Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Magenesium
Magenesium
Uploaded by
Kimberly Abellar LatoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Magenesium
Magenesium
Uploaded by
Kimberly Abellar LatoCopyright:
Available Formats
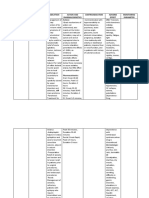
MAGNESIUM IMBALANCES
Signs and Symptoms:
Magnesium (Mg) is the second most
- respiratory depression
abundant cation in the intracellular fluid. It
- cardiac depression
functions by exerting its effects on the
- diminished deep tendon reflexes
myoneural junction, affecting neuromuscular
- flaccid paralysis
irritability. Magnesium is a cofactor in more
- drowsiness
than 300 enzyme systems that regulate diverse
- lethargy
biochemical reactions in the body, including
- ECG changed
protein synthesis, muscle and nerve function,
blood glucose control, and blood pressure
regulation.
NURSING INTERVENTIONS:
HYPOMAGNESEMIA
Hypomagnesemia frequently occurs in alcoholic
and critically ill patients and is often associated
The normal serum magnesium concentration
ranges from 1.5 to 2.5 mEq/L. Magnesium
imbalances, including hypermagnesemia and
with hypocalcemia and hypokalemia.
hypomagnesemia, require careful management
Signs and symptoms:
- tachycardia
- dyspnea and rapid shallow respirations
- hyperreflexia
- positive Chvostek’s and Trousseau’s signs
- nystagmus
- confusion, irritability, insomnia, seizure
- tetany
- ECG changes
to prevent potentially serious complications.
HYPERMAGNESEMIA
Hypermagnesemia is most commonly seen
patients with an inability to excrete Mg+ or
with increased intake of Mg+ from antacid.
Both neuromuscular and cardiac depression are NURSING INTERVENTIONS:
observed in hypermagnesemia.
Non-renal failure causes of
Hypermagnesemia:
1. increased intake of magnesium
2. decreased excretion of magnesium
3. adrenal insufficiency or hyperparathyroidism
You might also like
- Forbidden Cures PDFDocument380 pagesForbidden Cures PDFJacek Jurkowski100% (2)
- Why All Migraine Patients Should Be Treated With MDocument6 pagesWhy All Migraine Patients Should Be Treated With MBoom Design & DesenvolvimentoNo ratings yet
- Vet Clinical MedicineDocument222 pagesVet Clinical Medicineviswanathan periyasamy100% (1)
- Nclex Notes - Inf Control-Management-ProitizationDocument3 pagesNclex Notes - Inf Control-Management-ProitizationTasha100% (21)
- 2016 Pharmacology of Sedative-HypnoticDocument46 pages2016 Pharmacology of Sedative-HypnoticFansisca SiallaganNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification Indication Action and Pharmacokinetics Contraindication Adverse Effect Monitoring ParameterDocument5 pagesDrug Classification Indication Action and Pharmacokinetics Contraindication Adverse Effect Monitoring ParameteryssatNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes - 24 Hours or Less To Absolutely Crush The NCLEX Exam!Document45 pagesFluid and Electrolytes - 24 Hours or Less To Absolutely Crush The NCLEX Exam!KingBlack Canarsie100% (2)
- Part Agents Act NG On The Central Ner Ous System: Liu JuntianDocument89 pagesPart Agents Act NG On The Central Ner Ous System: Liu Juntianapi-19916399No ratings yet
- NCM 106 Learning Activities (Semis)Document12 pagesNCM 106 Learning Activities (Semis)Kimberly Abellar LatoNo ratings yet
- PHARMACOLOGY of ANS (Synopsis For Students)Document16 pagesPHARMACOLOGY of ANS (Synopsis For Students)JIEHASMARTNo ratings yet
- Magnesium OilDocument5 pagesMagnesium OilSoowkskkadjj DidiwkwjaoNo ratings yet
- HYPOMAGNESIMIADocument12 pagesHYPOMAGNESIMIAKeepItSecretNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY-Magnesium SulfateDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY-Magnesium SulfateCarissa Mae Tapec Estrada80% (5)
- Endocrine Disorders and The Neurologic ManifestationsDocument49 pagesEndocrine Disorders and The Neurologic ManifestationsRahmawati HamudiNo ratings yet
- Magnesium Imbalances - ReportDocument5 pagesMagnesium Imbalances - ReportCamelle DiniayNo ratings yet
- Hypermagnesemia Report ManuscriptDocument5 pagesHypermagnesemia Report ManuscriptDanica NuevaexcijaNo ratings yet
- Magnesium Sulphate in The EmergencyDocument12 pagesMagnesium Sulphate in The EmergencyNur AzizaNo ratings yet
- Hypomagnesemia-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesHypomagnesemia-WPS OfficeElsaye WCUNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesNervous Systemjanelle asiongNo ratings yet
- MagnesiumDocument2 pagesMagnesiumtuffie85No ratings yet
- Pcol 1 Prefinals Part 1 PDFDocument9 pagesPcol 1 Prefinals Part 1 PDFJillian Mae DacerNo ratings yet
- 7endocrine DrugsDocument2 pages7endocrine DrugsSOFIA ALYSSA MARIE ABUDENo ratings yet
- Al-Bayan University Pharmacy College 3 Stage Pharmacy: 5 Drugs Acting On ANS DR - Khulood SaadoonDocument42 pagesAl-Bayan University Pharmacy College 3 Stage Pharmacy: 5 Drugs Acting On ANS DR - Khulood SaadoonAsdar LeaqerNo ratings yet
- CNS 2022Document8 pagesCNS 2022Kathleen Kate MonsalveNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 22 Psychotherapeutic AgentsDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 22 Psychotherapeutic AgentsJewel SantosNo ratings yet
- Seifter 2010Document5 pagesSeifter 2010vidianka rembulanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study WengelDocument3 pagesDrug Study WengelWen SilverNo ratings yet
- Cuidado Critico HipomagenesmiaDocument3 pagesCuidado Critico HipomagenesmiaFernando CastroNo ratings yet
- YAWAADocument10 pagesYAWAAZyrene CapulongNo ratings yet
- Major Symptoms: Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pagesMajor Symptoms: Nursing ResponsibilitiesAraw GabiNo ratings yet
- Magnesium and The AnaesthetistDocument5 pagesMagnesium and The AnaesthetistHAPPINESS J. BASUTUNo ratings yet
- 28.autonomic and Neuromuscular PharmacologyDocument37 pages28.autonomic and Neuromuscular PharmacologyValentine MandelaNo ratings yet
- Renal Fabs 1Document15 pagesRenal Fabs 1sheynmalubayNo ratings yet
- Magnesium Metabolism in Health and Disease: 166 DM, April 1988Document53 pagesMagnesium Metabolism in Health and Disease: 166 DM, April 1988Yosoa OktavianusNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - BSN III Center For Behavioral Sciences: Generic Name: Psychosis Adult: PO Adverse Effects CNS:ExtrapyramidalDocument7 pagesDRUG STUDY - BSN III Center For Behavioral Sciences: Generic Name: Psychosis Adult: PO Adverse Effects CNS:ExtrapyramidalChris Denver BancaleNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - BSN III Center For Behavioral Sciences: Generic Name: Psychosis Adult: PO Adverse Effects CNS:ExtrapyramidalDocument10 pagesDRUG STUDY - BSN III Center For Behavioral Sciences: Generic Name: Psychosis Adult: PO Adverse Effects CNS:ExtrapyramidalChris Denver BancaleNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular PhysiologyDocument7 pagesCardiovascular PhysiologyJamesBond123098No ratings yet
- Novement Disorder EmergenciesDocument40 pagesNovement Disorder EmergenciesGamer MadaNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: HypomagnesemiaDocument1 pageThis Study Resource Was: HypomagnesemiaMaica LectanaNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System StimulantsDocument6 pagesCentral Nervous System StimulantsNathalia CabalseNo ratings yet
- Cns StimulantsDocument4 pagesCns StimulantsKienna GarciaNo ratings yet
- Epilepsy: Presented ByDocument43 pagesEpilepsy: Presented Bysaroj padhyNo ratings yet
- Q HypomagnesemiaDocument1 pageQ Hypomagnesemiamaangelamangampo.aringoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Presentation LGD-2 (GROUP 2)Document12 pagesPharmacology Presentation LGD-2 (GROUP 2)hhd29gsmb8No ratings yet
- Behavioral Science Lecture 2Document34 pagesBehavioral Science Lecture 2Natia BadridzeNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Neuropathy: Jurnal ReadingDocument23 pagesDiabetic Neuropathy: Jurnal ReadingSagu TechNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptic DrugsDocument3 pagesAntiepileptic DrugsPratham KhairnarNo ratings yet
- Antipsychotic Drugs - Pharmacology - An Illustrated ReviewDocument5 pagesAntipsychotic Drugs - Pharmacology - An Illustrated ReviewDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationBernadette Joyce PascualNo ratings yet
- Type of Neurotransmitter, Synthesis-Activation-Termination and Comparison Between Normal and DisorderDocument9 pagesType of Neurotransmitter, Synthesis-Activation-Termination and Comparison Between Normal and DisorderNehasish SahuNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Neuromuscular DisordersDocument4 pagesPharmacology Neuromuscular Disorders8dxf5bqv6gNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle Relaxants: DR RC AnakwueDocument24 pagesSkeletal Muscle Relaxants: DR RC AnakwuetemitopeNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia PharmacologyDocument12 pagesAnesthesia PharmacologyMagy SnowNo ratings yet
- Hypermagnesemia NCLEX Review NotesDocument3 pagesHypermagnesemia NCLEX Review NotesApple TreeNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Mgso4 For EclampsiaDocument23 pagesEvolution of Mgso4 For EclampsiaalbertrianthoNo ratings yet
- Anesthetics Fa 2022Document4 pagesAnesthetics Fa 2022Assanov AibekNo ratings yet
- NeurotransmitterDocument4 pagesNeurotransmitterVincent Lau Bi ShengNo ratings yet
- Analgesia and SedationDocument51 pagesAnalgesia and SedationEizetNo ratings yet
- PH - Karrar HaderDocument33 pagesPH - Karrar HaderAdnan YassinNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune Disorder of NMJDocument24 pagesAutoimmune Disorder of NMJMaluNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal NeuralgiaDocument22 pagesTrigeminal NeuralgiaamandarestykbNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Mechanism of Action: Side Effects/ Adverse Effects: Nursing Responsibilities: Brand NameDocument3 pagesGeneric Name: Mechanism of Action: Side Effects/ Adverse Effects: Nursing Responsibilities: Brand NameMacarayo AldemaeNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy Neuromuscular Junction: Clara NovenaDocument144 pagesNeuroanatomy Neuromuscular Junction: Clara NovenaAnggara HNo ratings yet
- Kinds of Neurodegenerative DisordersDocument4 pagesKinds of Neurodegenerative DisordersOctavius QuinNo ratings yet
- Magnesium Excess2Document3 pagesMagnesium Excess2Floriejane MarataNo ratings yet
- Nutrients 09 00813Document8 pagesNutrients 09 00813Stefan GerlemanNo ratings yet
- NCM 118 SemisDocument1 pageNCM 118 SemisKimberly Abellar LatoNo ratings yet
- NCM 121 Semifinal ActivitiesDocument4 pagesNCM 121 Semifinal ActivitiesKimberly Abellar LatoNo ratings yet
- NCM 118 AssignmentDocument5 pagesNCM 118 AssignmentKimberly Abellar LatoNo ratings yet
- Rizal AssignmentDocument1 pageRizal AssignmentKimberly Abellar LatoNo ratings yet
- NCM 119 MidtermDocument1 pageNCM 119 MidtermKimberly Abellar LatoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Med Ward Duty)Document6 pagesDrug Study (Med Ward Duty)Kimberly Abellar LatoNo ratings yet
- Family Care PlanDocument4 pagesFamily Care PlanKimberly Abellar LatoNo ratings yet
- NCM 104 Learning ActivitiesDocument1 pageNCM 104 Learning ActivitiesKimberly Abellar LatoNo ratings yet
- Factors Affectig Suicidal Ideations Among TeenagersDocument60 pagesFactors Affectig Suicidal Ideations Among TeenagersKimberly Abellar LatoNo ratings yet
- Review of Related Literature and Studies Review of Related LiteratureDocument7 pagesReview of Related Literature and Studies Review of Related LiteratureKimberly Abellar LatoNo ratings yet
- Animal Structure and FunctionDocument2 pagesAnimal Structure and FunctionKimberly Abellar LatoNo ratings yet
- Reflection: Name: Jean Kimberly A. Lato Group Topic: "Stress Management"Document2 pagesReflection: Name: Jean Kimberly A. Lato Group Topic: "Stress Management"Kimberly Abellar LatoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document6 pagesChapter 1Kimberly Abellar LatoNo ratings yet
- NCM 105: Basic Nutrition and Diet Therapy: Learning Activity 1: Case StudyDocument6 pagesNCM 105: Basic Nutrition and Diet Therapy: Learning Activity 1: Case StudyKimberly Abellar LatoNo ratings yet
- Violence Against WomenDocument3 pagesViolence Against WomenKimberly Abellar LatoNo ratings yet
- Application LetterDocument1 pageApplication LetterKimberly Abellar Lato100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 2Document9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lesson 2Kimberly Abellar LatoNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Case: PresentationDocument2 pagesDiabetes Case: PresentationKimberly Abellar LatoNo ratings yet
- Blog PDFDocument2 pagesBlog PDFKimberly Abellar LatoNo ratings yet
- RPH EssayDocument1 pageRPH EssayKimberly Abellar LatoNo ratings yet
- Magnesio para AnestesiologiaDocument23 pagesMagnesio para Anestesiologiamirna rodasNo ratings yet
- A Review of Drug Induced HypocalcemiaDocument8 pagesA Review of Drug Induced HypocalcemiaKrisna MulasimadhiNo ratings yet
- Surgery YbDocument67 pagesSurgery YbTamirat geletaNo ratings yet
- 11 Evidence-Based Health Benefits of BananasDocument6 pages11 Evidence-Based Health Benefits of Bananasballincat610No ratings yet
- Nausea and Vomiting of Pregnancy: Clinical Findings and Evaluation - UpToDateDocument1 pageNausea and Vomiting of Pregnancy: Clinical Findings and Evaluation - UpToDateKezia ImanuellaNo ratings yet
- Calixtro, LJ Hypomagnesemia NarrativeDocument2 pagesCalixtro, LJ Hypomagnesemia NarrativeKim SunooNo ratings yet
- F&E Sesh21: Rationalization Activity (This Will Be Done During The Face To Face Interaction)Document2 pagesF&E Sesh21: Rationalization Activity (This Will Be Done During The Face To Face Interaction)Cristine Lee DisuNo ratings yet
- Association of Serum Magnesium On Mortality in Patients Admitted To The Intensive Cardiac Care UnitDocument9 pagesAssociation of Serum Magnesium On Mortality in Patients Admitted To The Intensive Cardiac Care UnitDr Mohammed Nizam UddinNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Maternal BradycardiaDocument27 pagesPostpartum Maternal BradycardiaVero GlzNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Management of Patients With A Short BowelDocument12 pagesGuidelines For Management of Patients With A Short BowelMarselya GaniNo ratings yet
- Magensium SulfateDocument2 pagesMagensium SulfateAndrea ANo ratings yet
- Fluids PDFDocument50 pagesFluids PDFhuong LNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Calcium, Magnesium, and Phosphate BalanceDocument20 pagesDisorders of Calcium, Magnesium, and Phosphate BalanceMarcela HincapiéNo ratings yet
- Abbasi Et Al. - 2012 - The Effect of Magnesium Supplementation On Primary Insomnia in Elderly A Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled ClinicalDocument9 pagesAbbasi Et Al. - 2012 - The Effect of Magnesium Supplementation On Primary Insomnia in Elderly A Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled ClinicalFilipe Brito NutricionistaNo ratings yet
- Coartem Disp BPLDocument9 pagesCoartem Disp BPLsamy BOKABELANo ratings yet
- Pantosec 40mg HeteroDocument2 pagesPantosec 40mg Heteroopto careNo ratings yet
- 1 - Chap13-Fluid and Electrolyte - Balance and Disturbance 2017Document97 pages1 - Chap13-Fluid and Electrolyte - Balance and Disturbance 2017ahmadNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics NephrologyDocument25 pagesPediatrics NephrologyNujhat TabassumNo ratings yet
- Week 6 ElectrolytesDocument166 pagesWeek 6 ElectrolytesErica P. ManlunasNo ratings yet
- Hypomagnesaemia (Grass Staggers - Grass Tetany)Document39 pagesHypomagnesaemia (Grass Staggers - Grass Tetany)Sumit Sharma PoudelNo ratings yet
- Renal Exam Class TestDocument8 pagesRenal Exam Class Test1fleetingNo ratings yet
- Quiz No.1Document5 pagesQuiz No.1Charina AubreyNo ratings yet
- Combating COVID-19 and Building Immune Resilience: A Potential Role For Magnesium Nutrition?Document10 pagesCombating COVID-19 and Building Immune Resilience: A Potential Role For Magnesium Nutrition?witaNo ratings yet
- Neurologic Reflexes Assessment in Magnesium Sulfate AdministrationDocument30 pagesNeurologic Reflexes Assessment in Magnesium Sulfate AdministrationMaria Pina Barbado PonceNo ratings yet