Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electricity: Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
Electricity: Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
Uploaded by
Aesha Chalishazar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views31 pagesThe document discusses static and current electricity. It defines static electricity as electricity developed on insulating surfaces from friction, such as rubbing amber with fur. Current electricity deals with charges in motion. Key topics covered include electric charge, conductors and insulators, induction, the leaf electroscope, point discharge, lightning conductors, and how clouds become charged.
Original Description:
Class 8 olympiad electricity chapter
Original Title
AE- ELECTRICITY
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses static and current electricity. It defines static electricity as electricity developed on insulating surfaces from friction, such as rubbing amber with fur. Current electricity deals with charges in motion. Key topics covered include electric charge, conductors and insulators, induction, the leaf electroscope, point discharge, lightning conductors, and how clouds become charged.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views31 pagesElectricity: Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
Electricity: Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
Uploaded by
Aesha ChalishazarThe document discusses static and current electricity. It defines static electricity as electricity developed on insulating surfaces from friction, such as rubbing amber with fur. Current electricity deals with charges in motion. Key topics covered include electric charge, conductors and insulators, induction, the leaf electroscope, point discharge, lightning conductors, and how clouds become charged.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 31
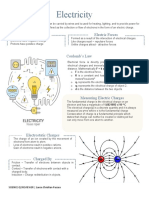
ELECTRICITY
Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
What We will Learn
Static Electricity
Current Electricity
Electric Charge
Source of Static Electricity
Induction Conductors and Insulators
Conduction Leaf Electroscope
Properties of Electric Point Discharge
charge Lightning Conductor
Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
Static Current
Electricity Electricity
Deals with Deals with
charges at charges in
rest motion
Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
History
• Electron means “amber” in Greek
• Thales of Miletus 600 BC discovered properties by
Greek.
• He rubbed amber (mineral) with fur and attracted
feathers.
Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
Static Electricity
The Electricity developed on the surfaces on insulating
bodies when rubbed against each other is called
‘Frictional Electricity’ or ‘Static Electricity’.
This is most noticeable when the rubbed substance is very
good insulating material.
Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
Electric Charge:
It is the property associated with matter due to which it
produces and experiences electrical and magnetic effects.
Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
Source of Static Electricity:
List of Objects acquiring two kinds of charges on rubbing
Sr No. Positive Charge Negative Charge
1 Glass rod Silk
2 Woolen Cloth or Fur Ebonite, Amber ,Rubber
3 Woolen Cloth Plastic
4 Dry Hair Plastic Comb
Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
Induction
The Process of charging a conductor from a charged body without touching
them together is called induction.
The distribution of charge that results from a change in the distribution of
electrons on an object when a charged object is placed near it is called
‘induced charge separation’.
Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
Induction
The electric potential of earth is always taken as zero .Electric
potential of a positively charged sphere will be positive. This
means electric potential of positively charged sphere will be
greater than that of earth.
When a positively charged sphere is earthed or grounded using
a conducting wire, the current flows from the sphere (High
potential ) to the ground (Low Potential)
Earthing is the process of transferring immediate discharge of
an electricity to directly earth plate, by means of low
resistance electrical cables and wires.
Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
Attraction of charged body for
uncharged conductor
Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
Properties of electric charge
Scalar quantity
Like charges repeal with each other while unlike charges attract
each other
Additivity of charge: charges can be added using simple rule of algebra
Conservation of electric charge
Quantisation of charge: Every charge is integral multiple of a certain
smallest amount of charge that exists in nature.
Charges is always associated with mass
Charge is transferable
The charge resides on the outer surface of a conductor
Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
Quantisation of charge:
Charges are associated with mass:
Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
Charge is transferable:
Charge resides on the outer surface of a
conductor
Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
Conductors and Insulators
Electrical conductivity depends upon how tightly the electrons
are bound to the nucleus of the atom.
Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
Distribution of charge is not uniform
on the surface of a conductor
The surface charge density is inversely proportional to radius
of curvature. It is maximum where the radius of curvature is
minimum.
Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
Leaf Electroscope
Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
Leaf Electroscope
DETECTION OF PRESENCE OF CHARGE ON A BODY USING ELECTROSCOPE:
(CONDUCTIION & INDUCTION)
Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
Charge on the
Charge on Effect on object to be
Electroscope leaves
tested
Positive Increase Positive
Decrease Negative or Neutral
Negative Increase Negative
Decrease Positive or Neutral
No charge Divergence Charged(+ or -)
No divergence Neutral
Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
Point Discharge
Charges leak out from sharp points.
The negative charges on reaching the
tip neutralize some positive charge,
hence lower its positive charge and
potential.
This is called Point discharge
The discharging of a sharply pointed charged conductor in atmosphere is
called point discharge or corona discharge.
The movement of positive charges(ions) and negative charges (electrons)near
a pointed charged conductor causes an air disturbance which is called electric
wind.
Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
Lightning Conductor
It is a device which protects
buildings from the lightning
either by neutralizing or by
conducting.
Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
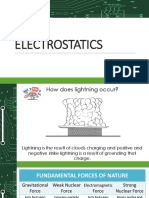
How clouds get charged?
Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
How clouds get charged?
Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
How clouds get charged?
Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
How clouds get charged?
Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
How clouds get charged?
Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
How clouds get charged?
Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
Why air becomes a conductor during
lightning?
Positive charges collect near the upper edges of
clouds
Negative charges collect near the lower edges of
clouds
Accumulation of positive charges near thr ground
also (Induction )
Negative and Positive charges meets ,producing a
streak of light and sound
Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
Unit of Electric charge
Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
Coulomb’s law
Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
Pre-Nurture and Career Foundation
You might also like
- CXC-CSEC Physics - Electricity and MagnetismDocument22 pagesCXC-CSEC Physics - Electricity and Magnetismdela278% (9)
- Air Release ValveDocument17 pagesAir Release Valvevikaskatheria100% (1)
- Migration Trend in PakistanDocument29 pagesMigration Trend in PakistanBaba ButtNo ratings yet
- Module 7: Be in Charge! Be Electrifying!Document49 pagesModule 7: Be in Charge! Be Electrifying!Camaddu GelaicaNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Some Natural PhenomenaDocument17 pagesClass 8 Some Natural PhenomenaChirag ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument22 pagesElectricity and Magnetismkhrisannmiller12No ratings yet
- 1 Basic ElectrostaticsDocument21 pages1 Basic ElectrostaticsAyera Fareenah JamelNo ratings yet
- EM1 - Electrostatics 1Document3 pagesEM1 - Electrostatics 1Kimberly MojeNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Physics1Document50 pagesGroup 4 Physics1cloud kumoishNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2 Module 1Document32 pagesGeneral Physics 2 Module 1GNC Tricia Faye DeleonNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2 Module 1Document32 pagesGeneral Physics 2 Module 1GNC Tricia Faye DeleonNo ratings yet
- Q3 - Lesson 1 PDFDocument85 pagesQ3 - Lesson 1 PDFTimothy Francisco100% (1)
- Science ReviewerDocument12 pagesScience ReviewerLance Christian PascuaNo ratings yet
- Check Point Notes - ElectricityDocument70 pagesCheck Point Notes - ElectricityaghayousufproNo ratings yet
- 10.1 Static ElectricityDocument82 pages10.1 Static ElectricityHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- Static ElectricityDocument82 pagesStatic ElectricityMadiha ShakilNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and FieldDocument18 pagesElectric Charges and FieldShanmuga PriyaNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2: ElectricityDocument33 pagesGeneral Physics 2: ElectricityMa. Alyzandra G. LopezNo ratings yet
- ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS ModifiedDocument65 pagesELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS Modifiedjirav34275No ratings yet
- GP2 Q3W1Document24 pagesGP2 Q3W1DonggadongNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS REVIEWER 3rd GradingDocument81 pagesPHYSICS REVIEWER 3rd GradingBeefWith PorkNo ratings yet
- Plus Two Physics Full Chapters-Seema TRDocument219 pagesPlus Two Physics Full Chapters-Seema TRanjimarv43No ratings yet
- GenPhy2 Lesson 1 ElectrostaticsDocument59 pagesGenPhy2 Lesson 1 ElectrostaticsKyle Cedric MitalNo ratings yet
- Electric Charge and FieldDocument28 pagesElectric Charge and FieldnancyNo ratings yet
- EM2 ElectrostaticsDocument5 pagesEM2 ElectrostaticsNathan TvascorNo ratings yet
- Static Electricity: Cambridge IGCSE PhysicsDocument27 pagesStatic Electricity: Cambridge IGCSE PhysicsSajayanKSNo ratings yet
- CH - 19 - Electric - Charges - and - Forces 2222Document50 pagesCH - 19 - Electric - Charges - and - Forces 2222Karl Sean Garma UbinaNo ratings yet
- Las 7 Q3 Week 7Document2 pagesLas 7 Q3 Week 7Darven CinchezNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xii Physics All in One Notes by Seema ElizabethDocument219 pagesHsslive Xii Physics All in One Notes by Seema ElizabethQWERtyNo ratings yet
- EM1 ElectrostaticsDocument5 pagesEM1 ElectrostaticspencymosothwaneNo ratings yet
- Static Electricity: Putri Puput AnggrainiDocument24 pagesStatic Electricity: Putri Puput AnggrainiMuhammad Rizki PratomoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 13: ElectrostaticsDocument6 pagesExperiment 13: ElectrostaticsZhie Lou0% (1)
- Q3 GenPhys 2 Week 1-2Document14 pagesQ3 GenPhys 2 Week 1-2R Jay GubatangaNo ratings yet
- 1ST Quarter 2ND Sem Week 1-4Document39 pages1ST Quarter 2ND Sem Week 1-4Ma. Alleli ChuaNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges: Third QuarterDocument25 pagesElectric Charges: Third QuarterJennifer MagangoNo ratings yet
- Physics 101Document1 pagePhysics 101Clarence Guimalan CapiendoNo ratings yet
- ELECTROSTATICS 1 - Form 1 Physics Notes: Positive ChargeDocument6 pagesELECTROSTATICS 1 - Form 1 Physics Notes: Positive Chargecatherine SitatiNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Force and Couloumbs LawDocument51 pagesElectrostatic Force and Couloumbs LawCyrus Flores,No ratings yet
- Physics All NotesDocument9 pagesPhysics All NotesPSYCHE JEAN QUESABANo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Fields:Chapter 1Document33 pagesElectric Charges and Fields:Chapter 1Maryam MehekNo ratings yet
- Genphy2 Electrostatics 1Document60 pagesGenphy2 Electrostatics 1Pamela AzurinNo ratings yet
- Electricity-Grade 7Document40 pagesElectricity-Grade 7Leanne Krystel CastroNo ratings yet
- Lec 13 - ElectrostaticsDocument22 pagesLec 13 - ElectrostaticsAna ZarateNo ratings yet
- PHYS102 Chp21 Part1Document22 pagesPHYS102 Chp21 Part1MA MammLNo ratings yet
- Phy CHP 1 NotesDocument33 pagesPhy CHP 1 Notesayaan ahmedNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-physics-Plus Two Chapter1Document19 pagesHsslive-physics-Plus Two Chapter1universeerNo ratings yet
- Lesson#1 - Electric ChargesDocument14 pagesLesson#1 - Electric Chargesjerikbenito46No ratings yet
- Keystone Universe of Education: CH-1 ElectrostaticsDocument60 pagesKeystone Universe of Education: CH-1 ElectrostaticsAakash RathiNo ratings yet
- Keystone Universe of Education: CH-1 ElectrostaticsDocument60 pagesKeystone Universe of Education: CH-1 ElectrostaticsAakash RathiNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges Physics SSS 1Document14 pagesElectric Charges Physics SSS 1aliutunde3495No ratings yet
- EMT Lecture 1Document21 pagesEMT Lecture 1Arslah ChaudaryNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument29 pagesElectrostaticsLance Dean EnteriaNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 Electric Charges and FieldDocument5 pagesChap 1 Electric Charges and Fieldhemangsharma2006No ratings yet
- Reviewer in PhysicsDocument3 pagesReviewer in PhysicsBeatrice MararacNo ratings yet
- ELECTROSTATICSIntroduction RevisedDocument136 pagesELECTROSTATICSIntroduction RevisedHollis CokerNo ratings yet
- Chap 1P Electric Charges and Field 2023Document106 pagesChap 1P Electric Charges and Field 2023Arush GautamNo ratings yet
- Physics Section D-Electricity and MagnetismDocument10 pagesPhysics Section D-Electricity and MagnetismNaomi JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument30 pagesChapter 1 IntroductionImaduddin SharafiNo ratings yet
- 1.9 Electrostatics (I)Document13 pages1.9 Electrostatics (I)Ferdnard WanjalaNo ratings yet
- (Charging by Contact) :: Rubbing of Two Materials Does Not Create AnDocument7 pages(Charging by Contact) :: Rubbing of Two Materials Does Not Create AnErika Jayne TipaNo ratings yet
- Drishtee Foundation Annual Report 2021 2022Document29 pagesDrishtee Foundation Annual Report 2021 2022Lalatendu RajuNo ratings yet
- PPE (Fuels)Document4 pagesPPE (Fuels)Vibin cvNo ratings yet
- Copyright Infringement Notice LetterDocument2 pagesCopyright Infringement Notice LetterTanya CharlesNo ratings yet
- 4th LectureDocument4 pages4th Lectureمحمد عدنان مصطفىNo ratings yet
- P-SYS-002 Control of Records Rev.1Document2 pagesP-SYS-002 Control of Records Rev.1chindita hokianaNo ratings yet
- Hickok 580 and 580A Fact Sheet: Circuit Design and Operation MethodDocument4 pagesHickok 580 and 580A Fact Sheet: Circuit Design and Operation MethodJorgeNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument16 pagesQuestionsMaram SyegNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan TemplateDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Templateapi-548511577No ratings yet
- Agricultural Policy and ProgramDocument390 pagesAgricultural Policy and Programibnebatuta103No ratings yet
- Rose Mount Analytical 1056 ManualDocument12 pagesRose Mount Analytical 1056 ManualFrancisco RomoNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 3 Formative-2Document3 pagesTopic 5 3 Formative-2api-296446683No ratings yet
- Implementing An Outcomes-Based Quality Assurance Process For Program Level Assessment at DLSU Gokongwei College of EngineeringDocument6 pagesImplementing An Outcomes-Based Quality Assurance Process For Program Level Assessment at DLSU Gokongwei College of Engineeringandyoreta6332No ratings yet
- Pinnacle Case Chapter 11Document4 pagesPinnacle Case Chapter 11Albertha PalmaNo ratings yet
- MSI DocumentDocument1 pageMSI DocumentjuballerNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Intez Type Water Tank Using SAP 2000 SoftwareDocument7 pagesDesign and Analysis of Intez Type Water Tank Using SAP 2000 SoftwareIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Horadric Cube Transmutation RecipesDocument5 pagesHoradric Cube Transmutation RecipesM HNo ratings yet
- Andrew Idoko Radiology GROUP 332 1. The Concept of Radical and Palliative Treatment. Indications, Contraindications Dose Limits. ExamplesDocument5 pagesAndrew Idoko Radiology GROUP 332 1. The Concept of Radical and Palliative Treatment. Indications, Contraindications Dose Limits. ExamplesdreNo ratings yet
- A Study On The Attitude of B.ed. Teacher Trainees Towards Internal AssessmentDocument5 pagesA Study On The Attitude of B.ed. Teacher Trainees Towards Internal AssessmentAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNo ratings yet
- Oral Care: Marlon C. Soliman, MAN, RNDocument25 pagesOral Care: Marlon C. Soliman, MAN, RNSoliman C. MarlonNo ratings yet
- US Standard Clothing SizeDocument28 pagesUS Standard Clothing Sizeinama33100% (1)
- Aros Install Manual Version 0.40aDocument30 pagesAros Install Manual Version 0.40aayranayranNo ratings yet
- Case Studies in US Trade NegotiationDocument391 pagesCase Studies in US Trade NegotiationzuppadipomodoroNo ratings yet
- ECE Faculty HandbookDocument48 pagesECE Faculty Handbookamir_shafiq123No ratings yet
- X10834 (Oce751)Document2 pagesX10834 (Oce751)Chockalingam100% (4)
- Permutations and Combination Set A 1Document3 pagesPermutations and Combination Set A 1Xoss ChannelNo ratings yet
- Drama SyllabusDocument57 pagesDrama Syllabusclaracheung100% (1)
- Q) What Is The Difference Between IAGDocument10 pagesQ) What Is The Difference Between IAGfufaNo ratings yet
- 305 MDocument23 pages305 MAmol KareNo ratings yet