocholithiasis
Used to make diagnosis of primary sclerosing cholangitis
Pathognomonic findings are multiple strictures of bile ducts with dilatations proximal to
strictures
Approximately 75% of patients with PSC have IBD
You might also like
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtFrom EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- PericarditisDocument52 pagesPericarditissanjivdasNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Heart DiseaseDocument8 pagesNeonatal Heart DiseaseDelphy VargheseNo ratings yet
- Portal HypertensionDocument11 pagesPortal Hypertensionsaeid seyedraoufiNo ratings yet
- Canine AscitesDocument7 pagesCanine AscitesGabriel Coelho GimenesNo ratings yet
- Sirosis KardiakDocument11 pagesSirosis KardiakKusno TriantoNo ratings yet
- AscitesascitesDocument15 pagesAscitesascitesKevinJuliusTanadyNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Medicine Unit 1Document95 pagesPresented By: Medicine Unit 1Abdullah Muceddidi100% (1)
- Edem Bhs InggrisDocument6 pagesEdem Bhs InggrisSyahdat NurkholiqNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Disease: Hema Rajendran B.SC (N) NICU Staff NurseDocument23 pagesCongenital Heart Disease: Hema Rajendran B.SC (N) NICU Staff NurseddNo ratings yet
- A Congenital Heart DefectDocument3 pagesA Congenital Heart DefectMarc Renz R. ChanNo ratings yet
- UW Step 2 CK IM GIDocument146 pagesUW Step 2 CK IM GISelena GajićNo ratings yet
- Portal Hypotension: Clinical AssignmentDocument8 pagesPortal Hypotension: Clinical AssignmentM shayan JavedNo ratings yet
- JURNAL Ascites PDFDocument9 pagesJURNAL Ascites PDFican_parlenteNo ratings yet
- Case Study PPT Patho NLNGDocument36 pagesCase Study PPT Patho NLNGKate ChavezNo ratings yet
- Pleural Effusion: Zubeir Ahmed BareDocument30 pagesPleural Effusion: Zubeir Ahmed BareAnisa Osman HassanNo ratings yet
- Portal HypertensionDocument23 pagesPortal HypertensionSumathi GopinathNo ratings yet
- Cardiac TamponadeDocument14 pagesCardiac Tamponadeirenekhatete1No ratings yet
- Pericardial EffusionDocument3 pagesPericardial EffusionNita Hurek100% (1)
- Portal HypertensionDocument23 pagesPortal HypertensionSumathi Gopinath100% (1)
- Cardiac TamponadeDocument10 pagesCardiac Tamponadetitusrop10No ratings yet
- CHF Left SidedDocument21 pagesCHF Left SidedSandie Daniel GabalunosNo ratings yet
- DD 16Document1 pageDD 16GOT7 for 7No ratings yet
- Portal HypertensionDocument41 pagesPortal HypertensionZia MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Coarctation of AortaDocument40 pagesCoarctation of Aortaaalok1903No ratings yet
- Obstructive ShockDocument2 pagesObstructive ShockningshofieNo ratings yet
- Ascites: Peritoneal Cavity MedicalDocument4 pagesAscites: Peritoneal Cavity MedicalVenkatesan VidhyaNo ratings yet
- Budd-Chiari SyndromeDocument4 pagesBudd-Chiari SyndromeKei Adam KurataNo ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument13 pagesHeart Failuremildred alidon100% (2)
- Ehad 883Document3 pagesEhad 883nhunhuochachNo ratings yet
- Pathohysiology of Ascites: Waleed Al-HamoudiDocument36 pagesPathohysiology of Ascites: Waleed Al-Hamoudiarina31No ratings yet
- Portal Hypertension in Adults - UpToDateDocument14 pagesPortal Hypertension in Adults - UpToDateEdwin VileloNo ratings yet
- Written Report in Edema: Physio IDocument6 pagesWritten Report in Edema: Physio IPaula ColeenNo ratings yet
- CardiologyDocument37 pagesCardiologyandreaNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis: DR AkhondeiDocument111 pagesCirrhosis: DR AkhondeiMuvenn KannanNo ratings yet
- Portal HypertensionDocument13 pagesPortal HypertensionEmmaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Aspect of Heart FailureDocument67 pagesClinical Aspect of Heart FailureAri Bandana TasrifNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cirrhosis - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument6 pagesCardiac Cirrhosis - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfKardiologi ManadoNo ratings yet
- Ed Ascites PDFDocument47 pagesEd Ascites PDFradicalmpNo ratings yet
- PericarditisDocument6 pagesPericarditisRaymundo RyanNo ratings yet
- Background: Congestive Heart FailureDocument5 pagesBackground: Congestive Heart FailureyasayyasayNo ratings yet
- ucu-CHDs 240114 230618Document68 pagesucu-CHDs 240114 230618BrianNo ratings yet
- All in BriefDocument8 pagesAll in BriefAikoP.NarcisoNo ratings yet
- KUIPER Et Al-2007-Alimentary Pharmacology & TherapeuticsDocument11 pagesKUIPER Et Al-2007-Alimentary Pharmacology & TherapeuticsJhonatan Efrain Lopez CarbajalNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DiseasesDocument121 pagesCongenital Heart DiseasesJayvee V. De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DiseasesDocument27 pagesCongenital Heart DiseasesJumar ValdezNo ratings yet
- B.SC Nursing Medical Surgical Nursing - I Unit: Iv - Nursing Management of Patients With Disorders of Digestive System Portal HypertensionDocument32 pagesB.SC Nursing Medical Surgical Nursing - I Unit: Iv - Nursing Management of Patients With Disorders of Digestive System Portal HypertensionPoova RagavanNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cirrhosis. Congestive Hepatopathy With Large Renal VeinDocument13 pagesCardiac Cirrhosis. Congestive Hepatopathy With Large Renal VeinmayaNo ratings yet
- PericarditisDocument19 pagesPericarditisxmitchxNo ratings yet
- DR Ali Cardiology-MergedDocument684 pagesDR Ali Cardiology-MergedK PradhanNo ratings yet
- Conginital Heart DiseaseDocument19 pagesConginital Heart DiseaseSanthosh.S.UNo ratings yet
- CHFSP 2005Document36 pagesCHFSP 2005Andy F MonroeNo ratings yet
- Esophageal-Varices 20240201 124908 0000Document25 pagesEsophageal-Varices 20240201 124908 0000Eurika P OrolfoNo ratings yet
- LME SelfDocument5 pagesLME SelfJM Mizraime Gallo Dela-peñaNo ratings yet
- PericarditisDocument3 pagesPericarditisKhalid Mahmud Arifin0% (1)
- (I..) KMU Peads CardicDocument88 pages(I..) KMU Peads CardicMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Gangguan Sistem Kardiovaskuler Pada AnakDocument29 pagesGangguan Sistem Kardiovaskuler Pada AnakMuhamadsafeiNo ratings yet
- I. Acute Heart Failure: What Every Physician Needs To KnowDocument13 pagesI. Acute Heart Failure: What Every Physician Needs To KnowRubie Ann TillorNo ratings yet
- Portal Hypertension, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandPortal Hypertension, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- FFF 19Document1 pageFFF 19GOT7 for 7No ratings yet
- FFF 6Document1 pageFFF 6GOT7 for 7No ratings yet
- FFF 16Document1 pageFFF 16GOT7 for 7No ratings yet
- Ee 27Document1 pageEe 27GOT7 for 7No ratings yet
- Ee 25Document1 pageEe 25GOT7 for 7No ratings yet
- Ee 37Document1 pageEe 37GOT7 for 7No ratings yet
- Ee 12Document2 pagesEe 12GOT7 for 7No ratings yet
- Ee 36Document2 pagesEe 36GOT7 for 7No ratings yet
- FFF 4Document1 pageFFF 4GOT7 for 7No ratings yet
- FFF 9Document1 pageFFF 9GOT7 for 7No ratings yet
- FFF 12Document1 pageFFF 12GOT7 for 7No ratings yet
- Ee 31Document1 pageEe 31GOT7 for 7No ratings yet
- FFF 7Document1 pageFFF 7GOT7 for 7No ratings yet
- Ee 20Document1 pageEe 20GOT7 for 7No ratings yet
- Ee 22Document2 pagesEe 22GOT7 for 7No ratings yet
- Ee 10Document1 pageEe 10GOT7 for 7No ratings yet
- DD 38Document1 pageDD 38GOT7 for 7No ratings yet
- Ee 15Document1 pageEe 15GOT7 for 7No ratings yet
- Ee 18Document2 pagesEe 18GOT7 for 7No ratings yet
- DD 26Document1 pageDD 26GOT7 for 7No ratings yet
- Ee 9Document1 pageEe 9GOT7 for 7No ratings yet
- Ee 13Document2 pagesEe 13GOT7 for 7No ratings yet
- Ee 1Document1 pageEe 1GOT7 for 7No ratings yet
- DD 33Document1 pageDD 33GOT7 for 7No ratings yet
- Ee 7Document1 pageEe 7GOT7 for 7No ratings yet
- DD 21Document1 pageDD 21GOT7 for 7No ratings yet
- DD 18Document1 pageDD 18GOT7 for 7No ratings yet
- DD 34Document1 pageDD 34GOT7 for 7No ratings yet
- DD 16Document1 pageDD 16GOT7 for 7No ratings yet
- DD 24Document1 pageDD 24GOT7 for 7No ratings yet