Professional Documents
Culture Documents
مفاهيم التطبيقات 2 - ث)
Uploaded by
mi172kaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
مفاهيم التطبيقات 2 - ث)
Uploaded by
mi172kaCopyright:
Available Formats
ورقة مفاهيم تطبيقات الرياضيات للصف الثانى الثانوى الفصل الدراسى االول
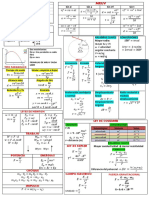
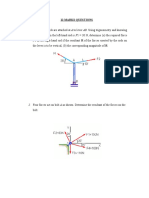
The result of the two forces ⃑⃑
𝒇𝟏 , ⃑⃑⃑⃑⃑
𝒇𝟐 meeting at a point 𝑓⃑2
𝑅⃑⃑
𝑅 2 = 𝐹12 + 𝐹22 + 2𝐹1 𝐹2 cos ∝
where ∝ is the angle between two forces α
𝑭𝟐 𝐬𝐢𝐧∝
𝑓⃑1
𝐭𝐚𝐧 𝜽 = where 𝜃 is the angle between R and first force
𝑭𝟏 +𝑭𝟐 𝐜𝐨𝐬∝
𝑭𝟐
1]if ∝= 90° ∴ 𝑹 = √𝑭𝟐𝟏 + 𝑭𝟐𝟐 , 𝐭𝐚𝐧 𝜽 =
𝑭𝟏
∝ ∝
2 ]𝑖𝑓 𝐹1 = 𝐹2 = 𝐹 ∴ 𝑹 = 𝟐𝑭 𝐜𝐨𝐬 , 𝜽 =
𝟐 𝟐
3] if ∝= 0 maximum force ∴ 𝑹 = 𝑭𝟏 + 𝑭𝟐
4 ]𝑖𝑓 ∝= 180 minimum force ∴ 𝑹 = |𝐹1 − 𝐹2 |
𝑦
Resolution of a force into two components
𝑅 sin θ2 𝑅 sin θ1
𝐹1 = , 𝐹2 = 𝑓⃑2
sin(θ1 +θ2 ) sin(θ1 +θ2 )
𝑅⃑⃑
𝑓⃑1
Resolution of a force into two perpendicular directions. in an inclined plane
F2
𝐹1 = 𝑅 cos 𝜃 , F2 Ө F1
𝐹2 = 𝑅 sin 𝜃 𝜃 F1 𝐹1 = 𝑤 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜃 , 𝐹2 = 𝑤 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃
The resultant of coplanar forces meeting at a point
𝑅⃑⃑ = (∑r 𝐹𝑟 cos θr )𝑖̂ + (∑r 𝐹𝑟 sin θr )𝑗̂ 𝑖̂ = (1,0) , 𝑗̂ = (0,1)
𝑦
𝑅⃑⃑ = 𝑥𝑖̂ + 𝑦𝑗̂ 𝑅 = √𝑥 2 + 𝑦 2 , tan 𝜃 =
𝑥
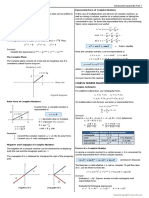
If a body is in equilibrium under the effect of three forces meeting at a point,
then the magnitude of each force is proportional to the sine of the angle
between the two other forces
F2 F1 F2 F1
Lam`s rule: Ө3
𝑓1 𝑓 𝑓3 Ө1 Ө2
= 2 = Ө1 Ө2 Or we can use lami`s rule as follows
sin 𝜃1 sin 𝜃2 sin 𝜃3
𝑓1 𝑓2 𝑓3
F3 = =
sin 𝜃1 sin 𝜃2 sin(𝜃1 +𝜃2 )
F3
"The triangle of force rule" B
F1
𝑓1 𝑓2 𝑓3 A
= = F2
AB 𝐵𝐶 𝐶𝐴 F3
C
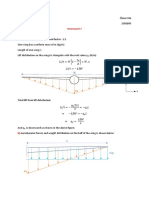
The equilibrium of a body on an inclined plane
R F F R
R
α
𝜃
F
θ
θ θ
𝜔
𝜔 𝜔
F in the direction of the f inclined on the greatest f is a horizontal
force Greatest slope slope by angle α
𝑅 𝐹 𝑤 𝑅 𝐹 𝑤 𝑅 𝐹 𝑤
= sin(180−𝜃) = sin(90) = sin(180−𝜃) = sin(90−𝛼) = sin(180−𝜃) = sin(90+𝜃)
sin(90+𝜃) sin(90+𝜃+𝛼) sin(90)
Solids
1
Lateral area of the pyramid = base perimeter x its slant height.
2
1
= perimeter of ABCDH x MX
2
Total area of the pyramid = its lateral area + its base area.
1
Volume of pyramid = x area of its base x its height.
3
1
= x area of ABCDH x MN
3
Lateral area of the right cone = 𝜋 L r,
where L is the length of the cone drawer
r is the length of its base radius.
Total area of the right cone = 𝜋 Lr +𝜋 r2 = 𝜋 r ( L + r)
1
Volume of cone = x area of its base x its height
3
Equation of a circle The equation is a circle whose centre the point (d , h), and
the length of its radius equal r is: (x - d)2 + (y - h)2 = r2
The general form of the equation of a circle its centre is the point (-L , -K), and
the length of its radius r is: x2 +y2 + 2Lx + 2ky + C = 0,
where r = √L2 + k 2 − C , L2 + k2 - C > 0
First verify to put the equation in the general form where the coefficient of x 2
= coefficient of y2 = unity.
r = (-L , - k) = ( -coefficient of x2 , - coefficient of y2)
You might also like
- 7and 8th Semester SCJan5Document48 pages7and 8th Semester SCJan5Maharghya BiswasNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamic Forces and MomentsDocument21 pagesAerodynamic Forces and Momentsاحمد عبد الله طنطاوى عبد الرحمن طنطاوى، 3615No ratings yet
- Components, Moment and Resultant of Spatial ForcesDocument10 pagesComponents, Moment and Resultant of Spatial ForcesBeverly Ann GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Songle Not A BotDocument36 pagesSongle Not A BotAyuguNo ratings yet
- Fluid CH-4Document5 pagesFluid CH-4Rebar QadrNo ratings yet
- SRB - Lecture 18 - Forces in Space (11!23!2023)Document27 pagesSRB - Lecture 18 - Forces in Space (11!23!2023)2022102538No ratings yet
- CaseDocument3 pagesCaseZeeshan MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Stress Elements: Hamrock - Fundamentals of MachineelementsDocument20 pagesStress Elements: Hamrock - Fundamentals of Machineelementsmohmmad saadNo ratings yet
- Sph4ue - Formula Sheet 2023Document2 pagesSph4ue - Formula Sheet 2023speedyz3377No ratings yet
- Rectangular Components of ForceDocument6 pagesRectangular Components of ForceAgri EngNo ratings yet
- 1 L2 Basic Interference (Step by Step) v.2Document7 pages1 L2 Basic Interference (Step by Step) v.2Vincent TionoNo ratings yet
- KSSM Physics Formula @Lin@Im@n@RifDocument39 pagesKSSM Physics Formula @Lin@Im@n@RifChew YiheNo ratings yet
- Math101 - Mathematics For Engineers: Plane and Spherical Trigonometry College Algebra Solid MensurationDocument3 pagesMath101 - Mathematics For Engineers: Plane and Spherical Trigonometry College Algebra Solid Mensurationrmm0415No ratings yet
- Antenna Lect4Document22 pagesAntenna Lect4fadwaalhadereeNo ratings yet
- Mechanics FormulasDocument5 pagesMechanics FormulasMarvin Dale WongNo ratings yet
- 6351PHY3 Unit 3 Cheat SheetDocument2 pages6351PHY3 Unit 3 Cheat Sheetmonika durairajNo ratings yet
- Moment of A ForceDocument4 pagesMoment of A ForceReeseNo ratings yet
- AERO213: Aeroengines: AERO213 School of Engineering DR David JC DennisDocument9 pagesAERO213: Aeroengines: AERO213 School of Engineering DR David JC DennisAhmed ElgamalNo ratings yet
- AERO213 MockExam2022Document9 pagesAERO213 MockExam2022JordanNo ratings yet
- Permittivity in Free Space (Shift Constant 1 4) Permeability in Free Space (Shift Constant 1 5)Document10 pagesPermittivity in Free Space (Shift Constant 1 4) Permeability in Free Space (Shift Constant 1 5)Jizelle JumaquioNo ratings yet
- MomentumDocument10 pagesMomentumdinurjNo ratings yet
- Stern-Gerlach Experiment-1921Document4 pagesStern-Gerlach Experiment-1921Madhu SudanNo ratings yet
- HT Equation SheetDocument8 pagesHT Equation SheetJohn GassonNo ratings yet
- 4.0 Harmonics - Fourier Transform IndicesDocument25 pages4.0 Harmonics - Fourier Transform IndicesHariz MuzaffarNo ratings yet
- Friction Clutches 2020 CompressedDocument14 pagesFriction Clutches 2020 Compressedfikadu435No ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions 2019Document10 pagesTrigonometric Functions 2019LeviNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-1Document51 pagesLecture 2-1ToshiNo ratings yet
- Heat Released (Exo) Heat Absorbed (Endo)Document2 pagesHeat Released (Exo) Heat Absorbed (Endo)Claire RallosNo ratings yet
- Difrraction 06-12-2022Document44 pagesDifrraction 06-12-2022Mahesh KhadarwadkarNo ratings yet
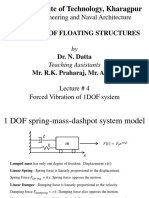
- Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur: Ocean Engineering and Naval ArchitectureDocument10 pagesIndian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur: Ocean Engineering and Naval ArchitectureSuraj GaikwadNo ratings yet
- 2022 - SynthèseDocument9 pages2022 - SynthèseThéo MélotteNo ratings yet
- Thales TheoremDocument4 pagesThales TheoremSHK-NiaziNo ratings yet
- Name: Sajeel Khan Roll#:M.phil-SSP-03-F19 Class: M.phil SSP (Morning) Subject: Optical Properties of Solid Submitted TODocument8 pagesName: Sajeel Khan Roll#:M.phil-SSP-03-F19 Class: M.phil SSP (Morning) Subject: Optical Properties of Solid Submitted TOAnonymous f7wV1lQKRNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Fields IPE 4M QuestionsDocument11 pagesElectric Charges and Fields IPE 4M Questionsbhanu010420No ratings yet
- Wave Nature of ParticlesDocument8 pagesWave Nature of ParticlesLinNo ratings yet
- AERO1001 Lecture 15 Stress and Strain - Mohrs Circle AnnotatedDocument33 pagesAERO1001 Lecture 15 Stress and Strain - Mohrs Circle AnnotatedNorberto DawinanNo ratings yet
- Tfy4280 T5BDocument9 pagesTfy4280 T5BMikael Yuan EstuariwinarnoNo ratings yet
- Extended Surfaces (Fin) : Heat Transfer Lectures Chemical Engineering Department University of Technology, IraqDocument22 pagesExtended Surfaces (Fin) : Heat Transfer Lectures Chemical Engineering Department University of Technology, IraqChemical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Formulario FisicaDocument1 pageFormulario Fisicanayely merchanNo ratings yet
- Lesson - 7 AC CircuitsDocument15 pagesLesson - 7 AC CircuitsMohamed Munseeth NMNo ratings yet
- Complex Numbers and Linear Algebra Lecture NotesDocument3 pagesComplex Numbers and Linear Algebra Lecture NotesFrance DanielNo ratings yet
- Force Vibration With Harmonic Excitation: Unit - IvDocument24 pagesForce Vibration With Harmonic Excitation: Unit - IvLathish KumarNo ratings yet
- Prof M. Rashid KhanDocument8 pagesProf M. Rashid KhanSumair Khan MasoodNo ratings yet
- Measurements Assignment Three FinalDocument8 pagesMeasurements Assignment Three FinalByonabye MosesNo ratings yet
- Summary Mona ShalanDocument39 pagesSummary Mona Shalanromaehab201912No ratings yet
- 2017 Magnetic Fields NotesDocument17 pages2017 Magnetic Fields NotesTSHIFHANGO TAHKHANINo ratings yet
- Ch02 Friction PDFDocument32 pagesCh02 Friction PDFNimalanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1e: Elementary Signals: Signals and Systems (Eeeb233)Document48 pagesLecture 1e: Elementary Signals: Signals and Systems (Eeeb233)Siti Nur DiniNo ratings yet
- Governors TheoryDocument37 pagesGovernors Theorymane prathameshNo ratings yet
- Homework 1Document3 pagesHomework 1öznur uluNo ratings yet
- AERODYN2 Part 5 Fundamentals of Flight Mechanics For Steady FlightDocument25 pagesAERODYN2 Part 5 Fundamentals of Flight Mechanics For Steady FlightSecretNo ratings yet
- 5 6262494773530068893Document33 pages5 6262494773530068893Adarsh pandeyNo ratings yet
- U-4 - L-5 To 8 - Free Damped VibrationDocument46 pagesU-4 - L-5 To 8 - Free Damped VibrationTIRO EDITSNo ratings yet
- 3 Chapter 3Document15 pages3 Chapter 3Mohamed TarekNo ratings yet
- Convolution and Equidistribution: Sato-Tate Theorems for Finite-Field Mellin Transforms (AM-180)From EverandConvolution and Equidistribution: Sato-Tate Theorems for Finite-Field Mellin Transforms (AM-180)No ratings yet
- Strong Rigidity of Locally Symmetric Spaces. (AM-78), Volume 78From EverandStrong Rigidity of Locally Symmetric Spaces. (AM-78), Volume 78No ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Discrete Series of GLn Over a Finite Field. (AM-81), Volume 81From EverandDiscrete Series of GLn Over a Finite Field. (AM-81), Volume 81No ratings yet
- The Plasma Dispersion Function: The Hilbert Transform of the GaussianFrom EverandThe Plasma Dispersion Function: The Hilbert Transform of the GaussianRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Lesson Plan in Remainders TheoremDocument5 pagesLesson Plan in Remainders TheoremJune SabatinNo ratings yet
- DI CaseletesDocument9 pagesDI Caseletessprem4353No ratings yet
- InfiniBand WikipediaDocument2 pagesInfiniBand WikipediaYoussef BoukhdimiNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion at An AngleDocument25 pagesProjectile Motion at An AngleKenneth Kent Stinson FloresNo ratings yet
- HD 70 CDocument101 pagesHD 70 CPhamVanGiangNo ratings yet
- 10 - Starting and ReversingDocument4 pages10 - Starting and ReversingAisha Zaheer100% (3)
- Class and ObjectsDocument15 pagesClass and ObjectsIwan SaputraNo ratings yet
- Service Manual - Amnc09gdba2, Amnc12gdba2Document6 pagesService Manual - Amnc09gdba2, Amnc12gdba2U Kyaw San OoNo ratings yet
- Answer To The Question No: (A) : Pattern Recognition Is The Process of Recognizing Patterns by UsingDocument4 pagesAnswer To The Question No: (A) : Pattern Recognition Is The Process of Recognizing Patterns by UsingKhaled faisalNo ratings yet
- Celonis Configuration Store Setup Guide 1.6Document11 pagesCelonis Configuration Store Setup Guide 1.6Venugopal JujhavarappuNo ratings yet
- Design of The Power Control Module of TDDocument9 pagesDesign of The Power Control Module of TDGurbir SinghNo ratings yet
- Fa4 Webinar Wincc Unified CompressedDocument56 pagesFa4 Webinar Wincc Unified CompressedNeuron StimNo ratings yet
- Luke Diosiek Fun With Electricity and MagnetismDocument21 pagesLuke Diosiek Fun With Electricity and MagnetismseablueNo ratings yet
- Srinivasan Engineering College, Perambalur: Part B Unit IDocument2 pagesSrinivasan Engineering College, Perambalur: Part B Unit IPrabhat SinghNo ratings yet
- Functions Equations Question BankDocument101 pagesFunctions Equations Question BankParth DesaiNo ratings yet
- Electrical BEE Latest 2022 2023 Quantum Series (Searchable)Document116 pagesElectrical BEE Latest 2022 2023 Quantum Series (Searchable)ritamlyrisNo ratings yet
- Thermal Engineering For The Construction of Large Concrete Arch DamsDocument10 pagesThermal Engineering For The Construction of Large Concrete Arch DamsOscar LopezNo ratings yet
- 638 - Servoregler Technical - ManualDocument123 pages638 - Servoregler Technical - ManualemfiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 Surface Area and Volume of A Right Circular ConeDocument19 pagesChapter 20 Surface Area and Volume of A Right Circular ConeMann GosarNo ratings yet
- Paper I & 11 Answer All Questions: (E) Explain The Use of Correlation and Regression Studies in Busainess?Document5 pagesPaper I & 11 Answer All Questions: (E) Explain The Use of Correlation and Regression Studies in Busainess?Suthaharan PerampalamNo ratings yet
- Registry TweaksDocument5 pagesRegistry TweaksArlie TaylorNo ratings yet
- Installation and Operation Manual: 3161 GovernorDocument48 pagesInstallation and Operation Manual: 3161 GovernorMiguel Sotelo100% (1)
- 12 MarksDocument23 pages12 Markslakshmigsr6610No ratings yet
- Mrs - Sanjana Jadhav: Mobile No-9422400137Document3 pagesMrs - Sanjana Jadhav: Mobile No-9422400137Sanjana JadhavNo ratings yet
- Notes: Edited by William AdkinsDocument6 pagesNotes: Edited by William Adkinsjorge mario durango petroNo ratings yet
- Casing and Tubing Crossovers: ScopeDocument4 pagesCasing and Tubing Crossovers: Scopeislam atifNo ratings yet
- Correlational ResearchDocument10 pagesCorrelational ResearchSari100% (1)
- Neraca energiATK-2Document29 pagesNeraca energiATK-2MauliyaLailaNo ratings yet
- Topcon GLS 2200Document2 pagesTopcon GLS 2200asepali005No ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Appraising Diagnostic Research StudiesDocument23 pagesLesson 5 Appraising Diagnostic Research StudiesProject MedbooksNo ratings yet