Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson Notes - Pascals Law
Uploaded by
toohnjooxzOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson Notes - Pascals Law
Uploaded by
toohnjooxzCopyright:
Available Formats
NAMATANAI SECCONDARY SCHOOL
SCIENCE DEPARTMENT
GRADE TWELVE PHYSICS
HAND OUT # 1
TOPIC: PASCALS LAW of PRESSURE.
Pascals Law or Pascals Principle states that when a change in pressure is applied to an enclosed fluid,
it is transmitted undiminished to all potion of the fluid and to the walls of the container.
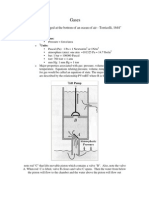
For example, suppose you fill a cylindrical container with water to a height (h) and a cross-sectional
area A and enclose the cylinder with a movable piston and add mass to the piston, the top of the piston
𝑚𝑔
will increase the pressure on the piston lid by 𝐴 . This can be illustrated as;
A Mg
h h
According to Pascals Principle, the pressure at all points in the water changes by the same amount,
𝑚𝑔
𝐴
. The pressure at the bottom of the tank now will be equal to the sum of;
a) Pressure due to weight of fluid.
b) Pressure due to mass
c) Atmospheric pressure.
d)
Deriving Pascals Law formula.
𝐹
The pressure that is exerted in a column is P=𝐴1 ……………………….1
1
The pressure is transmitted equally throughout the liquid. The force experienced by the second
surface is given by;
𝐹
F2 = PA2 or P=𝐴2 ……………………………….2
2
Since pressure is the same throughout,
𝐹1 𝐹 𝐹1 𝐴2
𝐴1
= 𝐴2 or F2= 𝐴1
……………………….3
2
The equation #3 is referred to as the Pascals Formula.
Exercises on Pressure.
1. Calculate the pressure at the bottom of an enclosed cylindrical tank of diameter 10m, if it
was filled petrol to a depth of 5m.
2. Assumed the tank above (Q1) was not enclosed, determine the pressure at the bottom of
that tank.
3. A column filled with water to a height of 75cm was enclosed with a movable piston of radius
15cm. If a mass of 2.5 kg was placed on the piston lid, calculate;
a. Pressure at base of cylinder before the addition of mass.
b. Force felt at the base of the cylinder.
4. A car jack consists of two cylinders of different diameters but equal height. The cross-
sectional area of the first cylinder is 0.1m2 and the second cylinders has a cross sectional
area of 0.05m2. Calculate;
a. Pressure on the first piston if a force of 100N is exerted.
b. Pressure on the first piston if a force of 150N is exerted.
c. Force felt by second piston due to a force of 50N being exerted.
d. Force felt by second piston due to an input force of 130N.
5. Calculate the water pressure at the base of a dam of height 50m.
6. Calculate the pressure exerted by a force of 30N on a square area of 5cm.
You might also like
- Name-Tamoghno Mukherjee Class-XI Section - Combined Roll Number-11 Subject-Physics Session-2019-2020Document8 pagesName-Tamoghno Mukherjee Class-XI Section - Combined Roll Number-11 Subject-Physics Session-2019-2020Tamoghno MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument32 pagesFluid MechanicsShristyNo ratings yet
- HYDROSTATICDocument8 pagesHYDROSTATICryan valerioNo ratings yet
- Phy433 Lab Report 4Document23 pagesPhy433 Lab Report 4Michael McBertNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1a GasesDocument12 pagesChapter 1a GasesKarunakarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-Fluid Statics 2003Document6 pagesLecture 1-Fluid Statics 2003Leonardo LibresNo ratings yet
- Fluid-Flow Theory: F MG V GDocument27 pagesFluid-Flow Theory: F MG V Gcarl domingoNo ratings yet
- Force and Matter: Force Area F ADocument3 pagesForce and Matter: Force Area F ARiaz Hussain LaghariNo ratings yet
- Part - 2Document81 pagesPart - 2aryanneet9599No ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Ecw 211-Fluid StaticsDocument82 pagesTopic 2 - Ecw 211-Fluid StaticssonghahoonNo ratings yet
- Fluids at RestDocument30 pagesFluids at RestJoel Mendoza100% (1)
- Fluid Flow TheoryDocument24 pagesFluid Flow TheoryjaydeepnaruleNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Pascals PrincipleDocument25 pagesLesson 3 Pascals PrincipleJojimar JulianNo ratings yet
- Liquid Pressure and Pascals LawDocument16 pagesLiquid Pressure and Pascals Lawitsamazing496No ratings yet
- Lec 5-6Document17 pagesLec 5-6Muhammad Muzammil EjazNo ratings yet
- Pressure Physics Form 4Document47 pagesPressure Physics Form 4Hairul Akmal100% (2)
- Lesson No. 2 in ES 65Document4 pagesLesson No. 2 in ES 65Salahudin H.jamelNo ratings yet
- 202301171673942857PRESSURE8Document40 pages202301171673942857PRESSURE8renjun gfNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11 FluidsDocument14 pagesLesson 11 FluidsJohn OliquianoNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Fluid StaticsDocument33 pages2.1 Fluid StaticsXienlyn BaybayNo ratings yet
- Lec. 1Document31 pagesLec. 1Ali. AboudNo ratings yet
- Ch. 5Document13 pagesCh. 5Sandy ShohdyNo ratings yet
- 3.) Principles of Hydrostatics PDFDocument7 pages3.) Principles of Hydrostatics PDFShan Yi HaiNo ratings yet
- Gage Pressure (P Absolute Pressure (PDocument2 pagesGage Pressure (P Absolute Pressure (PMarlo AristorenasNo ratings yet
- O Level Physics Pressure NotesDocument28 pagesO Level Physics Pressure NotesMarvel ComicsNo ratings yet
- 2nd and 3rd WeeksDocument51 pages2nd and 3rd WeeksnaverfallNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 FluidsDocument14 pagesCHAPTER 2 FluidsIvan JadeNo ratings yet
- Outcome 1 Static Fluid Systems Tutorial 1 Hydrostatics PDFDocument20 pagesOutcome 1 Static Fluid Systems Tutorial 1 Hydrostatics PDFMehdi SoltaniNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Pressure - CE 309-CE22S2 - Fluid MechanicsDocument3 pages2.1 Pressure - CE 309-CE22S2 - Fluid MechanicsRusselNo ratings yet
- 04 - Fluid StaticsDocument34 pages04 - Fluid Staticssky lewNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument7 pagesFluid MechanicsJim Bryan Wabina VergaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Hydrostatic Pressure and BouyancyDocument20 pagesChapter 6 Hydrostatic Pressure and BouyancyAbba MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Tank Blowdown Math: Dean Wheeler Brigham Young University March 13, 2019Document7 pagesTank Blowdown Math: Dean Wheeler Brigham Young University March 13, 2019khaledmosharrafmukutNo ratings yet
- Pressure Concept Derivation Sample ProblemsDocument22 pagesPressure Concept Derivation Sample ProblemsAyumi QuiomNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes - PressureDocument11 pagesPhysics Notes - PressureKenville Jack67% (3)
- SUMMARY - Fluid MechanicsDocument13 pagesSUMMARY - Fluid Mechanicssethupanic macanic gamedzeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction of FluidDocument27 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction of FluidFiqha ShashaNo ratings yet
- 3a. Fluid StaticsDocument33 pages3a. Fluid StaticsAhra AlegriaNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 ReviewerDocument6 pagesChapter2 ReviewerLJ IDANE ARANASNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Force & Pressure (Form 4)Document30 pagesChapter 3: Force & Pressure (Form 4)ruslawati100% (7)
- Principles of HydrostaticsDocument16 pagesPrinciples of Hydrostaticsmark galangNo ratings yet
- CE 521 - Reaction Paper On Introduction To Principles of HydrostaticsDocument8 pagesCE 521 - Reaction Paper On Introduction To Principles of HydrostaticsHipolito RarangolNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document21 pagesChapter 3hailemebrahtuNo ratings yet
- PascalDocument13 pagesPascalPrithviraj RandhawaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Lecture Notes: P GH P GH +P F (A /A B W Q V/ T Av A V A V P V Gy + (1/2) V Gy F Av/lDocument13 pagesChapter 10 Lecture Notes: P GH P GH +P F (A /A B W Q V/ T Av A V A V P V Gy + (1/2) V Gy F Av/lvijayabharathi_vijivijiNo ratings yet
- 4 - Pressure in Fluids and Atmospheric PressureDocument22 pages4 - Pressure in Fluids and Atmospheric Pressureprash_hingeNo ratings yet
- FM Sol Chap03-001Document34 pagesFM Sol Chap03-001scs1720No ratings yet
- Matter and Energy Tema 1Document4 pagesMatter and Energy Tema 1Miranda Urbina OlivaresNo ratings yet
- Pressure: Online Learning Resources For Malaysia StudentsDocument0 pagesPressure: Online Learning Resources For Malaysia StudentsJia HuiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5-Solid and FluidDocument21 pagesChapter 5-Solid and FluidTonya EnglandNo ratings yet
- 2.pressure and HeadDocument36 pages2.pressure and HeadIhsan Samoh เพี่อนดีดีNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document4 pagesTutorial 3HahaNo ratings yet
- Presentation-4 (Pressure Its Measurement)Document45 pagesPresentation-4 (Pressure Its Measurement)Ali Al AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Structure of Molecules Notes For MathsDocument47 pagesClass 9 Structure of Molecules Notes For MathsMUHAMMAD TAUSEEF SABIRNo ratings yet
- 10-Mechanical Properties of FluidsDocument16 pages10-Mechanical Properties of Fluidsjyothigoudar66No ratings yet
- HCUY CE17 (Hydraulics) LP2 MergedDocument29 pagesHCUY CE17 (Hydraulics) LP2 MergedGleanna NiedoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - FluidDocument45 pagesChapter 3 - Fluidfieyza adnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 FluidsDocument51 pagesChapter 4 FluidsshahrulNo ratings yet
- Indice Hocberg RheumatologyDocument8 pagesIndice Hocberg RheumatologyGerlando Russo IntroitoNo ratings yet
- DIO 20. ZAŠTITA PRI RADU I SMJEŠTAJ POSADE Jan 2015Document44 pagesDIO 20. ZAŠTITA PRI RADU I SMJEŠTAJ POSADE Jan 2015Samo SpontanostNo ratings yet
- B-64603en-1 - 01 (v3) - Vol2 - 0if Connection Manual (Function)Document900 pagesB-64603en-1 - 01 (v3) - Vol2 - 0if Connection Manual (Function)SergioNo ratings yet
- Iaph LNG Bunker Checklist Bunker Station To Ship Final v3.6 Incl GuidelinesDocument26 pagesIaph LNG Bunker Checklist Bunker Station To Ship Final v3.6 Incl Guidelines서창빈No ratings yet
- Psychosomatic DisordersDocument79 pagesPsychosomatic DisordersMONIKANo ratings yet
- Semi DetachedDocument1 pageSemi DetachedDhumal Mangesh DhumalNo ratings yet
- 06 Story StiffnessDocument2 pages06 Story StiffnessDigvijay GiraseNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Performance NPTELDocument538 pagesAircraft Performance NPTELShabbir Ali100% (2)
- System MDR 8400Document150 pagesSystem MDR 8400JESUSCALVILLONo ratings yet
- Nursing Research VariablesDocument33 pagesNursing Research Variablesdr.anu RkNo ratings yet
- Manila Revenue Code, As Amended (Ordinance No. 7988)Document121 pagesManila Revenue Code, As Amended (Ordinance No. 7988)Charles Augustine AlbañoNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Products KolkataDocument3 pagesPetroleum Products KolkatabrijeshkynNo ratings yet
- Dry-Heat Destruction of Destruction KineticsDocument5 pagesDry-Heat Destruction of Destruction KineticsFabioEspinolaNo ratings yet
- Spare Parts: LKH Centrifugal PumpDocument20 pagesSpare Parts: LKH Centrifugal PumpService CTANo ratings yet
- The Hidden Word Is: The CluesDocument2 pagesThe Hidden Word Is: The CluesИра НикулочкинаNo ratings yet
- K-90-1900 FM-200 AgentDocument1 pageK-90-1900 FM-200 AgentPutra LangitNo ratings yet
- Design, Analysis and Simulation of Linear Model of A STATCOM For Reactive Power Compensation With Variation of DC-link VoltageDocument7 pagesDesign, Analysis and Simulation of Linear Model of A STATCOM For Reactive Power Compensation With Variation of DC-link VoltageAtiqMarwatNo ratings yet
- Tesla in ChinaDocument9 pagesTesla in ChinaÁi Nhân Huỳnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Prelim Kimanis Micom 241Document5 pagesPrelim Kimanis Micom 241Shah Aizat RazaliNo ratings yet
- Type VBPDF: Pilot Operated Check ValvesDocument3 pagesType VBPDF: Pilot Operated Check ValvesAslam ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Consumer Studies GR 11 Revision Term 1 2023 FinalDocument20 pagesConsumer Studies GR 11 Revision Term 1 2023 FinalCerboh MazibukoNo ratings yet
- Front Axle, Tie Rod and Drag Link (A21) - 20: Parts ListDocument4 pagesFront Axle, Tie Rod and Drag Link (A21) - 20: Parts ListdgloshenNo ratings yet
- Report NovelDocument12 pagesReport NovelHasan Moh'd Al AtrashNo ratings yet
- C190Document64 pagesC190thelmagrNo ratings yet
- Inheritance: Compiled By: Brandon Freel Stolen and Edited From: IMS and Dr. Kyle Stutts (SHSU)Document25 pagesInheritance: Compiled By: Brandon Freel Stolen and Edited From: IMS and Dr. Kyle Stutts (SHSU)Mary Ann DimacaliNo ratings yet
- Procreate User GuideDocument75 pagesProcreate User GuideOmar Páez0% (1)
- BS 5655-14Document16 pagesBS 5655-14Arun Jacob Cherian100% (1)
- T 703Document4 pagesT 703Marcelo RojasNo ratings yet
- Nutella: Italian PronunciationDocument1 pageNutella: Italian PronunciationhbnjknwvnffkjrpaadttirvorgNo ratings yet
- Sealand Equipment GuideDocument5 pagesSealand Equipment GuidePool Jaime Quispe CordovaNo ratings yet