Professional Documents
Culture Documents
10 Phy CH 12 Conc Q by Estudent - PK
10 Phy CH 12 Conc Q by Estudent - PK
Uploaded by
muhammadbilalali895Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
10 Phy CH 12 Conc Q by Estudent - PK
10 Phy CH 12 Conc Q by Estudent - PK
Uploaded by
muhammadbilalali895Copyright:
Available Formats
10th Class - Physics, Chap # 12 (Conceptual Questions) www.eStudent.
pk Page 1 of 5
PHYSICS 10TH – Conceptual Questions
Chap # 12 - GEOMETRICAL OPTICS
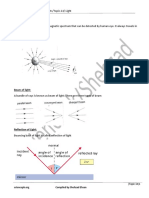
Q # 12.01: Describe the following terms used in Reflection?
(i) Normal (ii) Angle of incidence (iii) Angle of rejection
Normal: The perpendicular to a reflecting or refracting surface at the point of incidence of the ray
concerned is called normal.
Angle of incidence: The angle between the incident ray and the normal ls called angle of incidence.
Angle of reflection: The angle between the normal and the reflected fray is called angle of reflection
Q # 12.02: Define the following terms used in refraction: (i) Angle of incident (ii) Angle of
refraction.
Angle of incidence: The angle made by the incident ray with the normal is called angle of incidence.
Angle of refraction: The angle made by the refracted ray with the normal is called angle of refraction.
Q # 12.03: What is meant by refractive index of a material? How would you determine the
refractive index of a rectangular glass slab?
Refractive index: The refractive index of a medium is the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the
5peed of light ln the medium.
𝑆𝑝𝑒𝑒𝑑 𝑜𝑓 𝑙𝑖𝑔ℎ𝑡 𝑖𝑛 𝑣𝑎𝑐𝑢𝑢𝑚
Refractive index = 𝑆𝑝𝑒𝑒𝑑 𝑜𝑓 𝑙𝑖𝑔ℎ𝑡 𝑖𝑛 𝑚𝑒𝑑𝑖𝑢𝑚
If refractive index is denoted by n, speed of light in a vacuum by c and speed of light in medium by v,
𝑐
then 𝑛=𝑣
Q # 12.04: State the laws of refraction of light and show How, they may be verified using
rectangular glass slab and pins.
(i) The incident ray, the refracted ray, and the normal at the point of incidence all lie in the
same plane.
(ii) The ratio of the sine of angle of incidence ‘i’ to the sine of the angle of refraction ‘r’ is
always equal to constant.
sin 𝑖
= 𝐶𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡
sin 𝑟
Where the ratio sin i/sin r is known as. the refractive index of the second medium with
respect to the first medium. So, we have:
sin 𝑖 𝑛2
=𝑛=
sin 𝑟 𝑛1
This is also called Snell’s Law
www.eStudent.pk www.eStudent.pk Email: admin@eStudent.pk
10th Class - Physics, Chap # 12 (Conceptual Questions) www.eStudent.pk Page 2 of 5
Q # 12.05: A coin is placed at a focal point of a converging lens. Is an Image formed? What is its
nature?
When a coin is placed at the focal point of the principal focus, no image is formed because the refracted
rays are parallel and never meet.
Q # 12.06: What are differences between real and virtual images?
Real Image Virtual Image
It is formed by concave mirror only. It can be formed by convex as well as
concave mirror.
It is always inverted expiation. It is always erect sun small.
It is formed at real principle focus (F) It is formed at virtual principal focus
of a real object i.e. light rays actually (F) of a virtual object i.e. light rays
pass the angle F. appear the diverge from F.
Is has positive sign convention, It has negative sign conversion.
It is formed in front of the mirror. It is formed behind the mirror.
Focal length of real image is taken Focal length of a virtual image is taken
positive. negative.
Q # 12.07: How does a converging lens form a virtual image of a real object? How does a
diverging lens can form a real image of a real object?
When the object is placed between the convex lens and F, the image will be virtual. The ray diagram is
shown in the figure given below.
A concave lens cannot form a real image of a real object in the air. If the concave lens is placed in a
medium of refractive index greater than that of glass, then it will form real image of a real object.
Q # 12.08: A man raises his left hand in a plane mirror; the image facing hi is raising his right
hand. Explain why?
A man raises his left hand in a plane mirror; the image facing him is raising his right hand. Because
light rays are reflected in mirror causing us to see an inverted image.
Q # 12.09: In your own words, explain why light waves are refracted at a boundary between two
materials.
Light waves are reflected at a boundary between two materials due to change of speed of light while
traveling form one medium to another. This change of speed of light at the boundary is caused by the
change in the refractive indices of two materials.
Q # 12.10: Explain why a fish under water appears to be at a different depth below the surface
than actually is. Does it appear deeper or shallower?
A fish under water appear to the shallower that it really is, because of apparent depth, as a virtual image
is formed at I above O, where image seem to be formed due to refraction of light.
Q # 12.11: Why or why not concave mirrors are suitable for make up?
www.eStudent.pk www.eStudent.pk Email: admin@eStudent.pk
10th Class - Physics, Chap # 12 (Conceptual Questions) www.eStudent.pk Page 3 of 5
Concave mirrors are suitable for makeup as they act as magnifier to form large size erect image of
objects. When a person stands between principle focus and pole of mirror.
Q # 12.12: Why is the driver’s side mirror in many cars convex rather than plane or concave?
Driver’s side mirror is convex mirror as it gives an upright, erect although small image, it provides a
wider field of view as it ls curved outwards.
Q # 12.13: When an optician's testing room is small, he uses a mirror to help him test the eye
sight of his patients. Explain why?
To increase the distance of alphabets, form the patient, the optician uses plane mirror if his testing room
is small.
Q # 12.14: How does the thickness of lens affect its focal length?
lf the thickness of a lens is increased; the power of the lens is also increased. Hence the focal length of
the lens ls decreased.
Q # 12.15: Under what conditions will a converging lens form a real image?
Converging lens forms a virtual image when object is placed between optical center and its focal point.
The image formed will be erect and larger than the object.
Q # 12.16: Under what condition will a converging lens form a real image that is the same size as
the object?
When object is placed at 2F form the converging lens it forms a real and inverted image that has the
same size as the object.
Q # 12.17: Why do we use refracting telescope with large objective lens of large focal length?
In refracting telescope, we use objective lens of larger focal length so as to gather more light form weak
distant sources. It not only makes them more visible but also increases the resolving power of the
telescope.
Q # 12.18: In large shopping centers, convex mirrors are used for security purposes. Do you
know why? (Point to ponder - Page 42)
In large shopping centers, convex mirrors are used to see hidden areas or places, it helps to avoid any
stealing or theft and for better supervision.
Q # 12.19: Why the position of fish inside the water seems to be at less depth than that of its
actual position? (Point to Ponder – page 42)
Position of fish inside the water seems to be at less depth due to refraction of light at the surface or
water.
Q # 12.20: will the bending of the light be more or less for a medium with high refractive index?
(Self-assessment - Page 45)
Bending of light is more for a medium with high refractive index.
www.eStudent.pk www.eStudent.pk Email: admin@eStudent.pk
10th Class - Physics, Chap # 12 (Conceptual Questions) www.eStudent.pk Page 4 of 5
Q # 12.21: Where a pen is placed in front of a convex lens if the image is equal to the size of the
pen? What will be the power of the lens in diopters? (Self-Assessment - Page 55)
To obtain an Image of the pin where its size is equal to the size of the pen, the pen must be placed at
2F morn the convex lens.
Q # 12.22: How the size of the pupil of our eye will change: (a) in dim light (b) in bright light.
(Quick Quiz -Page 62)
a. In dim light, the size of the pupil of our eye increases.
b. In bright light, the size of the pupil of our eye decrease.
Q # 12.23: What do you understand by reflection of light? Draw a diagram to illustrate reflection
at a plane surface
See Long Question No. 12.01
Q # 12.24: State laws of reflection. Describe how they can be verified graphically?
See Long Question No. 12.01
Q # 12.25: Define refection of light. Describe the passage of light through parallel-sided
transparent material.
See Long Question No. 12.04
Q # 12.26: what is meant by the term total interval reflection?
See Long Question No. 12.05
Q # 12.27: State the conditions for total internal reflection.
See Long Question No. 12.05
Q # 12.28: What is critical angle Derive a relationship between the critical angle and the refractive
index of a substance?
See Long Question No. 12.05
Q # 12.29: What are optical fibers? Describe how total internal reflection is used in light
propagating trough optical fibers.
See Long Question No. 12.11
Q # 12.30: Define the Terms applied to a Lens.
See Long Question No. 12.07
Q # 12.31: What is meant by the principal focus of a (i) convex lens (ii) a concave lens, illustrate
you answer with ray diagram.
See Long Question No. 12.07
Q # 12.32: Describe how light is refracted through convex lens.
See Long Question No. 12.07
www.eStudent.pk www.eStudent.pk Email: admin@eStudent.pk
10th Class - Physics, Chap # 12 (Conceptual Questions) www.eStudent.pk Page 5 of 5
Q # 12.33: With the help of a ray diagram, how you can show the use of thin converging lens as
a magnifying glass.
See Long Question No. 12.08
Q # 12.34: Define power of a lens and its units.
See Long Question No. 12.07
Q # 12.35: Describe the passage of light through a glass prism and measure the angle of deviation.
See Long Question No. 12.04
Q # 12.36: Define the terms resolving power and magnifying power.
See Long Question No. 12.03
Q # 12.37: Draw the ray diagrams of (i) Simple microscope (ii) Compound microscope (iii)
Refracting telescope
See Long Question No. 12.01, 12.04 and 12.05
Q # 12.38: Draw ray diagrams to show the formation of images in the no› mal human eye.
See Long Question No. 12.06
Q # 1.2.39: What is meant by the terms nearsightedness and farsightedness? How can these
defects can be corrected?
See Long Question No. 12.07
--------------------------------The End--------------------------------
Note: Online practice / Test of all MCQs is Free available on our website.
Keep Visiting http://www.eStudent.pk
www.eStudent.pk www.eStudent.pk Email: admin@eStudent.pk
You might also like
- Detailed Lesson PLan - Image Formation by LensesDocument9 pagesDetailed Lesson PLan - Image Formation by LensesCyril Cauilan100% (1)
- Phys CsecDocument37 pagesPhys CsecBrandon SookdeoNo ratings yet
- CbseDocument15 pagesCbseYaaroNo ratings yet
- GR 10 - CH 10-Light QB With Solution-SubjectiveDocument25 pagesGR 10 - CH 10-Light QB With Solution-SubjectiveKishan MishraNo ratings yet
- X April Physics LightDocument2 pagesX April Physics Lightprasidh2021No ratings yet
- Light Reflection and RefractionDocument20 pagesLight Reflection and RefractionShaurya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Viva Questions Physics Section BDocument17 pagesViva Questions Physics Section Bgauravgrover613No ratings yet
- 10 Science NcertSolutions Chapter 10 ExercisesDocument9 pages10 Science NcertSolutions Chapter 10 Exercisesvikas9saraswatNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 9 Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocument60 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 9 Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsAnushreya SharmaNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics NcertSolutions Chapter 9 ExercisesDocument50 pages12 Physics NcertSolutions Chapter 9 ExercisessanjeeviNo ratings yet
- 116winter18 L16 Thin Lenses-Ray Tracing PDFDocument24 pages116winter18 L16 Thin Lenses-Ray Tracing PDFKarla PereraNo ratings yet
- WP2 Light Waves (SDA) 2Document11 pagesWP2 Light Waves (SDA) 2matsweamogelang89No ratings yet
- Chapter-10 - Light: Reflection and RefractionDocument15 pagesChapter-10 - Light: Reflection and RefractionVineet SierraNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics Viva QuestionsDocument2 pagesRay Optics Viva QuestionsAVERAGE ME100% (3)
- WP4 Light WavesDocument16 pagesWP4 Light Waveswarona letangNo ratings yet
- 10.light - Reflection and Refraction NCERT SolutionsDocument14 pages10.light - Reflection and Refraction NCERT Solutionsdiyanshud.thakurNo ratings yet
- Worksheet RefractionDocument3 pagesWorksheet RefractionNaman JimnaniNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics and Optical Instruments: Topicwise Analysis of Last 10 Years' CBSE Board Questions (2016-2007)Document10 pagesRay Optics and Optical Instruments: Topicwise Analysis of Last 10 Years' CBSE Board Questions (2016-2007)S SquareNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 10 NotesDocument21 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 10 NotesAnsh NarulaNo ratings yet
- M.E.S Indian School, Doha - Qatar Notes 2024 - 2025Document10 pagesM.E.S Indian School, Doha - Qatar Notes 2024 - 2025Rafiya95z MynirNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 12 Physics ReflectionDocument15 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 12 Physics ReflectionRaagul SaravanaKumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Physical Science 14th Edition Shipman Solutions ManualDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Physical Science 14th Edition Shipman Solutions ManualBradGonzalezrgeys100% (43)
- PHYSICS 1E Module 13.2 Plane MirrorsDocument29 pagesPHYSICS 1E Module 13.2 Plane MirrorsClaire G. MagluyanNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE10 Q2 M4 LightsMirrorsandLenses v3-EDITEDDocument22 pagesSCIENCE10 Q2 M4 LightsMirrorsandLenses v3-EDITEDRusty Gabriel Suyom100% (1)
- Ncert Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 16Document7 pagesNcert Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 16JollyNo ratings yet
- Light Class 7 Science Chapter 15Document11 pagesLight Class 7 Science Chapter 15Gaurav Sethi100% (1)
- 10 Science TP 10 1Document8 pages10 Science TP 10 1Ajjuu ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- CBSE Test Paper-01 Chapter 10 Light Reflection and RefractionDocument11 pagesCBSE Test Paper-01 Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refractionshubham sehgalNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 9 Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocument43 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 9 Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDanendra MandaviNo ratings yet
- Science10 Q2 Module 6Document15 pagesScience10 Q2 Module 6qwertyNo ratings yet
- Chap 1.4Document9 pagesChap 1.4smisbahul90No ratings yet
- OPTICSDocument16 pagesOPTICSSoumyajeet PradhanNo ratings yet
- FAQ PhysicsDocument30 pagesFAQ Physicsamit21oct2005No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 Geometrical Optics UpdatedDocument40 pagesCHAPTER 7 Geometrical Optics UpdatedPriyaa JayasankarNo ratings yet
- PhysicsRox Chapter 5 LightDocument8 pagesPhysicsRox Chapter 5 LightWinnie LimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 LIGHTDocument4 pagesChapter 15 LIGHTshravanvk35No ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document84 pagesChapter 9rohit murmuNo ratings yet
- Asm 8671Document3 pagesAsm 8671Taranpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- 2e. 6091 Sec 4 Compiled Lesson Notes-1Document175 pages2e. 6091 Sec 4 Compiled Lesson Notes-1Timothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Reflection and Refraction of LightDocument37 pagesChapter 14 Reflection and Refraction of LightAlicia WilliamsNo ratings yet
- K 9 Me XGF Ilo 6 Uw RN XFjy 5Document28 pagesK 9 Me XGF Ilo 6 Uw RN XFjy 5YogithaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document52 pagesChapter 11Mike JingNo ratings yet
- Class 8-Light-TB EX-SreejaDocument5 pagesClass 8-Light-TB EX-SreejaRAYAN ISWKNo ratings yet
- Physics 2Document11 pagesPhysics 2bort kortNo ratings yet
- 2 Ii We 7 TKB Es 6 CSN G3 S EoDocument6 pages2 Ii We 7 TKB Es 6 CSN G3 S Eony9197171No ratings yet
- Lakhmir Singh Solutions Feb23 Class 10 Physics Chapter 4 Reflection of LightDocument31 pagesLakhmir Singh Solutions Feb23 Class 10 Physics Chapter 4 Reflection of LightA.P. ABISEKNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Week 16Document6 pagesScience 10 - Week 16Mira VeranoNo ratings yet
- Session5&6 - HK NEWTONDocument48 pagesSession5&6 - HK NEWTONDenny Febian SetiawanNo ratings yet
- 06 ReflectionDocument9 pages06 ReflectionHelenNo ratings yet
- Refraction of Light Research PaperDocument6 pagesRefraction of Light Research Papergw08nnfr100% (1)
- Ray OpticsDocument11 pagesRay OpticsxkryxxzNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Solutions Chapter 16 LightDocument14 pagesNCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Solutions Chapter 16 Lightanvu4848100% (1)
- Properties of LightDocument10 pagesProperties of LightKesanam SpNo ratings yet
- Science10 Q2 E7 SLMDocument5 pagesScience10 Q2 E7 SLMCaryll BaylonNo ratings yet
- 5054 Handouts Topic-14 LightDocument22 pages5054 Handouts Topic-14 LightHira IqbalNo ratings yet
- Convex Mirror - Ray Diagram, Images Formed - With Steps - TeachooDocument1 pageConvex Mirror - Ray Diagram, Images Formed - With Steps - TeachooGarvit MehtaNo ratings yet
- Cylindrical Perspective: Cylindrical Perspective: Exploring Visual Perception in Computer VisionFrom EverandCylindrical Perspective: Cylindrical Perspective: Exploring Visual Perception in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Through a Microscope: Something of the Science, Together with many Curious Observations Indoor and Out and Directions for a Home-made MicroscopeFrom EverandThrough a Microscope: Something of the Science, Together with many Curious Observations Indoor and Out and Directions for a Home-made MicroscopeNo ratings yet
- Trumatic L 3050 4050 6050 TRUMPF BrochureDocument12 pagesTrumatic L 3050 4050 6050 TRUMPF BrochureMoez BellamineNo ratings yet
- HW9 Startingpoint AfterworkDocument150 pagesHW9 Startingpoint AfterworkMELISSA DESSIRE AYLAS BARRANCANo ratings yet
- Chapter Two (Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics)Document28 pagesChapter Two (Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics)ايات امجد امجدNo ratings yet
- International StandardDocument20 pagesInternational StandardRodrigo Simões100% (1)
- Numerical Problems - Casting PDFDocument14 pagesNumerical Problems - Casting PDFSubramanian Chidambaram100% (1)
- Kinematics of A Particle Moving in A Straight Line: Isam Al Hassan 0796988794Document51 pagesKinematics of A Particle Moving in A Straight Line: Isam Al Hassan 0796988794isamalhassanNo ratings yet
- DuraFuse Design Guide Z FoldDocument2 pagesDuraFuse Design Guide Z FoldHussain ZaranwalaNo ratings yet
- Grundfosliterature 5840064Document9 pagesGrundfosliterature 5840064cobraking.donNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Multivariable Calculus: Vietnam National University-Ho Chi Minh City International UniversityDocument88 pagesChapter 1. Multivariable Calculus: Vietnam National University-Ho Chi Minh City International UniversityHà Anh Minh LêNo ratings yet
- Budget of Work in General Physics 1Document5 pagesBudget of Work in General Physics 1Michael GabatNo ratings yet
- Flashback Block 1Document20 pagesFlashback Block 1lara hijaziNo ratings yet
- Bell's Inequality in Quantum Game TheoryDocument4 pagesBell's Inequality in Quantum Game TheorykameshwariNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Interaksi Kinematik Massa Bangunan Terhadap Respons Non Linier Inelastik Lapisan TanahDocument9 pagesPengaruh Interaksi Kinematik Massa Bangunan Terhadap Respons Non Linier Inelastik Lapisan Tanahyulia sari nstNo ratings yet
- Dap An - DE CUONG - ANH 8Document5 pagesDap An - DE CUONG - ANH 8KienNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme For Core Worksheet - Chapter 6Document3 pagesMarking Scheme For Core Worksheet - Chapter 6Anusha PatelNo ratings yet
- STPM ChemistryDocument19 pagesSTPM ChemistryAng chong beng50% (2)
- Original Operating Manual: Screw PumpsDocument24 pagesOriginal Operating Manual: Screw PumpsVlad KorzhovNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Combined Science 0653/51 May/June 2020Document7 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Combined Science 0653/51 May/June 2020Hin Wa LeungNo ratings yet
- AQA Double Award GCSE ScienceDocument20 pagesAQA Double Award GCSE SciencePaulNo ratings yet
- Memoria - Tanque N 1° La2326cDocument98 pagesMemoria - Tanque N 1° La2326cmile457100% (1)
- 1 Trench Type I: Input Data A Geometry of The SectionDocument16 pages1 Trench Type I: Input Data A Geometry of The Sectionbansal_sushenNo ratings yet
- Single Point Mooring SPM Systems With Buoys 2Document8 pagesSingle Point Mooring SPM Systems With Buoys 2K LandryNo ratings yet
- Bsi BS 9300 - 1969Document428 pagesBsi BS 9300 - 1969alferedNo ratings yet
- Material Model Mohr CoulombDocument8 pagesMaterial Model Mohr CoulombPuspa ChandNo ratings yet
- Emme-As enDocument20 pagesEmme-As enLeandro Francisco da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet For Hilti HIT HY 170 Injectable Mortar For Anchors in Concrete and Masonry Technical Information ASSET DOC 4398553Document42 pagesTechnical Data Sheet For Hilti HIT HY 170 Injectable Mortar For Anchors in Concrete and Masonry Technical Information ASSET DOC 4398553Kovacs Zsolt-Istvan100% (1)
- Infrastructures 08 00051Document15 pagesInfrastructures 08 00051DANIEL MATEO PARRADO VALLEJONo ratings yet
- BS en 472-95Document12 pagesBS en 472-95Pablo DMNo ratings yet
- 5000 Years of Geometry Mathematics in History and CultureDocument638 pages5000 Years of Geometry Mathematics in History and CultureMario VillegasNo ratings yet
- ASTM D429 14 - Standard Test Methods For Rubber Property-Adhesion To Rigid Substrates PDFDocument22 pagesASTM D429 14 - Standard Test Methods For Rubber Property-Adhesion To Rigid Substrates PDFAndre Rodriguez Spirim100% (1)