Professional Documents
Culture Documents
33 KV Equipment Design
Uploaded by
Hikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
33 KV Equipment Design
Uploaded by
Hikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरCopyright:
Available Formats
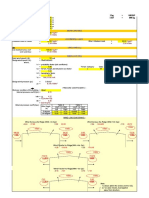
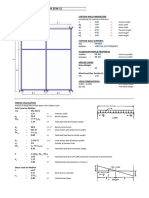
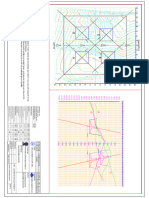
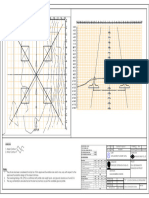
1 INPUT FOR DESIGN
System Voltage 33 kV
Equipment Post Insulator
1.1 Conductor details
1. Diameter of conductor 1xACSR DOG (6-4.72/7-1.57) = 0.014 m
2. Weight of conductor/meter = 0.39 kg/m
3. No. of conductor/phase = 1.00 No.
4. Effective span of conductor = 4.00 m
5. Sag percentage condidered (Only Flexible Conductor: Range 0 to 5) = 5.00 %
6. Sag due to self weight =[Length of conductor X Sag %]/100 d = 0.20 m
1.2 Equipment details
1.Dia. Of Equipment 330mm = 0.33 m
2. Weight of Equipment = 350.00 Kg
3. Height of equipment = 3.30 m
1.3 Structure details
1. Diameter of support Cold framed welded CHS as per EN 10219 = 0.22 m
2. Grade of structure steel = S355
2. Height of Support = 4.00 m
3. Weight of Structure/meter (Include 20% for plates) = 49.92
1.4 Total height = 7.30 m
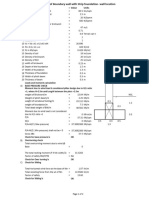
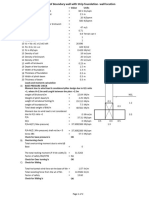
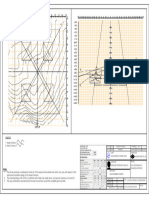
2 LOAD CALCULATION
2.1 SELF WEIGHT:
Weight of Equipment = 350.00 Kg
Weight of conductor w = 1.58 Kg
Self weight of structure = 199.68 Kg
Total vertical Load = 5.41 KN
Workmanship load = 1.00 KN
2.2 Conductor Loads:
Maximum conductor deviation
Horizontal qH = 10.00 Deg
Vertical qV = 10.00 Deg
Conductor Tension (NT)
i) Without conductor deviation
Longitudinal Horizontal Fx0 = w*l^2/8d = 0.04 KN
ii) With conductor deviation
Longitudinal Fx1 Fx0 COS( qH) COS( qV) = 0.04 KN
Transverse Fy1 Fx0 SIN( qH) COS( qV) = 0.01 KN
Vertical Fz1 Fx0 SIN (qV) = 0.01 KN
Short Circuit Force (SFC)
i) Without conductor deviation
Longitudinal Horizontal Fxs0 = 3.00 KN
ii) With conductor deviation
Longitudinal Fxs1 Fxs0 COS( qH) COS( qV) = 2.96 KN
Transverse Fys1 Fxs0 SIN( qH) COS( qV) = 0.51 KN
Vertical Fzs1 Fxs0 SIN (qV) = 0.52 KN
2.3 WIND LOAD:
Wind parameter:
1. Fundamental value of the basic wind velocity, Vb,0 = 33.00 m/s
2. Terrain category [Table 4.1 of EN 1991-1-4 = II
[Area with low vegetation such as grass and isolated obstacles (trees, buildings) with seperations of at least 20 obstacle heights]
As per terrain category-II, roughness length: Z0 = 0.05 & min = 2 z0 = 0.05
3. Basic wind speed velocity, Vb [Cl. 4.2 of EN 1991-1-4]
Vb = Cdir*Cseason*Vb,0
where, Cdir - directional factor = 1.00
Cseason - Seasonal factor = 1.00
Vb = 33.00 m/s
Wind load calculation as per EN 1991-1-4:
Air density, [cl. 4.5 Note 2] r = 1.25 Kg/m3
Height exposed above ground, (Structure + Equipment) z = 7.30 m
Basic wind pressure qb = 1/2*r*vb^2/1000 = 0.68 KN/sq.m
Kr = 0.19*(z0/z0,II)^0.07 where,
Z0,II = 0.05 m
Zmax = 200.00 m
Kr = 0.27 ≥ 0.18
Terrain roughness factor, Cr(z) = Kr*ln(z/z0) for zmin<z<zmax = 1.34
Terrain orography for flat terrain, Co(z) = 1.00
K1 = Turbulence factor K1 = 1.00
Wind turbulence factor, Iv(z) = K1/Co(z)*ln(z/z0) for zmin<z,zmax = 0.20
Exposure factor ce(z) = [1+7*Iv(z)]*Cr(z)*Co(z) = 3.22
Peak velocity pressure qp(z) = Ce(z)*qb 2.19240707 KN/sq.m
Peak wind velocity V(ze) at reference
V(Ze) = Vb*2*qp(z)/r)^0.5 = 61.81 m/s
height z
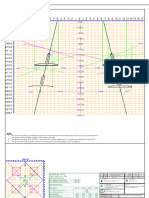
Force coefficient calculation for circular cylinder parts:
Reynolds Number Re = b.V(Ze)/u
where, b= dimeter of members,
V9Ze) = Peak wind velocity, = 61.81 m/s
u = Kinemetic viscosity of air 15*10-6 m2/s = 0.00 m2/s
For Conductor, Re = 5.83E+04
For Equipment Re = 1.36E+06
Equivalent surface roughness
for Galvanised structure k = 0.20 mm
k/b value
For Conductor, = 0.0100
For Equipment = 0.0006
Force coefficient without free-end flow Cf,0 = 1.2+(0.18*log(10*k/b))/(1+0.4*log(Re/10^6)
For, Conductor Cf,0 = 0.865
For, Equipment, Cf,0 = 0.811
Effective slenderness, = Min. {(l/b) & 70
For, Conductor = 70.00
For, Equipment, = 18.1818
End effect factor (solidity ratio)
For, Conductor yl = 0.90
For, Equipment, yl = 0.68
Force coefficient Cf = Cf,0*yl
For, Conductor Cf = 0.78
For, Equipment, Cf = 0.55
Wind on equipment = Ae*Cf*qp(z)
Wind on conductor = Ae*Cf*qp(z)
Wind loads on various component
Wind Direction
Equipment Conductor Structure Remarks
Wx (parallel to conductor span) 1.04 0.11 0.5 1.15
Wy (pepnd. to conductor span) 1.04 0.11 0.5 1.15
W45 (Diagonal) 0.74 0.08 0.35 Applied in X&Y 0.81
You might also like
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresFrom EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- IDT FoundationDocument15 pagesIDT FoundationARUN RAWATNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan Desain Girder BH.89-DSSDocument10 pagesPerhitungan Desain Girder BH.89-DSSMuhammad Abdul RozakNo ratings yet
- Pallavi Adss ReportDocument9 pagesPallavi Adss Reportraj patilNo ratings yet
- 15m RC TG Superstructure DesignDocument22 pages15m RC TG Superstructure DesignEngineeri TadiyosNo ratings yet
- Sub STR 2Document8 pagesSub STR 2Poshan DhunganaNo ratings yet
- Steel Truss Design for Romblon ProjectDocument3 pagesSteel Truss Design for Romblon ProjectJake CortezNo ratings yet
- Crane Girder Design-5T-5.7m SpanDocument32 pagesCrane Girder Design-5T-5.7m SpanKyatoor SantoshNo ratings yet
- Design of RCC Solid Slab - 2.0m-12.00Document27 pagesDesign of RCC Solid Slab - 2.0m-12.00Chandra Prakash Jyoti0% (1)
- Hat PurlinDocument3 pagesHat PurlinAniket DubeNo ratings yet
- Design of equipment foundation footingDocument1 pageDesign of equipment foundation footingdantevariasNo ratings yet
- Helicoidal Stair Design Spreadsheet by Olusegun - VerifiedDocument2 pagesHelicoidal Stair Design Spreadsheet by Olusegun - Verifiedsegun ajibola100% (2)
- Design of PurlinsDocument10 pagesDesign of PurlinsFranklyn GenoveNo ratings yet
- Concrete Steel: Selected Design Case: 2Document25 pagesConcrete Steel: Selected Design Case: 2venu manikantaNo ratings yet
- Ce 164Document84 pagesCe 164Carmel Buniel SabadoNo ratings yet
- Stability CheckDocument2 pagesStability ChecksaravananNo ratings yet
- AMLP - Check DeckingDocument5 pagesAMLP - Check DeckingNguyễn LâmNo ratings yet
- Staircase Beam Design - 2Document28 pagesStaircase Beam Design - 2Sai Sushank67% (3)
- Wind Load Calculations As Per Is 875 Part 3Document10 pagesWind Load Calculations As Per Is 875 Part 3ajNo ratings yet
- Deck Girder ExampleDocument28 pagesDeck Girder ExampleEng'r Mohammed HamzaNo ratings yet
- Calculation For Wave, Current & Wind Forces: (For The Piles at Grid B & C)Document3 pagesCalculation For Wave, Current & Wind Forces: (For The Piles at Grid B & C)MUTHUKKUMARAMNo ratings yet
- Design of Stair-Case: (Limit State Method As Per IS 456-2000)Document2 pagesDesign of Stair-Case: (Limit State Method As Per IS 456-2000)Sujan SinghNo ratings yet
- Design of ICOG Foundation for SECI 4Document16 pagesDesign of ICOG Foundation for SECI 4ARUN RAWAT100% (1)
- Example 20m Span RCDGDocument17 pagesExample 20m Span RCDGIyœ Møsisæ100% (2)
- Calculate bridge design parametersDocument25 pagesCalculate bridge design parametersanon_512117762No ratings yet
- 2-Col Bent On Bored PilesDocument29 pages2-Col Bent On Bored PilesHenry DiyokeNo ratings yet
- Slab Design (Pillai & Menon) (Ex 11.1)Document2 pagesSlab Design (Pillai & Menon) (Ex 11.1)Md Ghani HaiderNo ratings yet
- Steel Rafter Section For Eave Roof Section ReductionsDocument25 pagesSteel Rafter Section For Eave Roof Section ReductionsJanaka KarunarathnaNo ratings yet
- Calculation - Concrete BucketDocument7 pagesCalculation - Concrete BucketJuragan Iwal100% (1)
- Design of Column (C-1)Document3 pagesDesign of Column (C-1)Khael Angelo Zheus JaclaNo ratings yet
- FENCEDocument7 pagesFENCEARUN RAWATNo ratings yet
- BR No 290-Rev-01Document164 pagesBR No 290-Rev-01mohana t100% (1)
- Design of Sleeper Pedestal Reinforcement in CulvertDocument2 pagesDesign of Sleeper Pedestal Reinforcement in Culvertmunishant10% (1)
- Tank Mat Foundation DesignDocument1 pageTank Mat Foundation Designdantevarias100% (1)
- Wind Load (On Roof)Document11 pagesWind Load (On Roof)vinayNo ratings yet
- TWDESDocument8 pagesTWDESmunishant1No ratings yet
- Vechular Crossing U-Dicth Design: 1. DimensionsDocument13 pagesVechular Crossing U-Dicth Design: 1. DimensionsBest Tariku100% (1)
- Design of Retaining Wall: 1 Preliminary DataDocument3 pagesDesign of Retaining Wall: 1 Preliminary DataAjayvidyanand SharmaNo ratings yet
- Girder analysis and designDocument2 pagesGirder analysis and designReuben James BangaoilNo ratings yet
- BR No 290-Rev-01Document272 pagesBR No 290-Rev-01mohana tNo ratings yet
- Structural Design of Proposed Two Storey Apartment BuildingDocument30 pagesStructural Design of Proposed Two Storey Apartment BuildingGhiovani DayananNo ratings yet
- Pipe Rack Foundation DesignDocument29 pagesPipe Rack Foundation DesignYatendra TyagiNo ratings yet
- Design of L Shaped Cantilever Retaining Wall: 1 Preliminary DataDocument7 pagesDesign of L Shaped Cantilever Retaining Wall: 1 Preliminary Dataraghu kiranNo ratings yet
- Support STR & FDN Design Calculation For 66kV PT - R0 - SinghikDocument20 pagesSupport STR & FDN Design Calculation For 66kV PT - R0 - SinghikKRKA EngineersNo ratings yet
- Design of Crane Girder for Saudi Electricity CompanyDocument47 pagesDesign of Crane Girder for Saudi Electricity CompanyeljammalNo ratings yet
- Client Contractor Ujjain Municipal Corporation-Ujjain. Tata Projects Ltd.,-SecunderabadDocument32 pagesClient Contractor Ujjain Municipal Corporation-Ujjain. Tata Projects Ltd.,-Secunderabadepe civil1No ratings yet
- Wind Load CalculationsDocument1 pageWind Load CalculationsPrayas SubediNo ratings yet
- STP Design SheetsDocument86 pagesSTP Design Sheetskiran raghukiran100% (1)
- STP Design Sheets D PochampallyDocument121 pagesSTP Design Sheets D Pochampallykiran raghukiranNo ratings yet
- Ignacio EthicsDocument15 pagesIgnacio EthicsR O NNo ratings yet
- Calculate loads on octagonal sand model roofDocument8 pagesCalculate loads on octagonal sand model roofSiddhesh BajpaiNo ratings yet
- 6 - Abutment - A2 BargarhDocument197 pages6 - Abutment - A2 BargarhBINAY KUMARNo ratings yet
- Wind Loading Calculation - PEB FrameDocument2 pagesWind Loading Calculation - PEB Framemaruthiinfra structuresNo ratings yet
- CW Analysis Simple BeamDocument2 pagesCW Analysis Simple BeamNorman PalomoNo ratings yet
- Detailed design of a 2-column bridge bent pier on bored pilesDocument17 pagesDetailed design of a 2-column bridge bent pier on bored pileszxcNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis AprijanDocument6 pagesStructural Analysis AprijanRowena MoralaNo ratings yet
- Design Calculation: Base Pressure OkayDocument2 pagesDesign Calculation: Base Pressure Okaymassive85No ratings yet
- Footing Design - Studio AoartmentDocument23 pagesFooting Design - Studio AoartmentMUKESH RAJENDRANo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Wind & Weight Span Report (132 KV MCKT)Document3 pagesWind & Weight Span Report (132 KV MCKT)Hikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- DB RequirementDocument3 pagesDB RequirementHikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- DD RequirementDocument4 pagesDD RequirementHikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- Tower Packing ListDocument15 pagesTower Packing ListHikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- Boundry Wall Design (A)Document2 pagesBoundry Wall Design (A)Hikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- ACCC Drake File 2Document29 pagesACCC Drake File 2Hikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- Leg Profile of AP 47 01052022Document1 pageLeg Profile of AP 47 01052022Hikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- MCTLP Ap-15b-Ap-15bDocument1 pageMCTLP Ap-15b-Ap-15bHikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- Boundry Wall DesignDocument4 pagesBoundry Wall DesignHikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- Final Report of Kohalpur-Nepalgunj 132KV Transmisssion Line ProjectDocument100 pagesFinal Report of Kohalpur-Nepalgunj 132KV Transmisssion Line ProjectHikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- Leg Profile of AP-11Document1 pageLeg Profile of AP-11Hikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- Tower Profile and Tower Schedule Report - NKTLP-2Document63 pagesTower Profile and Tower Schedule Report - NKTLP-2Hikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- Leg Profile-AP-62-AP-62Document1 pageLeg Profile-AP-62-AP-62Hikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- MCTLP Ap-15b-Ap-15bDocument1 pageMCTLP Ap-15b-Ap-15bHikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- Leg Profile-AP-64-AP-64Document1 pageLeg Profile-AP-64-AP-64Hikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- Leg Profiles DDS - R2-AP-21-2Document1 pageLeg Profiles DDS - R2-AP-21-2Hikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- 04 Raft 30+5 T5Document14 pages04 Raft 30+5 T5Hikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- Leg Profile AP-13 Rev.1-AP-13Document1 pageLeg Profile AP-13 Rev.1-AP-13Hikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- Leg Profiles DDS - R2-AP-21-2Document1 pageLeg Profiles DDS - R2-AP-21-2Hikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- What Can Happen in 2023Document1 pageWhat Can Happen in 2023Hikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- Leg Profile-AP-62-1-AP-62-1Document1 pageLeg Profile-AP-62-1-AP-62-1Hikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- 04 Raft 30+5 T5Document14 pages04 Raft 30+5 T5Hikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- APPD BOM - QD+6m BEDocument6 pagesAPPD BOM - QD+6m BEHikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- FINAL GANTRY 132 KVDocument2 pagesFINAL GANTRY 132 KVHikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- Social StudiesDocument180 pagesSocial StudiesHikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- Substation DesignDocument764 pagesSubstation Designprashious100% (2)
- Revised Bom - Basic Tower - TB - 18.11.23Document11 pagesRevised Bom - Basic Tower - TB - 18.11.23Hikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- Kutechaur Master PlanDocument4 pagesKutechaur Master PlanHikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- Existing Ground: DateDocument1 pageExisting Ground: DateHikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- Gratings & Cycle RacksDocument31 pagesGratings & Cycle Rackswawan setiawanNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Separation of Mixtures - 0Document25 pages2.2 Separation of Mixtures - 0Arch Chellis OrongNo ratings yet
- Process Transmitter Model UPT-20, With Pressure Port Model UPT-21, With Flush DiaphragmDocument14 pagesProcess Transmitter Model UPT-20, With Pressure Port Model UPT-21, With Flush DiaphragmchauNo ratings yet
- CIE de 2000Document4 pagesCIE de 2000Ibatin Noa LaboratorioNo ratings yet
- Electronicbekm 2023Document159 pagesElectronicbekm 2023Bekir MouradNo ratings yet
- Installation and Maintenance Manual: Steam FlowmeterDocument36 pagesInstallation and Maintenance Manual: Steam FlowmeterSans K100% (1)
- Cement CalculationsDocument25 pagesCement CalculationsKristi MicheleNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument79 pagesOhm's Laweugene rellamaNo ratings yet
- 1946 Shanley The Column Paradox J Aero SciDocument1 page1946 Shanley The Column Paradox J Aero Scitraders joeNo ratings yet
- D E700 - D E705 - D E800 - D E805Document30 pagesD E700 - D E705 - D E800 - D E805mingwei pengNo ratings yet
- Transmission of Data and Voice over Fiber-Optic LinksDocument21 pagesTransmission of Data and Voice over Fiber-Optic LinksBhegz EscalonaNo ratings yet
- Takex PB-IN-50HF Data SheetDocument2 pagesTakex PB-IN-50HF Data SheetJMAC SupplyNo ratings yet
- Packaged, Dry, Rapid-Hardening Cementitious Materials For Concrete RepairsDocument4 pagesPackaged, Dry, Rapid-Hardening Cementitious Materials For Concrete RepairsJesús Luis Arce GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Diagnosti ControladorDocument198 pagesDiagnosti ControladorMONTACARGAS AVS100% (1)
- Thomson Clutches Brakes CatalogDocument152 pagesThomson Clutches Brakes CatalogElectromateNo ratings yet
- Metering SatamDocument3 pagesMetering SatamYohanes AzzisNo ratings yet
- Project Group 10Document26 pagesProject Group 10amitgourav9No ratings yet
- Ay2022 23 AsdaDocument6 pagesAy2022 23 AsdaWatermelon XSNo ratings yet
- Electrical Systems OverviewDocument16 pagesElectrical Systems OverviewCjoy MañiboNo ratings yet
- Piping Design GuideDocument65 pagesPiping Design GuideShrey PatelNo ratings yet
- Belzona 1121: Product Specification SheetDocument2 pagesBelzona 1121: Product Specification SheetQuy RomNo ratings yet
- Topic 4: Pumps and TurbinesDocument66 pagesTopic 4: Pumps and TurbinesSiddarth SharmaNo ratings yet
- Physics: Michelle Lao NMAT Review 2020 July 2020 Trans 01Document6 pagesPhysics: Michelle Lao NMAT Review 2020 July 2020 Trans 01Klee KazuhaNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument228 pagesPDFGayan Madushan KandethanthriNo ratings yet
- Boiling Point Increase of SolutionsDocument11 pagesBoiling Point Increase of Solutionsyola anjelinaNo ratings yet
- SuspensionDocument72 pagesSuspensionUkash sukarmanNo ratings yet
- Sludge Transfer Pump - Nmr-601 M13-G-0950A/B: Upgrade Pier Marine Facilities at TanajibDocument53 pagesSludge Transfer Pump - Nmr-601 M13-G-0950A/B: Upgrade Pier Marine Facilities at TanajibchaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Generator Details ReportDocument1 pageGenerator Details Reportwaseem kausarNo ratings yet
- 25 - Ray Optics and Optical Instruments - KeynotesDocument28 pages25 - Ray Optics and Optical Instruments - KeynotesthorNo ratings yet
- Process Dynamic and Control Lecture NoteDocument120 pagesProcess Dynamic and Control Lecture NoteUb UsoroNo ratings yet