Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Skeletal System
Uploaded by
juliamaesimbre0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesscience
Original Title
Skeletal-System
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentscience
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesSkeletal System
Uploaded by
juliamaesimbrescience
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
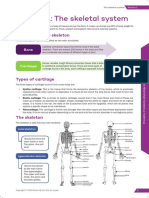
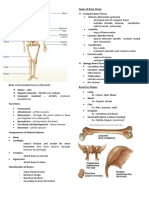
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM • Costal Cartilage – connects the sternum and • Attached to them are the wrist bones (8
the ribs carpals)
• Includes: Bones, Cartilages, Joints (where
1. Trapezium
two bones meet), and Ligaments (Bones to 3. SPINAL COLUMN (VERTEBRAL)
2. Trapezoid
bones)
• Composed of 26 Vertebrae and an 3. Lunate
• Divided into 2 major sections: Axial Skeleton 4. Scaphoid
Intervertebral disk between each vertebrae.
and Appendicular Skeleton 5. Pisiform
• Vertebrae: protects the spinal cord
• Axial Skeleton – Skull, Vertebral • Invertebral Disk: act as a shock absorber 6. Capitate
Column, thoracic cage (sternum, ribs, between each vertebra. 7. Hamate
costal cartilage). 8. Triquetrum
4. RIBS (COSTAE) • Attach to wrist bones are Hand bones
• Appendicular Skeleton – Arm and legs, - composed of 5 Metacarpals (palm)
pelvis, shoulders • Composed of 24 ribs or 12 pairs of ribs.
- 14 Phalanges (fingers and thumbs)
• 7 pair of true ribs and 5 pairs of false pair.
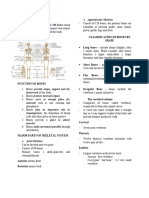
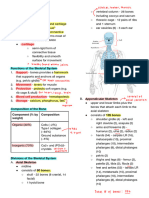
FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEN • The last 2 pairs are called the floating ribs. 3. PELVIC GIRDLE
• Protects vital organs such as the heart, major
• Support • Structure to which leg bones are attached.
blood vessels, and the lungs.
• Protection • Made up of 2 os coxae (Hip bones)
• Movements *These bones are responsible for HEMATOPOESIS – - divided into 3 sections: Ilium, Ischium,
• Storage production or creation of blood which takes place in Symphysis (pubis).
• Blood Cell Production the bone marrow
4. LEG BONES
AXIAL SKELETON APPENDICULAR SKELETON
• Acetabulum (pelvic sockets) – where the leg
• Forms the main trunk of the body • Forms the extremities of the body bone joins the pelvis.
• Each leg consists of Femur (thigh bone)
1. SKULL 1. SHOULDER GIRDLE
- In the upper leg and categorized as long
• 2 sets of skull bones: Cranium (brain case) • Composed of 4 bones bone.
and Facial Bone • 2 Clavicals (Collar Bones) • Pattela (knee cap) – between the upper and
• Cranium (brain case) • 2 Scapulas (Shoulder Bones) lower leg
- Composed of 8 bones • Where the arm bones are attached to • Lower leg composed of: Tibia (Shin Bone)
- Protects the brain and Fibula (runs parallel to tibia).
2. ARM BONES • Attached to the lower leg are the 7 tarsals
• Facial bone
- Composed of 14 bones • Composed of 3 bones (Ankle bones)
- give structure to the face • Humerus – upper bone 1. Calcaneus – ankle bone
• Categorized as long bone. 2. Talus – heel bone
2. STERNUM 3. Cuboid
• Radius and Ulna – lower bone
• Breast Bone 4. Navicular
- Connected by interosseous membrane.
5. Medial Cuneiform
6. Lateral Cuneiform
7. Intermediate Cuneiform Classification of Bones
- Attached to them are the 5 metatarsals
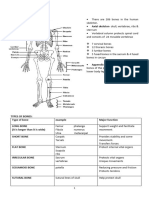
1. Long Bones – Femuar, Tibula, Fibula
- 14 Phalanges (Toes)
• Heel (Calcaneus) 2. Short Bones – Carpals, Tarsals
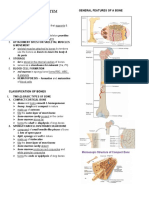
LONG BONES 3. Flat Bones – Cranial Bone, Scapulae
• Are hard dense bones that provide strength, 4. Sesamoid Bones - Patella
structure, and mobility (Ex. Femur)
5. Irregular Bones -Vetebrae
• Long bone has a shaft (diaphysis) and 2 ends
called Proximal Epiphysis and Distal
Epiphysis.
• Medullary Canal – in the diaphysis which is
filled with yellow marrow
- Endosteum – lines with medullary canal
and keeps the yellow marrow in tact.
• Periosteum – a tough membrane that covers
outside of the bone
JOINTS
• Joints are formed where two bones join
together.
• Divided into 3 major categories defined by
as how these joints move:
1. Diarthrosis (Synovial) – freely movable
- Ex. arm sockets and ball sockets of
hip and shoulders.
2. Amphiarthrosis – slightly movable
- Ex. vertebrae.
3. Synarthrosis – immovable
- Ex. sutures or joints in the cranium
Ligaments and Cartilage - Supportive structures
for the joint.
You might also like
- Rāmāya in Human Physiology PDFDocument739 pagesRāmāya in Human Physiology PDFrptitalia courses & sessions90% (10)
- Skeletal SystemDocument54 pagesSkeletal Systemanurag.dNo ratings yet
- Muscle and Skeletal FunctionDocument23 pagesMuscle and Skeletal FunctionLuan NguyenNo ratings yet
- L2 Reading 1Document62 pagesL2 Reading 1Milena RohenkohlNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology With PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology With PathophysiologyAngelika Park50% (4)
- Krillitane Storm Christopher CooperDocument256 pagesKrillitane Storm Christopher CooperRachelle McDonald100% (2)
- EMT Refresher Practice Exam ReviewDocument25 pagesEMT Refresher Practice Exam ReviewNimra NazeerNo ratings yet
- Amaurosis FugaxDocument11 pagesAmaurosis FugaxRexArtem100% (1)
- Alem Do Inconsciente (Jayme Cervino) PDFDocument85 pagesAlem Do Inconsciente (Jayme Cervino) PDFSimon BaushNo ratings yet
- Appendicular Skeleton Bones & GirdlesDocument4 pagesAppendicular Skeleton Bones & GirdlesRochelle Dorado BNo ratings yet
- Core 2 PDHPE - Body in Motion Study NotesDocument43 pagesCore 2 PDHPE - Body in Motion Study Notesmarissa.makhNo ratings yet
- Support Systems Grade 10Document51 pagesSupport Systems Grade 10Lance McGillNo ratings yet
- Support Systems Grade 10 - NEWDocument61 pagesSupport Systems Grade 10 - NEWLance McGillNo ratings yet
- Lab 7 Skeletal System PowerPointDocument19 pagesLab 7 Skeletal System PowerPointNguyen (Harry) Xuan HoangNo ratings yet
- BIOMECHANICS REVIEWERDocument12 pagesBIOMECHANICS REVIEWERJOHN EVAR LABASTILLANo ratings yet
- SkeletalDocument11 pagesSkeletalCrystal MaidenNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System: Two Subdivisions and Five Main FunctionsDocument12 pagesSkeletal System: Two Subdivisions and Five Main FunctionsAriane Shane BidoNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument37 pagesSkeletal Systemchiamaka anthonyNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument2 pagesSkeletal SystemMa Khristina S WongNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument4 pagesSkeletal SystemHenry BuñagNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Types of Bone Tissue: Phosphorus)Document10 pagesSkeletal System Types of Bone Tissue: Phosphorus)Arthea DavidNo ratings yet
- 5 NOTES - Skeletal SystemDocument18 pages5 NOTES - Skeletal SystemJoselle OrateNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System FinalDocument53 pagesSkeletal System FinalKyle Darren PunzalanNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System PowerPointDocument46 pagesSkeletal System PowerPointLucky RiaNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY SKELETAL SYSTEM MidtermsDocument12 pagesANAPHY SKELETAL SYSTEM MidtermsFraiza BirowaNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System: Rzgar F. RashidDocument27 pagesThe Skeletal System: Rzgar F. Rashidyıldız kubeNo ratings yet
- Part 4 - Human Skeletal SystemDocument25 pagesPart 4 - Human Skeletal SystemAmal Naeem JHNo ratings yet
- Bones and Joints OverviewDocument7 pagesBones and Joints OverviewGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Jo'rDocument124 pagesJo'rMade WidianantaraNo ratings yet
- Midterm TopicDocument5 pagesMidterm Topicjamesbaguia315No ratings yet
- LECTUREDocument56 pagesLECTUREjayye.aronceNo ratings yet
- L3-Musculoskeletal System I - 20190912Document118 pagesL3-Musculoskeletal System I - 20190912Carol LeeNo ratings yet
- PDHPE 2020 YR 11 NOTES mmmmDocument30 pagesPDHPE 2020 YR 11 NOTES mmmmicewallowhaNo ratings yet
- Anatomical IntroductionDocument17 pagesAnatomical Introductionllazoozllbraa 7372No ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument52 pagesSkeletal SystemNatinael DesalegnNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Skeletal SystemDocument26 pagesAnatomy - Skeletal SystemShereen AlobinayNo ratings yet
- 4-Structure and Function of The Body Systems 1Document26 pages4-Structure and Function of The Body Systems 1uxdan154No ratings yet
- Bones and skeletal system overviewDocument2 pagesBones and skeletal system overviewStephanie DimaculamganNo ratings yet
- Pointers To Review 3RDDocument7 pagesPointers To Review 3RDClarissa MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument51 pagesSkeletal SystemkrhimkrNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument25 pagesSkeletal SystemsoumilidescienceNo ratings yet
- Human Skeletal SystemDocument106 pagesHuman Skeletal SystemNirasha KodituwakkuNo ratings yet
- Code 802Document8 pagesCode 802Steph CaronanNo ratings yet
- LEC Orthopedic NursingDocument31 pagesLEC Orthopedic NursingAlthea Franz DuoNo ratings yet
- Bones and Muscles of the Human BodyDocument1 pageBones and Muscles of the Human BodyMarieta AlejoNo ratings yet
- Human Skeletal System OfficialDocument14 pagesHuman Skeletal System Officialconirv1No ratings yet
- Skeletal System (Use) - PESWDocument86 pagesSkeletal System (Use) - PESWAudrianna GaddyNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument18 pagesSkeletal Systemmia diazNo ratings yet
- Anatomy From The DoctorDocument208 pagesAnatomy From The DoctorSweet manNo ratings yet
- Bone Structure and ClassificationDocument35 pagesBone Structure and ClassificationVinod SharmaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Animal ScienceDocument16 pagesSkeletal System Animal Sciencealexenneth canilaNo ratings yet
- Label the Skeletal System and Describe its FunctionsDocument4 pagesLabel the Skeletal System and Describe its FunctionsLucía ChabletNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument105 pagesAnatomyHelena Pascual PérezNo ratings yet
- The Human Skeletal System: by Group 1 - Nurasmiati - Stevhani Febryaningsih - St. SyahiraDocument21 pagesThe Human Skeletal System: by Group 1 - Nurasmiati - Stevhani Febryaningsih - St. SyahiraVhani FebrianingsihNo ratings yet
- Human BonesDocument39 pagesHuman Bonesmuhammad ijazNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System PowerPointDocument50 pagesSkeletal System PowerPointEly QuijanoNo ratings yet
- 13 Skeletal SystemDocument12 pages13 Skeletal SystemSelvianti DjarudjuNo ratings yet
- Bones and Joints: Anatomy and FunctionsDocument38 pagesBones and Joints: Anatomy and FunctionssukunathNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 SkeletonDocument6 pagesChapter 14 SkeletonJian Leong ThoNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument73 pagesSkeletal SystemDEEPANKAR SAHANo ratings yet
- G-8 Skeletal SystemDocument30 pagesG-8 Skeletal SystemMarjun SalinasNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System NotesDocument5 pagesSkeletal System NotesNina IlaganNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument48 pagesThe Skeletal SystemLance PerezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy OSPEDocument17 pagesAnatomy OSPEjulietchiminyaNo ratings yet
- (Oct 1) THE SKELETAL SYSTEM PDFDocument7 pages(Oct 1) THE SKELETAL SYSTEM PDFBea GualbertoNo ratings yet
- CORRECTED Philosophy Q2Second Quarter M1 Freedom of The Human Person 1 PERINODocument22 pagesCORRECTED Philosophy Q2Second Quarter M1 Freedom of The Human Person 1 PERINOrheyangabriel123No ratings yet
- Study Guide in Contemporary Philippine ArtsDocument5 pagesStudy Guide in Contemporary Philippine ArtsjuliamaesimbreNo ratings yet
- DRRR Q1 M1 Concept-Of-Disaster EmpingDocument19 pagesDRRR Q1 M1 Concept-Of-Disaster EmpingjuliamaesimbreNo ratings yet
- Disaster Readiness & Risk Reduction: Quarter 1 - Module 2 Effects of DisasterDocument12 pagesDisaster Readiness & Risk Reduction: Quarter 1 - Module 2 Effects of DisasterKimberly Trocio Kim0% (1)
- DRRR Q1 M3 Exposurevulnerability EmpingDocument12 pagesDRRR Q1 M3 Exposurevulnerability EmpingjuliamaesimbreNo ratings yet
- Incision Access UrologyDocument47 pagesIncision Access UrologyHafizur RashidNo ratings yet
- Tratamiento Quirúrgico Del Mal Perforante Plantar: C.M. Hernández-Cañete, J. Borroto-PachecoDocument7 pagesTratamiento Quirúrgico Del Mal Perforante Plantar: C.M. Hernández-Cañete, J. Borroto-PachecoDiegoNo ratings yet
- 41 Emotions As Expressed Through Body LanguageDocument9 pages41 Emotions As Expressed Through Body LanguageSocaciu Gabriel100% (1)
- Elysia ChloroticaDocument2 pagesElysia ChloroticamckgbirdNo ratings yet
- Bill Nye RespirationDocument1 pageBill Nye RespirationJoseeNo ratings yet
- ATI Flash Cards 06, Medications Affecting The Cardiovascular SystemDocument48 pagesATI Flash Cards 06, Medications Affecting The Cardiovascular SystemWiilka QarnigaNo ratings yet
- Cell anatomy and divisionDocument4 pagesCell anatomy and divisionMarielle SaymanNo ratings yet
- Wim Hof MethodDocument4 pagesWim Hof MethodAdiMulahasanovicNo ratings yet
- Science Form 1 Chapter 2 Powerpoint SlidesDocument124 pagesScience Form 1 Chapter 2 Powerpoint SlidesADAM LOHNo ratings yet
- Final Defense (RVSD)Document37 pagesFinal Defense (RVSD)Torres Ken Robin DeldaNo ratings yet
- Sample Lesson PlansDocument8 pagesSample Lesson Plansapi-321385393No ratings yet
- Test Bank For Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 15th Edition by TortoraDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 15th Edition by TortoraKennethGarciabqej100% (35)
- JCB 201903033Document20 pagesJCB 201903033Purine ChengNo ratings yet
- Darkmourn Universe 1 - Alpha of Mortal FleshDocument352 pagesDarkmourn Universe 1 - Alpha of Mortal Fleshlopesjana579No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 11 (Muscles)Document5 pagesCHAPTER 11 (Muscles)eumarasiganNo ratings yet
- Genito-urinary Tract Imaging GuideDocument57 pagesGenito-urinary Tract Imaging GuideAnanya GoswamiNo ratings yet
- The Spreader Flap in Primary Rhinoplasty: BackgroundDocument8 pagesThe Spreader Flap in Primary Rhinoplasty: BackgroundAlex Rolando SuntaxiNo ratings yet
- Phytochemical Investigation of Eleusine Indica For in-Vivoanti-Hypertensive ActivityDocument12 pagesPhytochemical Investigation of Eleusine Indica For in-Vivoanti-Hypertensive ActivityInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (3)
- Studies on the vertically barred Haplochromis electra from Lake MalawiDocument5 pagesStudies on the vertically barred Haplochromis electra from Lake MalawiCenk Sururi KarabulutNo ratings yet
- Neet Code Yy Solution PDFDocument36 pagesNeet Code Yy Solution PDFPrakash RoyNo ratings yet
- New Born ExaminationDocument10 pagesNew Born ExaminationEn GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Lung Volumes and Lung VolumeDocument9 pagesLung Volumes and Lung VolumejuanNo ratings yet
- Cutaneous Manifestations of ANCA-associated Small Vessels Vasculitis.Document11 pagesCutaneous Manifestations of ANCA-associated Small Vessels Vasculitis.Diego Arenas LeytonNo ratings yet
- PMDC NEB Exams Free Course BookletDocument8 pagesPMDC NEB Exams Free Course BookletDaxtren HicksNo ratings yet